1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Engine timing
[x] Cancel search: Engine timingPage 1285 of 2627
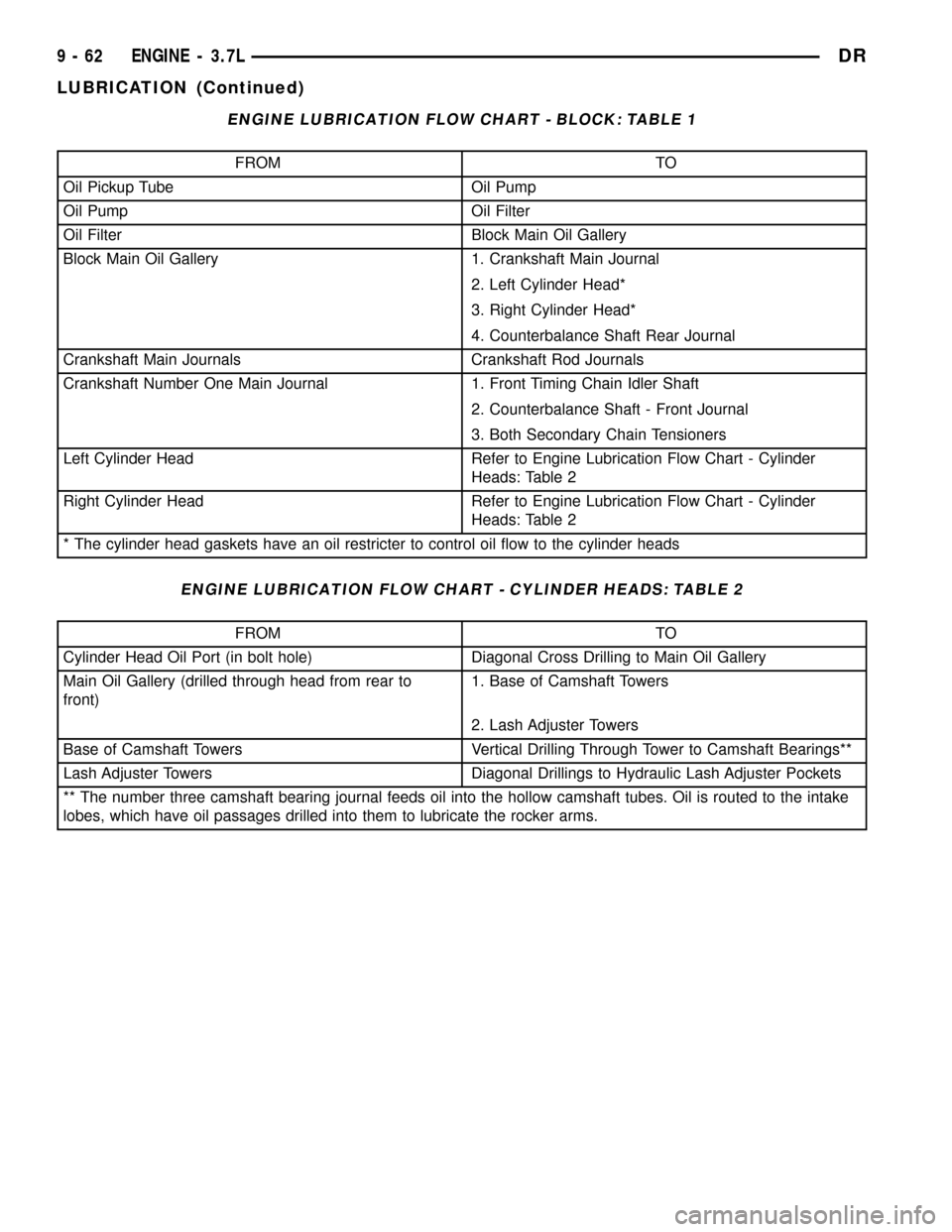
ENGINE LUBRICATION FLOW CHART - BLOCK: TABLE 1
FROM TO
Oil Pickup Tube Oil Pump
Oil Pump Oil Filter
Oil Filter Block Main Oil Gallery
Block Main Oil Gallery 1. Crankshaft Main Journal
2. Left Cylinder Head*
3. Right Cylinder Head*
4. Counterbalance Shaft Rear Journal
Crankshaft Main Journals Crankshaft Rod Journals
Crankshaft Number One Main Journal 1. Front Timing Chain Idler Shaft
2. Counterbalance Shaft - Front Journal
3. Both Secondary Chain Tensioners
Left Cylinder Head Refer to Engine Lubrication Flow Chart - Cylinder
Heads: Table 2
Right Cylinder Head Refer to Engine Lubrication Flow Chart - Cylinder
Heads: Table 2
* The cylinder head gaskets have an oil restricter to control oil flow to the cylinder heads
ENGINE LUBRICATION FLOW CHART - CYLINDER HEADS: TABLE 2
FROM TO
Cylinder Head Oil Port (in bolt hole) Diagonal Cross Drilling to Main Oil Gallery
Main Oil Gallery (drilled through head from rear to
front)1. Base of Camshaft Towers
2. Lash Adjuster Towers
Base of Camshaft Towers Vertical Drilling Through Tower to Camshaft Bearings**
Lash Adjuster Towers Diagonal Drillings to Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Pockets
** The number three camshaft bearing journal feeds oil into the hollow camshaft tubes. Oil is routed to the intake
lobes, which have oil passages drilled into them to lubricate the rocker arms.
9 - 62 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1290 of 2627

(12) Install the front crossmember(Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Fill engine oil.
(14) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
(15) Start engine and check for leaks.
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The 3 wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor
(sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure
gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They
are:
²A 5 volt power supply from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM)
²A sensor ground through the PCM's sensor
return
²A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3 wire electrical
function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pres-
sure (MAP) sensor. Meaning different pressures
relate to different output voltages.
A 5 volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM
to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage
signal back to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to theinstrument panel on either a CCD or PCI bus circuit
(depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure
gauge and the check gauges lamp. Ground for the
sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise
sensor return.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove front splash shield.
(4) Disconnect oil pressure sender wire (Fig. 75).
(5) Remove the pressure sender (Fig. 75).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pressure sender.
(2) Connect oil pressure sender wire.
(3) Install front splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan and pick-up tube (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 74 Oil Pan Mounting Bolt Sequence
Fig. 75 OIL PRESSURE SENDING UNIT
1 - BELT
2 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - OIL FILTER
4 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 67
OIL PAN (Continued)
Page 1291 of 2627
(3) Remove the timing chains and tensioners
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the four bolts, primary timing chain
tensioner and the oil pump.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove oil pump cover screws and lift off cover
plate.
(2) Remove pump inner and outer rotors.
NOTE: Once the oil pressure relief valve, cup plug,
and pin are removed, the pump assembly must be
replaced.
(3) If it is necessary to remove the pressure relief
valve, drive the roll pin from pump housing and
remove cup plug, spring and valve.
INSPECTION
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve and spring
should not be removed from the oil pump. If these com-
ponents are disassembled and or removed from the
pump the entire oil pump assembly must be replaced.
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the oil pump housing should be smooth. If the pump
cover is scratched or grooved the oil pump assembly
should be replaced.
(2) Lay a straight edge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 76). If a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
can be inserted between the cover and the straight
edge the oil pump assembly should be replaced.(3) Measure the thickness of the outer rotor (Fig.
77). If the outer rotor thickness measures at 12.005
mm (0.472 in.) or less the oil pump assembly must be
replaced.
(4) Measure the diameter of the outer rotor. If the
outer rotor diameter measures at 85.925 mm (3.382
in.) or less the oil pump assembly must be replaced.
(5) Measure the thickness of the inner rotor (Fig.
78). If the inner rotor thickness measures at 12.005
mm (0.472 in.) or less then the oil pump assembly
must be replaced.
Fig. 76 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - FEELER GAUGE
3 - OIL PUMP COVER
Fig. 77 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 78 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
9 - 68 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1292 of 2627

(6) Slide outer rotor into the body of the oil pump.
