1998 DODGE RAM 1500 torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1963 of 2627

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 234).
Under stall conditions the turbine is stationary and
the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of
the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a coun-
terclockwise direction. When this happens the over-
running clutch of the stator locks and holds the
stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil
strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller. This
circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maxi-
mum torque multiplication of about 1.75:1. As the
turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the
fluid that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied or released when fluid is feed or vented from
the hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in FOURTH gear, and in THIRD gear under various
conditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, orwhen the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after
the vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter
clutch can also be engaged in the MANUAL SEC-
OND gear position if high transmission temperatures
are sensed by the PCM. The torque converter clutch
may disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
Fig. 234 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1964 of 2627

(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 235). Surface of converter lugs
should be 19mm (0.75 in.) to the rear of the straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The tow/haul overdrive OFF (control) switch is
located in the shift lever arm (Fig. 236). The switch
is a momentary contact device that signals the PCM
to toggle current status of the overdrive function.
Fig. 235 Typical Method Of Checking Converter
Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
Fig. 236 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 261
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1970 of 2627

TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 248). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The Tow/Haul lamp in the instrument panel illumi-
nates when the shift back to third occurs. The trans-
mission will not allow fourth gear operation until
fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110ÉC
(230ÉF).
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 249), (Fig. 250), (Fig.
251), and (Fig. 252):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve
²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²9 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 248 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 267
Page 1977 of 2627
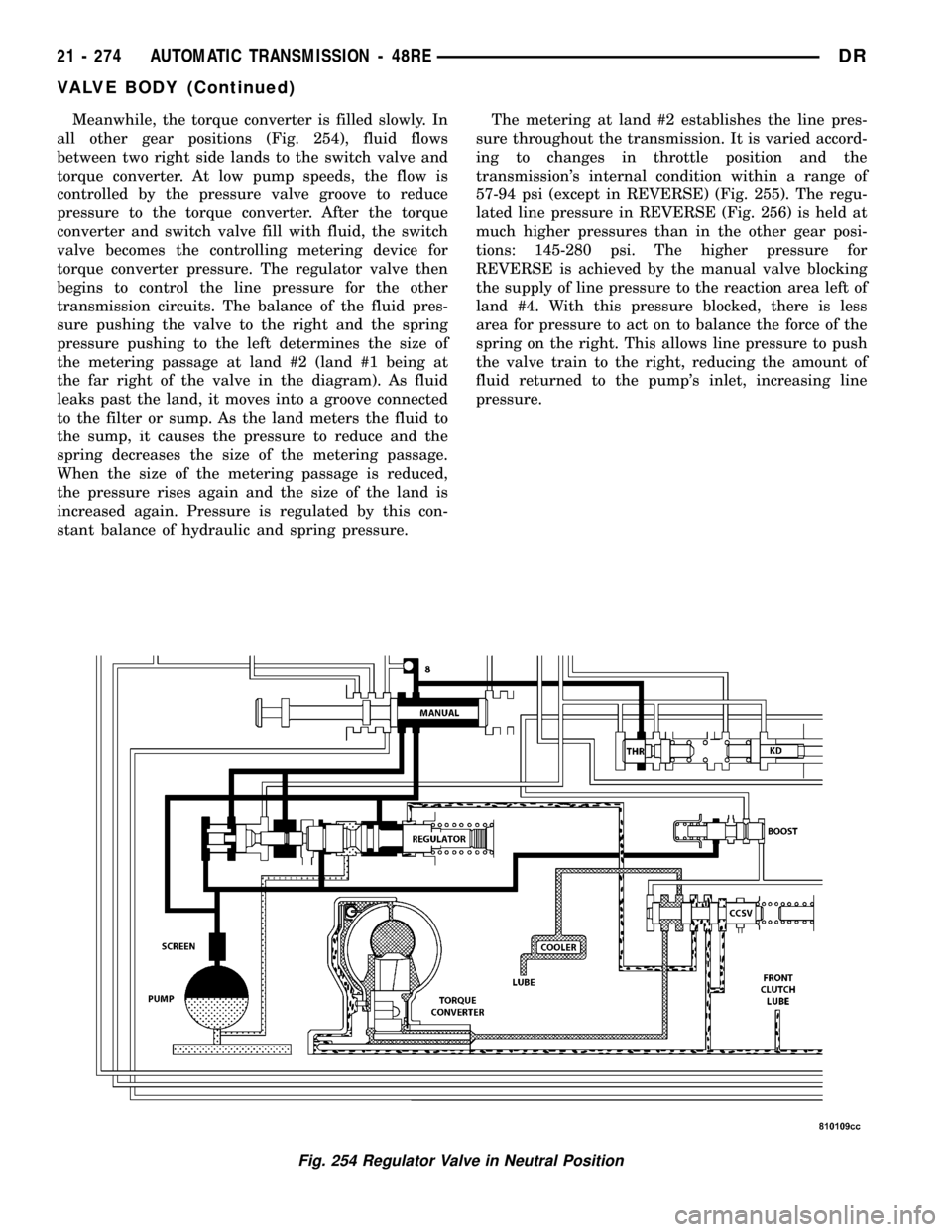
Meanwhile, the torque converter is filled slowly. In
all other gear positions (Fig. 254), fluid flows
between two right side lands to the switch valve and
torque converter. At low pump speeds, the flow is
controlled by the pressure valve groove to reduce
pressure to the torque converter. After the torque
converter and switch valve fill with fluid, the switch
valve becomes the controlling metering device for
torque converter pressure. The regulator valve then
begins to control the line pressure for the other
transmission circuits. The balance of the fluid pres-
sure pushing the valve to the right and the spring
pressure pushing to the left determines the size of
the metering passage at land #2 (land #1 being at
the far right of the valve in the diagram). As fluid
leaks past the land, it moves into a groove connected
to the filter or sump. As the land meters the fluid to
the sump, it causes the pressure to reduce and the
spring decreases the size of the metering passage.
When the size of the metering passage is reduced,
the pressure rises again and the size of the land is
increased again. Pressure is regulated by this con-
stant balance of hydraulic and spring pressure.The metering at land #2 establishes the line pres-
sure throughout the transmission. It is varied accord-
ing to changes in throttle position and the
transmission's internal condition within a range of
57-94 psi (except in REVERSE) (Fig. 255). The regu-
lated line pressure in REVERSE (Fig. 256) is held at
much higher pressures than in the other gear posi-
tions: 145-280 psi. The higher pressure for
REVERSE is achieved by the manual valve blocking
the supply of line pressure to the reaction area left of
land #4. With this pressure blocked, there is less
area for pressure to act on to balance the force of the
spring on the right. This allows line pressure to push
the valve train to the right, reducing the amount of
fluid returned to the pump's inlet, increasing line
pressure.
