1998 DODGE RAM 1500 air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 394 of 2627

RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION
GROUND STRAP
DESCRIPTION
Radio noise suppression devices are factory-in-
stalled standard equipment on this vehicle. Radio
Frequency Interference (RFI) and ElectroMagnetic
Interference (EMI) can be produced by any on-board
or external source of electromagnetic energy. These
electromagnetic energy sources can radiate electro-
magnetic signals through the air, or conduct them
through the vehicle electrical system.
When the audio system converts RFI or EMI to an
audible acoustic wave form, it is referred to as radio
noise. This undesirable radio noise is generally man-
ifested in the form of ªbuzzing,º ªhissing,º ªpopping,º
ªclicking,º ªcrackling,º and/or ªwhirringº sounds. In
most cases, RFI and EMI radio noise can be sup-
pressed using a combination of vehicle and compo-
nent grounding, filtering and shielding techniques.
This vehicle is equipped with factory-installed radio
noise suppression devices that were designed to min-
imize exposure to typical sources of RFI and EMI;
thereby, minimizing radio noise complaints.
Factory-installed radio noise suppression is accom-
plished primarily through circuitry or devices that
are integral to the factory-installed radios, audio
power amplifiers and other on-board electrical com-
ponents such as generators, wiper motors, blower
motors, and fuel pumps that have been found to be
potential sources of RFI or EMI. External radio noise
suppression devices that are used on this vehicle to
control RFI or EMI, and can be serviced, include the
following:
²Engine-to-body ground strap- This length of
braided ground strap has an eyelet terminal connec-
tor crimped to each end. One end is secured to the
engine cylinder head(s). The other is secured to the
plenum at the exhaust heat shield forward/outer
attaching stud.
²Resistor-type spark plugs- This type of spark
plug has an internal resistor connected in series
between the spark plug terminal and the center elec-
trode to help reduce the production of electromag-
netic radiation that can result in radio noise.
OPERATION
There are two common strategies that can be used
to suppress Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and
ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI) radio noise. The
first suppression strategy involves preventing the
production of RFI and EMI electromagnetic signals
at their sources. The second suppression strategy
involves preventing the reception of RFI and EMIelectromagnetic signals by the audio system compo-
nents.
The use of braided ground straps in key locations
is part of the RFI and EMI prevention strategy.
These ground straps ensure adequate ground paths,
particularly for high current components such as
many of those found in the starting, charging, igni-
tion, engine control and transmission control sys-
tems. An insufficient ground path for any of these
high current components may result in radio noise
caused by induced voltages created as the high cur-
rent seeks alternative ground paths through compo-
nents or circuits intended for use by, or in close
proximity to the audio system components or circuits.
Preventing the reception of RFI and EMI is accom-
plished by ensuring that the audio system compo-
nents are correctly installed in the vehicle. Loose,
corroded or improperly soldered wire harness connec-
tions, improperly routed wiring and inadequate audio
system component grounding can all contribute to
the reception of RFI and EMI. A properly grounded
antenna body and radio chassis, as well as a shielded
antenna coaxial cable with clean and tight connec-
tions will each help reduce the potential for reception
of RFI and EMI.
REMOVAL
BED TO CAB
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the attaching bolts and strap (Fig. 10).
Fig. 10 BED TO CAB GROUND STRAP
1 - BED
2 - CAB
3 - GROUND STRAP
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS
DRAUDIO/VIDEO 8A - 9
Page 411 of 2627

NOTE: ECM Inputs:
²Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) Volts
²APPS1 Signal Ð For off engine APPS
²APPS2 Signal Ð For off engine APPS
²APPS idle validation switches #1 and #2
²Battery Temperature
²Battery voltage
²Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
²Fuel pressure sensor
²Fan speed (engine cooling fan)
²Ground circuits
²Inlet air temperature sensor/pressure sensor
²Intake air temperature sensor/MAP sensor
²Oil Pressure switch
²Power ground
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor
NOTE: ECM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the ECM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the ECM. These are consideredECM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²CKP and APPS outputs to the PCM
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Fan Clutch PWM
²Five volt sensor supply
²Fuel Control Actuator
²Fuel transfer (lift) pump
²Intake manifold air heater relays #1 and #2 con-
trol circuits
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp)
(databus)
²Oil Pressure Swith/warning lamp (databus)
²Wait-to-start warning lamp (databus)
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) warning lamp (databus)
REMOVAL
The engine control module (ECM) is bolted to a
support bracket near the fuel filter. The support
bracket mounts to the block with four capscrews and
vibration isolators. A ground wire is fastened to the
bracket. The other end of the wire is fastened to the
engine block.