Press the outer rotor to one side of the oil pump body
and measure clearance between the outer rotor and
the body (Fig. 79). If the measurement is 0.235mm
(0.009 in.) or more the oil pump assembly must be
replaced.
(7) Install the inner rotor in the into the oil pump
body. Measure the clearance between the inner and
outer rotors (Fig. 80). If the clearance between the
rotors is .150 mm (0.006 in.) or more the oil pump
assembly must be replaced.
(8) Place a straight edge across the body of the oil
pump (between the bolt holes), if a feeler gauge of
.095 mm (0.0038 in.) or greater can be inserted
between the straightedge and the rotors, the pump
must be replaced (Fig. 81).
NOTE: The 3.7 Oil pump is released as an assem-
bly. There are no DaimlerChrysler part numbers for
Sub-Assembly components. In the event the oil
pump is not functioning or out of specification it
must be replaced as an assembly.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
(2) Install inner and outer rotors
(3) Install oil pump cover plate and install cover
bolts and tighten them to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
(5) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings or other
causes for oil pressure loss.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the oil pump onto the crankshaft and
install one oil pump retaining bolts.
(2) Position the primary timing chain tensioner
and install three retaining bolts.
(3) Tighten the oil pump and primary timing chain
tensioner retaining bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
the sequence shown (Fig. 82).
(4) Install the secondary timing chain tensioners
and timing chains (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 79 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 80 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
1 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - FEELER GAUGE
3 - INNER ROTOR
Fig. 81 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - FEELER GAUGE
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 69
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1293 of 2627

(5) Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the pick-up tube and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise (Fig. 83)
to remove it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
(4) When filter separates from cylinder block oil
filter boss, tip gasket end upward to minimize oil
spill. Remove filter from vehicle.
NOTE: Make sure filter gasket was removed with fil-
ter.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 84) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
Fig. 82 Oil Pump And Primary Timing Chain
Tensioner Tightening SequenceFig. 83 OIL FILTER
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
Fig. 84 Oil Filter Sealing Surface-Typical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
