1998 HONDA CIVIC Exhaust
[x] Cancel search: ExhaustPage 533 of 2189

Emission Gontrol System
Exhaust Gas Recirculation System (Dl6Y5 engine with M/Tl (cont'dl
lFrom page 11 263)EGR VALVE6P CONNECTOR {C144}
J
Wire sideof femaletermtnals
J
Check lor an op€n in the wire (E-
EGR line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM connector,A (32P)trom the ECM.3. Check lor continuity betweenECM connector terminal A7and the EGR valve 6P connec-torterminal No. 6.
Repair open in the wiro botweenthe EGR valv6.nd th€ ECM {A71.
Check tor a short in the wire {E-EGR lin6l:Check for continuity betweenECM connector terminal A7 andbody ground.
Reoair shorl in tho wiro belwe€nthe EGn vake rnd the ECM lA7l.ls there continuity?
Check fo. an open in tho wiro
IGND line):Check for continuity between theEGR valve 6P connector terminalNo.4 and body ground.
R6pai. open in th€ wir. betweenth6 EGF control solenoid v6lveand G101.
Substitute 8 known-good ECMand recheck. It symptom/indica-tion goes away, roplace the origi-nalECM.
CONNECTORA l32P)
2
a
I G101
Q) raur
-264
Page 534 of 2189

J\
Exhaust Gas Recirculation System
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble
Recirculation (EGRlvalve lift sensor circuit.
(D16Y5 enginel
Code {DTC) P1498: A high voltage problem in the Exhaust Gas
EGR VALVE LlFf SENSOR 3P {M/T: 6Pl CONNECTOR (C1441
cvT:
vcc2{YEL/BLUI
SG2 IGRN/BLK)
IM/T:sG2{GRN/BLKI
Wir€ side ol lemale terminals
ECM CONNECTOR D (16P)
vcc2(YEL/BLUIsG2(GRN/BLK)
Wir€ side of female terminals
PCM CONNECTORS C 131P)'
Wire side oI female terminals
11-265
- The MIL has been reportod on.- DTC P1498 is storod.
Probl€m verification:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce
dure.2. Stan the engine.
Intermittent tailure, sy3lem is OK
at lhis time. Check tor poor con'
nections or loose wire3 at C144
|EGR valvel and ECM/PCM.
ls DTC P1498 indicated?
Check for an open in tho EGRvalv6 lift sen3or:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve lift
sensor 3P (M/T: 6Pl connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. Measure voltage between the
EGR valve litt sensor 3P lM/T:6P) connector terminals No. 3and No.2.
ls there approx.5 V?
Check lor op€n in th€ wire (SG2
line):Measure voltage between ECM/PCM connector terminals 010 andD1l (C18 and C28)*.
Repair open in tho wiro betwoen
ECM/PCM lDl1 (Cl8)r) and EGR
valvo lift sensor.ls there approx. 5 V?
Substitute . known-good ECM/PCM and recheck. ll symptom/indicrtion goes away, replacothe original ECM/rcM.
*:'99 - 00 D16Y5 engine with CVT
Page 586 of 2189

Transmission Assembly
Removal (cont'dl
8. Remove the driveshafts (see section 161.
NOTE: Coat all the precision finished surfaces with
clean engine oil or grease. Tie plastic bags over the
driveshaft ends,
DRIVESHAFT
10 x 1.25 mrn43 N.m 14.4 kgt.m,32 rbf.frl
COTTER PINReplace. SELF12 x 1.25 mm49-59 N.m (5.0 -6.0 kgt.m,36-43 lbf.ft)
9. Remove exhaust pipe A.
Replace.12 x 1.25 mm64 N.m {6.5 kgt.m,47 lbf.tr)
GASKETSReplace.
IF\sELF-LocKtNG NUT.''1/Replace.8 x 1.25 mm16 N.m {1.6 kgf'm,12 tbf.ft)
EXHAUSTPIPE A
SELF-LOCKING NUTReplace.I x 1.25 mm22 N.m (2.2 kgf.m,16 tbt'fr)
SELF-LOCKING NUTReplace.D16Y5, D16Y7 engines:
33 N.m {3.4 kgf.m,25 lbt.ft)D16YB engine:10 x 1.25 mm54 N.m 15.5 kgl'm,40 lbf.ttl
SET RING
13-6
v'10. Remove the shift rod and extension rod.
SI'IIFT BOD
8x22mmSPRING PINReplace.
EXTENSION ROD
PIN PUNCH, 8.O mm(Commercially available)f-
'1'1. Remove the engine stiffeners and clutch cover.
D16Y5, D16Y8 engines:
10 x 1.25 mm44 N.m (4.5 kgt.m,33 tbf.tr)
I x 1.25 mm24 N.m (2.4 kgf.m17 lbt.frl
COVER
8 x 1.25 mm24 N.m 12.4 kgf'tn,17 tbt.tr)
Page 629 of 2189