(1) Record any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
found in the ECM.To avoid possible voltage spike damage to the
ECM, ignition key must be off, and both negative
battery cables must be disconnected before unplug-
ging ECM connectors.
(2) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(3) Remove the 50±way and 60±way connector
bolts at the ECM. Note: The connector bolt is a
female allen head. As bolt is being removed, very
carefully remove connectors from the ECM.
(4) Remove five ECM mounting bolts and remove
ECM from the vehicle (Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
Do not apply paint to ECM or a poor ground will
result.
(1) Position the ECM to the ECM support bracket
and install the five mounting bolts. Tighten the bolts
to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(2) Check pin connectors in ECM, 50±way and
60±way connectors for corrosion or damage. Repair
as necessary.
(3) Clean pins in the 50±way and 60±way electri-
cal connectors with a electrical contact cleaner.
(4) Install the 50±way and 60±way connectors to
ECM. Tighten connector bolts to 3 N´m (27 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect both negative battery cables.
(6) Use DRBIIItscan tool to erase any stored com-
panion DTC's from ECM.
Fig. 2 Diesel ECM
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - ECM MOUNTING BOLT
3 - 50-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SUPPORT PLATE
5 - 60-WAY CONNECTOR
8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 506 of 2627

SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
29). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 inch per 2000 miles of opera-
tion. This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat
range rating should be used. Over advanced ignition
timing, detonation and cooling system malfunctions
can also cause spark plug overheating.
REMOVAL
3.7L V-6
Each individual spark plug is located under each
ignition coil. Each individual ignition coil must be
removed to gain access to each spark plug. Refer to
Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.(1) Remove necessary air filter tubing at throttle
body.
(2) Prior to removing ignition coil, spray com-
pressed air around coil base at cylinder head.
(3) Prior to removing spark plug, spray com-
pressed air into cylinder head opening. This will help
prevent foreign material from entering combustion
chamber.
(4) Remove spark plug from cylinder head using a
quality socket with a rubber or foam insert. Also
check condition of ignition coil o-ring and replace as
necessary.
(5) Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Diagnos-
tics and Testing - Spark Plug Conditions.
4.7L V-8
Each individual spark plug is located under each
ignition coil. Each individual ignition coil must be
removed to gain access to each spark plug. Refer to
Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.
(1) Remove necessary air filter tubing at throttle
body.
(2) Prior to removing ignition coil, spray com-
pressed air around coil base at cylinder head.
(3) Prior to removing spark plug, spray com-
pressed air into cylinder head opening. This will help
prevent foreign material from entering combustion
chamber.
(4) Remove spark plug from cylinder head using a
quality socket with a rubber or foam insert. Also
check condition of ignition coil o-ring and replace as
necessary.
(5) Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Diagnos-
tics and Testing - Spark Plug Conditions.
5.7L V-8
Eight of the 16 spark plugs are located under an
ignition coil; the other 8 are not. If spark plug being
Fig. 27 CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE
3 - CHIPPED INSULATOR
Fig. 28 PREIGNITION DAMAGE
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE STARTING TO DISSOLVE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE DISSOLVED
Fig. 29 SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
1 - BLISTERED WHITE OR GRAY COLORED INSULATOR
DRIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 19
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 507 of 2627

removed is under coil, coil must be removed to gain
access to spark plug. Refer to Ignition Coil Removal/
Installation and observe all CAUTIONS and WARN-
INGS.
Before removing or disconnecting any spark plug
cables, note their original position. Remove cables
one-at-a-time. To prevent ignition crossfire, spark
plug cablesMUSTbe placed in cable tray (routing
loom) into their original position. Refer to Spark Plug
Cable Removal for a graphic.
Before installing spark plug cables to either the
spark plugs or coils, apply dielectric grease to inside
of boots.
