1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Shift lock
[x] Cancel search: Shift lockPage 1967 of 2627
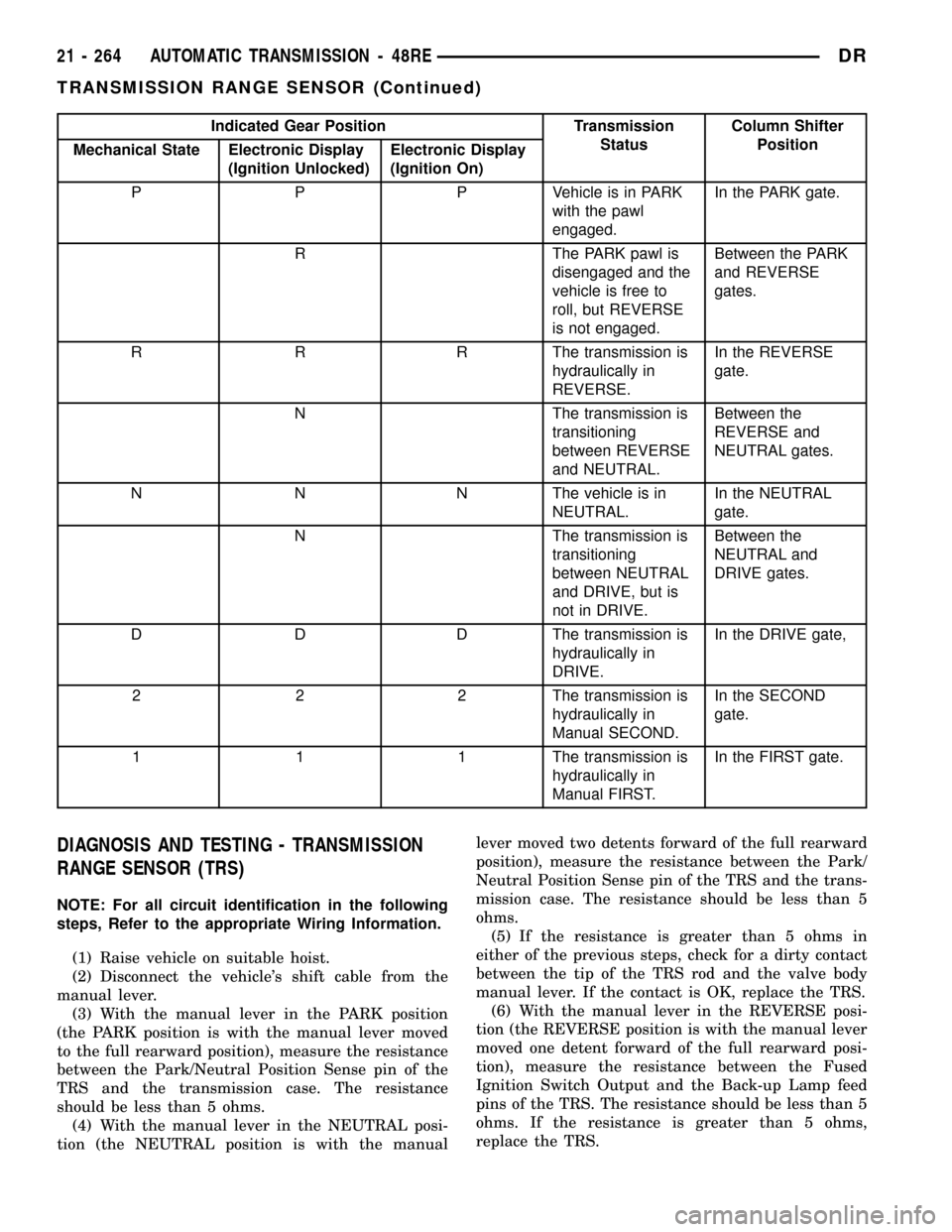
Indicated Gear Position Transmission
StatusColumn Shifter
Position
Mechanical State Electronic Display
(Ignition Unlocked)Electronic Display
(Ignition On)
P P P Vehicle is in PARK
with the pawl
engaged.In the PARK gate.
R The PARK pawl is
disengaged and the
vehicle is free to
roll, but REVERSE
is not engaged.Between the PARK
and REVERSE
gates.
R R R The transmission is
hydraulically in
REVERSE.In the REVERSE
gate.
N The transmission is
transitioning
between REVERSE
and NEUTRAL.Between the
REVERSE and
NEUTRAL gates.
