1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Body
[x] Cancel search: BodyPage 2226 of 2627

(3) Remove front tabbed thrust washer (Fig. 36).
(4) Remove input gear (Fig. 37).
(5) Remove rear tabbed thrust washer from low
range gear (Fig. 38).
CLEANING
Clean the transfer case parts with a standard
parts cleaning solvent. Remove all traces of sealer
from the cases and retainers with a scraper and
3MŸ all purpose cleaner. Use compressed air to
remove solvent residue from oil feed passages in the
case halves, retainers, gears, and shafts.
INSPECTION
MAINSHAFT/SPROCKET/HUB INSPECTION
Inspect the splines on the hub and shaft and the
teeth on the sprocket. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with an oilstone. However, replace any
part that is damaged.
Check the contact surfaces in the sprocket bore
and on the mainshaft. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth but do not
try to salvage the shaft if nicks or wear is severe.
INPUT GEAR AND PLANETARY CARRIER
Check the teeth on the gear (Fig. 39). Minor nicks
can be dressed off with an oilstone but replace the
gear if any teeth are broken, cracked, or chipped. The
bearing surface on the gear can be smoothed with
300-400 grit emery cloth if necessary.
Examine the carrier body and pinion gears for
wear or damage. The carrier will have to be replaced
as an assembly if the body, pinion pins, or pinion
gears are damaged.
Check the lock ring and both thrust washers for
wear or cracks. Replace them if necessary. Also
replace the lock retaining ring if bent, distorted, or
broken.
SHIFT FORKS/HUBS/SLEEVES
Check condition of the shift forks and mode fork
shift rail. Minor nicks on the shift rail can be
smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth.
Inspect the shift fork wear pads (Fig. 40). The
mode and range fork pads are serviceable and can be
replaced if necessary.
Check both of the sleeves for wear or damage,
especially on the interior teeth. Replace the sleeves if
wear or damage is evident.
Fig. 36 Front Tabbed Thrust Washer Removal
1 - FRONT TABBED THRUST WASHER
Fig. 37 Input Gear Removal
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - LOW RANGE GEAR
Fig. 38 Rear Tabbed Thrust Washer Removal
1 - LOW RANGE GEAR
2 - REAR TABBED THRUST WASHER
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII 21 - 523
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2257 of 2627

(8) Remove bottom tabbed thrust washer from low
range planetary (Fig. 38).
CLEANING
Clean the transfer case parts with a standard
parts cleaning solvent. Remove all traces of sealer
from the cases and retainers with a scraper and
3MŸ all purpose cleaner. Use compressed air to
remove solvent residue from oil feed passages in the
case halves, retainers, gears, and shafts.
INSPECTION
MAINSHAFT/SPROCKET/HUB INSPECTION
Inspect the splines on the hub and shaft and the
teeth on the sprocket. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with an oilstone. However, replace any
part that is damaged.
Check the contact surfaces in the sprocket bore
and on the mainshaft. Minor nicks and scratches can
be smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth but do not
try to salvage the shaft if nicks or wear is severe.
INPUT GEAR AND PLANETARY CARRIER
Check the teeth on the gear (Fig. 39). Minor nicks
can be dressed off with an oilstone but replace the
gear if any teeth are broken, cracked, or chipped. The
bearing surface on the gear can be smoothed with
300-400 grit emery cloth if necessary.
Examine the carrier body and pinion gears for
wear or damage. Check the pinion gear thrust wash-
ers on the pinon pins for damage. The carrier will
have to be replaced as an assembly if the body, pin-
ion pins, or pinion gears are damaged.
Check the lock ring and both thrust washers for
wear or cracks. Replace them if necessary. Also
replace the lock retaining ring if bent, distorted, or
broken.
Fig. 39 Input Gear And Carrier Components
1 - PLANETARY CARRIER 4 - CARRIER LOCK RING
2 - REAR THRUST WASHER 5 - CARRIER LOCK RETAINING RING
3 - FRONT THRUST WASHER 6 - INPUT GEAR
Fig. 38 Remove Bottom Input Gear Thrust Plate
1 - PLANETARY
2 - THRUST PLATE
21 - 554 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2296 of 2627

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE . . . 2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING . . 3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BUZZ, SQUEAK
& RATTLE...........................11
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE..............12SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY..............................14
TAILGATE..............................15
DOOR - FRONT.........................18
DOORS - REAR.........................28
EXTERIOR.............................36
HOOD.................................46
INSTRUMENT PANEL.....................49
INTERIOR..............................62
PAINT.................................73
SEATS................................75
STATIONARY GLASS.....................86
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS...................91
BODY STRUCTURE......................95
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING
SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
²Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use
when welding.
²Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from
the battery when servicing electrical components
that are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to
electrical system can result.²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
²Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning sol-
vents on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage
to finish or color can result.
²Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
DRBODY 23 - 1
Page 2297 of 2627

VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE
Wind noise is the result of most air leaks. Air leaks
can be caused by poor sealing, improper body compo-
nent alignment, body seam porosity, or missing plugs
in the engine compartment or door hinge pillar areas.
All body sealing points should be airtight in normal
driving conditions. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal airtight under all conditions. At times,
side glass or door seals will allow wind noise to be
noticed in the passenger compartment during high
cross winds. Over compensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop wind noise that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After a repair pro-
cedure has been performed, test vehicle to verify
noise has stopped before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place and
body components are aligned and sealed. If compo-
nent alignment or sealing is necessary, refer to the
appropriate section of this group for proper proce-
dures.
23 - 2 BODYDR
BODY (Continued)
Page 2298 of 2627

ROAD TESTING WIND NOISE
(1) Drive the vehicle to verify the general location
of the wind noise.
(2) Apply 50 mm (2 in.) masking tape in 150 mm
(6 in.) lengths along weatherstrips, weld seams or
moldings. After each length is applied, drive the vehi-
cle. If noise goes away after a piece of tape is applied,
remove tape, locate, and repair defect.
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
²Moldings standing away from body surface can
catch wind and whistle.
²Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body
flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
²Misaligned movable components.
²Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
²Weld burn through holes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY LUBRICATION
All mechanisms and linkages should be lubricated
when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation
and provide protection against rust and excessive
wear. The weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to
prolong their life as well as to improve door sealing.
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat-
ing mechanisms should be inspected and cleaned.
Pivot/sliding contact areas on the mechanisms should
then be lubricated.
(1) When necessary, lubricate the operating mech-
anisms with the specified lubricants.
(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas-
senger's clothing.
(3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch
striker, and safety latch should be lubricated period-
ically.
(5) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated
twice each year (preferably autumn and spring).
²Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant
directly into the lock cylinder.
²Apply a small amount to the key and insert it
into the lock cylinder.
²Rotate it to the locked position and then back to
the unlocked position several times.
²Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with
a clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING
(1) Remove trim panel.(2) Bend or move the trim panel components at
the heat staked joints. Observe the heat staked loca-
tions and/or component seams for looseness.
(3) Heat stake the components.
(a) If the heat staked or component seam loca-
tion is loose, hold the two components tightly
together and using a soldering gun with a flat tip,
melt the material securing the components
together. Do not over heat the affected area, dam-
age to the exterior of the trim panel may occur.
(b) If the heat staked material is broken or miss-
ing, use a hot glue gun to apply new material to
the area to be repaired. The panels that are being
heat staked must be held together while the apply-
ing the glue. Once the new material is in place, it
may be necessary to use a soldering gun to melt
the newly applied material. Do not over heat the
affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim
panel may occur.
(4) Allow the repaired area to cool and verify the
repair.
(5) Install trim panel.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR
There are many different types of plastics used in
today's automotive environment. We group plastics in
three different categories: Rigid, Semi-Rigid, and
Flexible. Any of these plastics may require the use of
an adhesion promoter for repair. These types of plas-
tic are used extensively on DaimlerChrysler Motors
vehicles. Always follow repair material manufactur-
er's plastic identification and repair procedures.
Rigid Plastics:
Examples of rigid plastic use: Fascias, Hoods,
Doors, and other Body Panels, which include SMC,
ABS, and Polycarbonates.
Semi-Rigid Plastics:
Examples of semi-rigid plastic use: Interior Panels,
Under Hood Panels, and other Body Trim Panels.
Flexible Plastics:
Examples of flexible plastic use: Fascias, Body
Moldings, and upper and lower Fascia Covers.
Repair Procedure:
The repair procedure for all three categories of
plastics is basically the same. The one difference is
the material used for the repair. The materials must
be specific for each substrate, rigid repair material
for rigid plastic repair, semi-rigid repair material for
semi-rigid plastic repair and flexible repair material
for flexible plastic repair.