(1) Remove necessary air filter tubing at throttle
body.
(2) Prior to removing ignition coil (if coil removal
is necessary), spray compressed air around coil base
at cylinder head cover.
(3) Prior to removing spark plug, spray com-
pressed air into cylinder head opening. This will help
prevent foreign material from entering combustion
chamber.
(4) Remove spark plug from cylinder head using a
quality socket with a rubber or foam insert.
(5) Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Diagnos-
tics and Testing - Spark Plug Conditions.
CLEANING
CLEANING AND ADJUSTMENT
The plugs may be cleaned using commercially
available spark plug cleaning equipment. After clean-
ing, file center electrode flat with a small point file or
jewelers file before adjusting gap.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean spark plugs. Metallic deposits will remain
on spark plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
Adjust spark plug gap with a gap gauging tool
(Fig. 30).
INSTALLATION
3.7L V-6
Special care should be taken when installing spark
plugs into the cylinder head spark plug wells. Be
sure the plugs do not drop into the plug wells as elec-
trodes can be damaged.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap or a cracked porcelain
insulator.
(1) Start the spark plug into the cylinder head by
hand to avoid cross threading.(2) Tighten spark plugs. Refer to torque specifica-
tions.
(3) Before installing ignition coil(s), check condi-
tion of coil o-ring and replace as necessary. To aid in
coil installation, apply silicone to coil o-ring.
(4) Install ignition coil(s). Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
4.7L V-8
CAUTION: The 4.7L V±8 engine is equipped with
copper core ground electrode spark plugs. They
must be replaced with the same type/number spark
plug as the original. If another spark plug is substi-
tuted, pre-ignition will result.
Special care should be taken when installing spark
plugs into the cylinder head spark plug wells. Be
sure the plugs do not drop into the plug wells as elec-
trodes can be damaged.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap or a cracked porcelain
insulator.
(1) Start the spark plug into the cylinder head by
hand to avoid cross threading.
(2) Tighten spark plugs. Refer to torque specifica-
tions.
(3) Before installing ignition coil(s), check condi-
tion of coil o-ring and replace as necessary. To aid in
coil installation, apply silicone to coil o-ring.
Fig. 30 SETTING SPARK PLUG GAP - TYPICAL
1 - GAUGE TOOL
2 - SPARK PLUG
8I - 20 IGNITION CONTROLDR
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 703 of 2627

interval at which to de-energize the wiper on/off
relay to complete the wipe-after-wash mode cycle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIPER &
WASHER SYSTEM
If the wiper motor operates, but the wipers do not
move on the windshield, replace the faulty wiper
module. If the washer pump/motor operates, but no
washer fluid is dispensed on the glass; or, if the wip-
ers operate, but chatter, lift, or do not clear the glass,
clean and inspect the wiper and washer system com-
ponents as required. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
WIPERS/WASHERS - CLEANING) and (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS - INSPECTION).
For diagnosis and testing of the multi-function
switch (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). Refer to the appropri-
ate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
The hard wired circuits and components of the
wiper and washer system may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. However, conventional diagnostic methods
may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the
instrument cluster, the Front Control Module (FCM),
or the electronic message inputs to or outputs from
the instrument cluster and the FCM that control the
various wiper and washer system operating modes.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the instrument cluster, the FCM, or the
electronic message inputs and outputs related to the
various wiper and washer system operating modes
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, AIRBAG, SEAT BELT
TENSIONER, IMPACT SENSOR, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGA-
TIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES
FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT.
CLEANING - WIPER & WASHER SYSTEM
WIPER SYSTEM
The squeegees of wiper blades exposed to the ele-
ments for a long time tend to lose their wiping effec-
tiveness. Periodic cleaning of the squeegees is
suggested to remove any deposits of salt or road film.
The wiper blades, arms, and windshield glass should
only be cleaned using a sponge or soft cloth and
windshield washer fluid, a mild detergent, or a non-
abrasive cleaner. If the wiper blades continue to
leave streaks, smears, hazing, or beading on the
glass after thorough cleaning of the squeegees and
the glass, the entire wiper blade assembly must be
replaced.
