1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Timing
[x] Cancel search: TimingPage 1263 of 2627

(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at three levels below top of bore. Start perpen-
dicular (across or at 90 degrees) to the axis of the
crankshaft and then take two additional reading.
(3) Measure the cylinder bore diameter crosswise
to the cylinder block near the top of the bore. Repeat
the measurement near the middle of the bore, then
repeat the measurement near the bottom of the bore.
(4) Determine taper by subtracting the smaller
diameter from the larger diameter.
(5) Rotate measuring device 90É and repeat steps
above.
(6) Determine out-of-roundness by comparing the
difference between each measurement.
(7) If cylinder bore taper does not exceed 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) and out-of-roundness does not
exceed 0.025 mm (0.001 inch), the cylinder bore can
be honed. If the cylinder bore taper or out- of-round
condition exceeds these maximum limits, the cylinder
block must be replaced. A slight amount of taper
always exists in the cylinder bore after the engine
has been in use for a period of time.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is constructed of nodular cast iron.
The crankshaft is a three throw split pin design with
six counterweights for balancing purposes. The
crankshaft is supported by four select fit main bear-
ings with the No. 2 serving as the thrust washer
location. The main journals of the crankshaft are
cross drilled to improve rod bearing lubrication. The
No. 6 counterweight has provisions for crankshaft
position sensor target wheel mounting. The select fit
main bearing markings are located on the rear side
of the target wheel (Fig. 31). The crankshaft oil seals
are one piece design. The front oil seal is retained in
the timing chain cover, and the rear seal is pressed
in to a bore formed by the cylinder block and the
bedplate assembly.
REMOVAL
NOTE: To remove the crankshaft from the engine,
the engine must be removed from the vehicle.
(1) Remove the engine(Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the engine oil pump(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).CAUTION: DO NOT pry on the oil pan gasket when
removing the oil pan, The oil pan gasket is mounted
to the cylinder block in three locations and will
remain attached to block when removing oil pan.
Gasket can not be removed with oil pan.
(3) Remove the bedplate mounting bolts. Note the
location of the two stud bolts for installation.
(4) Remove the connecting rods from the crank-
shaft.
CAUTION: The bedplate to cylinder block mating
surface is a critical sealing surface. Do not pry on
or damage this surface in anyway.
NOTE: The bedplate contains the lower main bear-
ing halves. Use care when handling bedplate as not
to drop or damage bearing halves. Installing main
bearing halves in the wrong position will cause
severe damage to the crankshaft.
Fig. 31 CRANKSHAFT AND TARGET RING
1 - CRANKSHAFT
2 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TARGET RING
9 - 40 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1269 of 2627

CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove A/C compressor mouning fasteners and
set aside.
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove upper radiator hose.
(6) Disconnect electrical connector for fan mounted
inside radiator shroud.
(7) Remove radiator shroud attaching fasteners.
NOTE: Transmission cooler line snaps into shroud
lower right hand corner.
(8)
Remove radiator cooling fan and shroud (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove crankshaft damper bolt.
(10) Remove damper using Special Tools 8513
Insert and 1026 Three Jaw Puller (Fig. 37).
(11) Using Special Tool 8511, remove crankshaft
front seal (Fig. 38).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: To prevent severe damage to the Crank-
shaft, Damper or Special Tool 8512, thoroughlyclean the damper bore and the crankshaft nose
before installing Damper.
(1) Using Special Tool 8348 and 8512, install
crankshaft front seal (Fig. 39).
(2) Install vibration damper (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTAL-
LATION).
Fig. 37 Crankshaft Damper Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8513 INSERT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 1026
Fig. 39 Crankshaft Front Seal Installation
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8348
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 8512
Fig. 38 Crankshaft Front Seal Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8511
9 - 46 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1275 of 2627

²Timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so the
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods or caps, as damage to
connecting rods could occur
NOTE: Connecting rods and bearing caps are not
interchangeable and should be marked before
removing to ensure correct reassembly.