DRBODY 23 - 3
BODY (Continued)
Page 2299 of 2627
Adhesion Promoter/Surface Modifier:
Adhesion Promoters/Surface Modifiers are required
for certain plastics. All three categories may have
plastics that require the use of adhesion promoter/
surface modifiers. Always follow repair material man-
ufacturer's plastic identification and repair
procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTION AND WARNINGS
WARNING:
²EYE PROTECTION SHOULD BE USED WHEN
SERVICING COMPONENTS. PERSONAL INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING MASK
WHEN MIXING EPOXY, GRINDING, AND SPRAYING
PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN A CONFINED AREA. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
RESIN, PETROLEUM, OR ALCOHOL BASED SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHI-
CLE THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON
SAFETY STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
NOTE:
²When holes must be drilled or cut in body pan-
els, verify locations of internal body components
and electrical wiring. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on undamaged painted surfaces around repair
areas. Damage to finish can result.
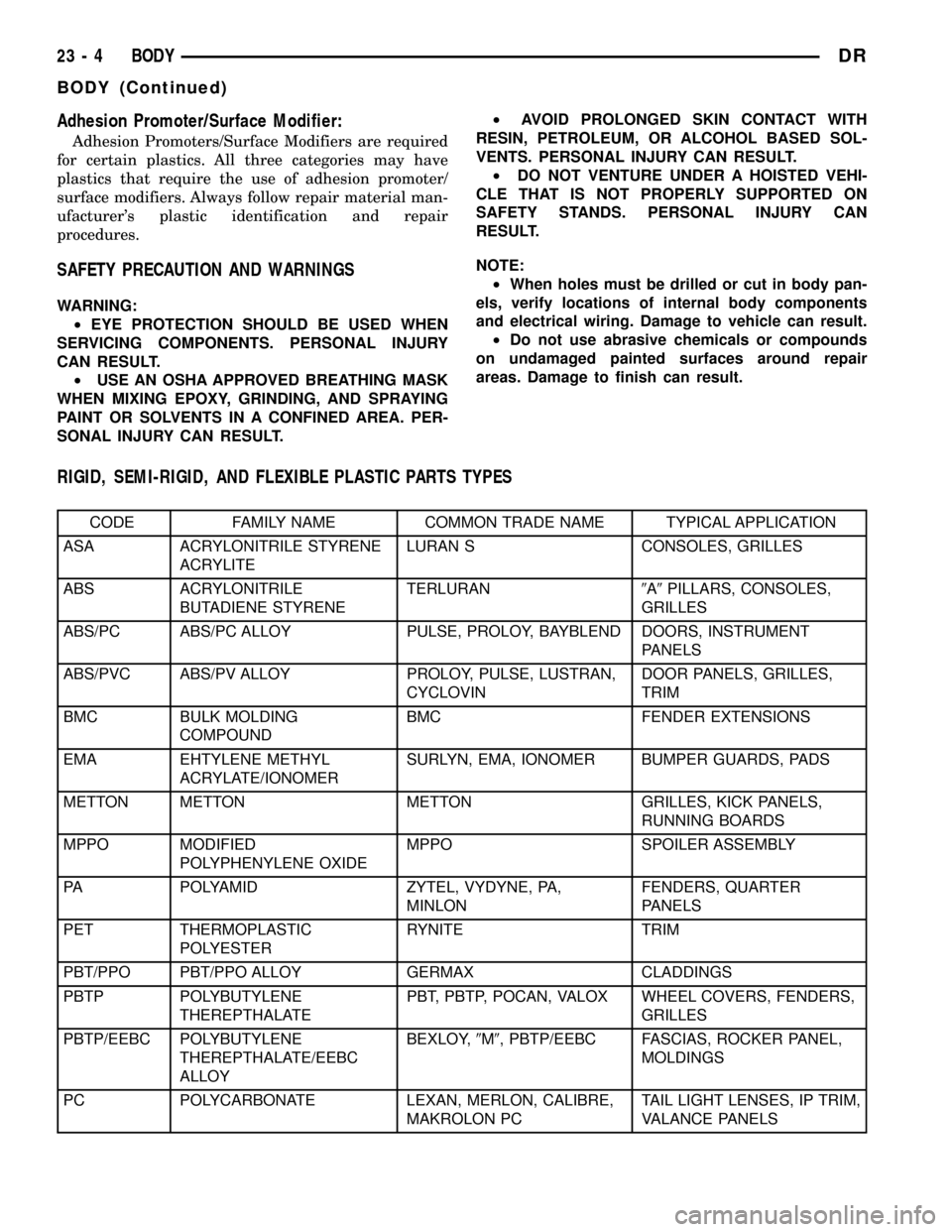
RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN9A9PILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY, BAYBLEND DOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER
PANELS
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,9M9, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VALANCE PANELS
23 - 4 BODYDR
BODY (Continued)
Page 2300 of 2627
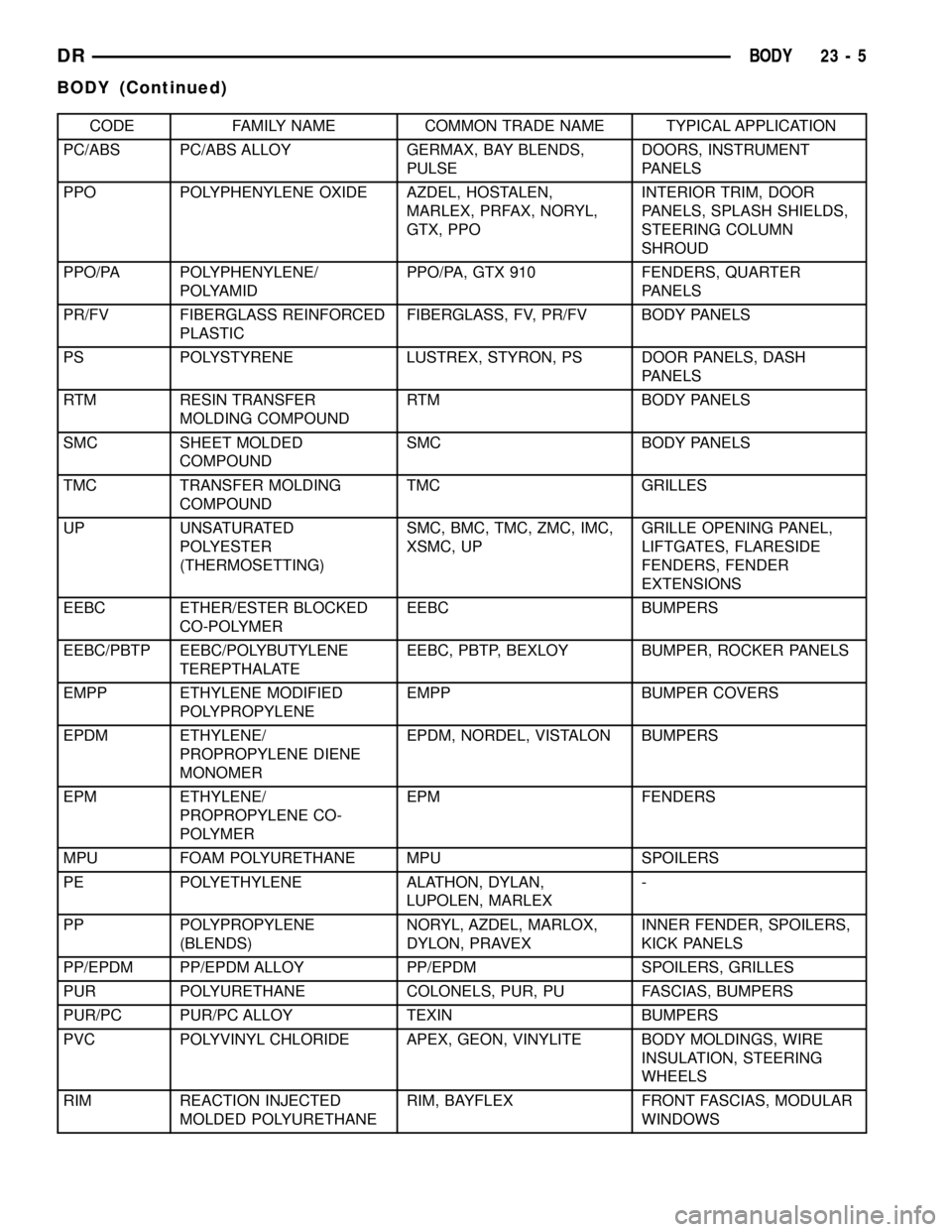
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PANELS
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PANELS
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
MPU FOAM POLYURETHANE MPU SPOILERS
PE POLYETHYLENE ALATHON, DYLAN,
LUPOLEN, MARLEX-
PP POLYPROPYLENE
