1998 DODGE RAM 1500 one
[x] Cancel search: onePage 1970 of 2627

TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 248). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The Tow/Haul lamp in the instrument panel illumi-
nates when the shift back to third occurs. The trans-
mission will not allow fourth gear operation until
fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110ÉC
(230ÉF).
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 249), (Fig. 250), (Fig.
251), and (Fig. 252):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve
²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²9 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 248 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 267
Page 1976 of 2627
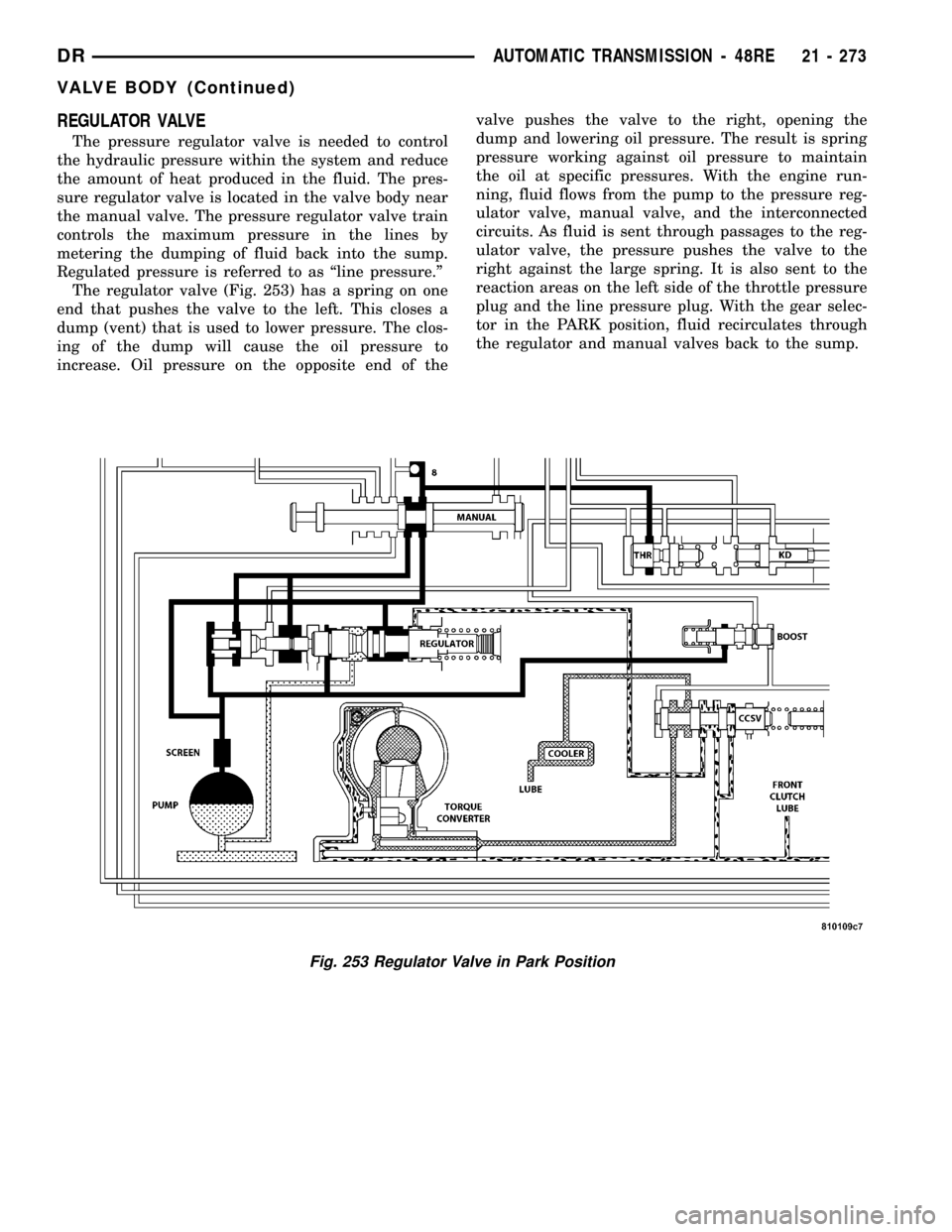
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 253) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 253 Regulator Valve in Park Position
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 273
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1982 of 2627
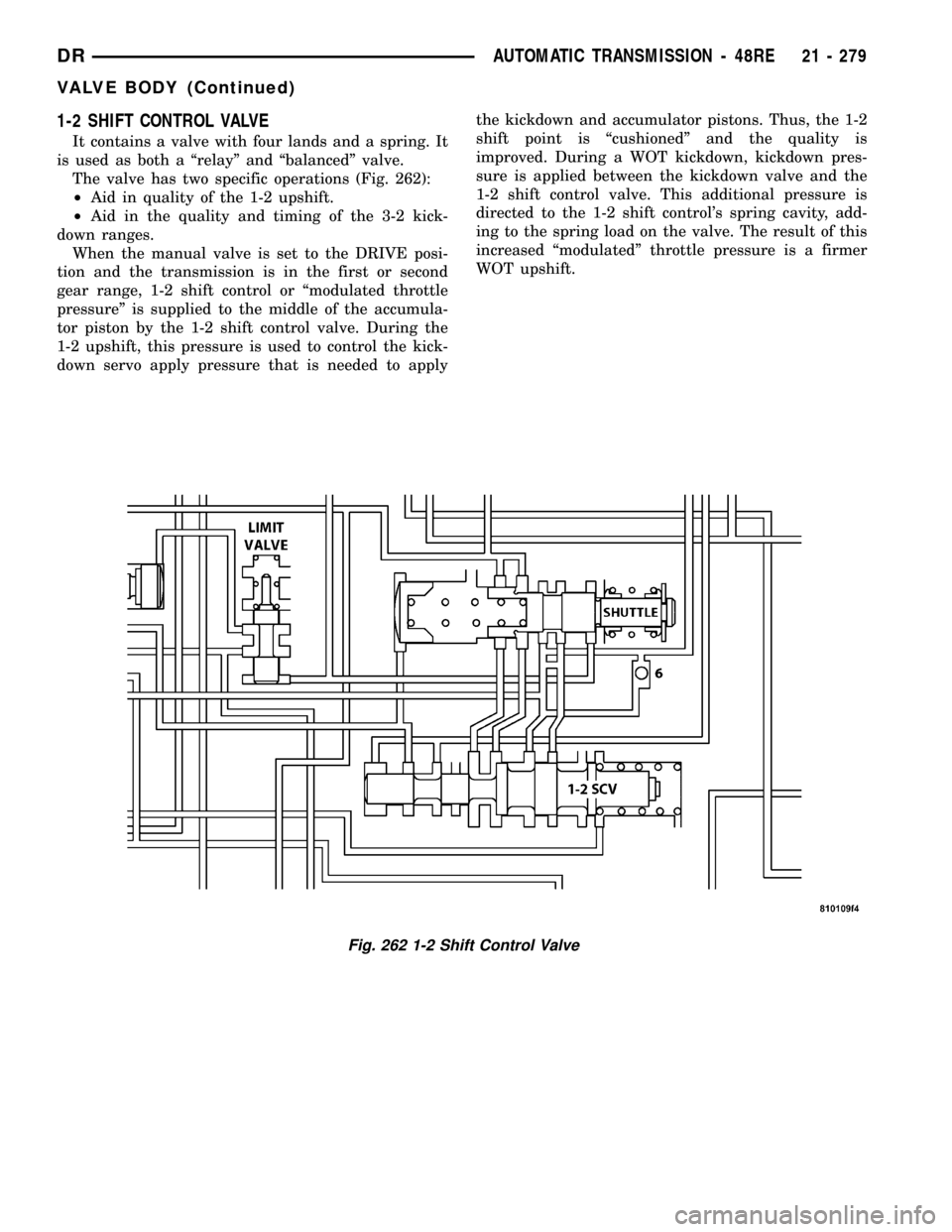
1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
It contains a valve with four lands and a spring. It
is used as both a ªrelayº and ªbalancedº valve.
The valve has two specific operations (Fig. 262):
²Aid in quality of the 1-2 upshift.
²Aid in the quality and timing of the 3-2 kick-
down ranges.