CAUTION: Protect the rubber squeegees of the
wiper blades from any petroleum-based cleaners,
solvents, or contaminants. These products can rap-
idly deteriorate the rubber squeegees.
WASHER SYSTEM
If the washer system is contaminated with foreign
material, drain the washer reservoir by removing the
washer pump/motor from the reservoir. Clean foreign
material from the inside of the washer pump/motor
inlet filter screen and the washer reservoir using
clean washer fluid, a mild detergent, or a non-abra-
sive cleaner. Flush foreign material from the washer
system plumbing by first disconnecting the washer
hoses from the washer nozzles, then running the
washer pump/motor to run clean washer fluid or
water through the system. Plugged or restricted
washer nozzles should be carefully back-flushed
using compressed air. If the washer nozzle obstruc-
tion cannot be cleared, replace the washer nozzle.
CAUTION: Never introduce petroleum-based clean-
ers, solvents, or contaminants into the washer sys-
tem. These products can rapidly deteriorate the
rubber seals and hoses of the washer system, as
well as the rubber squeegees of the wiper blades.
CAUTION: Never use compressed air to flush the
washer system plumbing. Compressed air pres-
sures are too great for the washer system plumbing
components and will result in further system dam-
age. Never use sharp instruments to clear a
plugged washer nozzle or damage to the nozzle ori-
fice and improper nozzle spray patterns will result.
8R - 6 WIPERS/WASHERSDR
WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 710 of 2627

(7) Reinstall both wiper arms onto the wiper piv-
ots. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/
WIPER ARM - INSTALLATION).
WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The washer pump/motor unit (Fig. 12) is located on
the rearward facing surface of the washer reservoir,
in the right (except diesel engine) or left (diesel
engine only) front corner of the engine compartment.
A small permanently lubricated and sealed electric
motor is coupled to the rotor-type washer pump. A
seal flange with a barbed inlet nipple on the pump
housing passes through a rubber grommet seal
installed in a dedicated mounting hole of the washer
reservoir. When the pump is installed in the reser-
voir a barbed outlet nipple on the pump housing con-
nects the unit to the washer system through a short
washer reservoir hose.
The washer pump/motor unit is retained on the
reservoir by the interference fit between the barbed
pump inlet nipple and the grommet seal, which is a
light press fit. The top of the washer pump is also
secured to the washer reservoir by the use of a snappost on the motor housing and a snap post receptacle
molded into the reservoir that allows for mounting of
the washer pump without the use of fasteners. An
integral connector receptacle on the top of the motor
housing connects the unit to the vehicle electrical
system. The washer pump/motor unit cannot be
repaired. If faulty or damaged, the entire washer
pump/motor unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The washer pump/motor unit features a small
Direct Current (DC) electric motor. The motor is con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a sin-
gle take out and two-cavity connector of the right
(except diesel engine) or left (diesel engine only)
headlamp and dash wire harness. The motor is
grounded at all times through another take out of
the right (except diesel engine) or left (diesel engine
only) headlamp and dash wire harness. On models
without the diesel engine, a single eyelet terminal
connector is secured by a nut to a ground stud
located on the right front fender inner shield in the
engine compartment. On models with a diesel engine,
an eyelet terminal connector is secured by a ground
screw to the left front fender inner shield in the
engine compartment. The motor receives battery cur-
rent on a washer pump/motor control circuit.
The washer pump/motor control circuit is energized
through a high side driver within the Front Control
Module (FCM) whenever the FCM receives an elec-
tronic message requesting washer system operation
from the instrument cluster over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus. The
instrument cluster monitors a resistor multiplexed
hard wired input from the momentary washer switch
contacts within the multi-function switch on the
steering column to determine when it should issue
the electronic message requesting washer system
operation.
Washer fluid is gravity-fed from the washer reser-
voir to the inlet side of the washer pump. When the
pump motor is energized, the motor spins the rotor
within the washer pump. The spinning pump rotor
pressurizes the washer fluid and forces it through
the pump outlet nipple, the washer plumbing, and
the washer nozzles onto the windshield glass.
The washer pump/motor unit may be diagnosed
using conventional diagnostic tools and methods.
However, conventional diagnostic methods may not
prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the instrument
cluster, the FCM, or the electronic message inputs to
or outputs from the instrument cluster and the FCM
that control the operation of the washer pump/motor
unit. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means
to diagnose the washer pump/motor unit, the instru-
ment cluster, the FCM, or the electronic message
Fig. 12 Washer Pump/Motor
1 - MOTOR
2 - SNAP POST
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
4 - PUMP
5 - OUTLET NIPPLE
6 - INLET NIPPLE
7 - FILTER SCREEN
DRWIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 13
WASHER NOZZLE (Continued)
Page 1227 of 2627
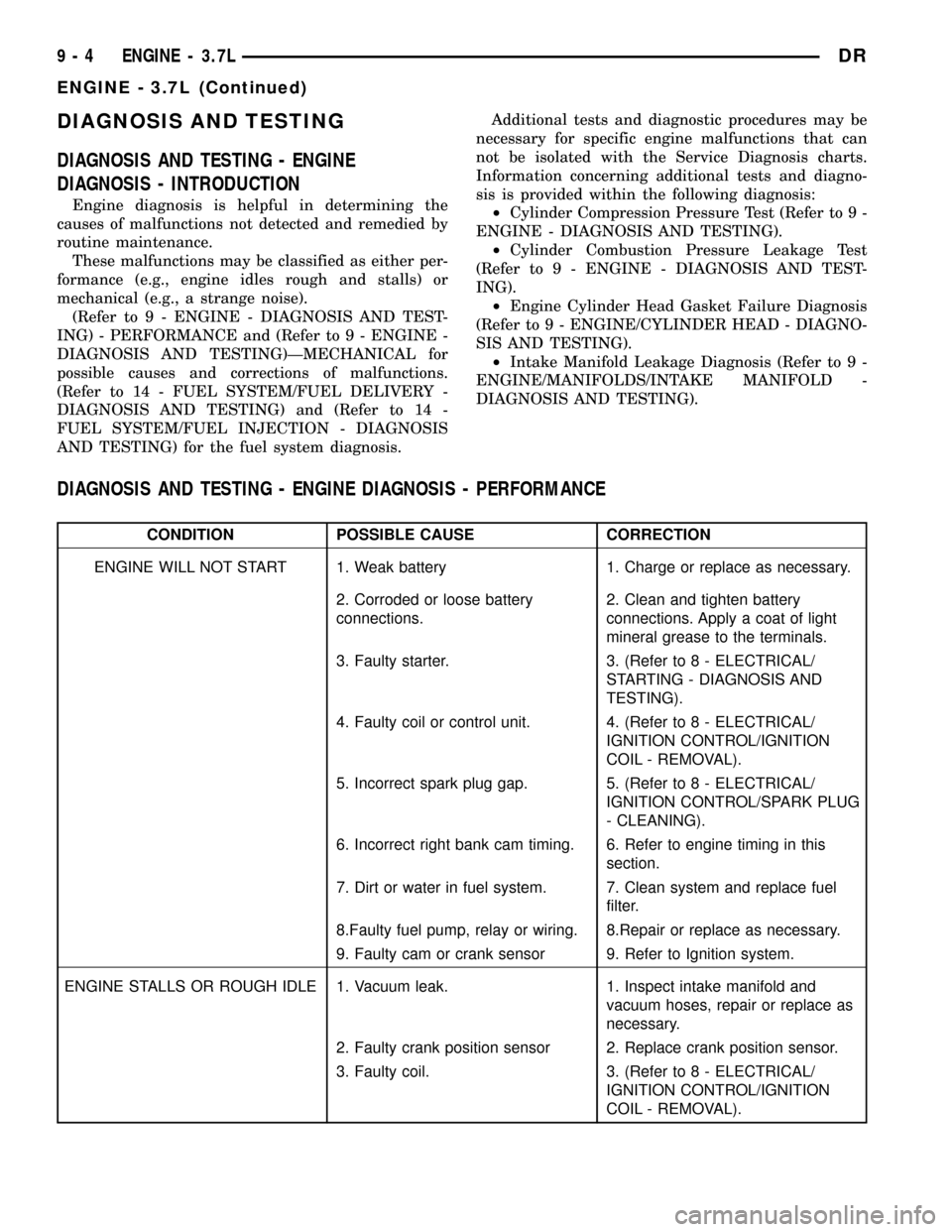
