Page 92 of 210

Use the built-in child seatonlyif the child is at least 9 months old,
weighs 9±29 kg (20±60 lb) and the child's shoulders (top) are below the
shoulder harness slots in the built-in child seat.
Children not meeting these requirements should be secured in an
approved aftermarket seat. Refer toChildren and infant or child
safety seatsin this chapter.
Placing your child in the built-in child seat
Failure to follow all of the instructions on the use of this child
restraint system can result in your child striking the vehicle's
interior during a sudden stop or crash.
The second row seatback must be fully locked before operating
the child restraint system. Check the position of the seatback
release lever.
Never use the Built-In Child Seat as a booster cushion with the
adult safety belts. A child using the adult belts could slide
forward and out from under the safety belts.
1. Grasp the strap and pull toward
you approximately 25 mm (1 inch),
then slide hand under the head
restraint and slide upwards to the
full position.
Seating and safety restraints
92
Page 96 of 210

9. Pull on the safety belt tongues to
ensure that they are both securely
latched. If they are not properly
latched, repeat steps seven and
eight.
If necessary, the shoulder belt may be put in automatic locking mode
(ALR) to limit the child's movement in the seat. The ALR mode should
be used if the child is sleeping or attempting to get out of the seat.
If not placed in ALR mode, the child seat shoulder belts are in vehicle
sensitive (emergency locking) mode, which allow some movement of the
shoulder belts (like adult shoulder belts).
In emergency locking mode, the shoulder belts of the child seat will lock
in response to hard braking, hard cornering or if your vehicle is involved
in a collision with an impact of 8 km/h (5 m.p.h.) or more.
Activating the automatic locking mode (ALR) on the built-in child
safety seat
1. Fully extend the right shoulder belt.
2. Allow the belts to tighten snugly against the child's shoulders.
Deactivating the automatic locking mode (ALR) on the built-in
child safety seat
1. Disconnect the chest clip and remove the left and right safety belt
tongues from the crotch buckle.
2. Allow the shoulder belts to fully retract.
Seating and safety restraints
96
Page 98 of 210
7. Press firmly on the top center of
the built-in child safety seat head
restraint to ensure it is stowed
properly.
Inspecting the built-in child seat after a collision
Inspect all built-in child restraints, including seats, buckles, retractors,
seat latches. Interlocks and attaching hardware should be inspected by a
qualified technician after any collision. If the child seat was in use during
a collision, Ford recommends replacing it. Built-in child restraints not in
use during a collision should be inspected and replaced if either damage
or improper operation is noted.
Seating and safety restraints
98
Page 102 of 210