9. Remove the three upper transmission mounting
bolts and lower starter motor mounting bolt.
'10. Remove the engine splash shieid.
TRANSMISSIONMOUNTINGBOLTS12 x 1.25 mm
6,1 N.m (6.5 kgd m, 47 lbf'ft|
STARTERMOTORMOUNTINGBOLT10 x 1.25 mm
a,t N.m 14.5 kgl.m.
33 tbf.trl
CONNECTOE
11. Disconnect the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) con-
nector, then remove exhaust pip€ A.
H02S
SELF.LOCKING NUTReplace.8 r 1.25 mm16 N.m (1.6 kgf.m, 12lbf'ft)
Replace.10 x 1,25 mm54 N.m {5.5 kgf.m,'lll lbf.ft)
12. Remove the cotter pins and loosen the castle nuts,
then separate the ball joints from the lower arm
(see section 18).
13. Remove the right damPer fork.
10 x 1.25 mma3 N.m lil.a kgf.m, 32 lbf'ft| ,
SELF.LOCKING NUTR6place.12 x 1.25 mm6a N.m (6.5 kgl.m,47 rbf ft)
RIGHTDAMPERFORK
CASTI.T NUT12 x 1,25 mma9 - 59 N.m (5.0 - 6.0 kgtm,36 - i(t lbf.ftl
(cont'd)
!-
ria -11: \/-/
't'''-a
SPLASH SHIELD
13-49
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 698 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Msin Valve Body
The main valve body houses the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve, the cpB valve, the modu-lator valve' the servo control valve, and the relief valve. The primary functions of the main valve body are to swatch fluidpressure on and off and to control the hydraulic pressure going to the hydraulic control svstem.
2ND ORIFICE CONTROTVALVE
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
CPC VAL
3-4 SHTFT V
VALVE
Socondary Valve Body
The secondary valve body is located on the main valve body. The secondary valve body houses the 2-3 shift vatve, the 3-4shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, and the CpC valve.
CONTROL
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
4TH EXHAUST VALV€
VALVE
14-20
VALVE
Page 802 of 2189

