1998 DODGE RAM 1500 instrument panel
[x] Cancel search: instrument panelPage 2415 of 2627
WELD LOCATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX
DESCRIPTION FIGURE
FENDER BRACE, CLOSURE TUBE AND FRAME MOUNTING BRACKET TO FRONT
FENDER SUPPORT, FRONT FENDER AND RADIATOR TUBE31
STEERING COLUMN SUPPORT, CONNECTOR WIRING BRACKET AND WELD NUTS
TO LOWER PLENUM PANEL32
WIPER ATTACHING WELD NUTS AND VACUUM RESERVOIR ATTACHING STUDS TO
COWL PAR PANEL33
DASH PANEL TO FRONT FLOOR PAN 34
DASH PANEL TO LOWER PLENUM PANEL 35
LOWER PLENUM PANEL TO COWL BACK PANEL 36
FRONT FENDER AND RADIATOR TUBE DASH PANEL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
MOUNTING BRACKET, AND WELD NUTS TO COWL SIDE PANEL - LEFT SIDE37
DASH PANEL, LOWER PLENUM PANEL AND COWL PANEL BAR TO COWL SIDE
PANEL - LEFT SIDE38
FRONT FENDER AND RADIATOR TUBE DASH PANEL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
MOUNTING BRACKET AND WELD NUTS TO COWL SIDE PANEL - RIGHT SIDE39
DASH PANEL, LOWER PLENUM PANEL AND COWL PANEL BAR TO COWL SIDE
PANEL - RIGHT SIDE40
REINFORCEMENT AND HEADLAMP MOUNTING PANEL TO OUTER FENDER PANEL 41
SEAT MOUNTING FRONT BRACKETS TO SEAT MOUNTING FRONT CROSSMEMBER
TO FRONT FLOOR PAN42
AIR BAG MODULE BRACKET SHIFTER MOUNTING PLATE AND REAR FLOOR PANE
TO FRONT FLOOR PAN43
RIGHT TO LEFT REAR FLOOR CROSSMEMBER AND RIGHT TO LEFT SEAT
MOUNTING CROSSMEMBER44
REAR FLOOR CROSSMEMBER, SEAT MOUNTING CROSSMEMBER AND
UNDERBODY SUPPORT TO FLOOR SILL45
SEAT MOUNTING FRONT CROSSMEMBER TO FRONT FLOOR PAN TO UNDERBODY
SUPPORT46
FRONT SEAT MOUNTING CROSSMEMBERS TO FRONT SEAT MOUNTING BRACKET
TO FRONT FLOOR PAN47
REAR FLOOR CROSSMEMBERS TO REAR FLOOR PAN 48
FLOOR SILL TO FRONT SEAT MOUNTING CROSSMEMBER, FRONT AND REAR
FLOOR PAN49
AIR BAG MODULE BRACKET, SHIFTER MOUNTING PLATE AND FRONT SEAT
MOUNTING CROSSMEMBER TO FRONT FLOOR PAN50
REAR SEAT MIDDLE MOUNTING PLATE TO REAR FLOOR PAN TO FRONT FLOOR
PA N51
REAR FLOOR CROSSMEMBER, SEAT MOUNTING CROSSMEMBER AND
UNDERBODY SUPPORT TO FLOOR SILL52
LEFT REAR CROSSMEMBER TO RIGHT REAR CROSSMEMBER TO REAR FLOOR
PA N53
23 - 120 BODY STRUCTUREDR
Page 2488 of 2627

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLING
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...............1
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................3DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST..................6
SPECIFICATIONS - A/C SYSTEM............7
CONTROLS.............................9
DISTRIBUTION..........................26
PLUMBING.............................41
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, the
engine cooling system must be properly maintained.
The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions in front of the radiator or A/C condenser
will reduce the performance of the A/C and engine
cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the radiator,
thermostat, radiator hoses and the engine coolant
pump. Refer to Cooling for more information before
opening or attempting any service to the engine cool-
ing system.
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
A manually controlled single zone type heating-air
conditioning system or a manually controlled dual
zone type heating-air conditioning system is available
on this model.
All vehicles are equipped with a common heater,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing (Fig.
1). The system combines air conditioning, heating,
and ventilating capabilities in a single unit housing
mounted within the passenger compartment under
the instrument panel. The HVAC housing includes:
²Blower motor
²Blower motor resistor block²Heater core
²Evaporator coil
²Blend door and actuator
²Defrost door and actuator
²Mode door and actuator
²Recirculation door and actuator
Based upon the system and mode selected, condi-
tioned air can exit the HVAC housing through one or
a combination of the three main housing outlets:
defrost, panel or floor. The defrost outlet is located on
the top of the housing, the panel outlet is located on
the face of the housing and the floor outlet is located
on the bottom of the housing. Once the conditioned
air exits the unit housing, it is further directed
through molded plastic ducts to the various outlets in
the vehicle interior. These outlets and their locations
are as follows:
²Defroster Outlet- A single large defroster out-
let is located in the center of the instrument panel
top cover, near the base of the windshield.
²Side Window Demister Outlets- There are
two side window demister outlets, one is located at
each outboard end of the instrument panel top cover,
near the belt line at the A-pillars.
²Panel Outlets- There are four panel outlets in
the instrument panel, one located near each outboard
end of the instrument panel facing the rear of the
vehicle and two located near the top of the instru-
ment panel center bezel.
²Front Floor Outlets- There are two front floor
outlets, one located above each side of the floor panel
center tunnel near the dash panel.
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heating and air conditioning systems pulls
outside (ambient) air through the cowl opening at the
base of the windshield, then into the plenum cham-
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 2489 of 2627

ber above the heating, ventilation and air condition-
ing (HVAC) housing. On models equipped with air
conditioning, the air passes through the evaporator
coil. Air flow can be directed either through or
around the heater core. This is done by adjusting the
blend door with the temperature control knob on the
A/C-heater control located the instrument panel. The
air flow can then be directed from the panel, floor
and defrost outlets in various combinations using the
mode control knob located on the A/C-heater control.
Air flow velocity can be adjusted with the blower
speed selector located on the A/C-heater control.
NOTE: It is important to keep the air intake opening
clear of debris. Leaf particles and other debris that
is small enough to pass through the cowl opening
screen can accumulate within the HVAC housing.
The closed, warm, damp and dark environment cre-
ated within the housing is ideal for the growth of
certain molds, mildews and other fungi. Any accu-mulation of decaying plant matter provides an addi-
tional food source for fungal spores, which enter
the housing with the fresh intake-air. Excess debris,
as well as objectionable odors created by decaying
plant matter and growing fungi can be discharged
into the passenger compartment during heater-A/C
operation if the air intake opening is not kept clear
of debris.
The heater and air conditioning systems are blend-
air type systems. In a blend-air system, a blend door
controls the amount of unconditioned air (or cooled
air from the evaporator on models with air condition-
ing) that is allowed to flow through, or around, the
heater core. A temperature control knob determines
the discharge air temperature by actuating an elec-
tric motor, which operates the blend door. This allows
an almost immediate control of the output air tem-
perature of the system.
On all models, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a electric actu-
ated recirculation air door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The air conditioning compressor can be engaged in
any mode by pressing the snowflake, A/C on/off but-
ton. It can also be engaged by placing the mode con-
trol in the mix to defrost positions. This will remove
heat and humidity from the air before it is directed
through or around the heater core. The mode control
knob on the A/C-heater control is used to also direct
the conditioned air to the selected system outlets.
The mode control switch uses an electric motor to
control the mode doors.
The defroster outlet receives airflow from the
HVAC housing through the molded plastic defroster
duct, which connects to the HVAC housing defroster
outlet. The airflow from the defroster outlets is
directed by fixed vanes in the defroster outlet grilles
and cannot be adjusted. The defroster outlet grilles
are integral to the instrument panel top cover.
The side window demister outlets receive airflow
from the HVAC housing through the molded plastic
defroster duct and two molded plastic demister ducts.
The airflow from the side window demister outlets is
directed by fixed vanes in the demister outlet grilles
and cannot be adjusted. The side window demister
outlet grilles are integral to the instrument panel.
The demisters direct air from the HVAC housing
through the outlets located on the top corners of the
instrument panel. The demisters operate when the
mode control knob is positioned in the floor-defrost
and defrost-only settings. Some air may be noticeable
from the demister outlets when the mode control is
in the bi-level to floor positions.
Fig. 1 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2490 of 2627

The panel outlets receive airflow from the HVAC
housing through a molded plastic main panel duct,
center panel duct and two end panel ducts. The two
end panel ducts direct airflow to the left and right
instrument panel outlets, while the center panel duct
directs airflow to the two center panel outlets. Each
of these outlets can be individually adjusted to direct
the flow of air.
The floor outlets receive airflow from the HVAC
housing through the floor distribution duct. The front
floor outlets are integral to the molded plastic floor
distribution duct, which is secured to the bottom of
the housing. The floor outlets cannot be adjusted.
The air conditioner for all models is designed for
the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant. The air con-
ditioning system has an evaporator to cool and dehu-
midify the incoming air prior to blending it with the
heated air. This air conditioning system uses a fixed
orifice tube in the liquid line near the condenser out-
let tube to meter refrigerant flow to the evaporator
coil. To maintain minimum evaporator temperature
and prevent evaporator freezing, a evaporator tem-
perature sensor is used. The JTEC control module is
programmed to respond to the evaporator tempera-
ture sensor input by cycling the air conditioning com-
pressor clutch as necessary to optimize air
conditioning system performance and to protect the
system from evaporator freezing.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to remove
heat and humidity from the air entering the passen-
ger compartment. The evaporator, located in the
HVAC housing, is cooled to temperatures near the
freezing point. As warm damp air passes over the
fins in the evaporator, moisture in the air condenses
to water, dehumidifying the air. Condensation on the
evaporator fins reduces the evaporators ability to
absorb heat. During periods of high heat and humid-
ity, an air conditioning system will be less effective.
With the instrument control set to Recirculation
mode, only air from the passenger compartment
passes through the evaporator. As the passenger com-
partment air dehumidifies, A/C performance levels
rise.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the air condition-
ing system. When humidity is high, the evaporator
has to perform a double duty. It must lower the air
temperature, and it must lower the temperature ofthe moisture in the air that condenses on the evapo-
rator fins. Condensing the moisture in the air trans-
fers heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing.
This reduces the amount of heat the evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the evaporator to lower the temperature
of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Wring-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from their
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
PERFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURE
Review Safety Warnings and Cautions before per-
forming this procedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - CAUTION). Air temperature in test
room and on vehicle must be 21É C (70É F) minimum
for this test.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge set
or A/C recycling/charging station.
(2) Set the A/C-heater mode control in the Recircu-
lation Mode position, the temperature control knob in
the full cool position, and the blower motor switch to
the highest speed position.
(3) Start the engine and hold at 1,000 rpm with
the A/C compressor clutch engaged.
(4) The engine should be warmed up to operating
temperature with the doors closed and windows
open.
(5) Insert a thermometer in the driver side center
panel A/C-heater outlet and operate the engine for
five minutes.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon the ambient temperature and humidity.
(7) With the compressor clutch engaged, record the
discharge air temperature and the compressor dis-
charge pressure.
(8) If the discharge air temperature fails to meet
the specifications in the A/C Performance Tempera-
ture chart, refer to the Pressure Diagnosis chart.
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2501 of 2627

spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The A/C compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (86) receives a ground
input from the PCM/ECM through the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay control circuit only when the PCM/
ECM electronically pulls the control circuit to
ground.
²The coil battery terminal (85) receives a battery
current input from PTC 1 in the IPM through a
fused ignition switch output (run) circuit only when
the ignition switch is in the On position.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the A/C compressor clutch relay output cir-
cuit only when the A/C compressor clutch relay coil is
energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout label on the
IPM cover for compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(4) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the IPM cover for A/C compressor
clutch relay location.
(2) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay in the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The heater and air conditioning systems use elec-
trical controls. These controls provide the vehicle
operator with a number of setting options to help
control the climate and comfort within the vehicle.
The A/C-heater control for the Single Zone system
(Fig. 12) or Dual Zone system (Fig. 13) is located to
the right of the instrument cluster on the instrument
panel.
The Single Zone control panel contains a rotary-
type temperature control switch, a rotary-type mode
control switch and a rotary-type blower motor speed
switch. The A/C-heater control also has a push but-
ton to activate the optional heated side view mirror
defroster elements and to turn the A/C on.
The Dual Zone control panel contains a pair of slid-
er-type temperature control switches, a rotary-type
mode control switch and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch. The control also has buttons to activate
the optional heated sideview mirror defroster ele-
ments, turn the A/C on and set the system to Max
A/C.
The A/C-heater control panel cannot be repaired. If
faulty or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced.
Fig. 11 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
24 - 14 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2502 of 2627

The illumination lamps are available for service
replacement.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center bezel from the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the screws that secure the A/C-heater
control to the instrument panel (Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the A/C-heater control onto the instru-
ment panel center bezel and install the retaining
screws. Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the instrument panel center bezel (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL CENTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION).
(3) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C pressure transducer is a switch that is
installed on a fitting located on the refrigerant dis-
charge line between the compressor and the con-
denser in the front corner of the engine
compartment. An internally threaded hex fitting on
the transducer connects it to the externally threaded
Schrader-type fitting on the discharge line. A rubber
O-ring seals the connection between the transducer
and the discharge line fitting. Three terminals within
a molded plastic connector receptacle on the top of
the transducer connect it to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a wire lead and connector of the head-
lamp and dash wire harness.
Fig. 12 Single Zone HVAC Control
1 - MOUNTING TAB (4)
2 - A/C BUTTON
3 - SIDEVIEW MIRROR DEFROSTER BUTTON (IF EQUIPED)
4 - MODE CONTROL SWITCH
5 - TEMPERATURE CONTROL SWITCH
6 - BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH
Fig. 13 Dual Zone A/C Control
1 - A/C BUTTON
2 - MAX. A/C BUTTON
3 - SIDEVIEW MIRROR DEFROSTER BUTTON (IF EQUIPED)
4 - MOUNTING TABS (4)
5 - DRIVERSIDE TEMPERATURE CONTROL
6 - PASSENGERSIDE TEMPERATURE CONTROL
7 - MODE CONTROL SWITCH
8 - BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH
Fig. 14 A/C-Heater Control - Typical, Rear View
1 - MOUNTING TAB (4)
2 - SCREW (4)
3 - A/C-HEATER CONTROL ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
4 - HEATED SIDEVIEW MIRROR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - A/C-HEATER CONTROL
DRCONTROLS 24 - 15
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2504 of 2627

(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The blend door actuators are reversible, 12-volt
Direct Current (DC), servo motors. Models with the
single zone heater and air conditioner system have a
single blend door, which is controlled by a single
blend door actuator. Models with the optional dual
zone front heater and air conditioner system have
dual blend doors, which are controlled by two blend
door actuators. The single zone blend door actuator is
located on the driver side end of the HVAC housing,
close to the dash panel. In the dual zone system, the
same blend door actuator used for the single zone
system becomes the driver side blend door actuator,
and is mechanically connected to only the driver side
blend door. In the dual zone system, a second sepa-
rate blend door actuator is also located on the top of
the HVAC housing and is mechanically connected to
only the passenger side blend door.
The blend door actuators are interchangeable with
each other, as well as with the actuators for the
mode door, defrost door and the recirculation door.
Each actuator is contained within an identical blackmolded plastic housing with an integral wire connec-
tor receptacle. Integral mounting tabs allow the
actuator to be secured with three screws to the
HVAC housing. Each actuator also has an identical
output shaft with splines that connects it to the link-
age that drives the proper door. The blend door
actuators do not require mechanical indexing to the
blend door linkage, as they are electronically cali-
brated by the heater-A/C control module. The blend
door actuators cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if
damaged or faulty, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
Each blend door actuator is connected to the A/C-
heater control through the vehicle electrical system by a
dedicated two-wire lead and connector from the HVAC
wire harness. The blend door actuator can move the
blend-air door in two directions. When the A/C-heater
control pulls the voltage on one side of the motor con-
nection high and the other connection low, the blend-air
door will move in one direction. When the A/C-heater
control reverses the polarity of the voltage to the motor,
the blend-air door moves in the opposite direction.
When the A/C-heater control makes the voltage to both
connections high or both connections low, the blend-air
door stops and will not move. The motor connections
also provide a feedback signal to the A/C-heater control.
This feedback signal allows the A/C-heater control to
monitor the operation and relative positions of the blend
door actuator and the blend-air door. The A/C-heater
control learns the blend door stop positions during the
calibration procedure and will store a diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) for any problems it detects in the blend door
actuator circuits.
The blend door actuator can be diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures for more information. The blend door actuators
cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if damaged or
faulty, they must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
Fig. 15 A/C Pressure Transducer - 3.7L Shown
1 - NUT
2 - FRONT UPPER CROSSMEMBER
3 - A/C CONDENSER
4 - NUT (2)
5 - SUCTION LINE
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
7 - A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
8 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
9 - A/C DISCHARGE LINE
DRCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)
Page 2505 of 2627
NOTE: The single zone heating and air conditioning
system is equipped with a single blend door actua-
tor. The dual zone system has two blend door
actuators, one for the driver side blend air door and
one for the passenger side blend air door. The
same service procedures can be used for each of
these actuators.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
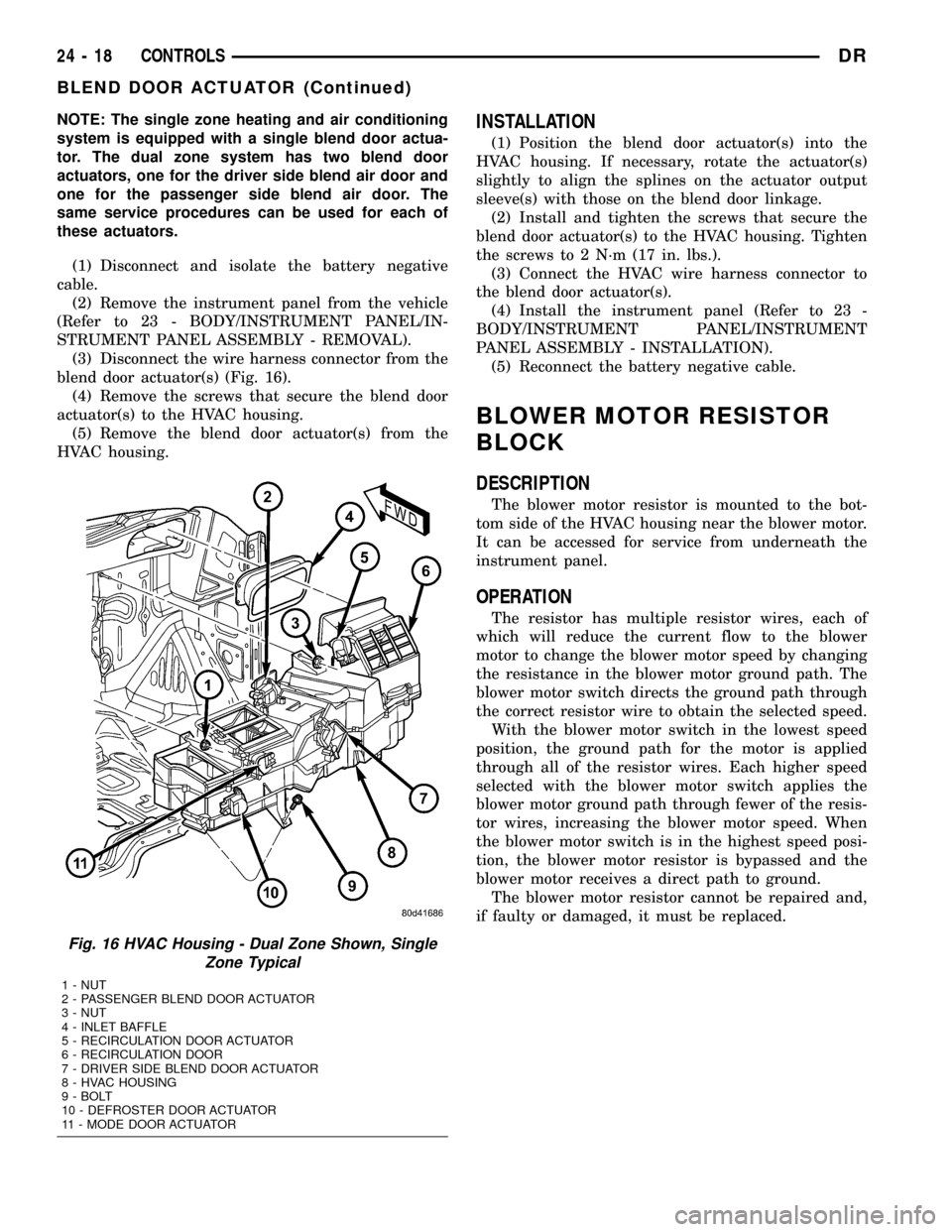
blend door actuator(s) (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove the screws that secure the blend door
actuator(s) to the HVAC housing.
(5) Remove the blend door actuator(s) from the
HVAC housing.INSTALLATION
(1) Position the blend door actuator(s) into the
HVAC housing. If necessary, rotate the actuator(s)
slightly to align the splines on the actuator output
sleeve(s) with those on the blend door linkage.
(2) Install and tighten the screws that secure the
blend door actuator(s) to the HVAC housing. Tighten
the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the blend door actuator(s).
(4) Install the instrument panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor resistor is mounted to the bot-
tom side of the HVAC housing near the blower motor.
It can be accessed for service from underneath the
instrument panel.
OPERATION
The resistor has multiple resistor wires, each of
which will reduce the current flow to the blower
motor to change the blower motor speed by changing
the resistance in the blower motor ground path. The
blower motor switch directs the ground path through
the correct resistor wire to obtain the selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through all of the resistor wires. Each higher speed
selected with the blower motor switch applies the
blower motor ground path through fewer of the resis-
tor wires, increasing the blower motor speed. When
the blower motor switch is in the highest speed posi-
tion, the blower motor resistor is bypassed and the
blower motor receives a direct path to ground.
The blower motor resistor cannot be repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
Fig. 16 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 18 CONTROLSDR
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)