1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Over drive
[x] Cancel search: Over drivePage 1964 of 2627

(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 235). Surface of converter lugs
should be 19mm (0.75 in.) to the rear of the straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The tow/haul overdrive OFF (control) switch is
located in the shift lever arm (Fig. 236). The switch
is a momentary contact device that signals the PCM
to toggle current status of the overdrive function.
Fig. 235 Typical Method Of Checking Converter
Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
Fig. 236 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 261
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1965 of 2627
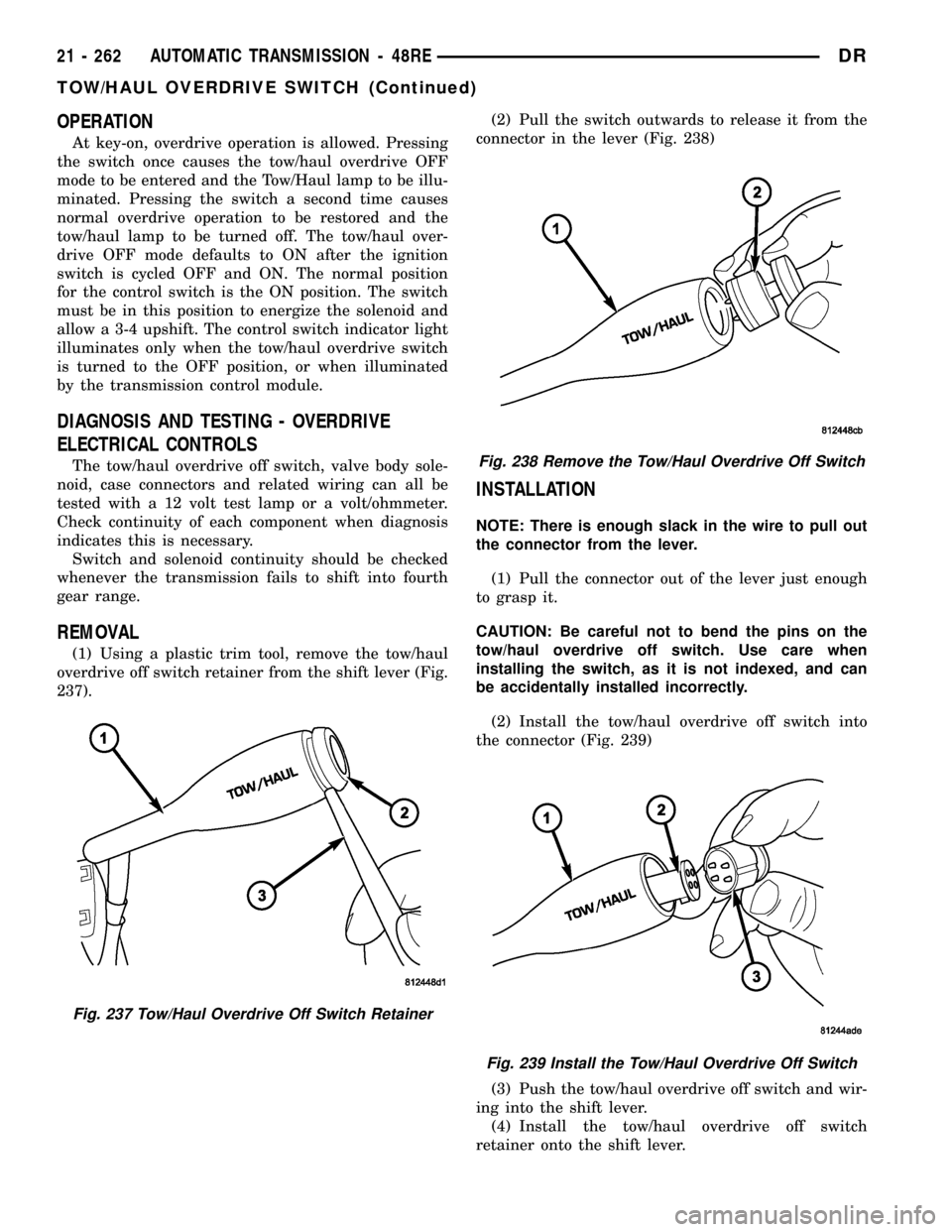
OPERATION
At key-on, overdrive operation is allowed. Pressing
the switch once causes the tow/haul overdrive OFF
mode to be entered and the Tow/Haul lamp to be illu-
minated. Pressing the switch a second time causes
normal overdrive operation to be restored and the
tow/haul lamp to be turned off. The tow/haul over-
drive OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition
switch is cycled OFF and ON. The normal position
for the control switch is the ON position. The switch
must be in this position to energize the solenoid and
allow a 3-4 upshift. The control switch indicator light
illuminates only when the tow/haul overdrive switch
is turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated
by the transmission control module.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS
The tow/haul overdrive off switch, valve body sole-
noid, case connectors and related wiring can all be
tested with a 12 volt test lamp or a volt/ohmmeter.
