1998 DODGE RAM 1500 gear shift indicator
[x] Cancel search: gear shift indicatorPage 1664 of 2627

(17) Remove the steering column assembly from
the vehicle. (Fig. 7)
INSTALLATION
WARNING: BEFORE SERVICING THE STEERING
COLUMN THE AIRBAG SYSTEM MUST BE DIS-
ARMED. REFER TO ELECTRICAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM FOR SERVICE PROCEDURES. FAILURE TO DO
SO MAY RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF
THE AIRBAG AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: All fasteners must be torqued to specifi-
cation to ensure proper operation of the steering
column.
(1) Position the steering column on the dash panel
support and loosely install the mounting nuts.
(2) Firmly slide the steering column upward
against the studs in dash panel and hand tighten the
nuts.
(3) Install the steering shaft coupler on the steer-
ing shaft and loosely install anewbolt.
(4) Center steering column in dash opening and
tighten mounting nuts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
NOTE: Torque the upper left nut first then the lower
right nut. Then torque the lower left nut then the
upper right nut.
NOTE: A new bolt must be used for reinstallation.
(5) Tighten the coupler bolt to 57 N´m (42 ft. lbs.).(6) Install a new brake light switch (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL).
(7) Install the shifter cable. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 32RH/GEAR
SHIFT CABLE - INSTALLATION)
(8) Connect the wiring harness to the column.
(9) Install the SKIM module.
(10) Install the clockspring(Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).
(11) Install the shrouds.
(12) Install the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Align the spline on the wheel hub to shaft.
(14) Then install the steering wheel and install a
newbolt. Tighten the bolt to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(15) Install the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install the two steering wheel switches.
(17) Install the tilt lever handle.
(18) Install the negative battery terminal.
(19) Test the operation of the horn, Electronic
PRNDL Indicator, lights and any other functions that
are steering column operated.
IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The ignition switch is located on the steering col-
umn. It is used as the main on/off switching device
for most electrical components. The mechanical key
cylinder is used to engage/disengage the electrical
ignition switch.
OPERATION
Vehicles equipped with an automatic trans-
mission and a steering column mounted shifter:
an interlock device is located within the shift cable.
This interlock device is used to lock the transmission
shifter in the PARK position when the key cylinder is
in any position and the brake pedal is not depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION SWITCH
TEST AND REPAIR
If the key removal effort is excessive on a vehicle
with a automatic transmission first adjust the shift
linkage, (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 46RE/GEAR SHIFT CABLE -
ADJUSTMENTS).
If the ignition switch effort is excessive remove the
ignition key cylinder from the steering column. (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK CYLINDER
Fig. 7 STEERING COLUMN
1 - Steering Wheel
2 - Key Cylinder
3 - Gear Shift Lever
4 - Steering Column
5 - Tilt Lever Cable
DRCOLUMN 19 - 9
COLUMN (Continued)
Page 1706 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. Leaks can occur at the
mating surfaces of the gear case, adaptor or exten-
sion housing, or from the front/rear seals. A sus-
pected leak could also be the result of an overfill
condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Shift component damage or damaged clutch pres-
sure plate or disc are additional probable causes of
increased shift effort. Worn/damaged pressure plate
or disc can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem
is advanced, gear clash during shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear and bearing
damage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot bezel screws and slide boot
upward on shift lever extension.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(7) Drain lubricant if transmission will be disas-
sembled for service.
(8) Mark propeller shaft/shafts and companion
flange yoke/yokes for installation reference and
remove propeller shaft/shafts.
(9) Disconnect harness from clips on transmission
housing.
(10) Remove transfer case linkage if equipped.
(11) Remove transfer case mounting nuts and
remove transfer case if equipped.