STARTING THE ENGINE
1. Turn the key to 5 (START)
without pressing the accelerator
pedal and release as soon as the
engine starts. The key will return to
4 (ON).
2. If the engine does not start within five seconds, wait ten seconds and
try again.
3. If the engine does not start in two attempts or if the temperature is
below -12ÉC (10ÉF), depress the accelerator and start the engine while
holding the accelerator down. Release the accelerator when the engine
starts.
4. After idling for a few seconds, apply the brake and release the parking
brake.
Using the engine block heater (if equipped)
An engine block heater warms the engine coolant, which improves
starting, warms up the engine faster and allows the heater-defroster
system to respond quickly. They are strongly recommended if you live in
a region where temperatures reach -23ÉC (-10ÉF) or below.
For best results, plug the heater in at least three hours before starting
the vehicle. Using the heater for longer than three hours will not harm
the engine, so the heater can be plugged in the night before starting the
vehicle.
To prevent electrical shock, do not use your heater with
ungrounded electrical systems or two-pronged (cheater)
adapters.
3
2
1
5
4
Starting
102
Page 104 of 210
BRAKES
Your brakes are self-adjusting. Refer to the ``Service Guide'' for scheduled
maintenance.
Occasional brake noise is normal and often does not indicate a
performance concern with the vehicle's brake system. In normal
operation, automotive brake systems may emit occasional or intermittent
squeal or groan noises when the brakes are applied. Such noises are
usually heard during the first few brake applications in the morning;
however, they may be heard at any time while braking and can be
aggravated by environmental conditions such as cold, heat, moisture,
road dust, salt or mud. If a ``metal-to-metal'', ``continuous grinding'' or
``continuous squeal'' sound is present while braking, the brake linings
may be worn-out and should be inspected by a qualified service
technician.
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
On vehicles equipped with an anti-lock braking system (ABS), a noise
from the hydraulic pump motor and pulsation in the pedal may be
observed during ABS braking events. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise
while braking under panic conditions or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or
snowy roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle's
anti-lock brake system. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder
while braking, felt mainly in the steering wheel, the vehicle most likely
needs service.
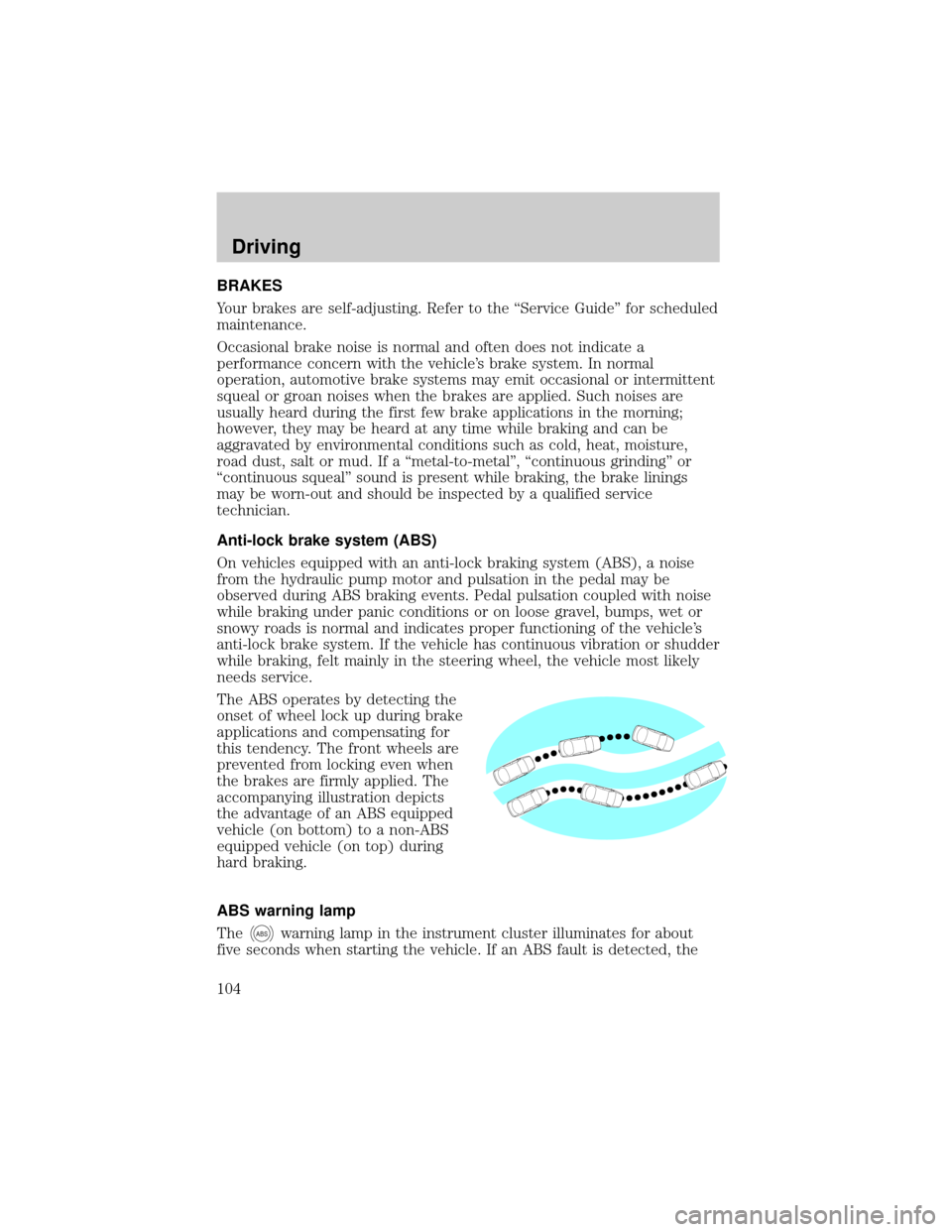
The ABS operates by detecting the
onset of wheel lock up during brake
applications and compensating for
this tendency. The front wheels are
prevented from locking even when
the brakes are firmly applied. The
accompanying illustration depicts
the advantage of an ABS equipped
vehicle (on bottom) to a non-ABS
equipped vehicle (on top) during
hard braking.
ABS warning lamp
The
ABSwarning lamp in the instrument cluster illuminates for about
five seconds when starting the vehicle. If an ABS fault is detected, the
Driving
104
Page 107 of 210