Check continuity of each component when diagnosis
indicates this is necessary.
Switch and solenoid continuity should be checked
whenever the transmission fails to shift into fourth
gear range.
REMOVAL
(1) Using a plastic trim tool, remove the tow/haul
overdrive off switch retainer from the shift lever (Fig.
237).(2) Pull the switch outwards to release it from the
connector in the lever (Fig. 238)
INSTALLATION
NOTE: There is enough slack in the wire to pull out
the connector from the lever.
(1) Pull the connector out of the lever just enough
to grasp it.
CAUTION: Be careful not to bend the pins on the
tow/haul overdrive off switch. Use care when
installing the switch, as it is not indexed, and can
be accidentally installed incorrectly.
(2) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch into
the connector (Fig. 239)
(3) Push the tow/haul overdrive off switch and wir-
ing into the shift lever.
(4) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch
retainer onto the shift lever.
Fig. 237 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch Retainer
Fig. 238 Remove the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
Fig. 239 Install the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
21 - 262 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1970 of 2627

TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 248). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The Tow/Haul lamp in the instrument panel illumi-
nates when the shift back to third occurs. The trans-
mission will not allow fourth gear operation until
fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110ÉC
(230ÉF).
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 249), (Fig. 250), (Fig.
251), and (Fig. 252):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve
²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²9 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 248 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 267
Page 1974 of 2627