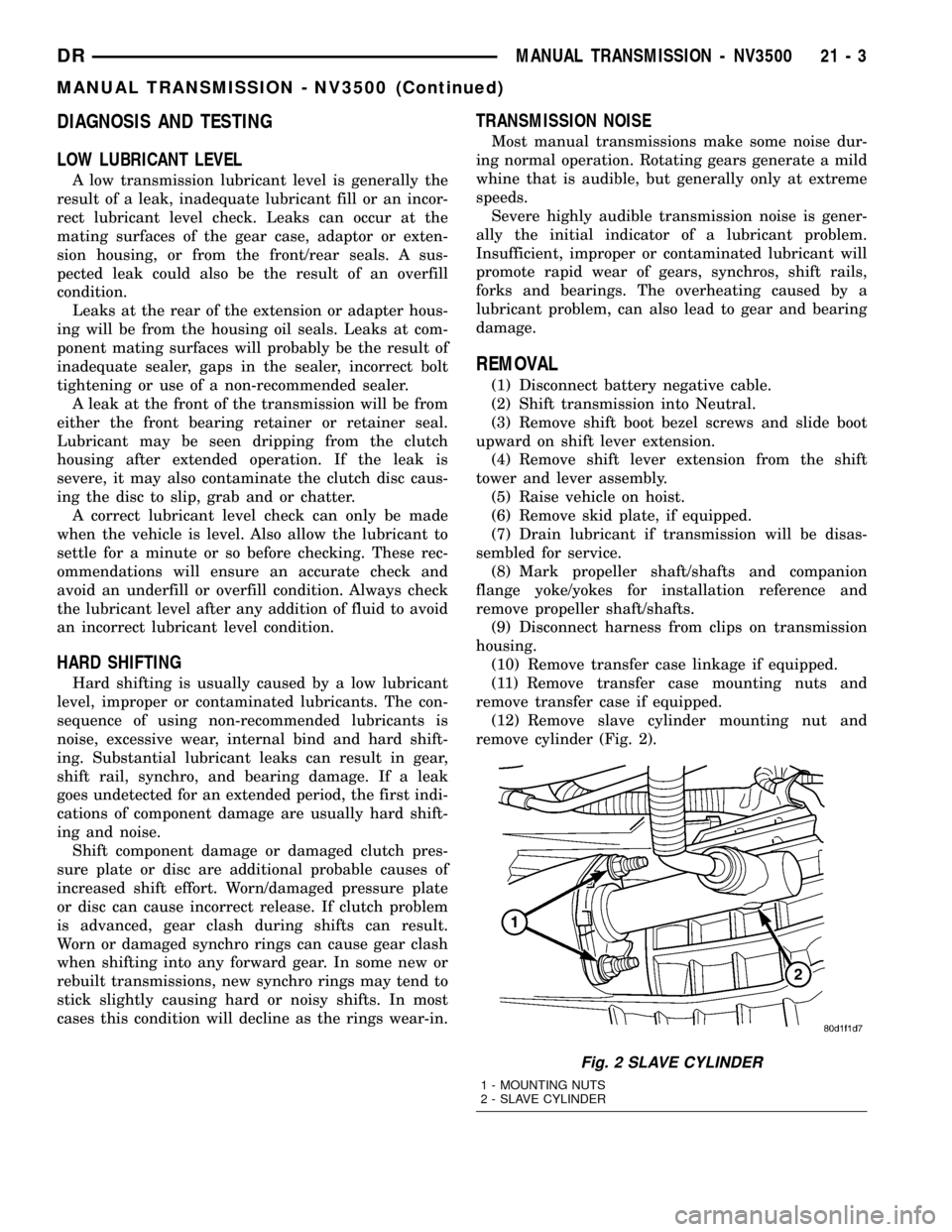
(12) Remove slave cylinder mounting nut and
remove cylinder (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SLAVE CYLINDER
1 - MOUNTING NUTS
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2627

The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether the
driver is up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchro-
nizer does this by having the synchronizer hub
splined to the mainshaft, or the countershaft in some
cases, and moving the blocker ring into contact with
the gear's friction cone. As the blocker ring and fric-
tion cone come together, the gear speed is brought up
or down to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two
speeds match, the splines on the inside of the syn-
chronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on
the blocker ring and the friction cone and eventually
will slide over the teeth, locking the gear to the
mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants isnoise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds. Severe highly audible transmission noise is
generally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant
will promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift
rails, forks and bearings. The overheating caused by
a lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Remove shift boot screws from floorpan and
slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(3) Remove shift lever extension from shift tower
and lever assembly.
(4) Remove shift tower bolts (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - SHIFTER
3 - BOLTS
21 - 44 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1793 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
The transmission has two identification tags
attached to the driver side upper clutch housing (Fig.
2). One tag provides the transmission part number.
The second tag provides sequencing and build date
information. The information on the tags are essen-
tial to correct parts ordering.