The air suspension shut-off switch is
located in the cargo area behind the
left rear quarter trim panel.
On vehicles equipped with
Air Suspension, turn OFF
the Air Suspension switch prior to
jacking, hoisting or towing your
vehicle.
Normal vehicle operation does not
require any action by the driver.
TRANSMISSION OPERATION
Automatic transmission operation
Brake-shift interlock
This vehicle is equipped with a brake-shift interlock feature that prevents
the gearshift from being moved from P (Park) unless the brake pedal is
depressed.
If you cannot move the gearshift out of P (Park) with the brake pedal
depressed:
1. Apply the parking brake, turn ignition key to LOCK, then remove the
key.
2. Insert the key and turn it to OFF. Apply the brake pedal and shift to N
(Neutral).
3. Start the vehicle.
If it is necessary to use the above procedure to move the gearshift, it is
possible that a fuse has blown. Refer toFuses and relaysin the
Roadside emergencieschapter.
Do not drive your vehicle until you verify that the brakelamps
are working.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by
shifting from forward and reverse gears in a steady pattern. Press lightly
on the accelerator in each gear.
Driving
107
Page 113 of 210
and will shift to 1 (First) after the vehicle decelerates to the proper
vehicle speed.
Driving a manual transmission (if equipped)
Using the clutch
Vehicles equipped with a manual
transmission have a starter interlock
that prevents cranking the engine
unless the clutch pedal is fully
depressed.
When starting a vehicle with a
manual transmission:
1. Hold down the brake pedal.
2. Put the gearshift lever in N
(Neutral).
3. Depress the clutch pedal.
4. Crank the engine and let it idle
for a few seconds.
²Put the gearshift in 1 (First) or R (Reverse).
5. Release the clutch slowly while pressing gradually down on the
accelerator pedal.
²Do not drive with your foot resting on the clutch pedal. Do not use
the clutch to hold your vehicle at a standstill while waiting on a hill.
These actions may reduce clutch life.
Driving
113
Page 116 of 210

You can shift into R (Reverse) only by moving the gearshift from left of 3
(Third) and 4 (Fourth) gears before you shift into R (Reverse). This is a
special lockout feature that protects you from accidentally shifting into R
(Reverse) when you downshift from 5 (Overdrive).
CONTROL-TRAC AUTOMATIC FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE SYSTEM
(IF EQUIPPED)
The 4WD system uses all four wheels to power the vehicle. This
increases traction, enabling you to drive your 4x4 over terrain and road
conditions not normally traveled by two-wheel drive vehicles.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case that allows
you to select a four-wheel drive mode best suited for your current
driving conditions.
Positions of the Control-Trac system
The Control-Trac system functions in three modes:
²The 4WD AUTO mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
delivered to the rear axle, and to
the front axle as required for
increased traction. This is
appropriate for normal on-road
operating conditions, such as dry
road surfaces, wet pavement,
snow and gravel.
²The 4WD HIGH mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
to both axles. It is only intended
for severe winter or off-road
conditions, such as deep snow
and ice (where no dry or wet
pavement remains uncovered),
and shallow sand.
HIGH
LOW AUTO
HIGH
LOW AUTO
Driving
116