1998 DODGE RAM 1500 clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 1985 of 2627
3-4 TIMING VALVE
The 3-4 timing valve is moved by line pressure
coming through the 3-4 shift valve (Fig. 266) or the
converter clutch valve. After the shift, the timing
valve holds the 2-3 shift valve in an upshift position.
The purpose is to prevent the 2-3 valve from down-
shifting while either the overdrive clutch or converter
clutch is applied (Fig. 265).
3-4 QUICK FILL VALVE
The 3-4 quick fill valve provides faster engagement
of the overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts. The valve
temporarily bypasses the clutch piston feed orifice at
the start of a 3-4 upshift (Fig. 265). This exposes a
larger passage into the piston retainer resulting in a
much faster clutch fill and apply sequence. The quick
fill valve does not bypass the regular clutch feed ori-
fice throughout the 3-4 upshift. Instead, once a pre-
determined pressure develops within the clutch, the
valve closes the bypass (Fig. 266). Clutch fill is then
completed through the regular feed orifice.
THROTTLE VALVE
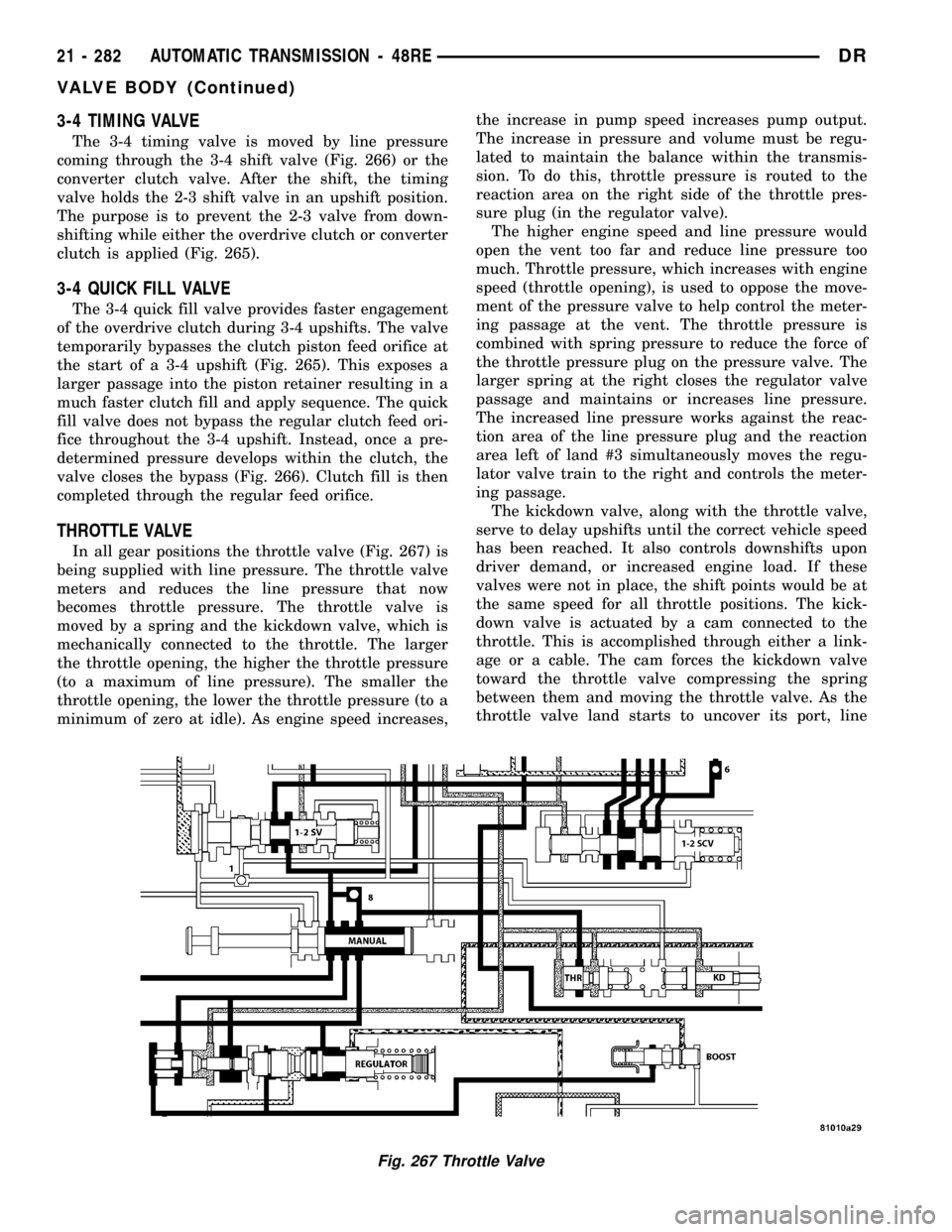
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 267) is
being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve
meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is
moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is
mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure
(to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the
throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure (to a
minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases,the increase in pump speed increases pump output.
The increase in pressure and volume must be regu-
lated to maintain the balance within the transmis-
sion. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the
reaction area on the right side of the throttle pres-
sure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would
open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too
much. Throttle pressure, which increases with engine
speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the move-
ment of the pressure valve to help control the meter-
ing passage at the vent. The throttle pressure is
combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of
the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The
larger spring at the right closes the regulator valve
passage and maintains or increases line pressure.
The increased line pressure works against the reac-
tion area of the line pressure plug and the reaction
area left of land #3 simultaneously moves the regu-
lator valve train to the right and controls the meter-
ing passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve,
serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed
has been reached. It also controls downshifts upon
driver demand, or increased engine load. If these
valves were not in place, the shift points would be at
the same speed for all throttle positions. The kick-
down valve is actuated by a cam connected to the
throttle. This is accomplished through either a link-
age or a cable. The cam forces the kickdown valve
toward the throttle valve compressing the spring
between them and moving the throttle valve. As the
throttle valve land starts to uncover its port, line
Fig. 267 Throttle Valve
21 - 282 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
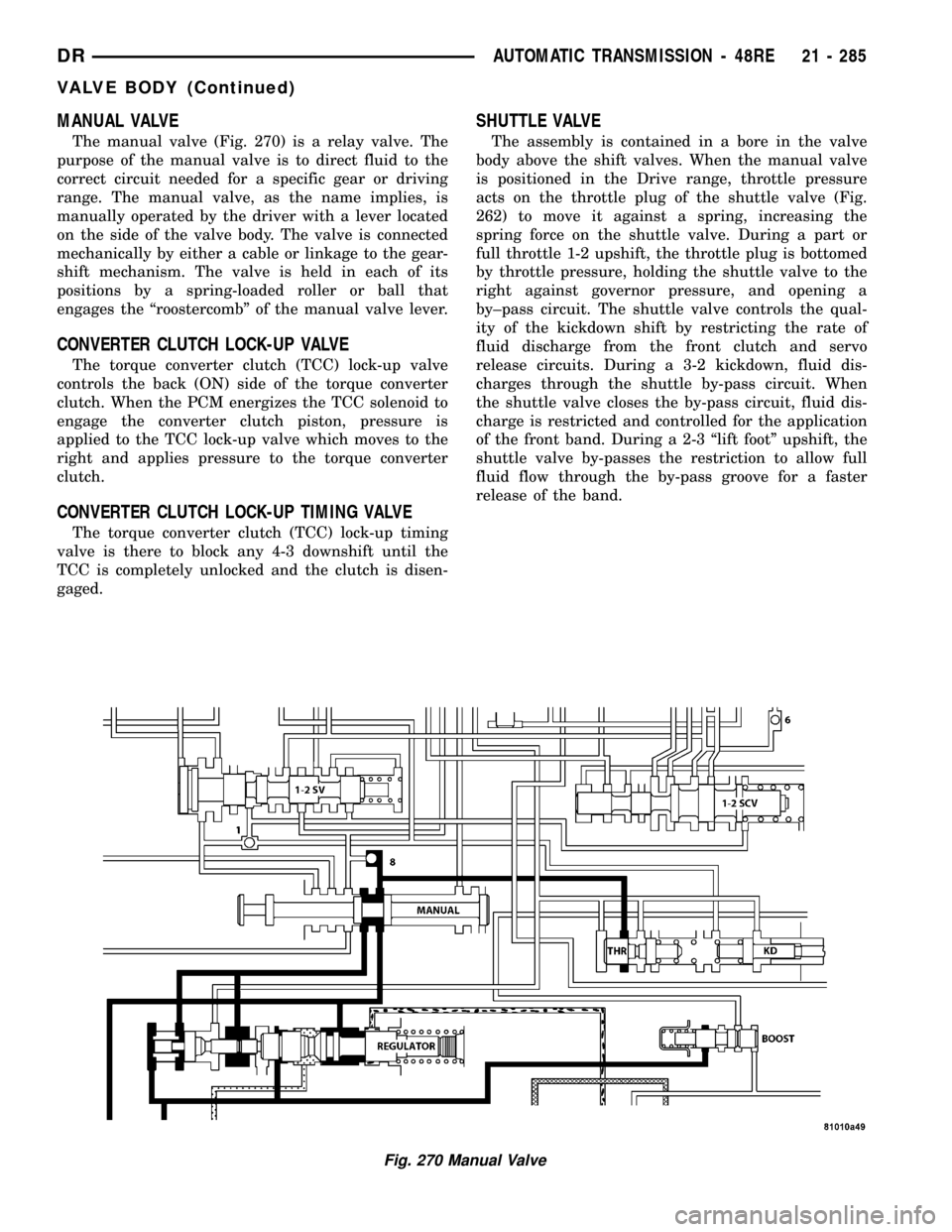
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1989 of 2627
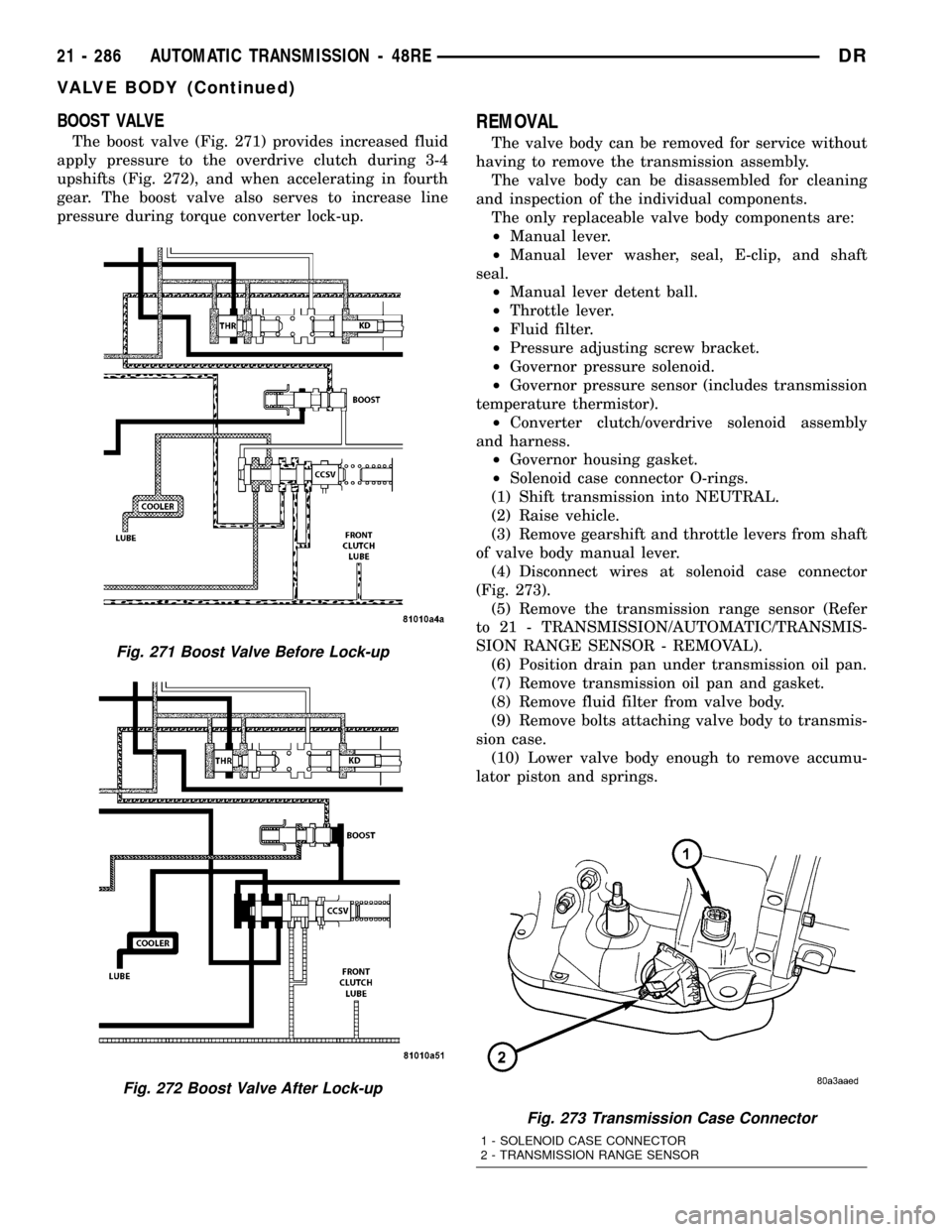
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 271) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 272), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 273).
(5) Remove the transmission range sensor (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/TRANSMIS-
SION RANGE SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(8) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(9) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(10) Lower valve body enough to remove accumu-
lator piston and springs.
Fig. 273 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 271 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 272 Boost Valve After Lock-up
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1991 of 2627

(8) Turn valve body over and remove screws that
attach overdrive/converter solenoid assembly to valve
body (Fig. 277).
(9) Remove solenoid and harness assembly from
valve body (Fig. 278).
(10) Remove boost valve cover (Fig. 279).
(11) Remove boost valve retainer, valve spring and
boost valve (Fig. 280).
Fig. 277 Solenoid Assembly Screws
1 - OVERDRIVE/CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID ASSEMBLY
2 - HARNESS
Fig. 278 Solenoid Assembly
1 - GOVERNOR SOLENOID WIRES
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
3 - SOLENOID SCREWS
4 - GOVERNOR SENSOR WIRES
5 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID
6 - HARNESS
7 - CASE CONNECTOR
Fig. 279 Boost Valve Cover Location
1 - BOOST VALVE HOUSING AND COVER
2 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
Fig. 280 Boost Valve Components
1 - SPRING AND VALVE RETAINER
2 - COVER SCREWS
3 - BOOST VALVE COVER
4 - BOOST VALVE PLUG
5 - BOOST VALVE
6 - BOOST VALVE SPRING
21 - 288 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1993 of 2627

(17) Remove screws attaching pressure adjusting
screw bracket to valve body and transfer plate (Fig.
286). Hold bracket firmly against spring tension
while removing last screw.
(18) Remove adjusting screw bracket, line pressure
adjusting screw, pressure regulator valve spring and
switch valve spring (Fig. 287). Do not remove throttle
pressure adjusting screw from bracket and do not
disturb setting of either adjusting screw during
removal.
(19) Turn upper housing over and remove switch
valve, regulator valve and spring, and manual valve
(Fig. 288).(20) Remove kickdown detent, kickdown valve, and
throttle valve and spring (Fig. 288).
(21) Loosen left-side 3-4 accumulator housing
attaching screw about 2-3 threads. Then remove cen-
ter and right-side housing attaching screws (Fig.
289).
(22) Carefully rotate 3-4 accumulator housing
upward and remove 3-4 shift valve spring and con-
verter clutch valve plug and spring (Fig. 290).
Fig. 287 Adjusting Screw Bracket
1 - SWITCH VALVE SPRING
2 - LINE PRESSURE SCREW
3 - THROTTLE PRESSURE ADJUSTING SCREW
4 - ADJUSTING SCREW BRACKET
5 - PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE SPRING
Fig. 286 Adjusting Screw Bracket Fastener
1 - T25 TORXŸ BIT
2 - REMOVE THESE SCREWS FIRST
3 - BRACKET
4 - BRACKET
5 - REMOVE THIS SCREW LAST
21 - 290 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1994 of 2627

Fig. 288 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
Fig. 289 Accumulator Housing Screw Locations
1 - LOOSEN THIS SCREW
2 - REMOVE THESE SCREWS
3 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSINGFig. 290 3-4 Shift And Converter Clutch Valve
Springs and Plug
1 - ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE SPRING
3 - CLUTCH VALVE PLUG
4 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 291
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1995 of 2627

(23) Remove left-side screw and remove 3-4 accu-
mulator housing from valve body (Fig. 291).
(24) Bend back tabs on boost valve tube brace (Fig.
292).(25) Remove boost valve connecting tube (Fig.
293). Disengage tube from upper housing port first.
Then rock opposite end of tube back and forth to
work it out of lower housing.
CAUTION: Do not use tools to loosen or pry the
connecting tube out of the valve body housings.
Loosen and remove the tube by hand only.
(26) Turn valve body over so lower housing is fac-
ing upward (Fig. 294). In this position, the two check
balls in upper housing will remain in place and not
fall out when lower housing and separator plate are
removed.
(27) Remove screws attaching valve body lower
housing to upper housing and transfer plate (Fig.
294). Note position of boost valve tube brace for
assembly reference.
(28) Remove lower housing and overdrive separa-
tor plate from transfer plate (Fig. 294).
Fig. 293 Boost Valve Tube
1 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
2 - LOWER HOUSING
3 - DISENGAGE THIS END OF TUBE FIRST
4 - UPPER HOUSING
Fig. 294 Lower Housing
1 - LOWER HOUSING
2 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE
3 - TRANSFER PLATE AND UPPER HOUSING
Fig. 291 Accumulator Housing, Valve Springs, and
Plug
1 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE SPRING AND PLUG
3 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
Fig. 292 Boost Valve Tube Brace
1 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
2 - TUBE BRACE (DOUBLE TAB)
21 - 292 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1996 of 2627

(29) Remove the Number 10 check ball from the
transfer plate (Fig. 295). The check ball is approxi-
mately 4.8 mm (3/16 in.) in diameter.
(30) Remove transfer plate from upper housing
(Fig. 296).
(31) Turn transfer plate over so upper housing sep-
arator plate is facing upward.
(32) Remove upper housing separator plate from
transfer plate (Fig. 297). Note position of filter in
separator plate for assembly reference.(33) Remove rear clutch and rear servo check balls
from transfer plate. Note check ball location for
assembly reference (Fig. 298).
Fig. 295 Number 10 Check Ball
1 - NUMBER 10 CHECK BALL (3/169)
Fig. 296 Transfer Plate
1 - UPPER HOUSING
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 297 Upper Housing Separator Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
2 - UPPER HOUSING SEPARATOR PLATE
3 - FILTER SCREEN
4 - BRACE
Fig. 298 Rear Clutch and Rear Servo Check Ball
Locations
1 - REAR CLUTCH CHECK BALL
2 - REAR SERVO CHECK BALL
3 - TRANSFER PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 293
VALVE BODY (Continued)