1998 DODGE RAM 1500 system
[x] Cancel search: systemPage 1942 of 2627

(14) Position overdrive piston retainer on trans-
mission case and align bolt holes in retainer, gasket
and case (Fig. 187). Then install and tighten retainer
bolts to 17 N´m (13 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Install new seals on overdrive piston.
(16) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(17) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(18) Position Seal Guide 8114-3 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(19) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by: aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston
to the two mating holes in retainer.
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.
(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-3 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches, while others are used to apply bands.
They all have in common the fact that they are
round or circular in shape, located within a smooth
walled cylinder, which is closed at one end and con-
verts fluid pressure into mechanical movement. The
fluid pressure exerted on the piston is contained
within the system through the use of piston rings or
seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 188) is nothing more than force
(lbs.) divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit
area. Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in.
on the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
Fig. 187 Aligning Overdrive Piston Retainer
1 - PISTON RETAINER
2 - GASKET
3 - RETAINER BOLTS
Fig. 188 Force and Pressure Relationship
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 239
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1943 of 2627
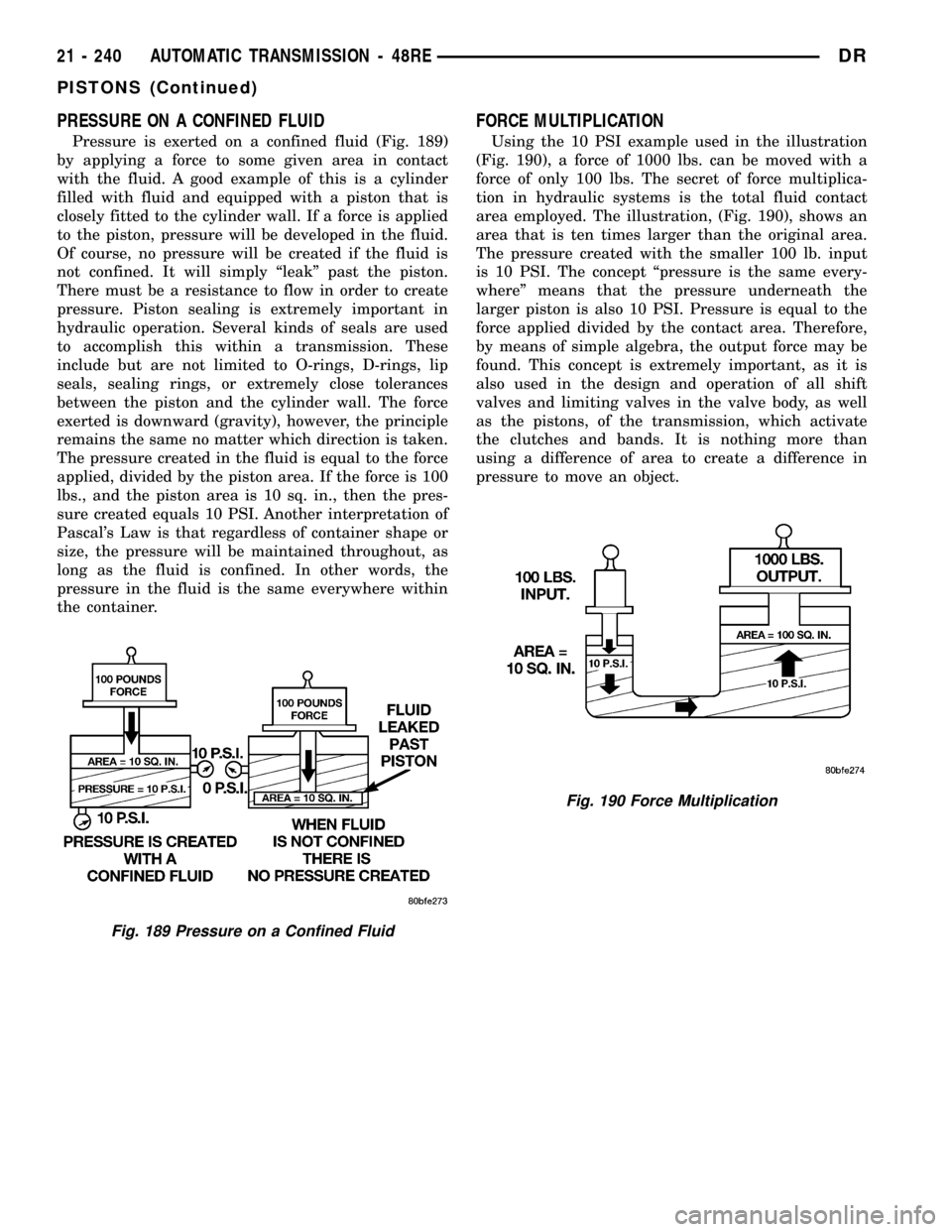
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 189)
by applying a force to some given area in contact
with the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder
filled with fluid and equipped with a piston that is
closely fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied
to the piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid.
Of course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is
not confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston.
There must be a resistance to flow in order to create
pressure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 190), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 190), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
Fig. 189 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
Fig. 190 Force Multiplication
21 - 240 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 1959 of 2627