N N N The vehicle is in
NEUTRAL.In the NEUTRAL
gate.
N The transmission is
transitioning
between NEUTRAL
and DRIVE, but is
not in DRIVE.Between the
NEUTRAL and
DRIVE gates.
D D D The transmission is
hydraulically in
DRIVE.In the DRIVE gate,
2 2 2 The transmission is
hydraulically in
Manual SECOND.In the SECOND
gate.
1 1 1 The transmission is
hydraulically in
Manual FIRST.In the FIRST gate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSMISSION
RANGE SENSOR (TRS)
NOTE: For all circuit identification in the following
steps, Refer to the appropriate Wiring Information.
(1) Raise vehicle on suitable hoist.
(2) Disconnect the vehicle's shift cable from the
manual lever.
(3) With the manual lever in the PARK position
(the PARK position is with the manual lever moved
to the full rearward position), measure the resistance
between the Park/Neutral Position Sense pin of the
TRS and the transmission case. The resistance
should be less than 5 ohms.
(4) With the manual lever in the NEUTRAL posi-
tion (the NEUTRAL position is with the manuallever moved two detents forward of the full rearward
position), measure the resistance between the Park/
Neutral Position Sense pin of the TRS and the trans-
mission case. The resistance should be less than 5
ohms.
(5) If the resistance is greater than 5 ohms in
either of the previous steps, check for a dirty contact
between the tip of the TRS rod and the valve body
manual lever. If the contact is OK, replace the TRS.
(6) With the manual lever in the REVERSE posi-
tion (the REVERSE position is with the manual lever
moved one detent forward of the full rearward posi-
tion), measure the resistance between the Fused
Ignition Switch Output and the Back-up Lamp feed
pins of the TRS. The resistance should be less than 5
ohms. If the resistance is greater than 5 ohms,
replace the TRS.
21 - 264 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1970 of 2627

TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 248). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The Tow/Haul lamp in the instrument panel illumi-