Fig. 254 Regulator Valve in Neutral Position
21 - 274 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1986 of 2627
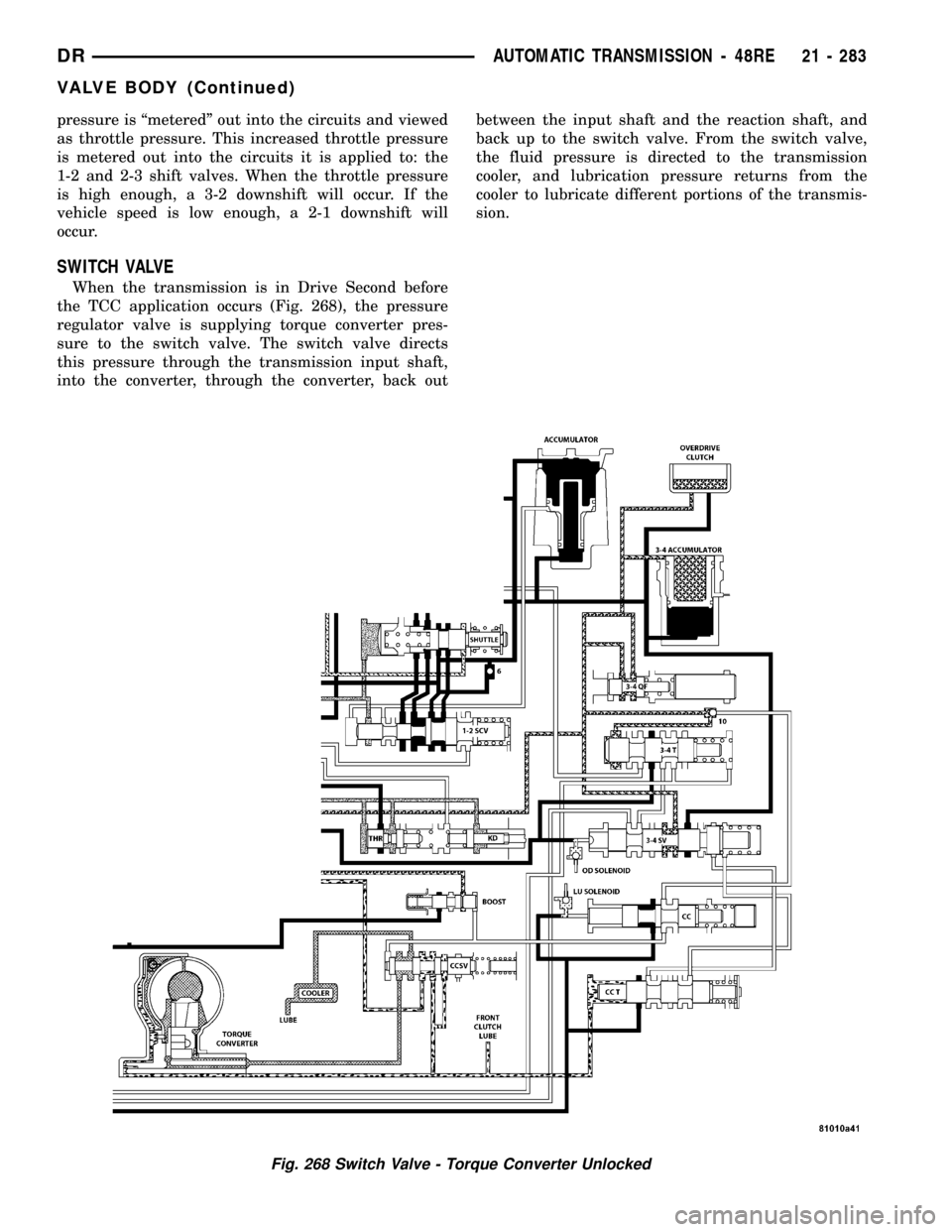
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
SWITCH VALVE
When the transmission is in Drive Second before
the TCC application occurs (Fig. 268), the pressure
regulator valve is supplying torque converter pres-
sure to the switch valve. The switch valve directs
this pressure through the transmission input shaft,
into the converter, through the converter, back outbetween the input shaft and the reaction shaft, and
back up to the switch valve. From the switch valve,
the fluid pressure is directed to the transmission
cooler, and lubrication pressure returns from the
cooler to lubricate different portions of the transmis-
sion.