OPERATION
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. As the shift
lever moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork
attached to that rail begins to move. The fork is posi-
tioned in a groove in the outer circumference of the
synchronizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the syn-
chronizer sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up
or slow down the selected gear (depending on
whether we are up-shifting or down-shifting). The
synchronizer does this by having the synchronizer
hub splined to the mainshaft or the countershaft in
some cases, and moving the blocker ring into contact
with the gear's friction cone. As the blocker ring and
friction cone come together, the gear speed is brought
up or down to the speed of the synchronizer. As the
two speeds match, the splines on the inside of the
synchronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on
the blocker ring and friction cone and eventually will
slide over the teeth, locking the gear to the main-
shaft or countershaft through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or sobefore checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds. Severe highly audible transmission noise is
generally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant
will promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift
rails, forks and bearings. The overheating caused by
a lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
Fig. 2 IDENTIFICATION TAG LOCATION
1 - IDENTIFICATION TAGS
21 - 90 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1821 of 2627

(2) Measure mainshaft endplay with Dial Indicator
Set C-3339 and Extension Rod 8161 installed onto
the rear of the transmission gear case (Fig. 84).
(3) Measure countershaft end-play with Dial Indi-
cator Set C-3339 and Extension Rod 8161 installed
onto the rear of the transmission gear case (Fig. 85).
(4) Rotate transmission into a horizontal position
and remove the input shaft retainer.
(5) Install shims necessary to achieve an end-play
of 0-0.10 mm (0-0.004 in.) for the mainshaft and
countershaft.
NOTE: Countershaft shims go between the bearing
race and spacer. Mainshaft shims go into the input
shaft retainer.
(6) Install anewinput shaft seal into the input
shaft retainer with Installer C-4965.
(7) Install input shaft oil guide with C-3972-A and
Handle C-4171.
(8) Apply sealer to the input shaft retainer and
install retainer onto the clutch housing. Install bolts
and tighten to 28 N´m (20 ft.lbs.).
REVERSE GEAR
(1) Install reverse shift fork and synchronizer as
an assembly onto the reverse shift rail and output
shaft (Fig. 86).NOTE: Raised square shoulder and snap-ring on
the synchro face the case.
Fig. 84 MEASURE MAINSHAFT ENDPLAY
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - EXTENSION ROD
3 - MAIN SHAFT
Fig. 85 MEASURE COUNTERSHAFT END-PLAY
1 - EXTENSION ROD
2 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - COUNTERSHAFT
Fig. 86 REVERSE SHIFT FORK AND SYNCHRO
1 - REVERSE SYNCHRO
2 - REVERSE SHIFT FORK
21 - 118 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1965 of 2627
OPERATION
At key-on, overdrive operation is allowed. Pressing
the switch once causes the tow/haul overdrive OFF
mode to be entered and the Tow/Haul lamp to be illu-
minated. Pressing the switch a second time causes
normal overdrive operation to be restored and the
tow/haul lamp to be turned off. The tow/haul over-
drive OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition
switch is cycled OFF and ON. The normal position
for the control switch is the ON position. The switch
must be in this position to energize the solenoid and
allow a 3-4 upshift. The control switch indicator light
illuminates only when the tow/haul overdrive switch
is turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated
by the transmission control module.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS
The tow/haul overdrive off switch, valve body sole-
noid, case connectors and related wiring can all be
tested with a 12 volt test lamp or a volt/ohmmeter.
Check continuity of each component when diagnosis
indicates this is necessary.
Switch and solenoid continuity should be checked
whenever the transmission fails to shift into fourth
gear range.