nates when the shift back to third occurs. The trans-
mission will not allow fourth gear operation until
fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110ÉC
(230ÉF).
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 249), (Fig. 250), (Fig.
251), and (Fig. 252):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve
²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²9 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 248 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 267
Page 1975 of 2627
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
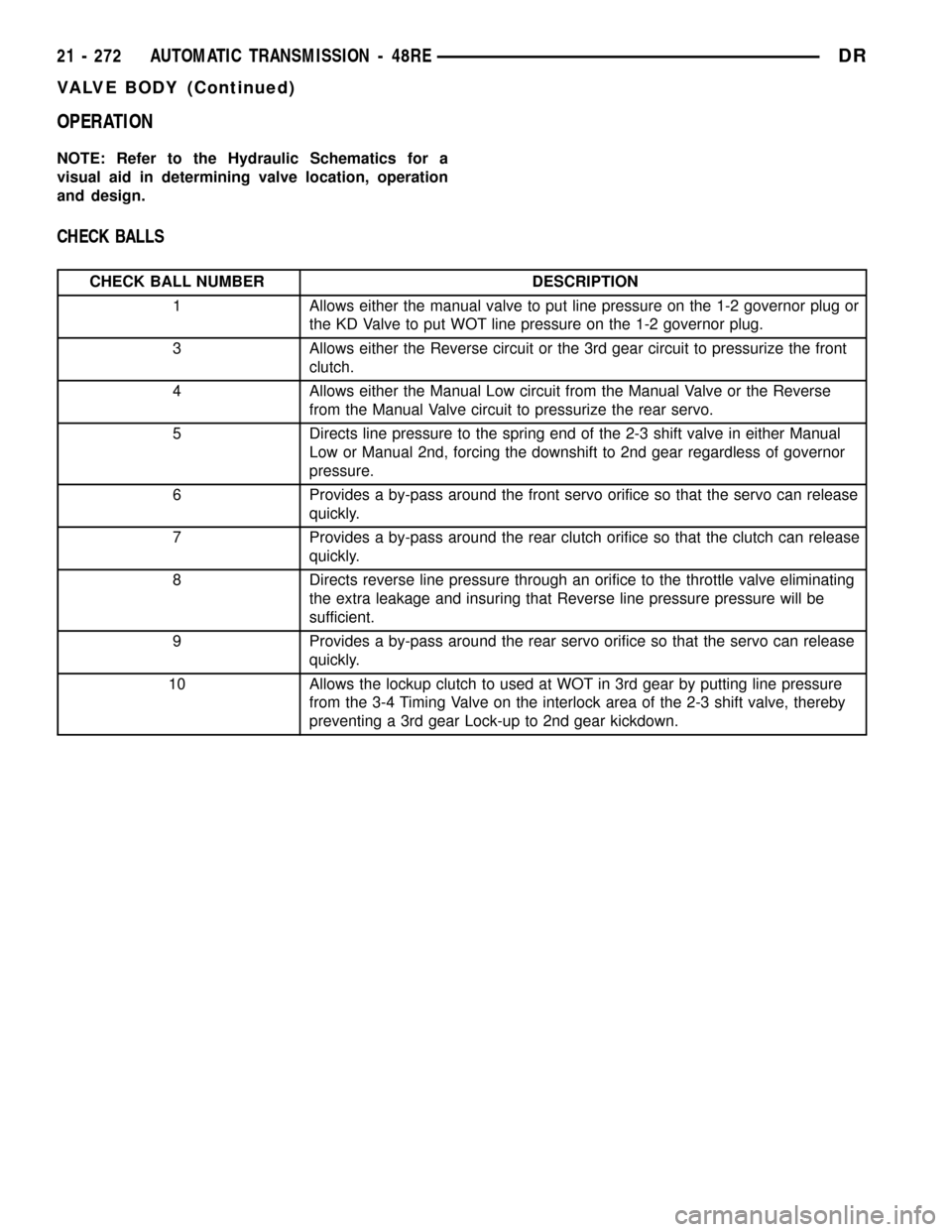
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
10 Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
21 - 272 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1981 of 2627
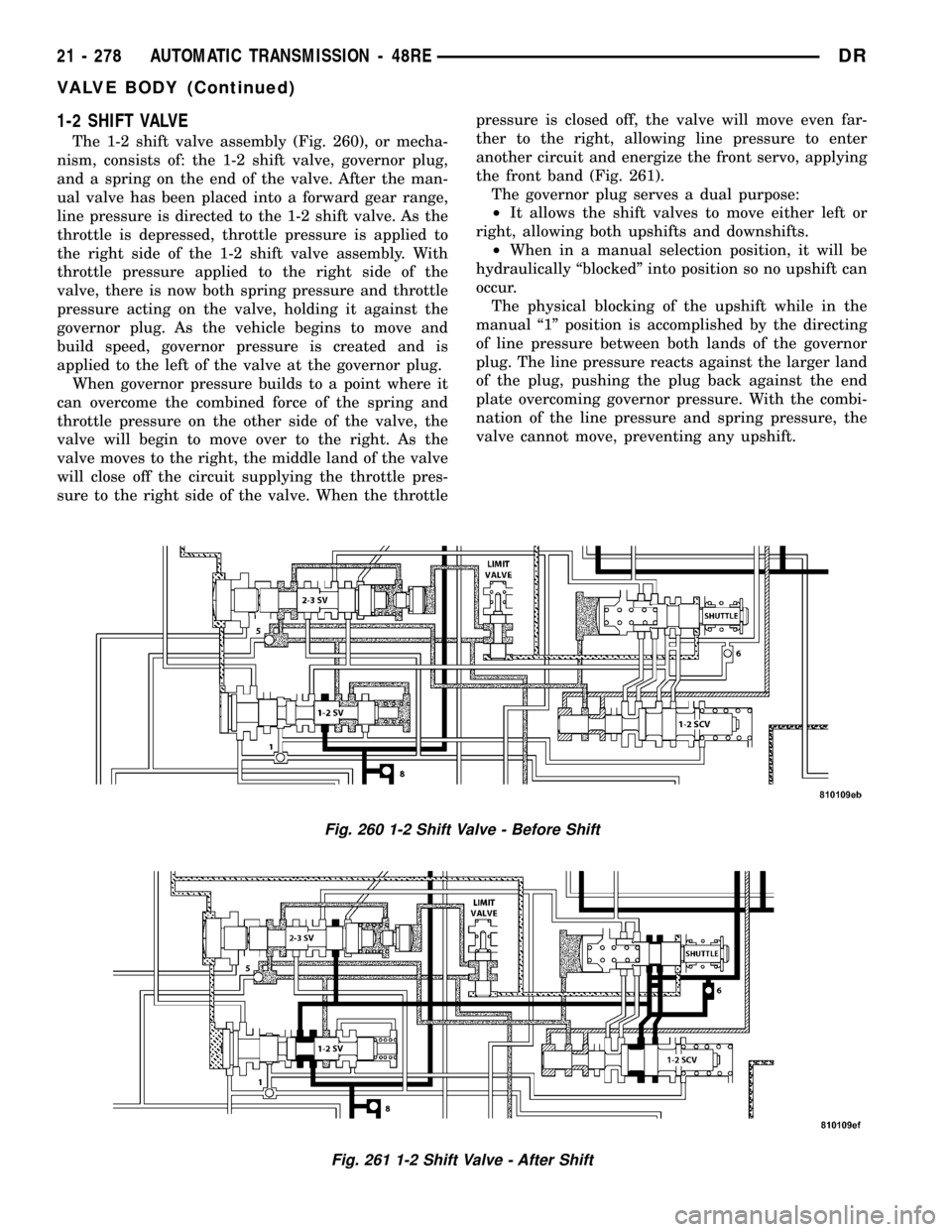
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
The 1-2 shift valve assembly (Fig. 260), or mecha-
nism, consists of: the 1-2 shift valve, governor plug,
and a spring on the end of the valve. After the man-
ual valve has been placed into a forward gear range,
line pressure is directed to the 1-2 shift valve. As the
throttle is depressed, throttle pressure is applied to
the right side of the 1-2 shift valve assembly. With
throttle pressure applied to the right side of the
valve, there is now both spring pressure and throttle
pressure acting on the valve, holding it against the
governor plug. As the vehicle begins to move and
build speed, governor pressure is created and is
applied to the left of the valve at the governor plug.
When governor pressure builds to a point where it
can overcome the combined force of the spring and
throttle pressure on the other side of the valve, the
valve will begin to move over to the right. As the
valve moves to the right, the middle land of the valve
will close off the circuit supplying the throttle pres-
sure to the right side of the valve. When the throttlepressure is closed off, the valve will move even far-
ther to the right, allowing line pressure to enter