Fig. 268 Switch Valve - Torque Converter Unlocked
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 283
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1987 of 2627
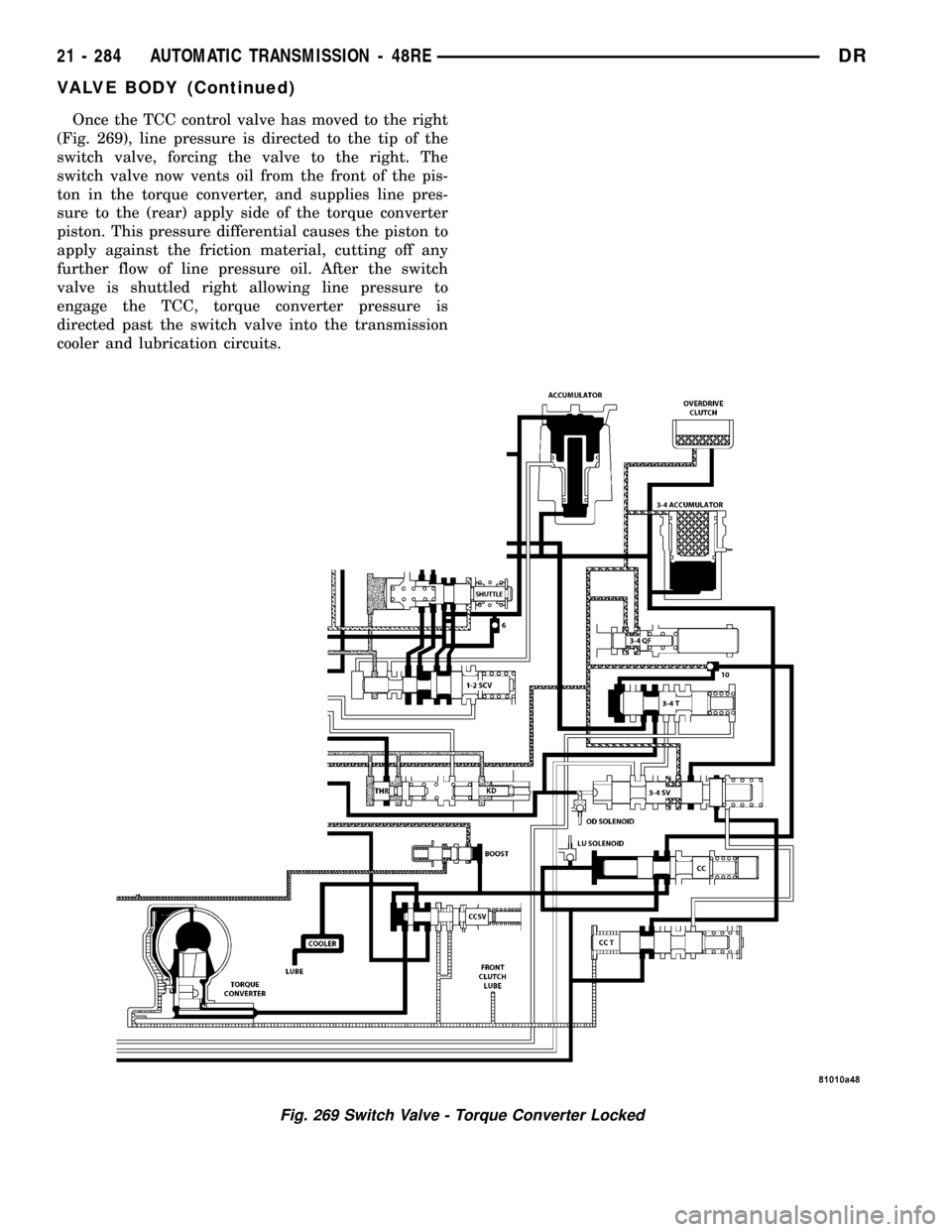
Once the TCC control valve has moved to the right
(Fig. 269), line pressure is directed to the tip of the
switch valve, forcing the valve to the right. The
switch valve now vents oil from the front of the pis-
ton in the torque converter, and supplies line pres-
sure to the (rear) apply side of the torque converter
piston. This pressure differential causes the piston to
apply against the friction material, cutting off any
further flow of line pressure oil. After the switch
valve is shuttled right allowing line pressure to
engage the TCC, torque converter pressure is
directed past the switch valve into the transmission
cooler and lubrication circuits.
