1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Engine control 2
[x] Cancel search: Engine control 2Page 431 of 2627

NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 80ÉF (27ÉC).
(1) With the vehicle engine running, select reverse
gear for over 2 seconds.
(2) Shift the transmission to Drive and accelerate
the vehicle from a stop at a steady 15 degree throttle
opening and perform a 2-3 shift while noting the 1st
2-3 OD CVI.
(3) Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 until the 1st 2-3
upshift becomes smooth and the 1st 2-3 OD CVI sta-
bilizes.
LEARN A SMOOTH 2-3 AND 3-4 UPSHIFT
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).
Use the following steps to have the TCM learn the
OD and 4C CVI's.
(1) Accelerate the vehicle from a stop at a steady
15 degree throttle opening and perform multiple 1-2,
2-3, and 3-4 upshifts. The 2nd 2-3 shift following a
restart or shift to reverse will be shown during the
shift as a value between the 1st 2-3 OD CVI and the
normal OD CVI. Updates to the normal OD CVI will
occur after the 2nd shift into 3rd gear, following a
restart or shift to reverse.
(2) Repeat Step 1 until the 2-3 and 3-4 shifts
become smooth and the OD and 4C CVI become sta-
ble.
LEARN A SMOOTH 4-3 COASTDOWN AND PART
THROTTLE 4-3 KICKDOWN
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).
Use the following steps to have the TCM learn the
UD shift volume.
(1) At a vehicle speed between 64-97 km/h (40-60
MPH), perform repeated 4-3 kickdown shifts.
(2) Repeat Step 1 until the UD volume becomes
somewhat stable and the shift becomes smooth.
LEARN A SMOOTH 1-2 UPSHIFT AND 3-2
KICKDOWN
Use the following steps to have the TCM learn the
2C shift volume.
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).(1) With a vehicle speed below 48 km/h (30 MPH)
and the transmission in 3rd gear, perform multiple
3-2 kickdowns.
(2) Repeat Step 1 until the 3-2 kickdowns become
smooth and the 2C CVI becomes stable.
LEARN A SMOOTH MANUAL 2-1 PULLDOWN
SHIFT AS WELL AS A NEUTRAL TO REVERSE
SHIFT
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).
Use the following steps to have the TCM learn the
LR volume.
(1) With the vehicle speed around 40-48 km/h
(25-30 MPH) in Manual 2nd, perform manual pull-
downs to Low or 1st gear at closed throttle.
(2) Repeat Step 1 until the LR CVI becomes stable
and the manual 2-1 becomes smooth.
LEARN A SMOOTH NEUTRAL TO REVERSE SHIFT
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).
(1) With the vehicle at a stop, perform Neutral to
Reverse shifts until the shift is smooth. An unlearned
Neutral to Reverse shift may be harsh or exhibit a
double bump.
(2) If any of the shifts are still not smooth after
the clutch volume stabilizes, an internal transmis-
sion problem may be present.
LEARN A SMOOTH 4-5 UPSHIFT
NOTE: The transmission oil temperature must be
above 110ÉF (43ÉC).
Use the following steps to have the TCM learn the
Alt 2C CVI.
(1) Accelerate the vehicle through 88 km/h
(55mph) at a steady 10-15 degree throttle opening
and perform multiple 4-5 upshifts.
(2) Repeat Step 1 until the 4-5 shift become
smooth and theAlt 2C CVI become stable. There is a
separate 2C volume used and learned for 4-5 shifts,
2CA. It is independent of the 2C CVI learned on 3-2
kickdowns.
8E - 24 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 433 of 2627