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
3. Faulty coil. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9 - 4 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1228 of 2627
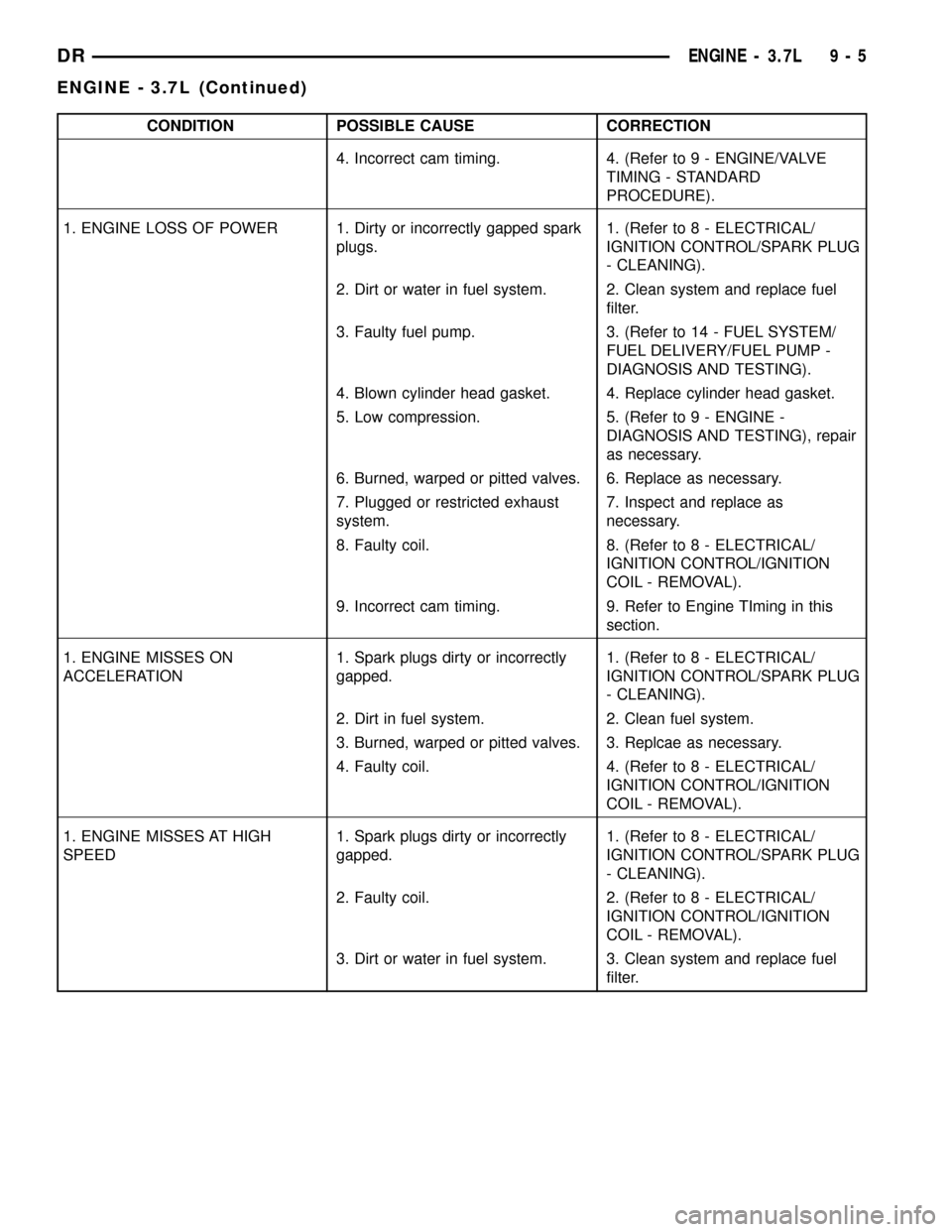
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
4. Incorrect cam timing. 4. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
1. ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING), repair
as necessary.
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9. Incorrect cam timing. 9. Refer to Engine TIming in this
section.
1. ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH
SPEED1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 5
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)