When the manual valve is set to the DRIVE posi-
tion and the transmission is in the first or second
gear range, 1-2 shift control or ªmodulated throttle
pressureº is supplied to the middle of the accumula-
tor piston by the 1-2 shift control valve. During the
1-2 upshift, this pressure is used to control the kick-
down servo apply pressure that is needed to applythe kickdown and accumulator pistons. Thus, the 1-2
shift point is ªcushionedº and the quality is
improved. During a WOT kickdown, kickdown pres-
sure is applied between the kickdown valve and the
1-2 shift control valve. This additional pressure is
directed to the 1-2 shift control's spring cavity, add-
ing to the spring load on the valve. The result of this
increased ªmodulatedº throttle pressure is a firmer
WOT upshift.
Fig. 262 1-2 Shift Control Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 279
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
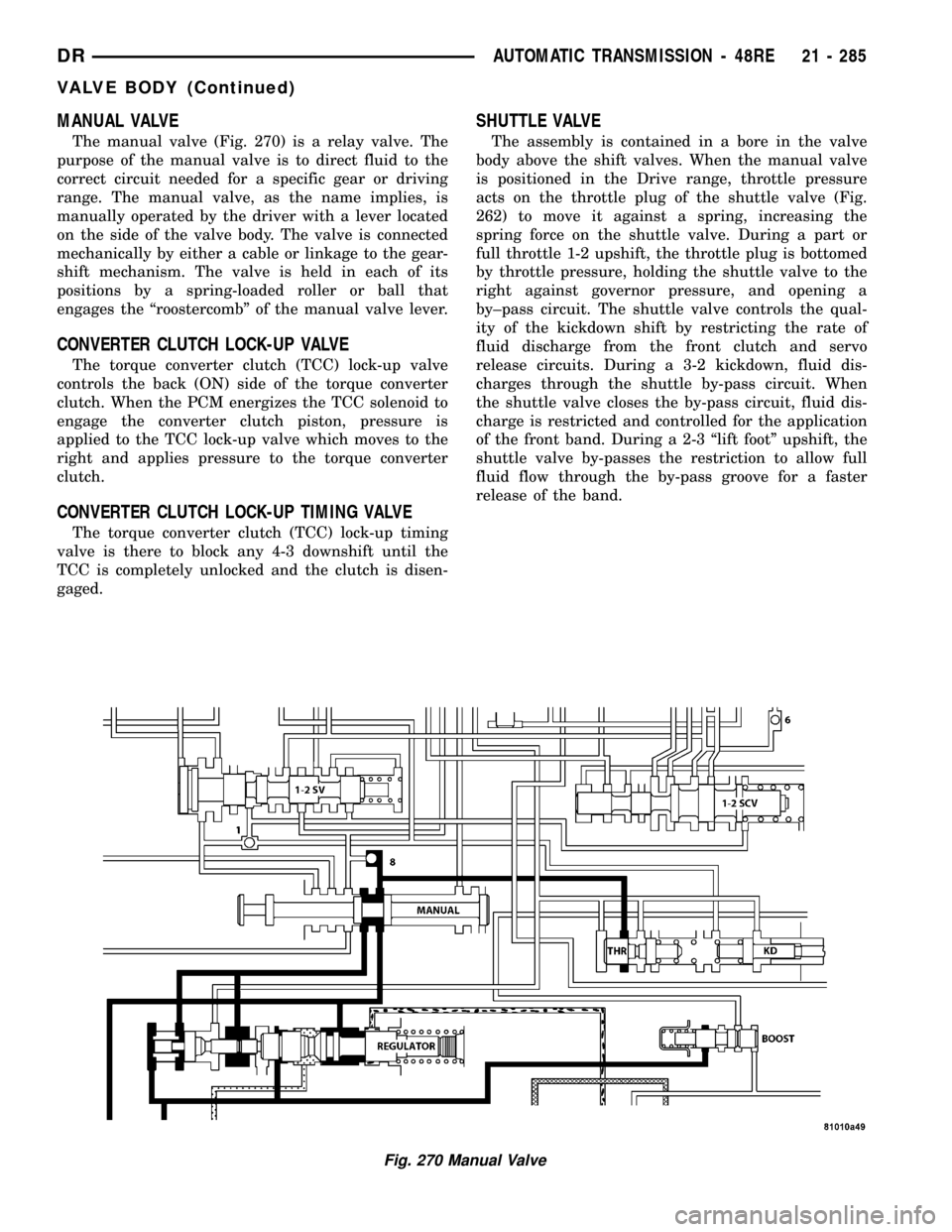