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 228) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 228 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1976 of 2627
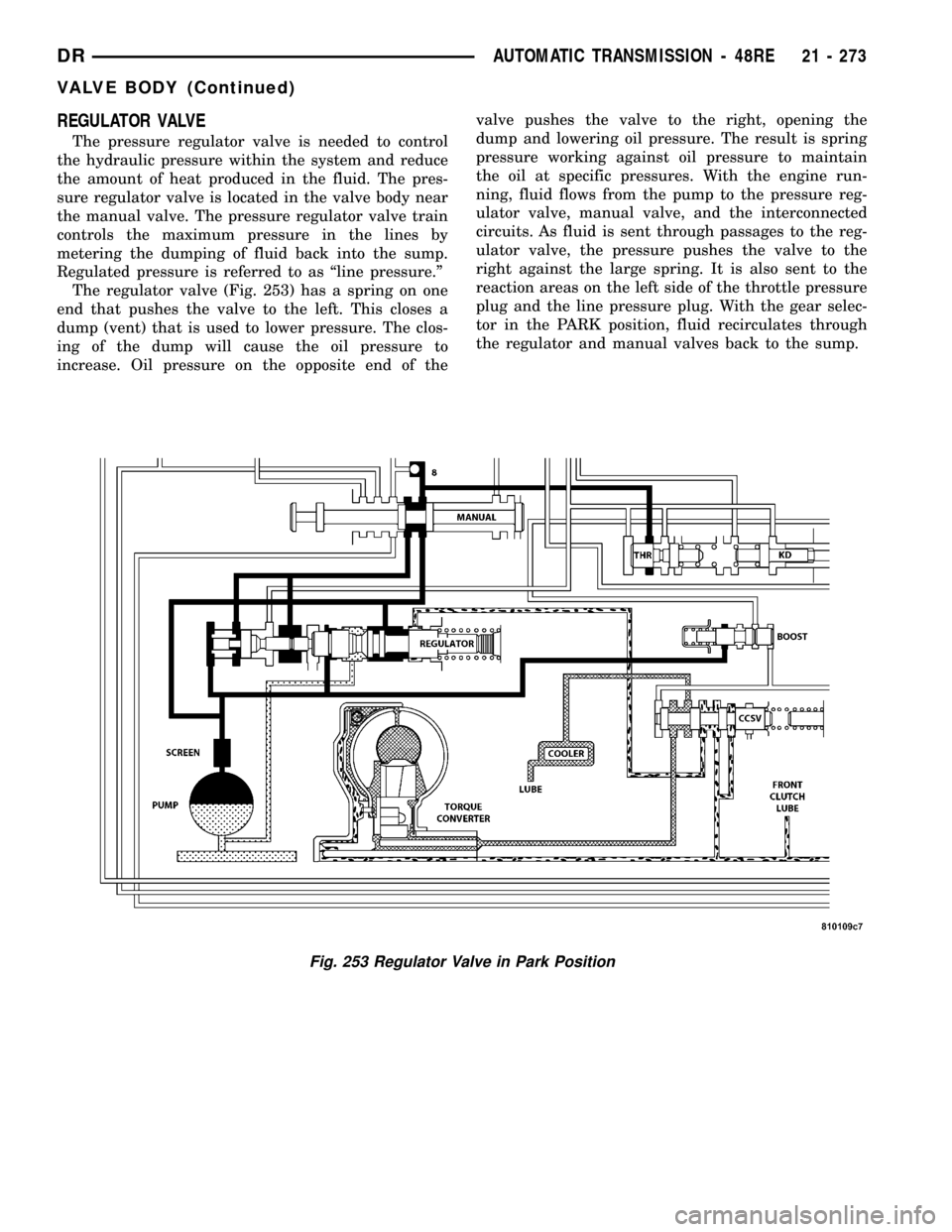
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 253) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 253 Regulator Valve in Park Position
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 273
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2014 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
DESCRIPTION........................312
OPERATION..........................313
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
PRELIMINARY.......................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................316
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION....317
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................318
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................318
REMOVAL............................318
DISASSEMBLY........................320
CLEANING...........................326
INSPECTION.........................326
ASSEMBLY...........................326
INSTALLATION........................333
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............337
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................358
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION.................359
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY........................362
ASSEMBLY...........................363
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................364
INSTALLATION........................364
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION........................364
OPERATION..........................364
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......364
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................365
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............366
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................366DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............367
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................368
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................368
REMOVAL............................369
INSTALLATION........................370
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE..................370
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................371
OPERATION..........................372
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................373
OPERATION..........................373
DISASSEMBLY........................374
ASSEMBLY...........................378
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................382
REMOVAL............................382
INSTALLATION........................382
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................383
REMOVAL............................383
INSTALLATION........................383
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
DISASSEMBLY........................384
CLEANING...........................385
INSPECTION.........................385
ASSEMBLY...........................385
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................386
OPERATION..........................386
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK.....................387
DISASSEMBLY........................388
CLEANING...........................390
INSPECTION.........................390
ASSEMBLY...........................390
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL............................391
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 311
Page 2015 of 2627