(4) Mark connecting rod and bearing cap positions
using a permanent ink marker or scribe tool.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint face surfaces, as engine
damage may occur.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap. Install Special Tool
8507 Connecting Rod Guides into the connecting rod
being removed. Remove piston from cylinder bore.
Repeat this procedure for each piston being removed.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to nick crank-
shaft journals, as engine damage may occur
(6) Immediately after piston and connecting rod
removal, install bearing cap on the mating connect-
ing rod to prevent damage to the fractured cap and
rod surfaces.
CLEANING
CAUTION: DO NOT use a wire wheel or other abra-
sive cleaning devise to clean the pistons or con-
necting rods. The pistons have a Moly coating, this
coating must not be damaged.
(1) Using a suitable cleaning solvent clean the pis-
tons in warm water and towel dry.
(2) Use a wood or plastic scraper to clean the ring
land grooves.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove the piston pin from the
piston and connecting rod assembly.
INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings.
(2) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure posi-
tion of rings do not change during this opera-
tion.
(3) Position bearing onto connecting rod. Ensure
that hole in bearing shell aligns with hole in connect-
ing rod. Lubricate bearing surface with clean engine
oil.
(4) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads (Fig. 53).
(5) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº indicating installation
position. This mark must be pointing toward the
front of engine on both cylinder banks. The connect-
ing rod oil slinger slot faces the front of the engine
(Fig. 54).
(6) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(7) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(8) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 90É.
(10) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
9 - 52 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1276 of 2627

²Timing chain and cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- INSTALLATION).
²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Fill crankcase with proper engine oil to cor-
rect level.
(12) Connect negative cable to battery.
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
Before reinstalling used rings or installing new