(BLENDS)NORYL, AZDEL, MARLOX,
DYLON, PRAVEXINNER FENDER, SPOILERS,
KICK PANELS
PP/EPDM PP/EPDM ALLOY PP/EPDM SPOILERS, GRILLES
PUR POLYURETHANE COLONELS, PUR, PU FASCIAS, BUMPERS
PUR/PC PUR/PC ALLOY TEXIN BUMPERS
PVC POLYVINYL CHLORIDE APEX, GEON, VINYLITE BODY MOLDINGS, WIRE
INSULATION, STEERING
WHEELS
RIM REACTION INJECTED
MOLDED POLYURETHANERIM, BAYFLEX FRONT FASCIAS, MODULAR
WINDOWS
DRBODY 23 - 5
BODY (Continued)
Page 2301 of 2627

CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
RRIM REINFORCED REACTION
INJECTED MOLDEDPUR, RRIM FASCIAS, BODY PANELS,
BODY TRIMS
TPE THERMO POLYETHYLENE TPE, HYTREL, BEXLOY-V FASCIAS, BUMPERS,
CLADDINGS
TPO THERMOPOLYOLEFIN POLYTROPE, RENFLEX,
SANTOPRENE, VISAFLEX,
ETA, APEX, TPO, SHIELDS,
CLADDINGSBUMPERS, END CAPS,
TELCAR, RUBBER, STRIPS,
SIGHT, INTERIOR B POST
TPP THERMO-POLYPROPYLENE TPP BUMPERS
TPU THERMOPOLYURETHANE,
POLYESTERTPU, HYTREL, TEXIN,
ESTANEBUMPERS, BODY SIDE,
MOLDINGS, FENDERS,
FASCIAS
PANEL SECTIONING
If it is required to section a large panel for a plas-
tic repair, it will be necessary to reinforce the panel
(Fig. 1). To bond two plastic panels together, a rein-
forcement must overlap both panels. The panels
must be ªV'dº at a 20 degree angle. The area to be
reinforced should be washed, then sanded. Be sure to
wipe off any excess soap and water when finished.
Lightly sand or abrade the plastic with an abrasive
pad or sandpaper. Blow off any dust with compressed
air or wipe with a clean dry rag.
When bonding plastic panels, Follow repair mate-
rial manufacturers recommendations. Be sure that
enough adhesive has been applied to allow squeeze
out and to fill the full bond line. Once the pieces
have been brought together, do not move them until
the adhesive is cured. The assembly can be held
together with clamps, rivets, etc. A faster cure can be
obtained by heating with a heat lamp or heat gun.After the parts have been bonded and have had time