Transmission
Removal(cont'd)
'10. Remove the cotter pins and castle nuts, th€n separatethe balljoints from the lower arms (see section 1gl.
DAMPER PINCH BOLT
NUT
FORI(FORK BOLT
11. Remove the right damper fork bolt. th€nright damper fork and dampor.
COTTER PINReplace.
separate
12.
1a
14.
Pry the right and left driveshafts out ofthe differential.
Pull on the inboard joint to remove the right and leftdrivsshafts (see section 16).
Tie plastic bags over the driveshaft onds.
NOTE: Coat all precision finished surfaces with cleanengine oil.
Remove the exhaust pipe A,
NOTE: Dl6YB engine is shown; D16y7 engine issimilar.
t9.
SELF-LOCKING NUTReplace.
L
14-124
EXHAUST PIPE AMOUNT/BRACKET
17.
18.
16. Remove the shift cable cover. then remove the shiftcable by removing the control lever,
CAUTION: Take car6 not to bond the shift cable.
Remove the right front mounvbracket.
Remove the ATF cooler hoses at the ATF coolerlines. Tufn the ends of the ATF cooler hoses uo toprevent ATF from flowing out, then plug the ATFcooler hosgs and lines.
NOTE: Check for any sign of leakage at the hoseioints.
WASHER
Page 822 of 2189
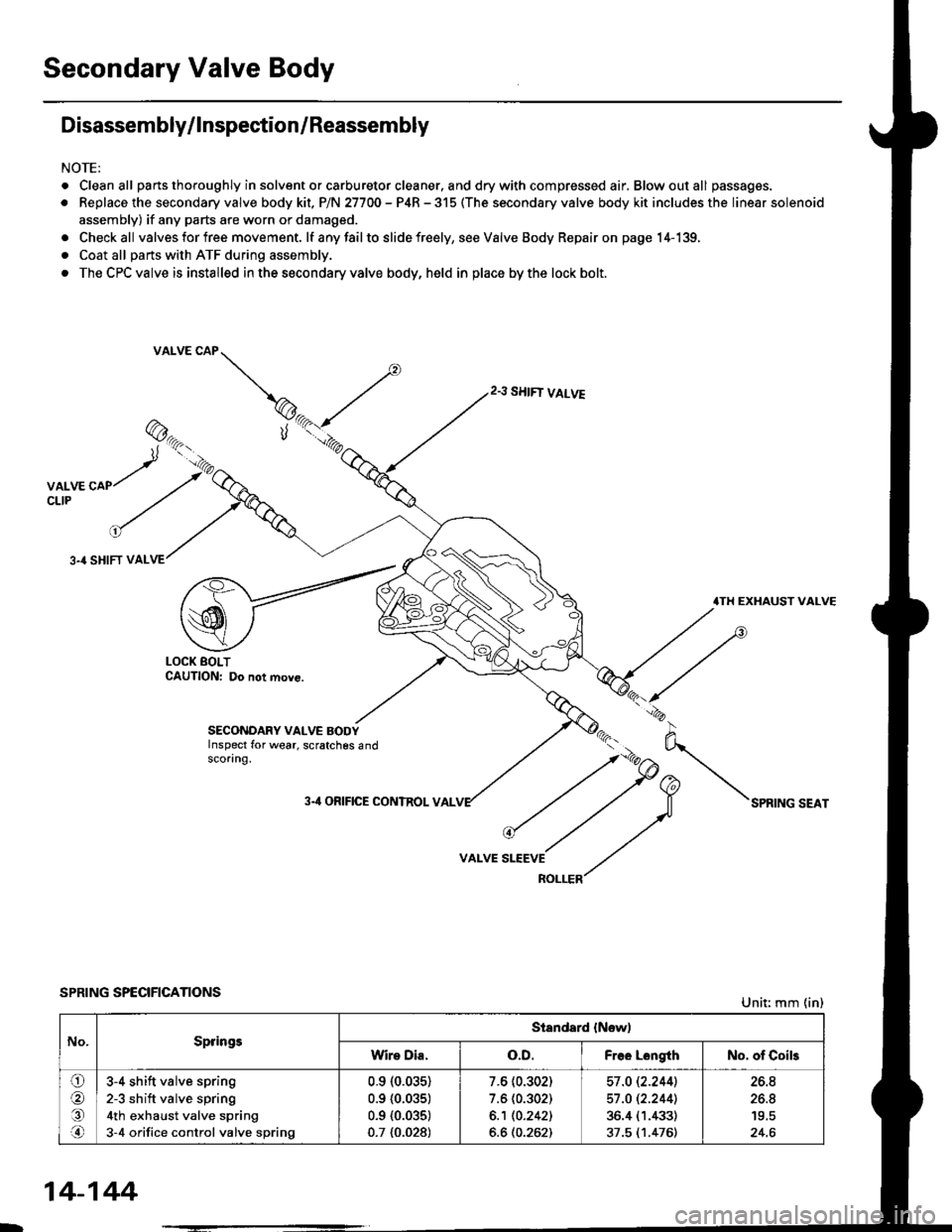
Secondary Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
NOTE:
. Cleanall parts thoroughly in solvent or carburetor cleaner. and drywith compressed air, Blowoutall passages.
. Replace the secondary valve body kit. P/N 27700 - P4R - 315 (The secondary valve body kit includes the linear solenoid
assembly) if any parts are worn or damaged.
. Checkall valves for free movement. lf anyfailto slide freely, seeValveBody Repairon page 14-139,
. Coat all parts with ATF during assembly.
. The CPC valve is installed in the secondary valve body, held in place by the lock bolt.
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
3.4 SHIFT VAL
.TH EXHAUST VALVE
LOCK BOLTCAUTION: Do not move.
SECONDARY VALVE BODYInspect for wear, scratches 6ndscoring.
3-'l ORIFICE CONTROL VAL
VALVE
SPRING SPECIFICATIONSUnit: mm (in)
No.SpringsStandard {New)
Wire Dia.o.D.Free LongthNo. of Coils
ora,.n
3-4 shift valve spring
2-3 sh ift valve spring
4th exhaust valve spring
3-4 orifice control valve spring
0.910.035)
0.9 {0.035)
0.9 {0.035)
0.7 {0.028)
7.6 (0.302)
7.6 (0.302)
6.1 10.2421
6.6 (0.262)
57 .O 12.2441
57 .O 12.2441
36.4 (1.433)
37.5 (1.476)
26.8
26.8
24.6
14-144