1998 DODGE RAM 1500 oil leak
[x] Cancel search: oil leakPage 2014 of 2627

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE
DESCRIPTION........................312
OPERATION..........................313
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
PRELIMINARY.......................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................314
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................316
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION....317
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................318
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................318
REMOVAL............................318
DISASSEMBLY........................320
CLEANING...........................326
INSPECTION.........................326
ASSEMBLY...........................326
INSTALLATION........................333
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............337
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................358
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION.................359
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY........................362
ASSEMBLY...........................363
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................364
INSTALLATION........................364
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION........................364
OPERATION..........................364
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......364
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................365
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............366
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................366DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................366
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............367
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................368
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................368
REMOVAL............................369
INSTALLATION........................370
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE..................370
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................371
OPERATION..........................372
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................373
OPERATION..........................373
DISASSEMBLY........................374
ASSEMBLY...........................378
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................382
REMOVAL............................382
INSTALLATION........................382
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................382
OPERATION..........................383
REMOVAL............................383
INSTALLATION........................383
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
DISASSEMBLY........................384
CLEANING...........................385
INSPECTION.........................385
ASSEMBLY...........................385
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................386
OPERATION..........................386
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK.....................387
DISASSEMBLY........................388
CLEANING...........................390
INSPECTION.........................390
ASSEMBLY...........................390
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL............................391
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 311
Page 2017 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a RFE
automatic transmission, check for Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch oper-
ation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift
cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line pressure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application charts
provide a basis for analyzing road test results.
21 - 314 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2021 of 2627

is applied. The clutch application can also be felt by
touching the appropriate element while applying air
pressure. As the air pressure is released, the clutch
should also release.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
two items must be established before repair.
(1) Verify that a leak condition actually exists.
(2) Determined the true source of the leak.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair. Torque converter seal leaks tend to move
along the drive hub and onto the rear of the con-
verter. Pump cover seal tend to run down the cover
and the inside surface of the bellhousing.
Some leaks, or suspected leaks, may be particu-
larly difficult to locate. If necessary, a Mopart
approved dye may be used to locate a leak.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAK POINTS
Possible sources of converter leaks are:
(1) Leaks at the weld joint around the outside
diameter weld (Fig. 7).