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1989 of 2627
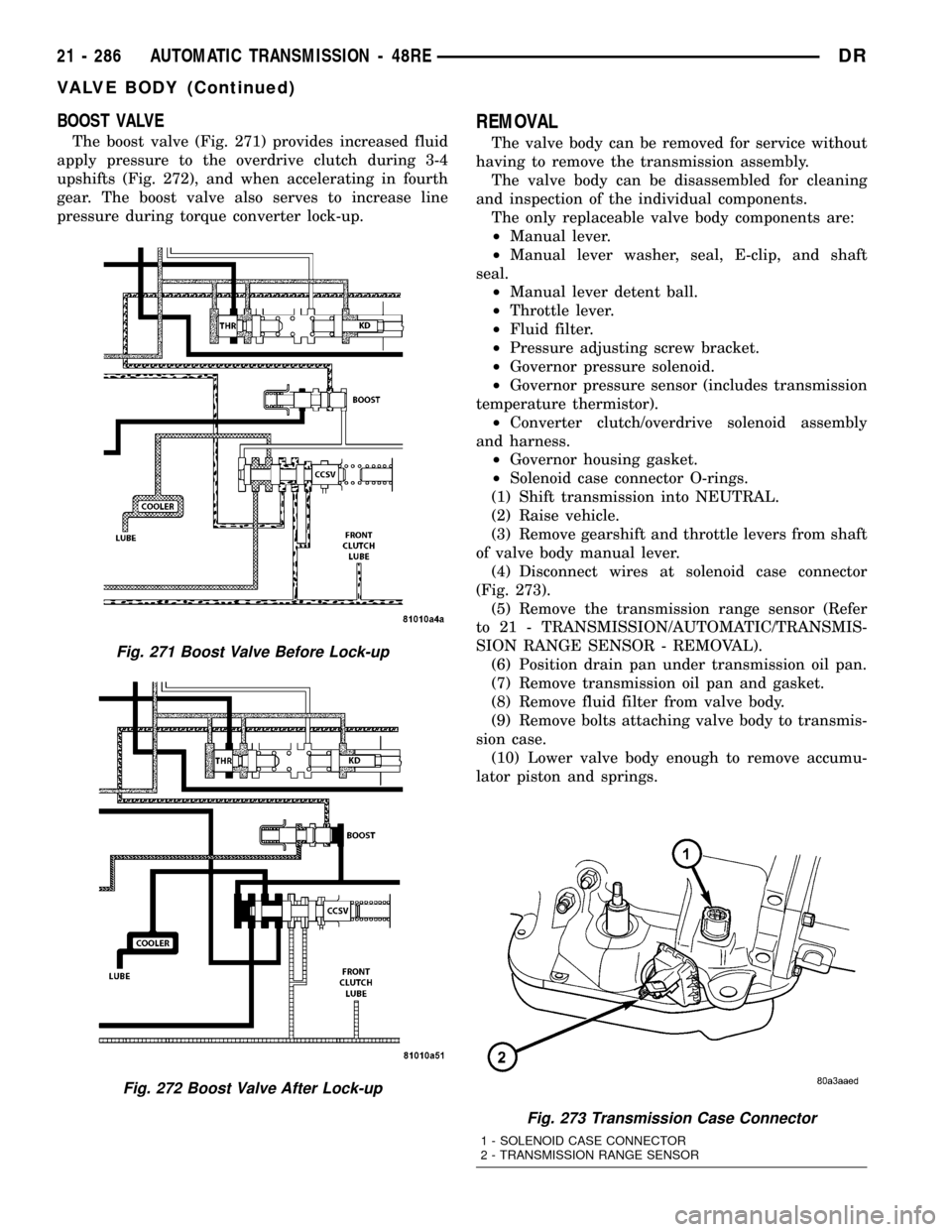
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 271) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 272), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 273).
(5) Remove the transmission range sensor (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/TRANSMIS-
SION RANGE SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(8) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(9) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(10) Lower valve body enough to remove accumu-
lator piston and springs.
Fig. 273 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 271 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 272 Boost Valve After Lock-up
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1990 of 2627

(11) Work manual lever shaft and electrical con-
nector out of transmission case.