For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to the Lubri-
cation and Maintenance section of this manual for
the proper battery jump starting procedure. While
battery charging can be considered a maintenance
procedure, the battery charging procedure and
related information are located later in this section of
the service manual. This was done because the bat-
tery must be fully-charged before any battery system
diagnosis or testing procedures can be performed.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-
sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the engine to start
and the battery to maintain its charge properly, all of
the components that are used in these systems must
perform within specifications. It is important thatthe battery, starting, and charging systems be thor-
oughly tested and inspected any time a battery needs
to be charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal bat-
tery discharge, overcharging or early battery failure
must be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester), a 12-volt test lamp and/or special service
tools may be required. All OBD-sensed systems are
monitored by the PCM. Each monitored circuit is
assigned a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM
will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failure
it detects. Always check the PCM for stored trouble
codes before returning the vehicle to service. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system test
procedures. Refer to Starting System for the proper
starting system test procedures.
MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER
The Micro 420 automotive battery tester is
designed to help the dealership technician diagnose a
defective battery. Follow the instruction manual sup-
plied with the tester to properly diagnose a battery.
If the instruction manual is not available, refer to
the standard procedure in this section, which
includes the directions for using the Micro 420 bat-
tery tester.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMDR
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 448 of 2627

(2) Disconnect and isolate the remote battery neg-
ative cable terminal.
(3) Remove the battery from the vehicle. Refer to
the procedure in this group.
(4) One at a time, trace the battery cable retaining
pushpins, fasteners and routing clips until the cable
is free from the vehicle.
(5) Remove the battery cable from the engine com-
partment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery cable in the engine com-
partment.
(2) One at a time, install the battery cable retain-
ing pushpins, fasteners and routing clips until the
cable is installed exactly where it was in the vehicle.
Refer to Wiring for illustrations.
(3) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
procedure in this group.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable terminal.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The molded plastic tray battery tray is located in
the left front corner of the engine compartment. On
this model, the battery tray also provides an anchor
point for the anti-lock brake controller, cruise control
servo (if equipped) and the integrated power module
(Fig. 15). The battery hold down hardware is con-
tained within the battery tray. A hole in the bottom
of the battery tray is fitted with a battery tempera-
ture sensor. Refer to Charging System for more infor-
mation on the battery temperature sensor.
OPERATION
The battery tray and the battery hold down hard-
ware combine to secure and stabilize the battery in
the engine compartment, which prevents battery
movement during even the most extreme vehicle
operation. Unrestrained battery movement during
vehicle operation could result in damage to the vehi-
cle, the battery, or both.
REMOVAL
LEFT SIDE
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the integrated power module (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTEL-
LIGENT POWER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness retainers from the
battery tray assembly.
(4) Remove the anti-lock brake controller (if
equipped) retaining bolts and support the brake con-
troller with mechanics wire. It is not necessary to
completely remove the anti-lock brake control unit.
(5) Remove the left front wheelhouse splash shiel-
d(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/LF WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL).
(6) Mark the location of the cruise servo (if
equipped) and remove the retaining screws. Position
the servo out of the way.
(7) Remove the battery temperature sensor from
the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARG-
ING/BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
REMOVAL).
(8) Disconnect the purge solenoid from its mount-
ing bracket.
(9) Disconnect the left front fender ground wire.
(10) Remove the remaining battery tray retaining
bolts (Fig. 16).
(11) Remove the battery tray from the vehicle.
RIGHT SIDE
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
Fig. 15 DR Battery Tray
1 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
2 - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - ANTI-LOCK BRAKE CONTROLLER MOUNTING LOCATION
4 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING SANCTION
DRBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 17
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 450 of 2627

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM............................19
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS.................20
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - GENERATOR
/ CHARGING SYSTEM..................20
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................21OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................24
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................25
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Elec-
tronic Control Module (ECM) for diesel engines.
²Ignition switch
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing Diagrams for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM (ECM Diesel). This voltage
is connected through the PCM (ECM Diesel) and sup-
plied to one of the generator field terminals (Gen.
Source +) at the back of the generator.
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by the EVR (field control) cir-
cuitry contained within the PCM (ECM Diesel). This
circuitry is connected in series with the second rotor
field terminal and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM (ECM
Diesel) to vary the battery charging rate. This isdone by cycling the ground path to control the
strength of the rotor magnetic field. The PCM then
compensates and regulates generator current output
accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM
(ECM Diesel). Each monitored circuit is assigned a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a
DTC in electronic memory for certain failures it
detects.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Panel and Gauges for addi-
tional information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
DRCHARGING 8F - 19
Page 451 of 2627

²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The PCM (Powertrain Control Module), or ECM
(Diesel) monitors critical input and output circuits of
the charging system, making sure they are opera-
tional. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned
to each input and output circuit monitored by the
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system. Some charging
system circuits are checked continuously, and some
are checked only under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-
form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES
DENSO 56029700AA 136 3.7L / 4.7L
BOSCH 56041120AC 136 3.7L / 4.7L
DENSO 56028696AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
BOSCH 56028699AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - GENERATOR /
CHARGING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Mounting Bolts
- 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Support
Bracket Bolt/Nuts - 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Upper Mounting
Bolt - 5.9L Diesel Engine41 30 -
Generator Vertical
Mounting Bolt - 3.7L / 4.7L
Engines55 40 -
Generator (long)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines55 40 -
8F - 20 CHARGINGDR
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 452 of 2627
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator (short)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines74 55 -
Generator B+ Output
Cable Terminal Nut12 - 108
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
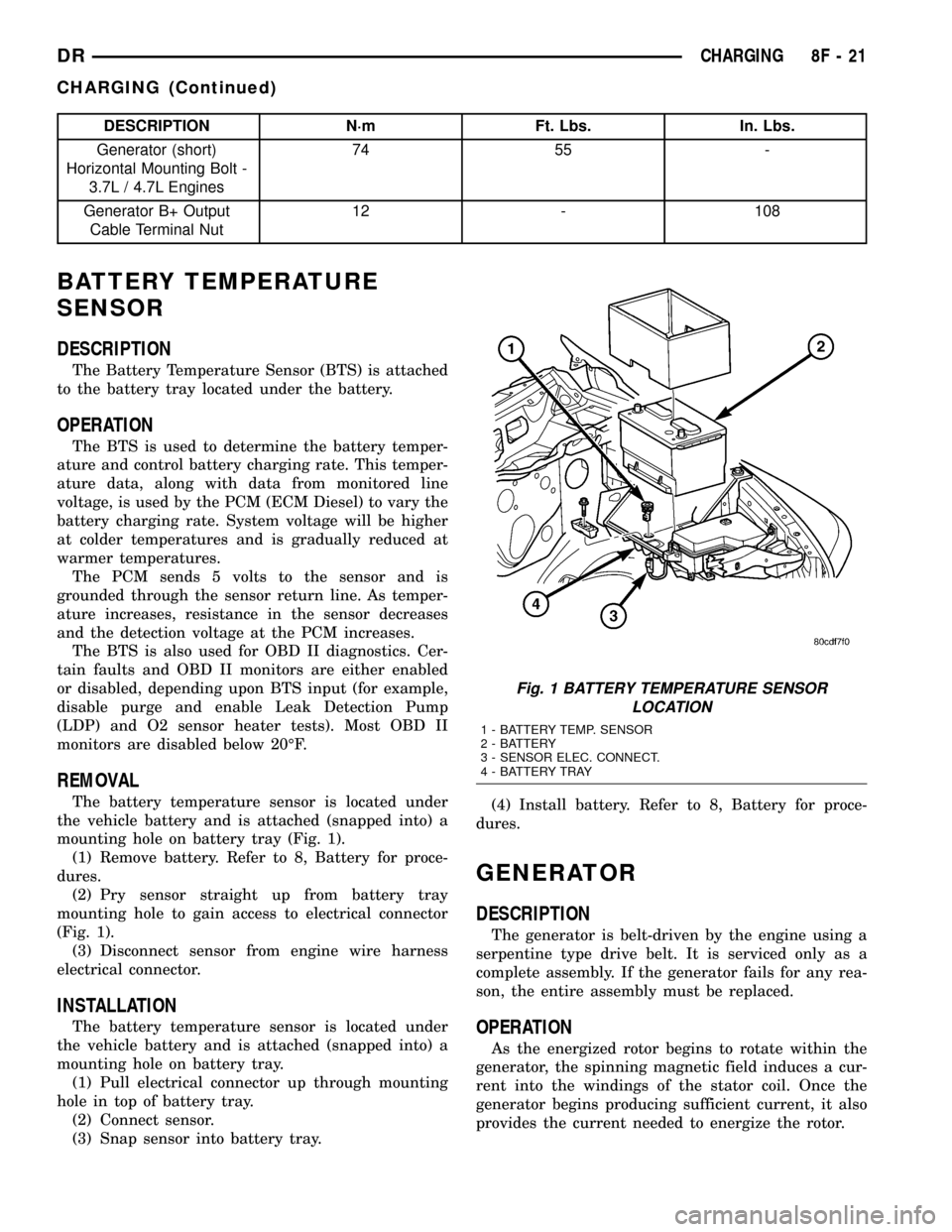
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM (ECM Diesel) to vary the
battery charging rate. System voltage will be higher
at colder temperatures and is gradually reduced at
warmer temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.
The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray (Fig. 1).
(1) Remove battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
(2) Pry sensor straight up from battery tray
mounting hole to gain access to electrical connector
(Fig. 1).
(3) Disconnect sensor from engine wire harness
electrical connector.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray.
(1) Pull electrical connector up through mounting
hole in top of battery tray.
(2) Connect sensor.
(3) Snap sensor into battery tray.(4) Install battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine using a
serpentine type drive belt. It is serviced only as a
complete assembly. If the generator fails for any rea-
son, the entire assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
Fig. 1 BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
LOCATION
1 - BATTERY TEMP. SENSOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - SENSOR ELEC. CONNECT.
4 - BATTERY TRAY
DRCHARGING 8F - 21
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 456 of 2627