9 - 70 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1299 of 2627
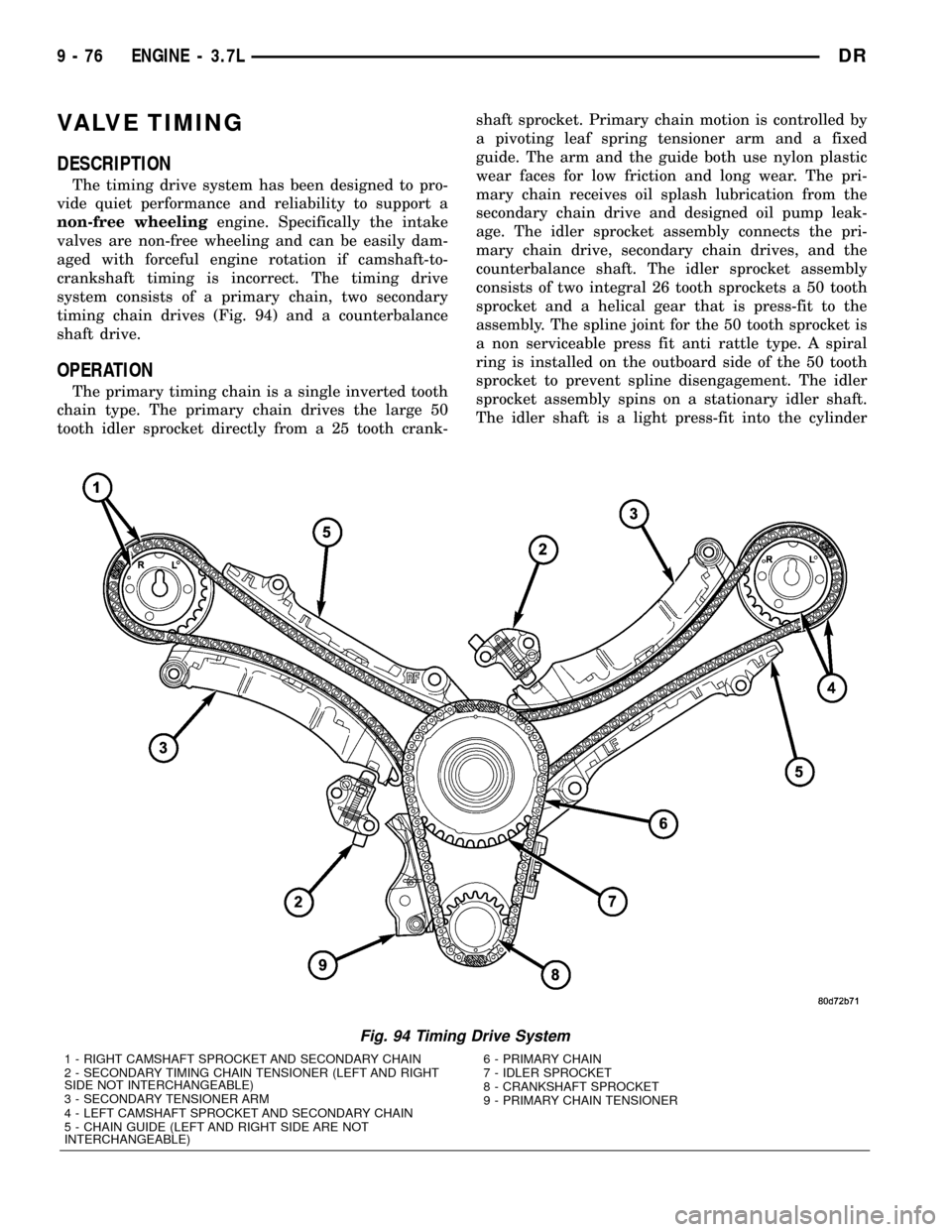
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION
The timing drive system has been designed to pro-
vide quiet performance and reliability to support a
non-free wheelingengine. Specifically the intake
valves are non-free wheeling and can be easily dam-
aged with forceful engine rotation if camshaft-to-
crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing drive
system consists of a primary chain, two secondary
timing chain drives (Fig. 94) and a counterbalance
shaft drive.
OPERATION
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
chain type. The primary chain drives the large 50
tooth idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crank-shaft sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by
a pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed
guide. The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic
wear faces for low friction and long wear. The pri-
mary chain receives oil splash lubrication from the
secondary chain drive and designed oil pump leak-
age. The idler sprocket assembly connects the pri-
mary chain drive, secondary chain drives, and the
counterbalance shaft. The idler sprocket assembly
consists of two integral 26 tooth sprockets a 50 tooth
sprocket and a helical gear that is press-fit to the
assembly. The spline joint for the 50 tooth sprocket is
a non serviceable press fit anti rattle type. A spiral
ring is installed on the outboard side of the 50 tooth
sprocket to prevent spline disengagement. The idler
sprocket assembly spins on a stationary idler shaft.
The idler shaft is a light press-fit into the cylinder
Fig. 94 Timing Drive System
1 - RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
2 - SECONDARY TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER (LEFT AND RIGHT
SIDE NOT INTERCHANGEABLE)
3 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
4 - LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
5 - CHAIN GUIDE (LEFT AND RIGHT SIDE ARE NOT
INTERCHANGEABLE)6 - PRIMARY CHAIN
7 - IDLER SPROCKET
8 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
9 - PRIMARY CHAIN TENSIONER
9 - 76 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1300 of 2627

block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt and the
rear flange of the idler shaft are used to control
sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is routed
through the center of the idler shaft to provide lubri-
cation for the two bushings used in the idler sprocket
assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
roller type, one to drive the camshaft in each SOHC
cylinder head. There are no shaft speed changes in
the secondary chain drive system. Each secondary
chain drives a 26 tooth cam sprocket directly from
the 26 tooth sprocket on the idler sprocket assembly.