Fig. 252 Lower Housing Shift Valves and Springs
1 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING 11 - TIMING VALVE COVER
2 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 12 - PLUG
3 - PLUG 13 - 3-4 TIMING VALVE AND SPRING
4 - SPRING RETAINER 14 - LOWER HOUSING
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE AND SPRING 15 - ACCUMULATOR END PLATE
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH TIMING VALVE AND SPRING 16 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR PISTON AND SPRING
7 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE 17 - E-CLIP
8 - CASE CONNECTOR 18 - 3-4 QUICK FILL SPRING AND VALVE
9 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID 19 - SOLENOID GASKET
10 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID 20 - HARNESS
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 271
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1979 of 2627
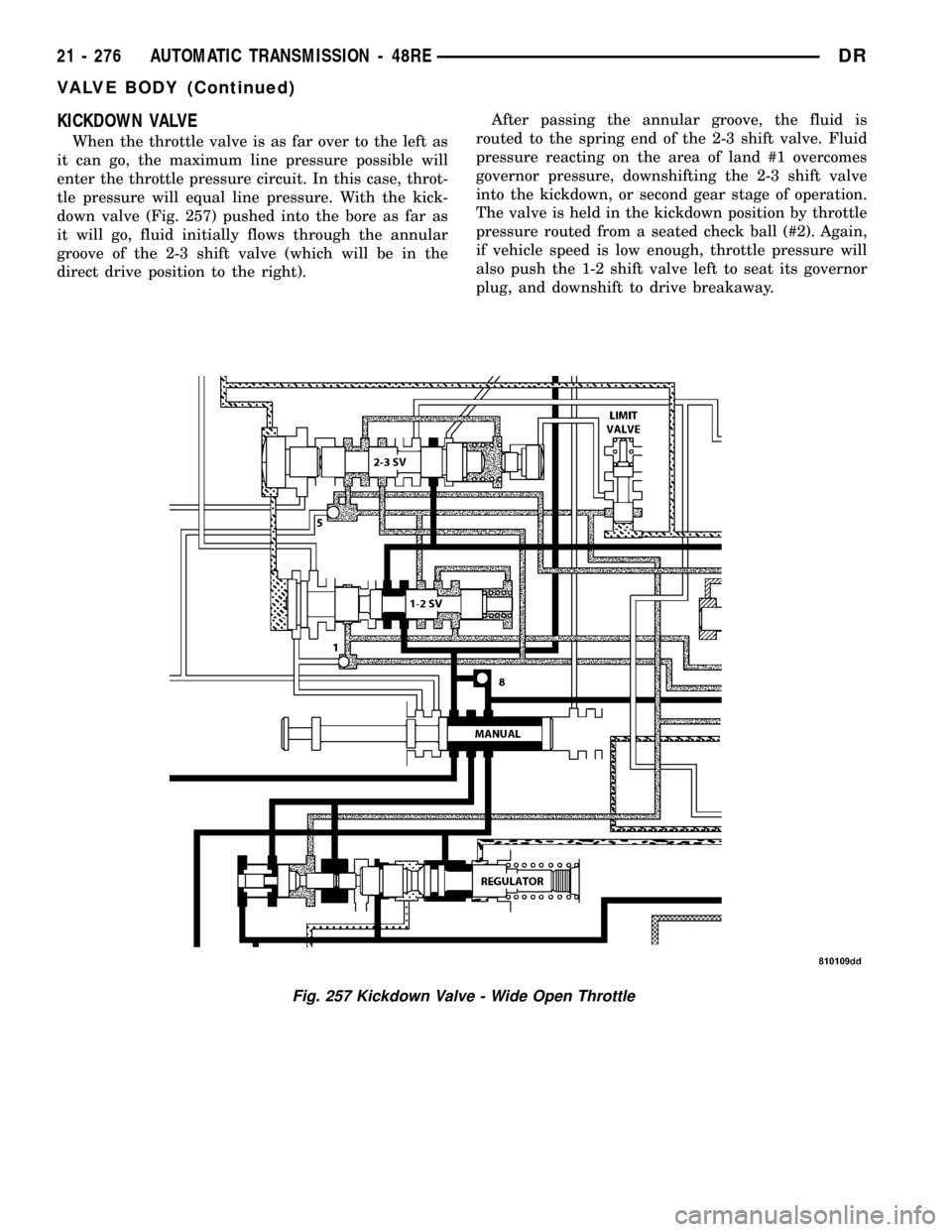
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 257) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 257 Kickdown Valve - Wide Open Throttle
21 - 276 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1983 of 2627
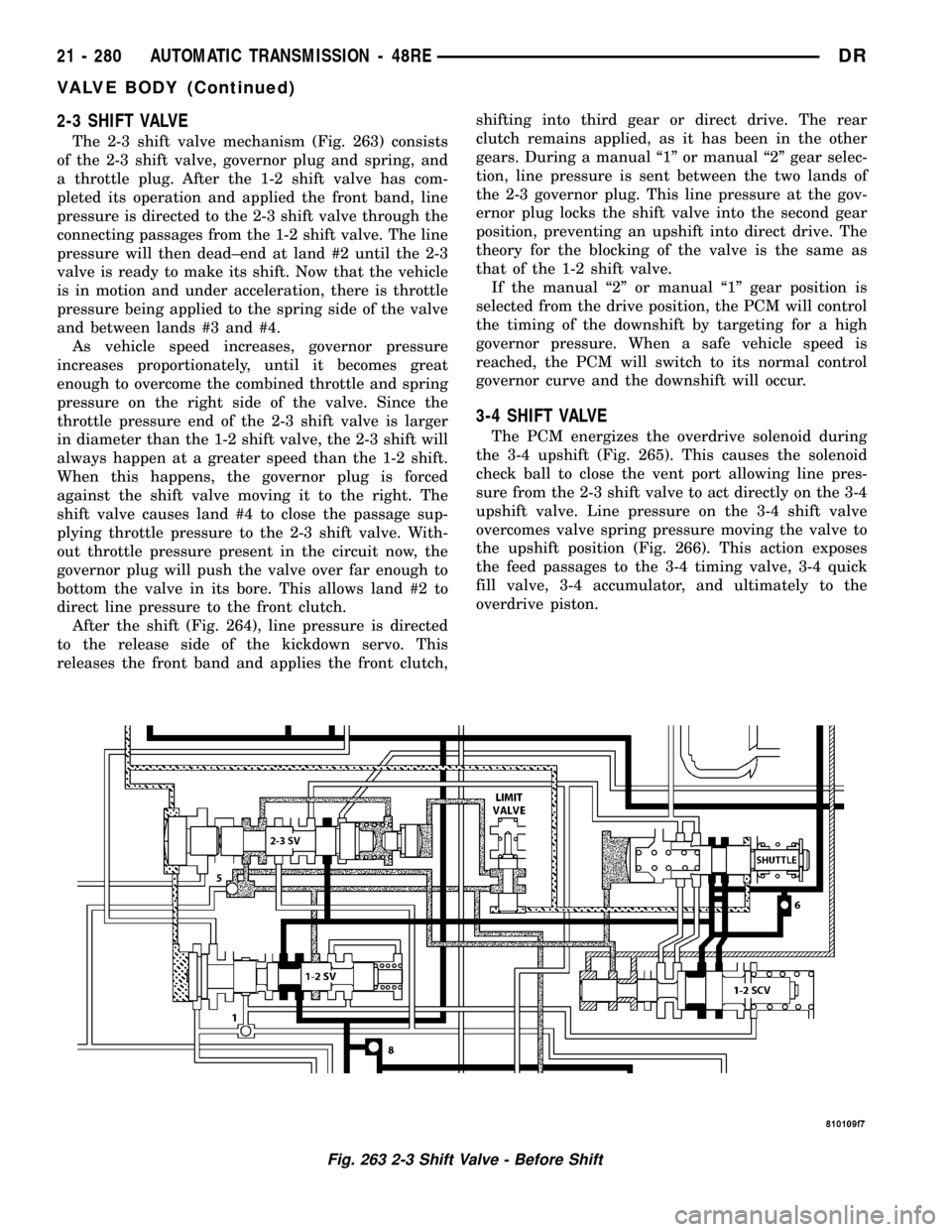
2-3 SHIFT VALVE
The 2-3 shift valve mechanism (Fig. 263) consists
of the 2-3 shift valve, governor plug and spring, and
a throttle plug. After the 1-2 shift valve has com-
pleted its operation and applied the front band, line
pressure is directed to the 2-3 shift valve through the
connecting passages from the 1-2 shift valve. The line
pressure will then dead±end at land #2 until the 2-3
valve is ready to make its shift. Now that the vehicle
is in motion and under acceleration, there is throttle
pressure being applied to the spring side of the valve
and between lands #3 and #4.
As vehicle speed increases, governor pressure
increases proportionately, until it becomes great
enough to overcome the combined throttle and spring
pressure on the right side of the valve. Since the