REMOVAL
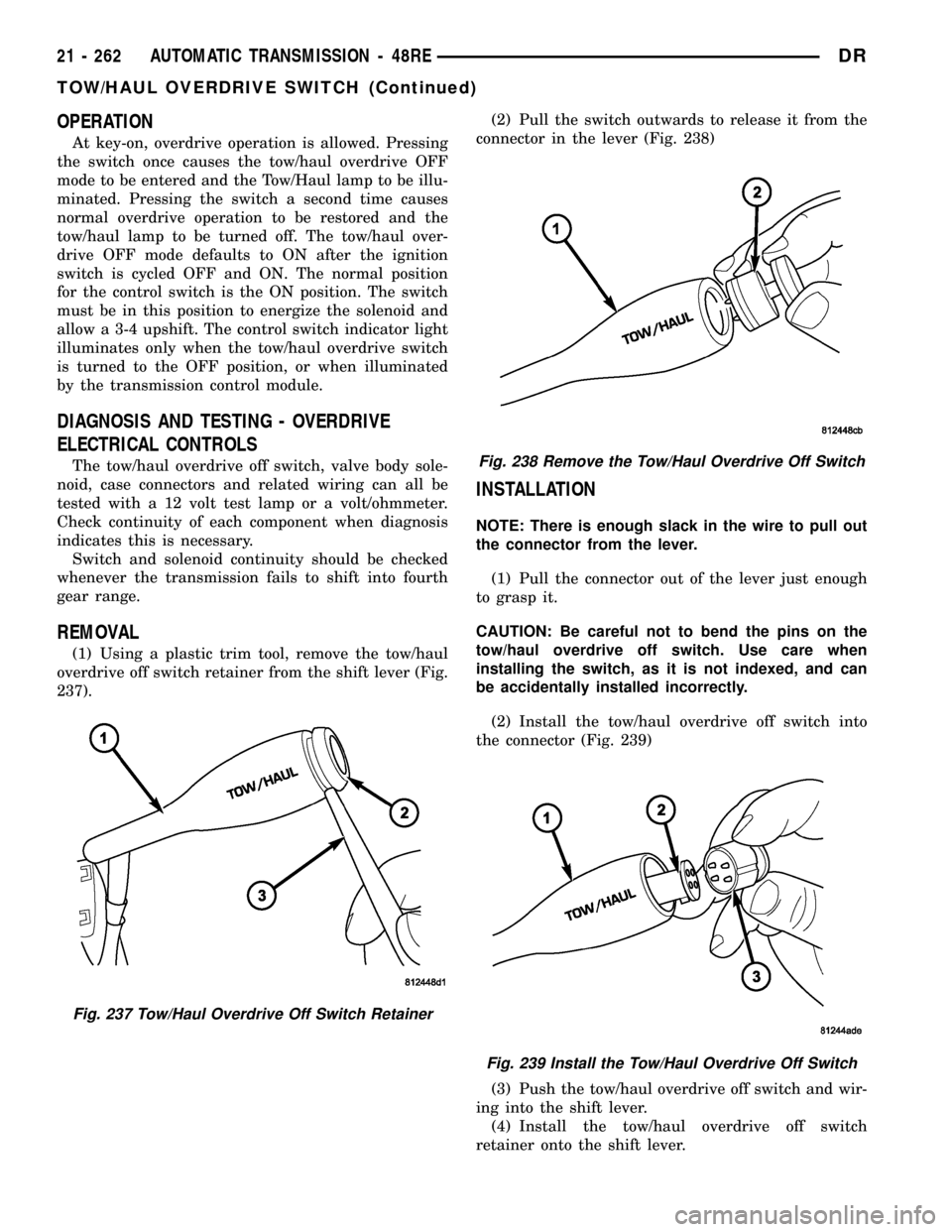
(1) Using a plastic trim tool, remove the tow/haul
overdrive off switch retainer from the shift lever (Fig.
237).(2) Pull the switch outwards to release it from the
connector in the lever (Fig. 238)
INSTALLATION
NOTE: There is enough slack in the wire to pull out
the connector from the lever.
(1) Pull the connector out of the lever just enough
to grasp it.
CAUTION: Be careful not to bend the pins on the
tow/haul overdrive off switch. Use care when
installing the switch, as it is not indexed, and can
be accidentally installed incorrectly.
(2) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch into
the connector (Fig. 239)
(3) Push the tow/haul overdrive off switch and wir-
ing into the shift lever.
(4) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch
retainer onto the shift lever.