(6) Install both negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the PCM (Powertrain Con-
trol Module) (within the ECM for diesel engines). The
EVR is not serviced separately. If replacement is nec-
essary, the PCM must be replaced.
OPERATION
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by EVR circuitry contained
within the PCM. This circuitry is connected in series
with the generators second rotor field terminal and
its ground.Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
EVR circuitry monitors system line voltage (B+) and
battery temperature (refer to Battery Temperature
Sensor for more information). It then determines a
target charging voltage. If sensed battery voltage is
0.5 volts or lower than the target voltage, the PCM
grounds the field winding until sensed battery volt-
age is 0.5 volts above target voltage. A circuit in the
PCM cycles the ground side of the generator field up
to 100 times per second (100Hz), but has the capabil-
ity to ground the field control wire 100% of the time
(full field) to achieve the target voltage. If the charg-
ing rate cannot be monitored (limp-in), a duty cycle
of 25% is used by the PCM in order to have some
generator output. Also refer to Charging System
Operation for additional information.
DRCHARGING 8F - 25
GENERATOR (Continued)
Page 457 of 2627

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM............................27
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM...................31
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM............................32
STARTER MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER
MOTOR .............................32REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................34
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY . 36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
The starting system consists of:
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
Other components to be considered as part of start-
ing system are:
²Battery
²Battery cables
²Ignition switch and key lock cylinder
²Clutch pedal position switch (manual transmis-
sion)
²Park/neutral position switch (automatic trans-
mission)
²Wire harnesses and connections.
The Battery, Starting, and Charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct operation of
starting/charging systems, all components used in
these 3 systems must perform within specifications.
When attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it
is important that you keep their interdependency in
mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.Certain starting system components are monitored
by the PCM and may produce a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC). Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
Emission Control for a list of codes.
OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes (700
amperes - diesel engine), and a low-amperage control
circuit that operates on less than 20 amperes. The
high-amperage feed circuit components include the
battery, the battery cables, the contact disc portion of
the starter solenoid, and the starter motor. The low-
amperage control circuit components include the igni-
tion switch, the clutch pedal position switch (manual
transmission), the park/neutral position switch (auto-
matic transmission), the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmis-
sion, it has a clutch pedal position switch installed in
series between the ignition switch and the coil bat-
tery terminal of the starter relay. This normally open
switch prevents the starter relay from being ener-
gized when the ignition switch is turned to the Start
position, unless the clutch pedal is depressed. This
feature prevents starter motor operation while the
clutch disc and the flywheel are engaged. The starter
relay coil ground terminal is always grounded on
vehicles with a manual transmission.
8F - 26 STARTINGDR