throttle pressure end of the 2-3 shift valve is larger
in diameter than the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift will
always happen at a greater speed than the 1-2 shift.
When this happens, the governor plug is forced
against the shift valve moving it to the right. The
shift valve causes land #4 to close the passage sup-
plying throttle pressure to the 2-3 shift valve. With-
out throttle pressure present in the circuit now, the
governor plug will push the valve over far enough to
bottom the valve in its bore. This allows land #2 to
direct line pressure to the front clutch.
After the shift (Fig. 264), line pressure is directed
to the release side of the kickdown servo. This
releases the front band and applies the front clutch,shifting into third gear or direct drive. The rear
clutch remains applied, as it has been in the other
gears. During a manual ª1º or manual ª2º gear selec-
tion, line pressure is sent between the two lands of
the 2-3 governor plug. This line pressure at the gov-
ernor plug locks the shift valve into the second gear
position, preventing an upshift into direct drive. The
theory for the blocking of the valve is the same as
that of the 1-2 shift valve.
If the manual ª2º or manual ª1º gear position is
selected from the drive position, the PCM will control
the timing of the downshift by targeting for a high
governor pressure. When a safe vehicle speed is
reached, the PCM will switch to its normal control
governor curve and the downshift will occur.
3-4 SHIFT VALVE
The PCM energizes the overdrive solenoid during
the 3-4 upshift (Fig. 265). This causes the solenoid
check ball to close the vent port allowing line pres-
sure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly on the 3-4
upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4 shift valve
overcomes valve spring pressure moving the valve to
the upshift position (Fig. 266). This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston.