INSTALLATION........................391
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................391
OPERATION..........................391
REMOVAL............................391
INSTALLATION........................392
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................392
OPERATION..........................392
REMOVAL............................392
INSTALLATION........................393
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................393
OPERATION..........................393
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................395
OPERATION..........................396
DISASSEMBLY........................396
CLEANING...........................396
INSPECTION.........................397
ASSEMBLY...........................397
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................398
OPERATION..........................398
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................398
OPERATION..........................398
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION........................398OPERATION..........................399
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................399
OPERATION..........................403
REMOVAL............................404
INSTALLATION........................404
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................405
OPERATION..........................405
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................405
OPERATION..........................405
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................406
OPERATION..........................406
REMOVAL............................407
INSTALLATION........................408
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................408
OPERATION..........................408
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................408
OPERATION..........................408
REMOVAL............................410
DISASSEMBLY........................410
CLEANING...........................412
INSPECTION.........................413
ASSEMBLY...........................414
INSTALLATION........................414
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
45RFE/545RFE
DESCRIPTION
The 45RFE/545RFE automatic transmissions is a
sophisticated, multi-range, electronically controlled
transmission which combines optimized gear ratios
for responsive performance, state of the art efficiency
features and low NVH. Other features include driver
adaptive shifting and three planetary gear sets to
provide wide ratio capability with precise ratio steps
for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear
sets also make available a unique alternate second
gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between
1st and 3rd gears for normal through-gear accelera-
tions. The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows
smoother 4-2 kickdowns at high speeds to provide
2nd gear passing performance over a wider highway
cruising range.
The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists
of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic
valves, and various line pressure control components.The primary mechanical components of the trans-
mission consist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Three multiple disc holding clutches
²Five hydraulic accumulators
²Three planetary gear sets
²Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid pack
The TCM is the ªheartº or ªbrainº of the electronic
control system and relies on information from vari-
ous direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)
to determine driver demand and vehicle operating
conditions. With this information, the TCM can cal-
culate and perform timely and quality shifts through
various output or control devices (solenoid pack,
transmission control relay, etc.).
21 - 312 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2016 of 2627

TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS
The 45RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
GEAR RATIOS
The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 45RFE/545RFE offers full electronic control of
all automatic up and downshifts, and features real-
time adaptive closed-loop shift and pressure control.
Electronic shift and torque converter clutch controls
help protect the transmission from damage due to
high temperatures, which can occur under severe
operating conditions. By altering shift schedules, line
pressure, and converter clutch control, these controls
reduce heat generation and increase transmission
cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmissions includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 45RFE/545RFE pump-pressure
control system monitors input torque and adjusts the
pump pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the
pump works continuously; the second stage is
bypassed when demand is low. The control system
also monitors input and output speed and, if incipi-
ent clutch slip is observed, the pressure control sole-
noid duty cycle is varied, increasing pressure in
proportion to demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 45RFE/545RFE is packaged in
a one-piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH,
the case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiff-
ness. It is also designed to maximize the benefit of
the structural dust cover that connects the bottom of
the bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing
overall power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRBtscan tool.
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS (STAMPED)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 313
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2067 of 2627

ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transfer case from the transmis-
sion.
(2) Using a screw mounted on a slide hammer,
remove the adapter housing seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the adapter seal bore in the adapter
housing of any residue or particles remaining from
the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the adapter housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 63). A properly
installed seal is flush to the face of the seal bore.
(3) Install the transfer case onto the transmission.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The Brake Transmission Shifter Interlock (BTSI)
(Fig. 64), is a solenoid operated system. It consists of
a solenoid permanently mounted on the gearshift
cable.
OPERATION
The system locks the shifter into the PARK position.
The interlock system is engaged whenever the ignition
switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY position. An
additional electrically activated feature will prevent
shifting out of the PARK position unless the brake pedalis depressed approximately one-half an inch. A magnetic
holding device in line with the park lock cable is ener-
gized when the ignition is in the RUN position. When
the key is in the RUN position and the brake pedal is
depressed, the shifter is unlocked and will move into
any position. The interlock system also prevents the
ignition switch from being turned to the LOCK or
ACCESSORY position, unless the shifter is fully locked
into the PARK position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
(1) Verify that the key can only be removed in the
PARK position
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK And the shift
handle pushbutton is in the ªOUTº position, the igni-
tion key cylinder should rotate freely from OFF to
LOCK. When the shifter is in any other gear or neu-
tral position, the ignition key cylinder should not
rotate to the LOCK position.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the OFF posi-
tion.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal pushbutton force and ignition
key cylinder is in the RUN or START positions
unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi-
mately 1/2 inch (12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the ACCESSORY
or LOCK positions.
(6)
Shifting between any gears, NEUTRAL or into
PARK may be done without depressing foot brake pedal
with ignition switch in RUN or START positions.
Fig. 63 Adapter Housing Seal Installation
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
Fig. 64 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
21 - 364 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR