1998 DODGE RAM 1500 spark
[x] Cancel search: sparkPage 1231 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(4) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the 3rd
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(7) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
(1) Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
(2) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
(3) Remove the spark plugs.
(4) Remove the oil filler cap.
(5) Remove the air cleaner hose.
(6) Calibrate the tester according to the manufac-
turer's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
(7) Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
Set piston of cylinder to be tested at TDC compres-
sion,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART.
9 - 8 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1255 of 2627

VALVE GUIDE SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve guide seals are made of rubber and
incorporate an integral steel valve spring seat. The
integral garter spring maintains consistent lubrica-
tion control to the valve stems.
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. The springs are NOT common
for intake and exhaust applications. The exhaust
spring has an external damper. The valve spring seat
is integral with the valve stem seal, which is a posi-
tive type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed.
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(5) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(6) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(7) Remove the valve spring compressor.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(8) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
(9) Remove the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(1) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place while the spring is installed.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(2) Install the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(3) Install the spring retainer, and the spring.
(4) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
(5) Install the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(7) Disconnect the shop air to the cylinder.
(8) Install the spark plug for the cylinder the valve
spring and seal was installed on.
(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
9 - 32 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1261 of 2627

VALVE GUIDE SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve guide seals are made of rubber and
incorporate an integral steel valve spring seat. The
integral garter spring maintains consistent lubrica-
tion control to the valve stems.
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. There are different springs for
intake and exhaust applications. The exhaust spring
has an external damper. The valve spring seat is
integral with the valve stem seal, which is a positive
type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed.
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(5) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(6) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(7) Remove the valve spring compressor.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(8) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
(9) Remove the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: All six valve springs and seals are removed
in the same manner; this procedure only covers
one valve seal and valve spring.
(1) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place while the spring is installed.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
(2) Install the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve springs are NOT common between
intake and exhaust.
(3) Install the spring retainer, and the spring.
(4) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
(5) Install the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(6) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(7) Disconnect the shop air to the cylinder.
(8) Install the spark plug for the cylinder the valve
spring and seal was installed on.
(9) Using Special Tool 8516 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, install the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters.
(10) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder block is made of cast iron. The block
is a closed deck design with the left bank forward. To
provide high rigidity and improved NVH an
enhanced compacted graphite bedplate is bolted to
the block. The block design allows coolant flow
between the cylinders bores, and an internal coolant
bypass to a single poppet inlet thermostat is included
in the cast aluminum front cover.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
9 - 38 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1313 of 2627
ENGINE - 4.7L
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Idle speed set to low. 1. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL INJECTION/IDLE AIR
CONTROL MOTOR - REMOVAL).
2. Idle mixture too lean or too rich. 2. Refer to Powertrain Diagnosis
Information.
3. Vacuum leak. 3. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect engine timing. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
9 - 90 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1314 of 2627
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
1. ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH
SPEED1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 91
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
(4) Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUT DOWN
RELAY - REMOVAL).
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6)
Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revo-
lution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
(7) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
(1) Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
(2) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
(3) Remove the spark plugs.
(4) Remove the oil filler cap.
(5) Remove the air cleaner hose.
(6) Calibrate the tester according to the manufac-
turer's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
(7) Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
Set piston of cylinder to be tested at TDC compres-
sion,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 93
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1349 of 2627
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Disconnect the battery negative cable to pre-
vent accidental starter engagement.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 3 and 5
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(3) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 2 and 8
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 4 and 6
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(5) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 1 and 7
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
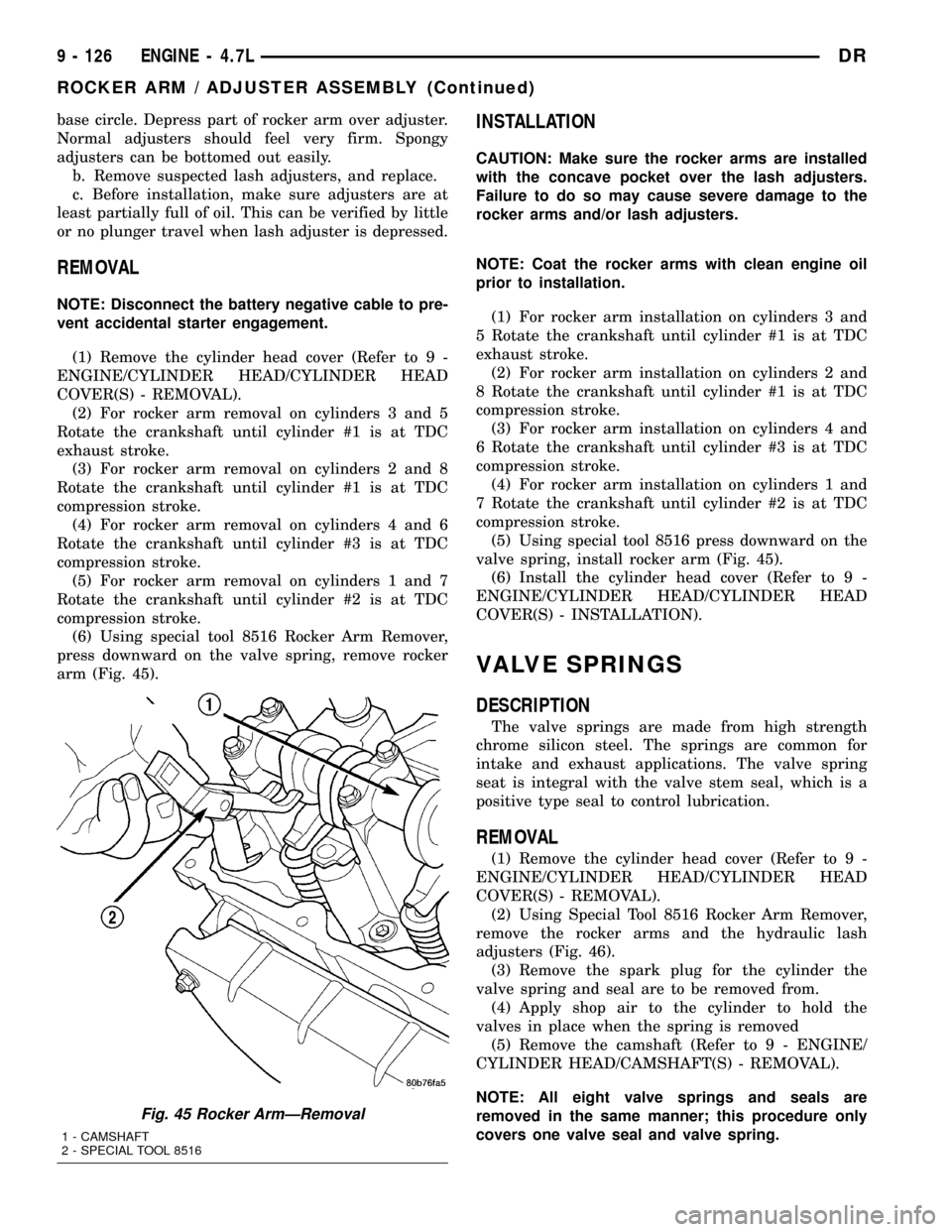
(6) Using special tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover,
press downward on the valve spring, remove rocker
arm (Fig. 45).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Make sure the rocker arms are installed
with the concave pocket over the lash adjusters.
Failure to do so may cause severe damage to the
rocker arms and/or lash adjusters.
NOTE: Coat the rocker arms with clean engine oil
prior to installation.
(1) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 3 and
5 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(2) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 2 and
8 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(3) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 4 and
6 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 1 and
7 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(5) Using special tool 8516 press downward on the
valve spring, install rocker arm (Fig. 45).
(6) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. The springs are common for
intake and exhaust applications. The valve spring
seat is integral with the valve stem seal, which is a
positive type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover,
remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters (Fig. 46).
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed
(5) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: All eight valve springs and seals are
removed in the same manner; this procedure only
covers one valve seal and valve spring.
Fig. 45 Rocker ArmÐRemoval
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
9 - 126 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1405 of 2627
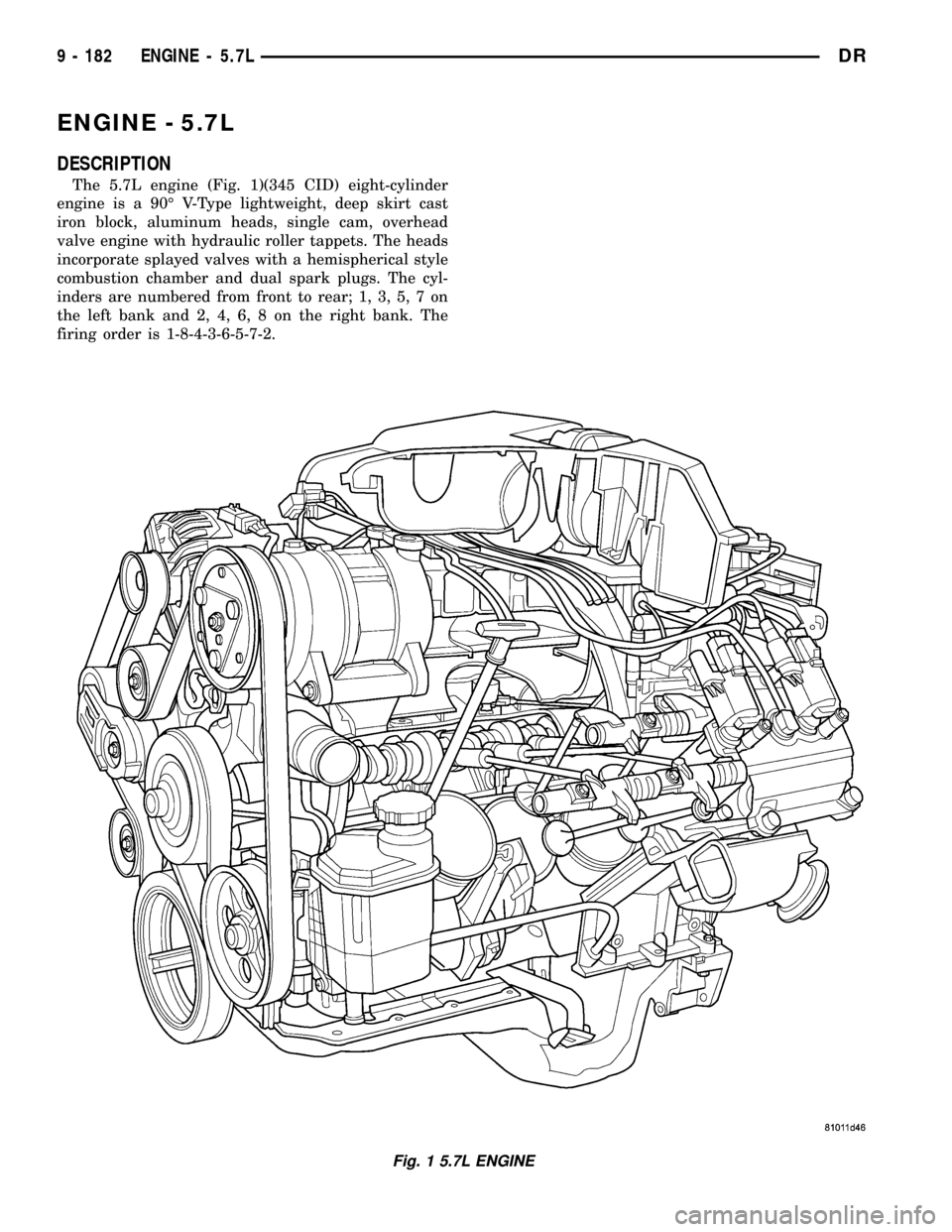
ENGINE - 5.7L
DESCRIPTION
The 5.7L engine (Fig. 1)(345 CID) eight-cylinder
engine is a 90É V-Type lightweight, deep skirt cast
iron block, aluminum heads, single cam, overhead
valve engine with hydraulic roller tappets. The heads
incorporate splayed valves with a hemispherical style
combustion chamber and dual spark plugs. The cyl-
inders are numbered from front to rear; 1, 3, 5, 7 on
the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right bank. The
firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2.
Fig. 1 5.7L ENGINE
9 - 182 ENGINE - 5.7LDR