to cure, rough sand the seam and apply the final
adhesive filler to the area being repaired. Smooth the
filler with a spreader, wooden tongue depressor, or
squeegee. For fine texturing, a small amount of
water can be applied to the filler surface while
smoothing. The cured filler can be sanded as neces-
sary and, as a final step, cleanup can be done with
soapy water. Wipe the surface clean with a dry cloth
allowing time for the panel to dry before moving on
with the repair.
PANEL REINFORCEMENT
Structural repair procedures for rigid panels with
large cracks and holes will require a reinforcement
backing. Reinforcements can be made with several
applications of glass cloth saturated with structural
adhesive. Semi-rigid or flexible repair materials
should be used for semi-rigid or flexible backing rein-
forcement (Fig. 2) and (Fig. 3). Open meshed fiber-
glass dry wall tape can be used to form a
reinforcement. The dry wall tape allows the resin to
penetrate through and make a good bond between
the panel and the adhesive. Structurally, the more
dry wall tape used, the stronger the repair.
Another kind of repair that can be done to repair
large cracks and holes is to use a scrap piece of sim-
ilar plastic and bond with structural adhesive. The
reinforcement should cover the entire break and
should have a generous amount of overlap on either
side of the cracked or broken area.
When repairing plastic, the damaged area is first
ªV'dº out, or beveled. Large bonding areas are desir-
able when repairing plastic because small repairs are
less likely to hold permanently. Beveling the area
around a crack at a 20 degree angle will increase the
bonding surface for a repair (Fig. 4). It is recom-
mended that sharp edges be avoided because the
joint may show through after the panel is refinished.
Fig. 1 PANEL SECTIONING
1 - EXISTING PANEL
2 - NEW PANEL
3 - PANEL ADHESIVE
4 - BONDING STRIP
23 - 6 BODYDR
BODY (Continued)