Fig. 237 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch Retainer
Fig. 238 Remove the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
Fig. 239 Install the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
21 - 262 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2592 of 2627
BURNT FLUID - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CAUSES OF..........21-201,21-366
BUSHING - INSTALLATION.............19-19
BUSHING - INSTALLATION, TORSION
BAR CROSS MEMBER..................2-15
BUSHING - REMOVAL.................19-19
BUSHING - REMOVAL, TORSION BAR
CROSSMEMBER......................2-13
BUSHING AND SEAL - INSTALLATION,
EXTENSION HOUSING................21-440
BUSHING AND SEAL - REMOVAL,
EXTENSION HOUSING................21-440
BUSHINGS - 2WD (LD) - INSTALLATION,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-15
BUSHINGS - 2WD (LD) - REMOVAL,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-13
BUSHINGS - 4WD (LD) - INSTALLATION,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-14
BUSHINGS - 4WD (LD) - REMOVAL,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-13
BUSHINGS - INSTALLATION.............2-43
BUSHINGS - REMOVAL.................2-43
BUZZ, SQUEAK & RATTLE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................23-11
BYPASS - DESCRIPTION, WATER PUMP . . . 7-59
BYPASS - OPERATION, WATER PUMP.....7-60
C205F - ADJUSTMENTS, FRONT AXLE.....3-32
C205F - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
FRONT AXLE.........................3-27
C205F - INSTALLATION, FRONT AXLE.....3-31
C205F - REMOVAL, FRONT AXLE...........3-31
C205F - SPECIAL TOOLS, FRONT AXLE....3-40
C205F - SPECIFICATIONS, FRONT AXLE....3-39
CAB - INSTALLATION, QUAD......8O-36,8O-61
CAB - INSTALLATION, STANDARD . . 8O-35,8O-61
CAB - REMOVAL, QUAD..........8O-33,8O-60
CAB - REMOVAL, STANDARD......8O-32,8O-59
CAB BACK PANEL TRIM -
INSTALLATION, REAR.................23-69
CAB BACK PANEL TRIM - REMOVAL,
REAR..............................23-68
CAB CLEARANCE LAMP - INSTALLATION . . 8L-12
CAB CLEARANCE LAMP - REMOVAL.....8L-11
CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS, THROTTLE
VALVE ............................21-254
CABLE - DESCRIPTION.................8P-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, ANTENNA BODY . . . 8A-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, SPARK PLUG.....8I-21
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, THROTTLE
VALVE ............................21-253
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ANTENNA BODY......................8A-4
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
GEARSHIFT..................21-210,21-368
CABLE - INSTALLATION................8P-5
CABLE - INSTALLATION, ANTENNA BODY . . 8A-6
CABLE - INSTALLATION, CHECK.........23-15
CABLE - INSTALLATION, FRONT
PARKING BRAKE......................5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, GEARSHIFT....21-211,
21-370
CABLE - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL ANTENNA......................8A-7
CABLE - INSTALLATION, LEFT REAR......5-39
CABLE - INSTALLATION, REAR PARK
BRAKE..............................5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, RIGHT REAR.....5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, SPARK PLUG....8I-22
CABLE - INSTALLATION, THROTTLE
CONTROL.....................14-40,14-84
CABLE - OPERATION...................8P-4
CABLE - OPERATION, ANTENNA BODY
.....8A-4
CABLE - OPERATION, SPARK PLUG
.......8I-21
CABLE - REMOVAL
....................8P-4
CABLE - REMOVAL, ANTENNA BODY
......8A-6
CABLE - REMOVAL, CHECK
.............23-15
CABLE - REMOVAL, FRONT PARKING
BRAKE
..............................5-36
CABLE - REMOVAL, GEARSHIFT
. . 21-210,21-369
CABLE - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
ANTENNA
...........................8A-7
CABLE - REMOVAL, LEFT REAR
..........5-38
CABLE - REMOVAL, REAR PARK BRAKE
. . . 5-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, RIGHT REAR
.........5-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, SPARK PLUG
........8I-22
CABLE - REMOVAL, THROTTLE
CONTROL
.....................14-38,14-83CABLE, ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT . . . 21-212,
21-370
CABLE RESISTANCE, SPECIFICATIONS -
SPARK PLUG.........................8I-4
CABLE ROUTING, 5.7L V-8 ENGINE -
FIRING ORDER........................8I-4
CABLE/HANDLE ASSEMBLY -
INSTALLATION, LATCH RELEASE........23-47
CABLE/HANDLE ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL,
LATCH RELEASE.....................23-47
CABLES - DESCRIPTION, BATTERY.......8F-14
CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BATTERY...........................8F-15
CABLES - INSTALLATION, BATTERY......8F-17
CABLES - OPERATION, BATTERY........8F-15
CABLES - REMOVAL, BATTERY..........8F-16
CALIBRATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COMPASS...........................8M-3
CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT -
INSTALLATION, DISC BRAKE............5-22
CALIPERS - DESCRIPTION, DISC BRAKE . . . 5-16
CALIPERS - OPERATION, DISC BRAKE.....5-16
CAM BORE REPAIR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................9-267
CAMBER AND CASTER ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................2-4
CAMBER, CASTER AND TOE
ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................2-4
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
ASSEMBLY, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH....21-237
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
CLEANING, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH.....21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
DESCRIPTION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH . . 21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
DISASSEMBLY, OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH...........................21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
INSPECTION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH . . . 21-237
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
OPERATION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH....21-236
CAMSHAFT - INSTALLATION.......9-206,9-271