rings, the ring clearances must be checked.
(1) Wipe the cylinder bore clean.
(2) Insert the ring in the cylinder bore.NOTE: The ring gap measurement must be made
with the ring positioned at least 12mm (0.50 inch.)
from bottom of cylinder bore.
(3) Using a piston, to ensure that the ring is
squared in the cylinder bore, slide the ring downward
into the cylinder.
(4) Using a feeler gauge check the ring end gap
(Fig. 55). Replace any rings not within specification.
Fig. 53 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
INSTALLATION
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 54 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
ORIENTATION
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
Fig. 55 Ring End Gap Measurement - Typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 53
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1285 of 2627
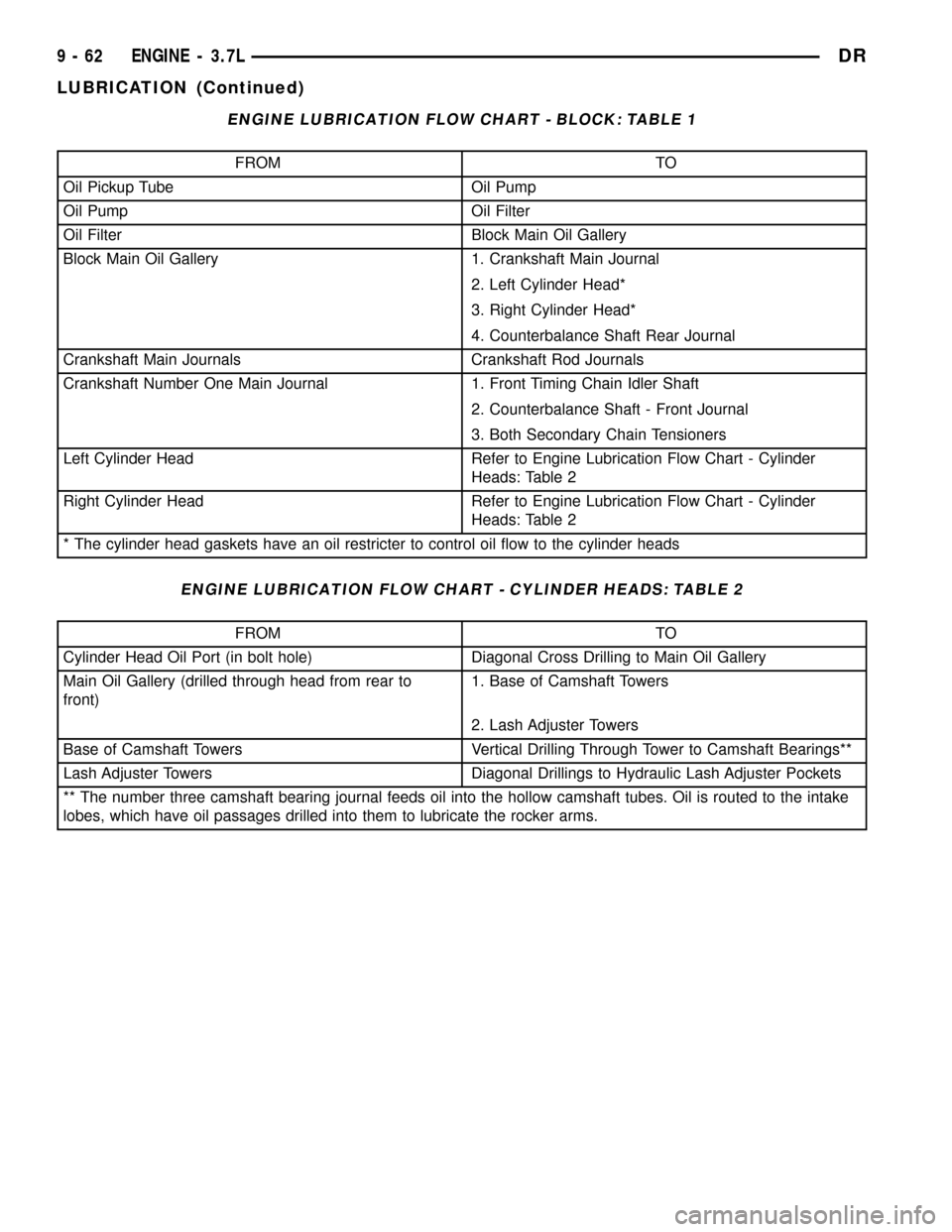
ENGINE LUBRICATION FLOW CHART - BLOCK: TABLE 1
FROM TO
Oil Pickup Tube Oil Pump
Oil Pump Oil Filter
Oil Filter Block Main Oil Gallery
Block Main Oil Gallery 1. Crankshaft Main Journal
2. Left Cylinder Head*
3. Right Cylinder Head*
4. Counterbalance Shaft Rear Journal
Crankshaft Main Journals Crankshaft Rod Journals
Crankshaft Number One Main Journal 1. Front Timing Chain Idler Shaft
2. Counterbalance Shaft - Front Journal
3. Both Secondary Chain Tensioners
Left Cylinder Head Refer to Engine Lubrication Flow Chart - Cylinder
Heads: Table 2
Right Cylinder Head Refer to Engine Lubrication Flow Chart - Cylinder
Heads: Table 2
* The cylinder head gaskets have an oil restricter to control oil flow to the cylinder heads
ENGINE LUBRICATION FLOW CHART - CYLINDER HEADS: TABLE 2
FROM TO
Cylinder Head Oil Port (in bolt hole) Diagonal Cross Drilling to Main Oil Gallery
Main Oil Gallery (drilled through head from rear to
front)1. Base of Camshaft Towers
2. Lash Adjuster Towers
Base of Camshaft Towers Vertical Drilling Through Tower to Camshaft Bearings**
Lash Adjuster Towers Diagonal Drillings to Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Pockets
** The number three camshaft bearing journal feeds oil into the hollow camshaft tubes. Oil is routed to the intake
lobes, which have oil passages drilled into them to lubricate the rocker arms.
9 - 62 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1290 of 2627

(12) Install the front crossmember(Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Fill engine oil.