Fig. 263 2-3 Shift Valve - Before Shift
21 - 280 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1985 of 2627
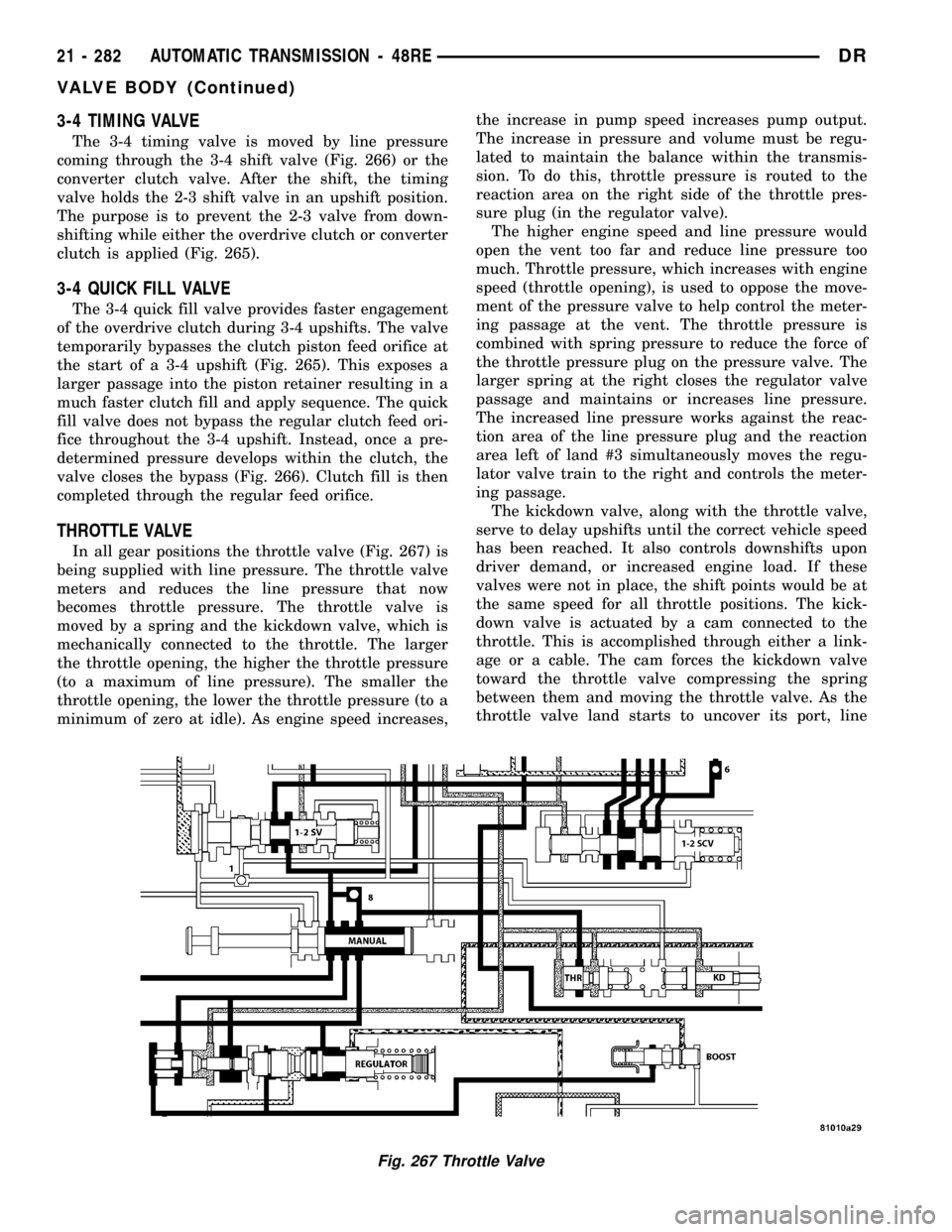
3-4 TIMING VALVE
The 3-4 timing valve is moved by line pressure
coming through the 3-4 shift valve (Fig. 266) or the
converter clutch valve. After the shift, the timing
valve holds the 2-3 shift valve in an upshift position.
The purpose is to prevent the 2-3 valve from down-
shifting while either the overdrive clutch or converter
clutch is applied (Fig. 265).
3-4 QUICK FILL VALVE
The 3-4 quick fill valve provides faster engagement
of the overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts. The valve
temporarily bypasses the clutch piston feed orifice at
the start of a 3-4 upshift (Fig. 265). This exposes a
larger passage into the piston retainer resulting in a
much faster clutch fill and apply sequence. The quick
fill valve does not bypass the regular clutch feed ori-
fice throughout the 3-4 upshift. Instead, once a pre-
determined pressure develops within the clutch, the
valve closes the bypass (Fig. 266). Clutch fill is then
completed through the regular feed orifice.