A fixed chain guide and a hydraulic oil damped ten-
sioner are used to maintain tension in each second-
ary chain system. The hydraulic tensioners for the
secondary chain systems are fed pressurized oil from
oil reservoir pockets in the block. Each tensioner
incorporates a controlled leak path through a device
known as a vent disc located in the nose of the piston
to manage chain loads. Each tensioner also has a
mechanical ratchet system that limits chain slack if
the tensioner piston bleeds down after engine shut
down. The tensioner arms and guides also utilize
nylon wear faces for low friction and long wear. The
secondary timing chains receive lubrication from a
small orifice in the tensioners. This orifice is pro-
tected from clogging by a fine mesh screen which is
located on the back of the hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN
AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(2) To determine if the secondary timing chains
are worn, rotate the engine clockwise until maximum
tensioner piston extension is obtained. Measure the
distance between the secondary timing chain ten-
sioner housing and the step ledge on the piston. The
measurement at point (A) must be less than 15mm
(.5906 inches) (Fig. 95).
(3) If the measurement exceeds the specification
the secondary timing chains are worn and require
replacement (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
SERVICE PROCEDURE - TIMING VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 3.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.
NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
NOTE: The blue link plates on the chains and the
dots on the camshaft drive sprockets may not line
up during the timing verification procedure. The
blue link plates are lined up with the sprocket dots
only when re-timing the complete timing drive.
Once the timing drive is rotated blue link-to-dot
alignment is no longer valid.
Engine base timing can be verified by the following
procedure:
(1) Remove the cylinder head covers. Refer to the
procedure in this section.
Fig. 95 Measuring Secondary Timing Chains For
Wear
1 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
2 - SECONDARY CHAIN TENSIONER PISTON
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 77
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1301 of 2627

(2) Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the
front cover (Fig. 96). Rotate the crankshaft until the
mark on the crankshaft damper is aligned with the
TDC arrow on the front cover. The engine is now at
TDC.
(3) Note the location of the V6 mark stamped into
the camshaft drive gears. If the V6 mark on each
camshaft drive gear is at the twelve o'clock position,
the engine is at TDC on the exhaust stroke. If the V6
mark on each gear is at the six o'clock position, the
engine is at TDC on the compression stroke. (Fig.
100)
(4) If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in
the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or
both secondary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing
Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
(5) If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off
and the other is correct, the problem is confined to
one secondary chain. Refer to Single camshaft tim-
ing, in this procedure.
(6) If both camshaft drive gear V6 marks are at
the twelve o'clock or the six o'clock position the
engine base timing is correct. Reinstall the cylinder
head covers.
COUNTER BALANCE SHAFT TIMING
(1) Ensure that the engine is at TDC with both
camshaft sprocket V6 marks in the 12 o'clock posi-
tion. (Fig. 100)(2) Look down the left cylinder head chain cavity.
The timing dot on the counter balance shaft drive
gear should be in the 6 o'clock position (Fig. 97).
TIMING - SINGLE CAMSHAFT
NOTE: to adjust the timing on one camshaft, pre-
form the following procedure.
(1) Using Chain Tensioner Wedge (Fig. 99), Special
Tool 8379, stabilize the secondary chain drive. For
reference purposes, mark the chain-to-sprocket posi-
tion. (Fig. 98)
(2) Remove the camshaft drive gear retaining bolt.
(3) Carefully remove the camshaft drive gear from
the camshaft.
(4) Re-index the camshaft drive gear in the chain
until the V6 mark is at the same position as the V6
mark on the opposite camshaft drive gear.
(5) Using Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench,
rotate the camshaft until the alignment dowel on the
camshaft is aligned with the slot in the camshaft
drive gear.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt before reinstalling bolt. Fail-
ure to do so may cause over-torqueing of bolt
resulting in bolt failure.
Fig. 96 Engine Top Dead Center (TDC) Indicator
Mark
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
Fig. 97 COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT ALIGNMENT
MARKS
1 - COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT GEAR
2 - TIMING MARK
3 - IDLER SPROCKET GEAR
9 - 78 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
VALVE TIMING (Continued)