1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Trans temp
[x] Cancel search: Trans tempPage 2152 of 2627
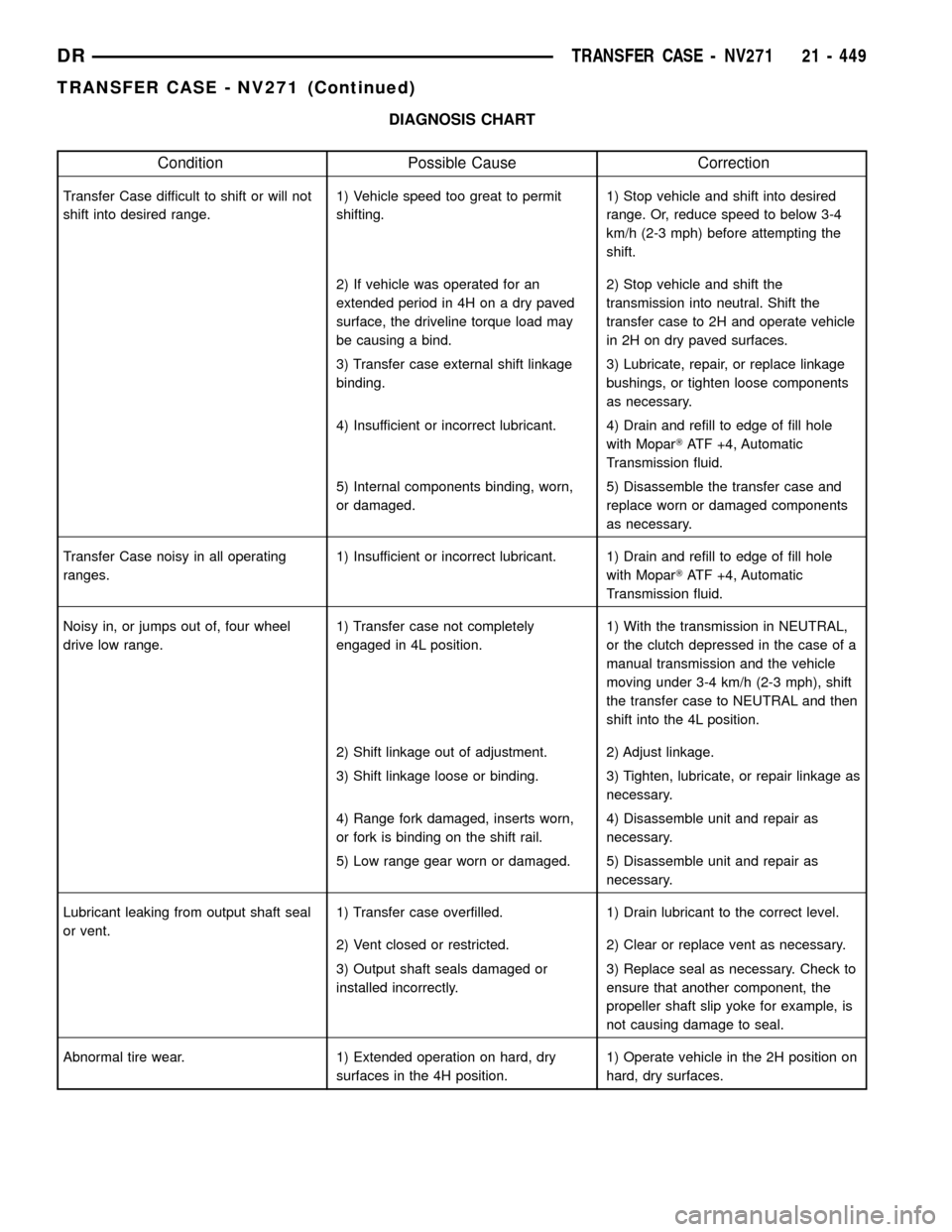
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer Case difficult to shift or will not
shift into desired range.1) Vehicle speed too great to permit
shifting.1) Stop vehicle and shift into desired
range. Or, reduce speed to below 3-4
km/h (2-3 mph) before attempting the
shift.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4H on a dry paved
surface, the driveline torque load may
be causing a bind.2) Stop vehicle and shift the
transmission into neutral. Shift the
transfer case to 2H and operate vehicle
in 2H on dry paved surfaces.
3) Transfer case external shift linkage
binding.3) Lubricate, repair, or replace linkage
bushings, or tighten loose components
as necessary.
4) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 4) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, Automatic
Transmission fluid.
5) Internal components binding, worn,
or damaged.5) Disassemble the transfer case and
replace worn or damaged components
as necessary.
Transfer Case noisy in all operating
ranges.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, Automatic
Transmission fluid.
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in NEUTRAL,
or the clutch depressed in the case of a
manual transmission and the vehicle
moving under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift
the transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair linkage as
necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts worn,
or fork is binding on the shift rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or damaged. 5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft seal
or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary. Check to
ensure that another component, the
propeller shaft slip yoke for example, is
not causing damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H position on
hard, dry surfaces.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV271 21 - 449
TRANSFER CASE - NV271 (Continued)
Page 2164 of 2627

DRIVE CHAIN
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
replace the chain if stretched, distorted, or if any of
the links bind. Replace the bearings if rough, or
noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 43)
FRONT CASE AND REAR CASE
Inspect the cases for wear and damage.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
BEARINGS AND SEALS
(1) Remove the input shaft bearing snap-ring from
the front case half with suitable snap-ring pliers.
(2)
Remove the input shaft bearing from the front case
half with Installer 6953 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 44).
(3) Install the input shaft bearing into the front
case half with Installer 8151 inverted on Handle
C-4171 (Fig. 45).
(4) Install the input shaft bearing snap-ring into
the front case half with suitable snap-ring pliers.
Fig. 43 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEARFig. 44 Remove Input Gear Bearing
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 6953
Fig. 45 Install Input Gear Bearing
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 8151 (INVERTED)
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV271 21 - 461
TRANSFER CASE - NV271 (Continued)
Page 2198 of 2627

Inspect the shift fork wear pads (Fig. 41). The
mode and range fork pads are serviceable and can be
replaced if necessary.
Check both of the sleeves for wear or damage,
especially on the interior teeth. Replace the sleeves if
wear or damage is evident.
REAR EXTENSION HOUSING
Inspect the extension housing seal and bushing.
Replace both components if either show any sign of
wear or damage.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 42)
FRONT AND REAR CASES
Inspect the cases for wear and damage.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with Helicoiltstain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
Fig. 41 Shift Fork And Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 42 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 495
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 (Continued)
Page 2212 of 2627
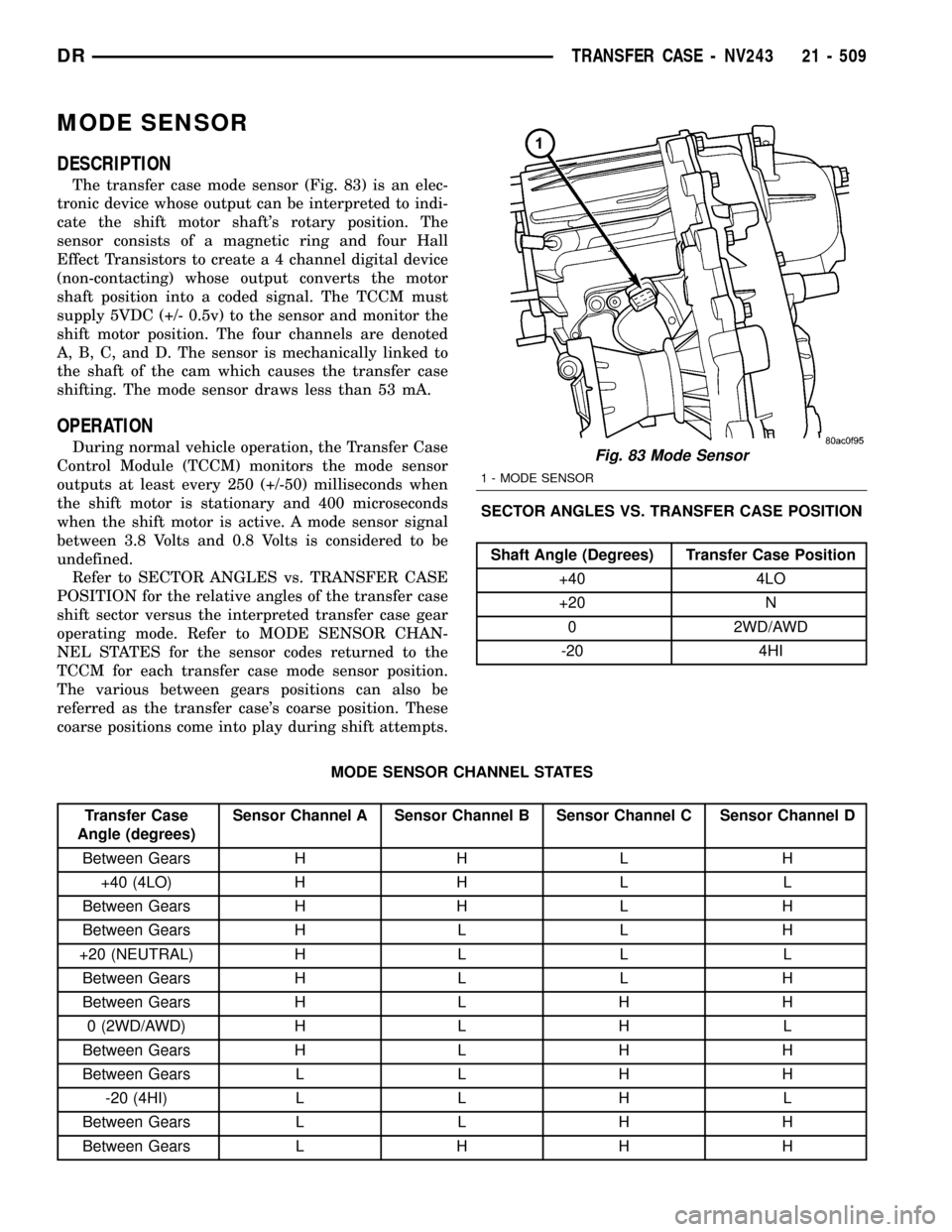
MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case mode sensor (Fig. 83) is an elec-
tronic device whose output can be interpreted to indi-
cate the shift motor shaft's rotary position. The
sensor consists of a magnetic ring and four Hall
Effect Transistors to create a 4 channel digital device
(non-contacting) whose output converts the motor
shaft position into a coded signal. The TCCM must
supply 5VDC (+/- 0.5v) to the sensor and monitor the
shift motor position. The four channels are denoted
A, B, C, and D. The sensor is mechanically linked to
the shaft of the cam which causes the transfer case
shifting. The mode sensor draws less than 53 mA.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Transfer Case
Control Module (TCCM) monitors the mode sensor
outputs at least every 250 (+/-50) milliseconds when
the shift motor is stationary and 400 microseconds
when the shift motor is active. A mode sensor signal
between 3.8 Volts and 0.8 Volts is considered to be
undefined.
Refer to SECTOR ANGLES vs. TRANSFER CASE
POSITION for the relative angles of the transfer case
shift sector versus the interpreted transfer case gear
operating mode. Refer to MODE SENSOR CHAN-
NEL STATES for the sensor codes returned to the
TCCM for each transfer case mode sensor position.
The various between gears positions can also be
referred as the transfer case's coarse position. These
coarse positions come into play during shift attempts.SECTOR ANGLES VS. TRANSFER CASE POSITION
Shaft Angle (Degrees) Transfer Case Position
+40 4LO
+20 N
0 2WD/AWD
-20 4HI
MODE SENSOR CHANNEL STATES
Transfer Case
Angle (degrees)Sensor Channel A Sensor Channel B Sensor Channel C Sensor Channel D
Between Gears H H L H
+40 (4LO) H H L L
Between Gears H H L H
Between Gears H L L H
+20 (NEUTRAL) H L L L
Between Gears H L L H
Between Gears H L H H
0 (2WD/AWD) H L H L
Between Gears H L H H
Between Gears L L H H
-20 (4HI) L L H L
Between Gears L L H H
Between Gears L H H H
Fig. 83 Mode Sensor
1 - MODE SENSOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 509
Page 2214 of 2627

²A flashing operating mode LED for the desired
gear indicates that a shift to that position has been
requested, but all of the driver controllable conditions
have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify the
driver that the transmission needs to be put into NEU-
TRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some other con-
dition outlined (other than a diagnostic failure that
would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANS-
FER CASE CONTROL MODULE - OPERATION) is not
met. Note that this flashing will continue indefinitely
until the conditions are eventually met, or the selector
switch position is changed, or if diagnostic routines no
longer allow the requested shift.
²If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 85) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to a
shaft which internally moves the mode and range forks
that change the transfer case operating ranges. The
motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F with 10
volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the Transfer
Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to move the
transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as required, to
obtain the transfer case operating mode indicated by
the instrument panel mounted selector switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in the
2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assembly will
be installed, it will be necessary to shift the transfer
case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to motor removal.
(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case opera-
tion.
Fig. 85 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 511
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2227 of 2627

REAR EXTENSION HOUSING
Inspect the extension housing seal and bushing.
Replace both components if either show any sign of
wear or damage.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
Inspect the shaft splines and bearing surfaces.