another circuit and energize the front servo, applying
the front band (Fig. 261).
The governor plug serves a dual purpose:
²It allows the shift valves to move either left or
right, allowing both upshifts and downshifts.
²When in a manual selection position, it will be
hydraulically ªblockedº into position so no upshift can
occur.
The physical blocking of the upshift while in the
manual ª1º position is accomplished by the directing
of line pressure between both lands of the governor
plug. The line pressure reacts against the larger land
of the plug, pushing the plug back against the end
plate overcoming governor pressure. With the combi-
nation of the line pressure and spring pressure, the
valve cannot move, preventing any upshift.
Fig. 260 1-2 Shift Valve - Before Shift
Fig. 261 1-2 Shift Valve - After Shift
21 - 278 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1983 of 2627
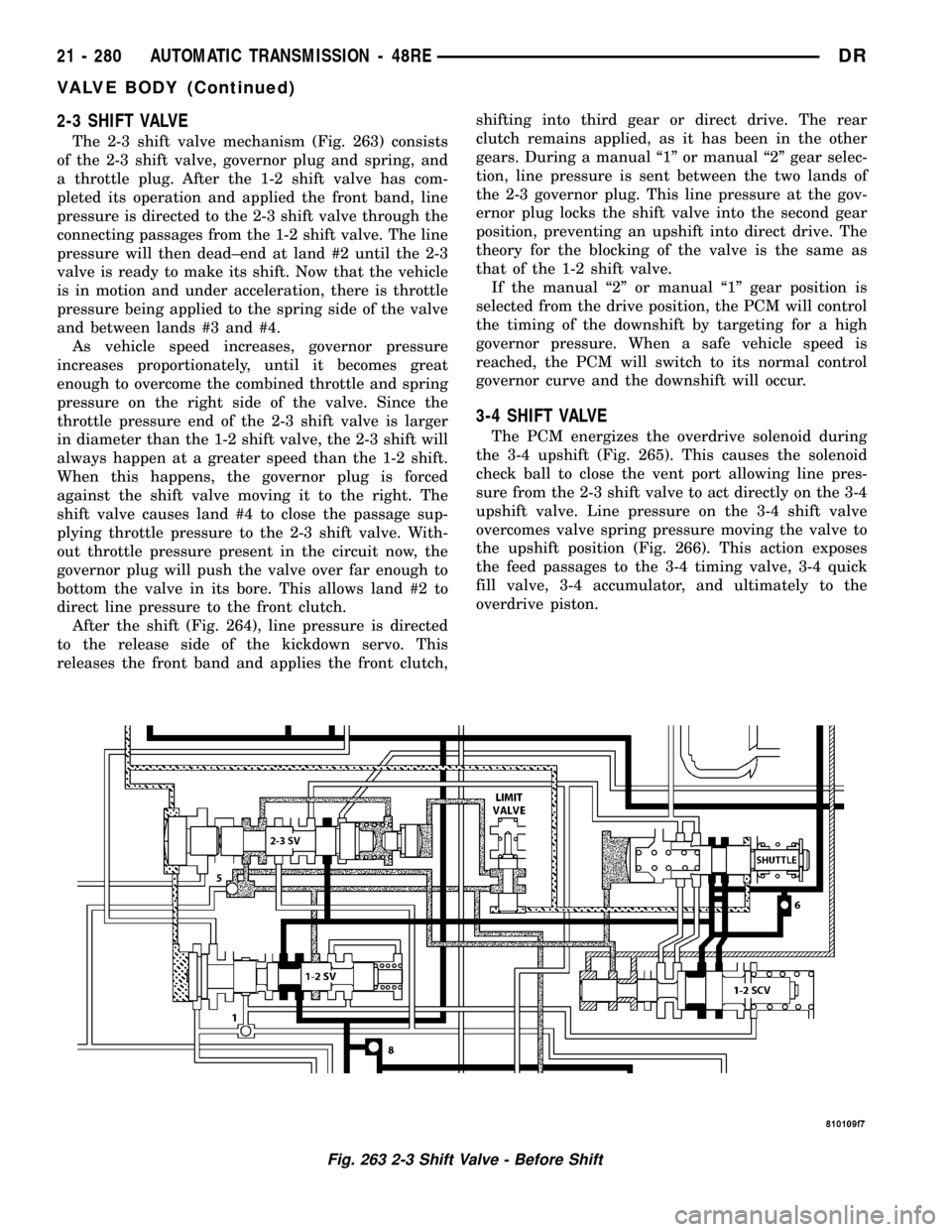
2-3 SHIFT VALVE
The 2-3 shift valve mechanism (Fig. 263) consists
of the 2-3 shift valve, governor plug and spring, and
a throttle plug. After the 1-2 shift valve has com-
pleted its operation and applied the front band, line
pressure is directed to the 2-3 shift valve through the
connecting passages from the 1-2 shift valve. The line
pressure will then dead±end at land #2 until the 2-3
valve is ready to make its shift. Now that the vehicle
is in motion and under acceleration, there is throttle
pressure being applied to the spring side of the valve
and between lands #3 and #4.
As vehicle speed increases, governor pressure
increases proportionately, until it becomes great
enough to overcome the combined throttle and spring
pressure on the right side of the valve. Since the
throttle pressure end of the 2-3 shift valve is larger
in diameter than the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift will
always happen at a greater speed than the 1-2 shift.
When this happens, the governor plug is forced
against the shift valve moving it to the right. The
shift valve causes land #4 to close the passage sup-