(14) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(15) Start engine and check for leaks.
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The 3 wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor
(sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure
gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They
are:
²A 5 volt power supply from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM)
²A sensor ground through the PCM's sensor
return
²A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3 wire electrical
function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pres-
sure (MAP) sensor. Meaning different pressures
relate to different output voltages.
A 5 volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM
to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage
signal back to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to theinstrument panel on either a CCD or PCI bus circuit
(depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure
gauge and the check gauges lamp. Ground for the
sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise
sensor return.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove front splash shield.
(4) Disconnect oil pressure sender wire (Fig. 75).
(5) Remove the pressure sender (Fig. 75).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pressure sender.
(2) Connect oil pressure sender wire.
(3) Install front splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan and pick-up tube (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 74 Oil Pan Mounting Bolt Sequence
Fig. 75 OIL PRESSURE SENDING UNIT
1 - BELT
2 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 67
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1291 of 2627
(3) Remove the timing chains and tensioners
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the four bolts, primary timing chain
tensioner and the oil pump.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove oil pump cover screws and lift off cover
plate.
(2) Remove pump inner and outer rotors.
NOTE: Once the oil pressure relief valve, cup plug,
and pin are removed, the pump assembly must be
replaced.
(3) If it is necessary to remove the pressure relief
valve, drive the roll pin from pump housing and
remove cup plug, spring and valve.
INSPECTION
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve and spring
should not be removed from the oil pump. If these com-
ponents are disassembled and or removed from the
pump the entire oil pump assembly must be replaced.
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the oil pump housing should be smooth. If the pump
cover is scratched or grooved the oil pump assembly
should be replaced.
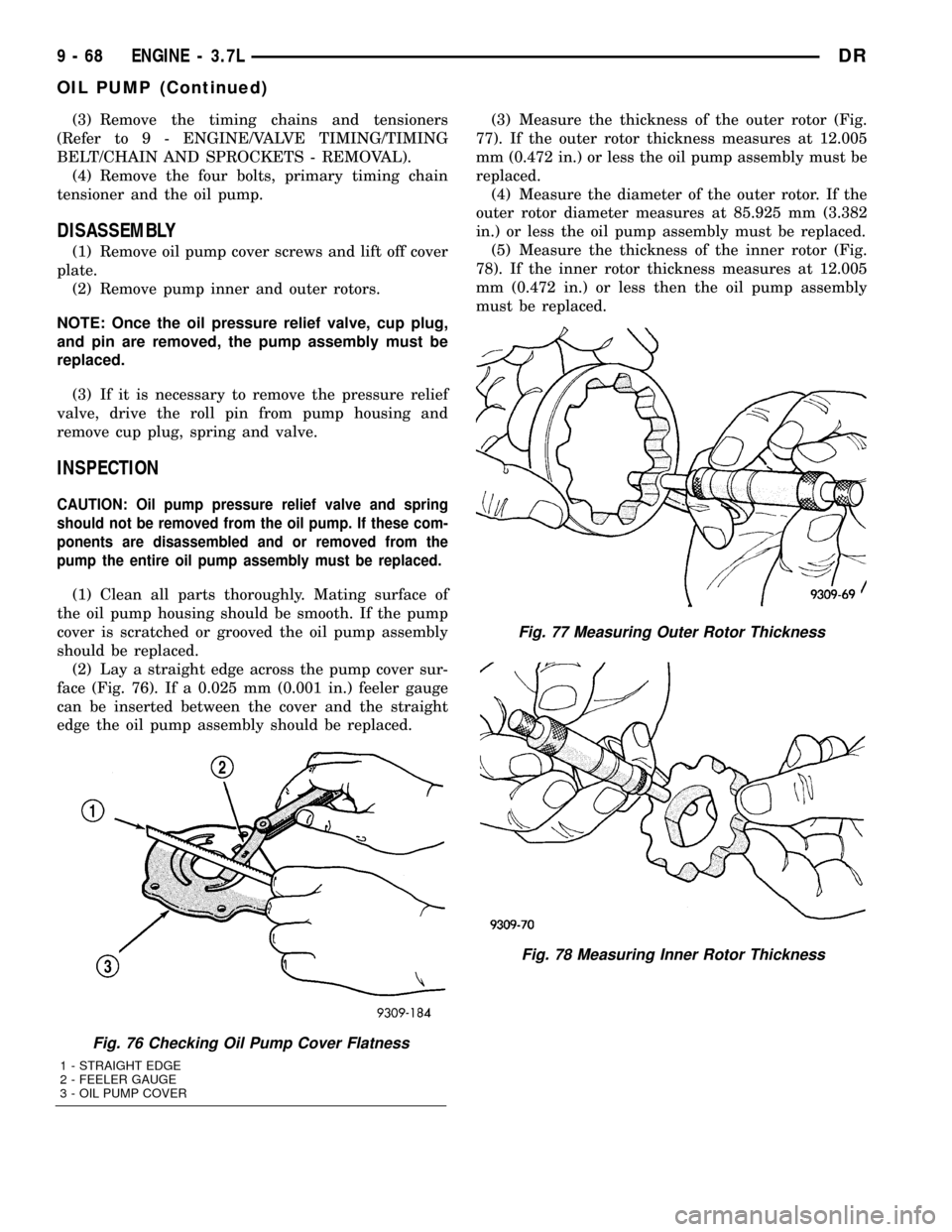
(2) Lay a straight edge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 76). If a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
can be inserted between the cover and the straight
edge the oil pump assembly should be replaced.(3) Measure the thickness of the outer rotor (Fig.
77). If the outer rotor thickness measures at 12.005
mm (0.472 in.) or less the oil pump assembly must be
replaced.
(4) Measure the diameter of the outer rotor. If the
outer rotor diameter measures at 85.925 mm (3.382
in.) or less the oil pump assembly must be replaced.
(5) Measure the thickness of the inner rotor (Fig.
78). If the inner rotor thickness measures at 12.005
mm (0.472 in.) or less then the oil pump assembly
must be replaced.
Fig. 76 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - FEELER GAUGE
3 - OIL PUMP COVER
Fig. 77 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 78 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
9 - 68 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1292 of 2627

(6) Slide outer rotor into the body of the oil pump.
Press the outer rotor to one side of the oil pump body
and measure clearance between the outer rotor and
the body (Fig. 79). If the measurement is 0.235mm
(0.009 in.) or more the oil pump assembly must be
replaced.
(7) Install the inner rotor in the into the oil pump
body. Measure the clearance between the inner and
outer rotors (Fig. 80). If the clearance between the
rotors is .150 mm (0.006 in.) or more the oil pump
assembly must be replaced.
(8) Place a straight edge across the body of the oil
pump (between the bolt holes), if a feeler gauge of
.095 mm (0.0038 in.) or greater can be inserted
between the straightedge and the rotors, the pump
must be replaced (Fig. 81).
NOTE: The 3.7 Oil pump is released as an assem-
bly. There are no DaimlerChrysler part numbers for
Sub-Assembly components. In the event the oil
pump is not functioning or out of specification it
must be replaced as an assembly.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
(2) Install inner and outer rotors
(3) Install oil pump cover plate and install cover
bolts and tighten them to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
(5) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings or other
causes for oil pressure loss.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the oil pump onto the crankshaft and
install one oil pump retaining bolts.
(2) Position the primary timing chain tensioner
and install three retaining bolts.
(3) Tighten the oil pump and primary timing chain
tensioner retaining bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
the sequence shown (Fig. 82).
(4) Install the secondary timing chain tensioners
and timing chains (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 79 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 80 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
1 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - FEELER GAUGE
3 - INNER ROTOR
Fig. 81 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - FEELER GAUGE
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 69
OIL PUMP (Continued)