THROTTLE VALVE
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 267) is
being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve
meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is
moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is
mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure
(to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the
throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure (to a
minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases,the increase in pump speed increases pump output.
The increase in pressure and volume must be regu-
lated to maintain the balance within the transmis-
sion. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the
reaction area on the right side of the throttle pres-
sure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valve
passage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
Fig. 267 Throttle Valve
21 - 282 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
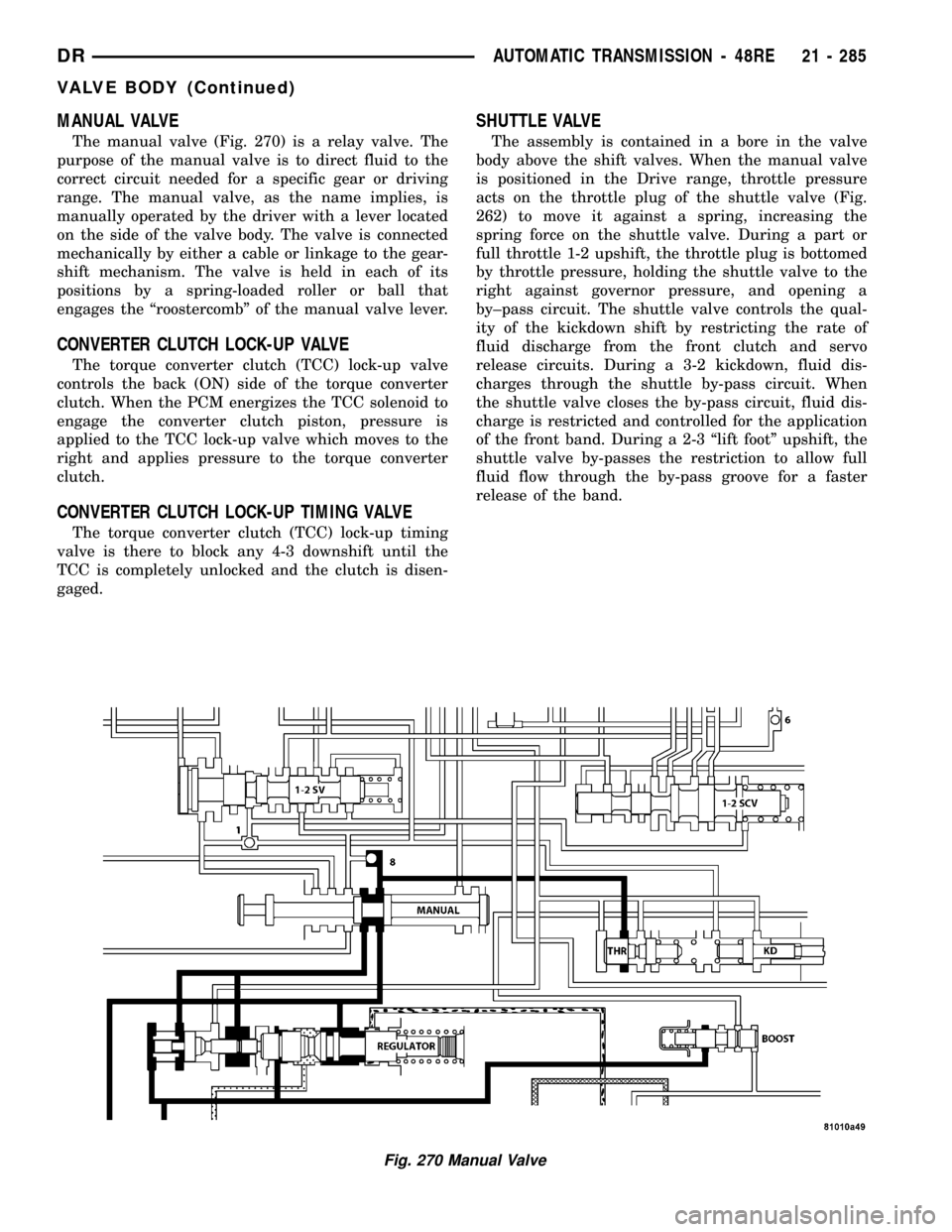
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)