Minor nicks on the splines can be smoothed with an
oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to smooth minor
scratches on the shaft bearing surfaces. Replace the
shaft if the bearing surfaces are scored or if any of
the splines are cracked or broken.Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 41)
Fig. 39 Input Gear and Carrier Components
1 - PLANETARY CARRIER 4 - CARRIER LOCK RING
2 - REAR THRUST WASHER 5 - CARRIER LOCK RETAINING RING
3 - FRONT THRUST WASHER 6 - INPUT GEAR
Fig. 40 Shift Fork and Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 41 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
21 - 524 TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENIIDR
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2242 of 2627
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Transfer Case
Control Module (TCCM) monitors the mode sensor
outputs at least every 250 (+/-50) milliseconds when
the shift motor is stationary and 400 microseconds
when the shift motor is active. A mode sensor signal
between 3.8 Volts and 0.8 Volts is considered to be
undefined.
Refer to SECTOR ANGLES vs. TRANSFER CASE
POSITION for the relative angles of the transfer case
shift sector versus the interpreted transfer case gear
operating mode. Refer to MODE SENSOR CHAN-
NEL STATES for the sensor codes returned to the
TCCM for each transfer case mode sensor position.The various between gears positions can also be
referred as the transfer case's coarse position. These
coarse positions come into play during shift attempts.
SECTOR ANGLES VS. TRANSFER CASE POSITION
Shaft Angle (Degrees) Transfer Case Position
+40 4LO
+20 N
0 2WD/AWD
-20 4HI
MODE SENSOR CHANNEL STATES
Transfer Case
Angle (degrees)Sensor Channel A Sensor Channel B Sensor Channel C Sensor Channel D
Between Gears H H L H
+40 (4LO) H H L L
Between Gears H H L H
Between Gears H L L H
+20 (NEUTRAL) H L L L
Between Gears H L L H
Between Gears H L H H
0 (2WD/AWD) H L H L
Between Gears H L H H
Between Gears L L H H
-20 (4HI) L L H L
Between Gears L L H H
Between Gears L H H H
SELECTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The selector switch assembly is mounted in the left
side of the vehicle's Instrument Panel (IP) and con-
sists of a rotary knob connected to a resistive net-
work for the mode and range shift selections. Also
located in this assembly is a recessed, normally open
momentary switch for making shifts into and out of
transfer case NEUTRAL. A pen, or similar instru-
ment, is used to make a NEUTRAL shift selection,
thus reducing the likelihood of an inadvertent shift
request.The selector switch also contains light emitting
diode's (LED's) to indicate the transfer case position
and whether a shift is in progress.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII 21 - 539
MODE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2243 of 2627

OPERATION
As the position of the selector switch varies, the
resistance between the Mode Sensor supply voltage
pin and the Mode Sensor output will vary. Hardware,
software, and calibrations within the Transfer Case
Control Module (TCCM) are provided that interpret
the selector switch resistance as given in the table
below: SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
Step Resistance
Range (ohms)Required
Interpretation
A <200 Shorted
B 400-700 NEUTRAL
C 1050-1450 4LO
D 1850-2300 4H
E 3050-5950 AWD (Default)
F 9.5-12.5K In between
positions
G >15.5K Open
For resistances between the ranges B-E shown for
each valid position (T-Case NEUTRAL, 4LO, 4HI,
AWD), the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
²either of the neighboring valid positions.
²as an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges E and F shown
for AWD and in-between positions, the TCCM may
interpret the resistance as:
²the AWD position.
²an invalid fault position.
²a valid in-between position.
For resistances between the ranges F and G shown
for in-between positions and fault condition (open),
the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
²a valid in-between position.
²an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges A and B shown
for the fault condition (short) and , T-Case NEU-
TRAL, the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:²the T-Case NEUTRAL position.
²an invalid fault position.
The LED's in the selector assembly are illuminat-
ed/flashed in the following manner to indicate a par-
ticular condition or state.
²A solidly illuminated LED indicates a success-
fully completed shift and the current operating mode
of the transfer case. While a shift has been requested
but not yet completed, the LED for the desired trans-
fer case position is flashed.
²A flashing operating mode LED for the desired
gear indicates that a shift to that position has been
requested, but all of the driver controllable conditions
have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify
the driver that the transmission needs to be put into
NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some
other condition outlined (other than a diagnostic fail-
ure that would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION) is not met. Note that this flashing will
continue indefinitely until the conditions are eventu-
ally met, or the selector switch position is changed,
or if diagnostic routines no longer allow the
requested shift.
²If the driver attempts to make a shift into trans-
fer case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controlla-
ble conditions are not met, the request will be
ignored until all of the conditions are met or until
the NEUTRAL select button is released. Additionally
the neutral lamp will flash, or begin to flash while
the button is depressed and operator controllable
conditions are not being met. All of the LED's except
the Neutral will flash if any of the operator control-
lable conditions for shifting are not met while the
Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9type of fea-
ture is necessary because the TCCM would interpret
another request immediately after the shift into
transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
21 - 540 TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENIIDR
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)