(2) Leaks at the converter hub weld (Fig. 7).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
mission case and valve body can be repaired by the
use of Heli-CoilsŸ, or equivalent. This repair con-
sists of drilling out the worn-out damaged threads.
Then tap the hole with a special Heli-CoilŸ tap, or
equivalent, and installing a Heli-CoilŸ insert, or
equivalent, into the hole. This brings the hole back to
its original thread size.
Heli-CoilŸ, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle
(3) Remove any necessary skid plates. (Refer to 13
- FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - REMOVAL)
(4) Mark propeller shaft and axle companion
flanges for assembly alignment.
(5) Remove the rear propeller shaft
(6) Remove the front propeller shaft, if necessary.
(7) Remove the engine to transmission collar (Fig.
8).
(8) Remove the exhaust support bracket from the
rear of the transmission.
(9) Disconnect and lower or remove any necessary
exhaust components.
Fig. 7 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
Fig. 8 Transmission Collar
1 - ENGINE
2 - STRUCTURAL DUST COVER
3 - TRANSMISSION
21 - 318 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2070 of 2627
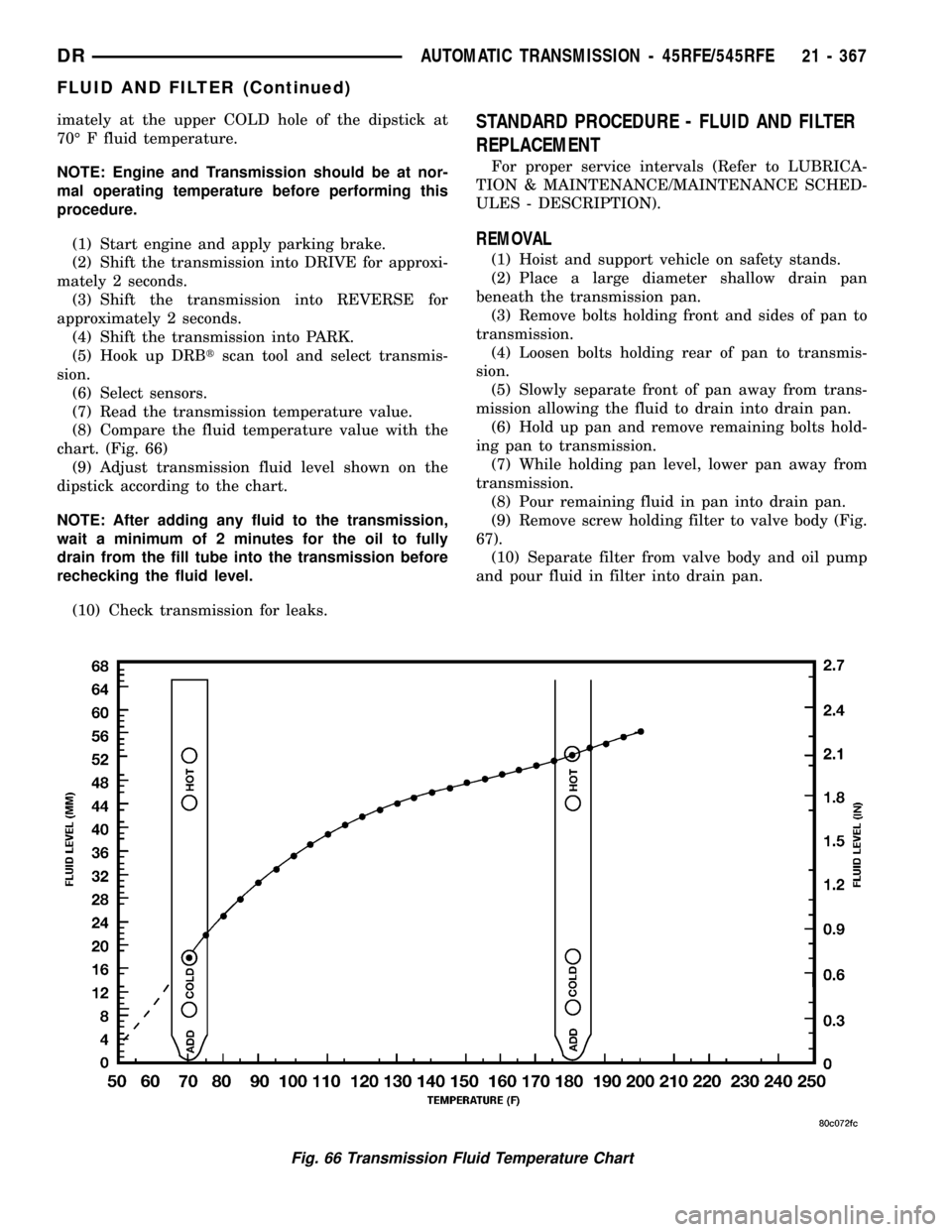
imately at the upper COLD hole of the dipstick at
70É F fluid temperature.
NOTE: Engine and Transmission should be at nor-
mal operating temperature before performing this
procedure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select transmis-
sion.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart. (Fig. 66)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission.
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan away from trans-
mission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan away from
transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screw holding filter to valve body (Fig.
67).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and oil pump
and pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
Fig. 66 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 367
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 2117 of 2627

Inspect all the fluid seals on the valve body (Fig.
141). Replace any seals that are cracked, distorted, or
damaged in any way. These seals pass fluid pressure
directly to the clutches. Any pressure leak at these
points, may cause transmission performance prob-
lems.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve bores with clean transmission fluid.
(2) Install solenoid switch valve, manual valve,
and the low/reverse switch valve into the valve body.
(3) Install the retainers to hold each valve into the
valve body.
(4) Install the valve body check balls into their
proper locations.
(5) Position the transfer plate onto the valve body.
(6) Install the screws to hold the transfer plate to
the valve body. Tighten the screws to 5.6 N´m (50 in.
lbs.).
(7) Install the accumulator pistons and springs
into the valve body in the location from which they
were removed. Note that all accumulators except the
overdrive have two springs. The overdrive accumula-
tor piston has only one spring.
(8) Position the accumulator cover onto the valve
body.(9) Install the screws to hold the accumulator
cover onto the valve body. Tighten the screws to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the TRS selector plate onto the valve
body and the manual valve.
(11) Install the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly onto the valve body.
(12) Install the screws to hold the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly onto the valve body.
Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Tighten
the screws adjacent to the arrows cast into the bot-
tom of the transfer plate first.
(13) Position the detent spring onto the valve body.
(14) Install the screw to hold the detent spring
onto the valve body. Tighten the screw to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(15) Install new clutch passage seals onto the
valve body, if necessary
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of seals on valve body and the
solenoid and pressure switch assembly. Replace seals
if cut or worn.
(2) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(3) Place the transmission in the PARK position.
(4) Lubricate seal on the solenoid and pressure
switch assembly connector with petroleum jelly.
(5) Position valve body in transmission and align
the manual lever on the valve body to the pin on the
transmission manual shift lever.
(6) Seat valve body in case and install one or two
bolts to hold valve body in place.
(7) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and evenly
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(9) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(10) Install screw to hold filter to valve body.
Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector.
(12) Install oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4.
(14) Check and adjust gearshift cable, if necessary.
Fig. 141 Valve Body Seals
1 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
2 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
3 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
5 - LOW/REVERSE PASSAGE SEAL
6 - 2ND CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
7 - 4TH CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
8 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (1 SPRING)
21 - 414 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2120 of 2627
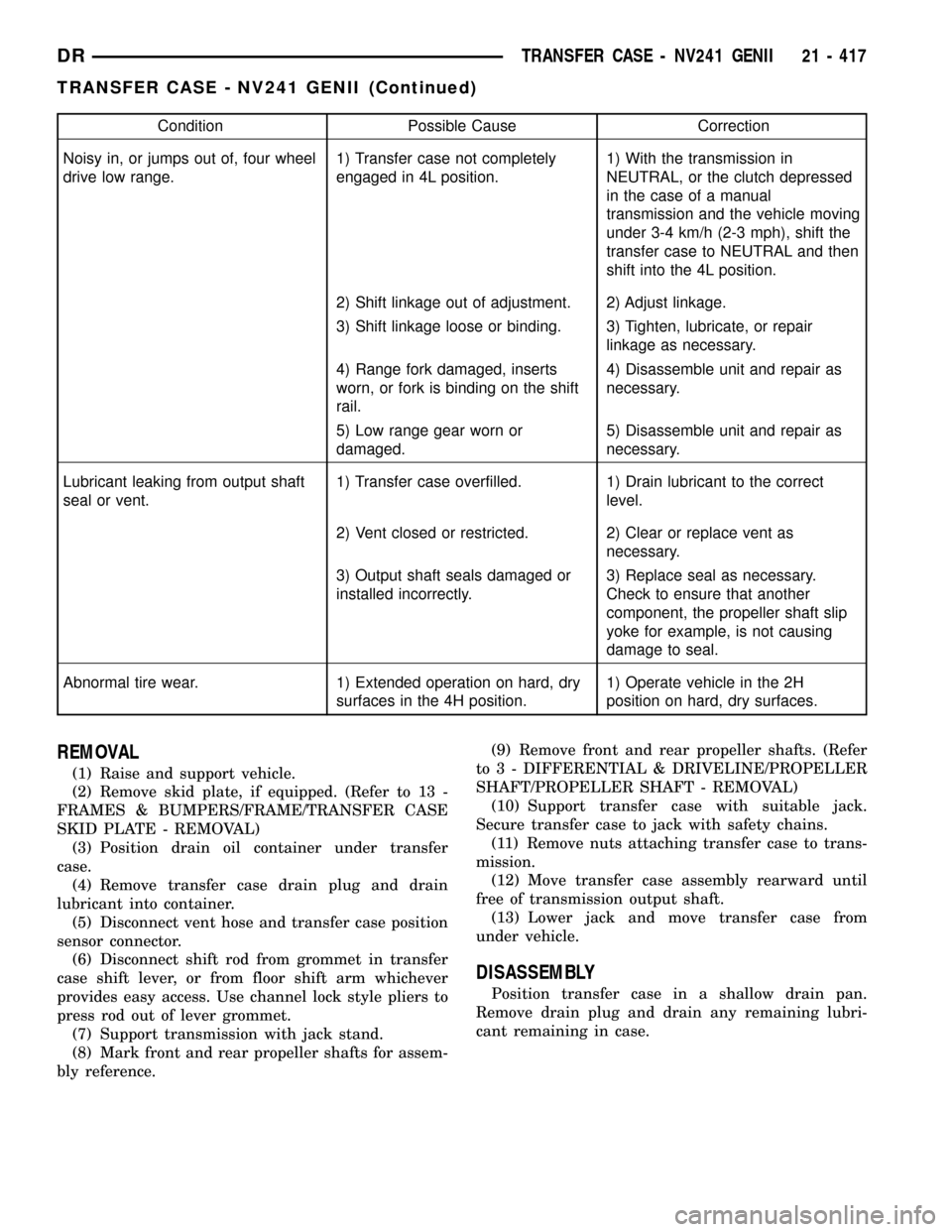
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in
NEUTRAL, or the clutch depressed
in the case of a manual
transmission and the vehicle moving
under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift the
transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair
linkage as necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or
damaged.5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft
seal or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary.
Check to ensure that another
component, the propeller shaft slip
yoke for example, is not causing
damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H
position on hard, dry surfaces.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove skid plate, if equipped. (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - REMOVAL)
(3) Position drain oil container under transfer
case.
(4) Remove transfer case drain plug and drain
lubricant into container.
(5) Disconnect vent hose and transfer case position
sensor connector.
(6) Disconnect shift rod from grommet in transfer
case shift lever, or from floor shift arm whichever
provides easy access. Use channel lock style pliers to
press rod out of lever grommet.
(7) Support transmission with jack stand.
(8) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for assem-
bly reference.(9) Remove front and rear propeller shafts. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(10) Support transfer case with suitable jack.
Secure transfer case to jack with safety chains.
(11) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission.
(12) Move transfer case assembly rearward until
free of transmission output shaft.
(13) Lower jack and move transfer case from
under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubri-
cant remaining in case.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII 21 - 417
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII (Continued)
Page 2131 of 2627

DRIVE CHAIN
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
replace the chain if stretched, distorted, or if any of
the links bind. Replace the bearings if rough, or
noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 43)
FRONT CASE AND REAR CASE
Inspect the cases for wear and damage.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
BEARINGS AND SEALS
(1) Remove the input shaft bearing (Fig. 44) from
the front case with suitable snap-ring pliers.
(2) Transfer the retaining ring to the new bearing
if necessary and install the bearing into the front
case.
Fig. 42 Shift Fork And Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 43 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Fig. 44 Remove Input Gear Bearing
1 - INPUT GEAR BEARING
2 - FRONT CASE
21 - 428 TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENIIDR
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII (Continued)