plying throttle pressure to the 2-3 shift valve. With-
out throttle pressure present in the circuit now, the
governor plug will push the valve over far enough to
bottom the valve in its bore. This allows land #2 to
direct line pressure to the front clutch.
After the shift (Fig. 264), line pressure is directed
to the release side of the kickdown servo. This
releases the front band and applies the front clutch,shifting into third gear or direct drive. The rear
clutch remains applied, as it has been in the other
gears. During a manual ª1º or manual ª2º gear selec-
tion, line pressure is sent between the two lands of
the 2-3 governor plug. This line pressure at the gov-
ernor plug locks the shift valve into the second gear
position, preventing an upshift into direct drive. The
theory for the blocking of the valve is the same as
that of the 1-2 shift valve.
If the manual ª2º or manual ª1º gear position is
selected from the drive position, the PCM will control
the timing of the downshift by targeting for a high
governor pressure. When a safe vehicle speed is
reached, the PCM will switch to its normal control
governor curve and the downshift will occur.
3-4 SHIFT VALVE
The PCM energizes the overdrive solenoid during
the 3-4 upshift (Fig. 265). This causes the solenoid
check ball to close the vent port allowing line pres-
sure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly on the 3-4
upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4 shift valve
overcomes valve spring pressure moving the valve to
the upshift position (Fig. 266). This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston.
Fig. 263 2-3 Shift Valve - Before Shift
21 - 280 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1986 of 2627
pressure is ªmeteredº out into the circuits and viewed
as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure
is metered out into the circuits it is applied to: the
1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure
is high enough, a 3-2 downshift will occur. If the
vehicle speed is low enough, a 2-1 downshift will
occur.