CAMSHAFT - REMOVAL..........9-205,9-268
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS - INSTALLATION . . . 9-271
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS - REMOVAL......9-268
CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG -
INSTALLATION.......................9-206
CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG -
REMOVAL..........................9-205
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-71
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.........................8I-7
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
INSTALLATION.......................14-72
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
INSTALLATION.......................8I-10
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
OPERATION.........................14-71
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
OPERATION..........................8I-7
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL..........................14-72
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL............................8I-9
CAMSHAFT(S) - DESCRIPTION.......9-25,9-35
CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION......9-27,9-36
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - DESCRIPTION....9-114
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - INSTALLATION....9-116
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - REMOVAL.......9-115
CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL..........9-25,9-35
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - DESCRIPTION . . . 9-119
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - INSTALLATION . . 9-120
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - REMOVAL......9-119
CANISTER - DESCRIPTION, VAPOR......25-22
CANISTER - INSTALLATION, VAPOR......25-22
CANISTER - OPERATION, VAPOR........25-22
CANISTER - REMOVAL, VAPOR..........25-22
CAP - DESCRIPTION, FUEL FILLER.......25-13
CAP - DESCRIPTION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE
..........................7-57
CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
RADIATOR
...........................7-58
CAP - OPERATION, FUEL FILLER
........25-13
CAP - OPERATION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE
..........................7-58
CAPACITIES, SPECIFICATIONS - FLUID
......0-5CAPACITOR - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - INSTALLATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - OPERATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - REMOVAL, IGNITION COIL . . . 8I-21
CAP-TO-FILLER NECK SEAL -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, RADIATOR.....7-58
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
ASSEMBLY, DOUBLE...................3-17
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
DISASSEMBLY, DOUBLE................3-16
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION...........23-37
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION, WITH.....8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION, WITHOUT . . 8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-8,8L-9
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL...............23-37
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL, WITH....8L-22,8L-24,
8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL, WITHOUT.....8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - TIE DOWN -
INSTALLATION.......................23-38
CARGO BOX - TIE DOWN - REMOVAL....23-38
CARGO LAMP INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-20
CARGO LAMP INDICATOR - OPERATION . . 8J-20
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION.......................23-65
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS - REMOVAL . . . 23-65
CASCADE OVERFLOW VALVE -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-66
CASCADE OVERFLOW VALVE -
OPERATION.........................14-66
CASE - DESCRIPTION, TRANSFER.........0-4
CASE - NV241 GENII - ASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-428
CASE - NV241 GENII - CLEANING,
TRANSFER.........................21-426
CASE - NV241 GENII - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-415
CASE - NV241 GENII - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-416
CASE - NV241 GENII - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-417
CASE - NV241 GENII - INSPECTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-426
CASE - NV241 GENII - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-438
CASE - NV241 GENII - OPERATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-415
CASE - NV241 GENII - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER.........................21-417
CASE - NV243 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER . . 21-496
CASE - NV243 - CLEANING, TRANSFER . . 21-493
CASE - NV243 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-482
CASE - NV243 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-483
CASE - NV243 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-484
CASE - NV243 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER . 21-493
CASE - NV243 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-505
CASE - NV243 - OPERATION, TRANSFER . 21-483
CASE - NV243 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER . . 21-484
CASE - NV244 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-513
CASE - NV244 GENII - ASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-525
CASE - NV244 GENII - CLEANING,
TRANSFER.........................21-523
CASE - NV244 GENII - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-512
CASE - NV244 GENII - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-514
CASE - NV244 GENII - INSPECTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-523
CASE - NV244 GENII - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-534
CASE - NV244 GENII - OPERATION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-513
CASE - NV244 GENII - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER
.........................21-514
CASE - NV271 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER
. . 21-461
CASE - NV271 - CLEANING, TRANSFER
. . 21-459
DRINDEX 5
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page