Fig. 269 Switch Valve - Torque Converter Locked
21 - 284 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
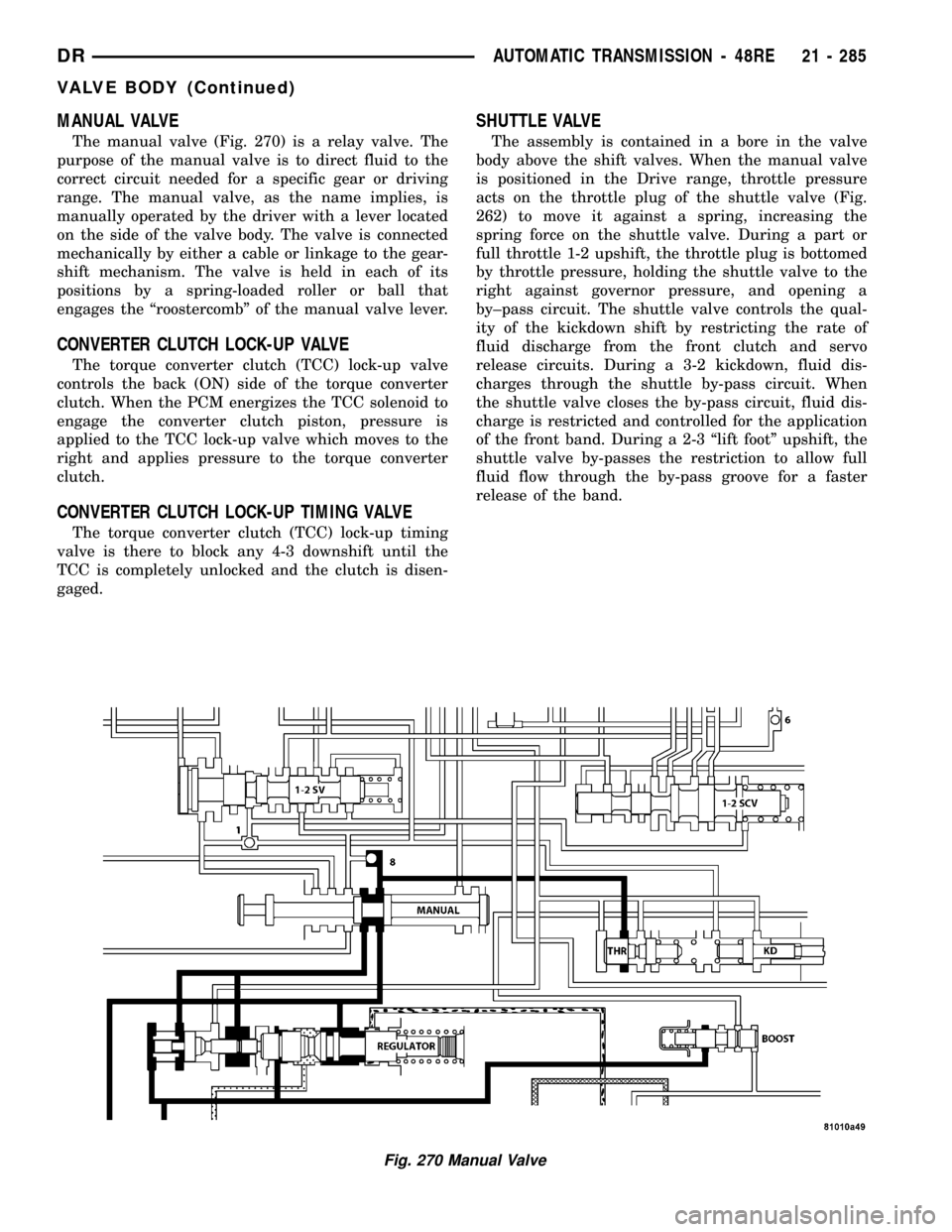
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1989 of 2627
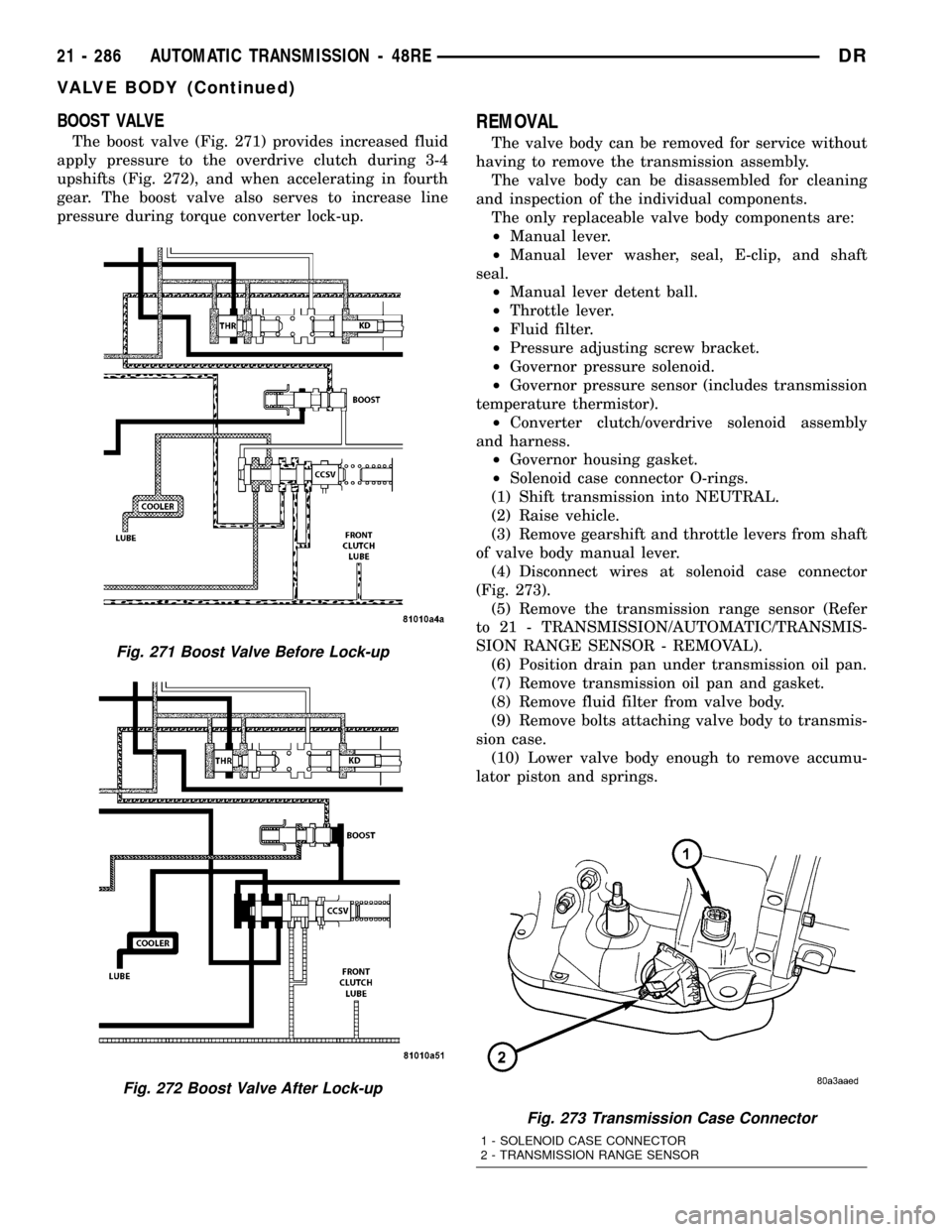
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 271) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 272), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 273).
(5) Remove the transmission range sensor (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/TRANSMIS-
SION RANGE SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(8) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(9) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(10) Lower valve body enough to remove accumu-
lator piston and springs.
Fig. 273 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 271 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 272 Boost Valve After Lock-up
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)