(12) Lower valve body, rotate valve body away
from case, pull park rod out of sprag, and remove
valve body (Fig. 274).
DISASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Do not clamp any valve body component
in a vise. This practice can damage the component
resulting in unsatisfactory operation after assembly
and installation. Do not use pliers to remove any of
the valves, plugs or springs and do not force any of
the components out or into place. The valves and
valve body housings will be damaged if force is
used. Tag or mark the valve body springs for refer-
ence as they are removed. Do not allow them to
become intermixed.
(1) Disconnect wires from governor pressure sen-
sor and solenoid.
(2) Remove screws attaching governor body and
retainer plate to transfer plate.
(3) Remove retainer plate, governor body and gas-
ket from transfer plate.(4) Remove governor pressure sensor from gover-
nor body.
(5) Remove governor pressure solenoid by pulling
it straight out of bore in governor body. Remove and
discard solenoid O-rings if worn, cut, or torn.
(6) Remove small shoulder bolt that secures sole-
noid harness case connector to 3-4 accumulator hous-
ing (Fig. 275). Retain shoulder bolt. Either tape it to
harness or thread it back into accumulator housing
after connector removal.
(7) Unhook overdrive/converter solenoid harness
from 3-4 accumulator cover plate (Fig. 276).
Fig. 275 Solenoid Harness Case Connector
Shoulder Bolt
1 - SOLENOID HARNESS CASE CONNECTOR
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
Fig. 276 Solenoid Harness Routing
1 - OVERDRIVE/CONVERTER SOLENOID WIRE HARNESS
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR COVER PLATE
Fig. 274 Valve Body
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - WIRE HARNESS
3 - PARK ROD
4 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
5 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 287
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1991 of 2627

(8) Turn valve body over and remove screws that
attach overdrive/converter solenoid assembly to valve
body (Fig. 277).
(9) Remove solenoid and harness assembly from
valve body (Fig. 278).
(10) Remove boost valve cover (Fig. 279).
(11) Remove boost valve retainer, valve spring and
boost valve (Fig. 280).
Fig. 277 Solenoid Assembly Screws
1 - OVERDRIVE/CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID ASSEMBLY
2 - HARNESS
Fig. 278 Solenoid Assembly
1 - GOVERNOR SOLENOID WIRES
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
3 - SOLENOID SCREWS
4 - GOVERNOR SENSOR WIRES
5 - OVERDRIVE SOLENOID
6 - HARNESS
7 - CASE CONNECTOR
Fig. 279 Boost Valve Cover Location
1 - BOOST VALVE HOUSING AND COVER
2 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
Fig. 280 Boost Valve Components
1 - SPRING AND VALVE RETAINER
2 - COVER SCREWS
3 - BOOST VALVE COVER
4 - BOOST VALVE PLUG
5 - BOOST VALVE
6 - BOOST VALVE SPRING
21 - 288 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1992 of 2627

(12) Secure detent ball and spring with Retainer
Tool 6583 (Fig. 281).
(13) Remove park rod E-clip and separate rod from
manual lever (Fig. 282).
(14) Remove E-clip and washer that retains throt-
tle lever shaft in manual lever (Fig. 283).
(15) Remove manual lever and throttle lever (Fig.
284). Rotate and lift manual lever off valve body and
throttle lever shaft. Then slide throttle lever out of
valve body.
(16) Position pencil magnet next to detent housing
to catch detent ball and spring. Then carefully
remove Retainer Tool 6583 and remove detent ball
and spring (Fig. 285).
Fig. 281 Detent Ball Spring
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6583 POSITIONED ON DETENT HOUSING
Fig. 282 Park Rod
1 - MANUAL LEVER
2 - E-CLIP
3 - PARK ROD
Fig. 283 Throttle Lever E-Clip And Washer
1 - THROTTLE LEVER SHAFT
2 - E-CLIP AND WASHER
3 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 284 Manual And Throttle Lever
1 - PARK ROD
2 - MANUAL LEVER ASSEMBLY
3 - THROTTLE LEVER
Fig. 285 Detent Ball And Spring
1 - DETENT HOUSING
2 - DETENT SPRING
3 - DETENT BALL
4 - PENCIL MAGNET
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 289
VALVE BODY (Continued)