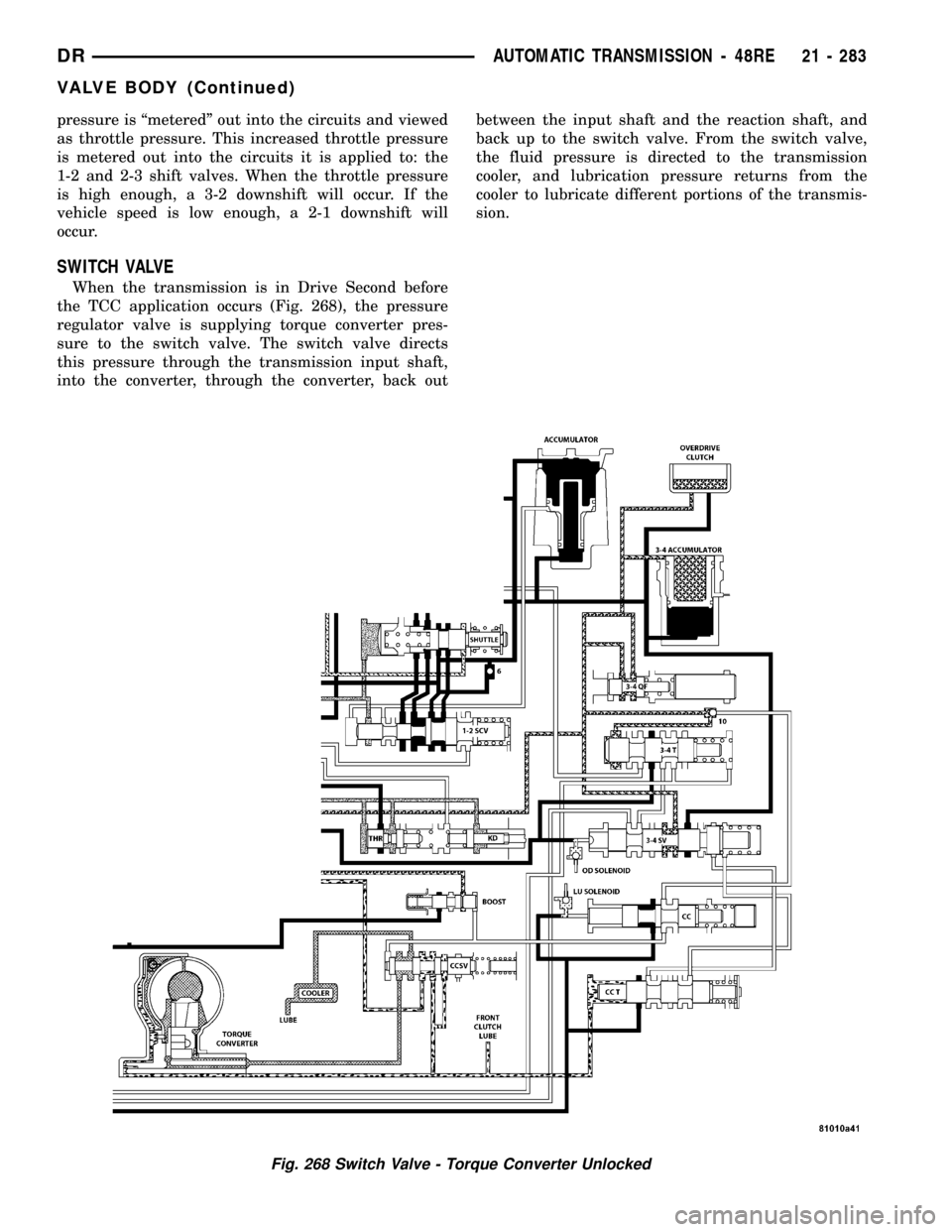
SWITCH VALVE
When the transmission is in Drive Second before
the TCC application occurs (Fig. 268), the pressure
regulator valve is supplying torque converter pres-
sure to the switch valve. The switch valve directs
this pressure through the transmission input shaft,
into the converter, through the converter, back outbetween the input shaft and the reaction shaft, and
back up to the switch valve. From the switch valve,
the fluid pressure is directed to the transmission
cooler, and lubrication pressure returns from the
cooler to lubricate different portions of the transmis-
sion.
Fig. 268 Switch Valve - Torque Converter Unlocked
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 283
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
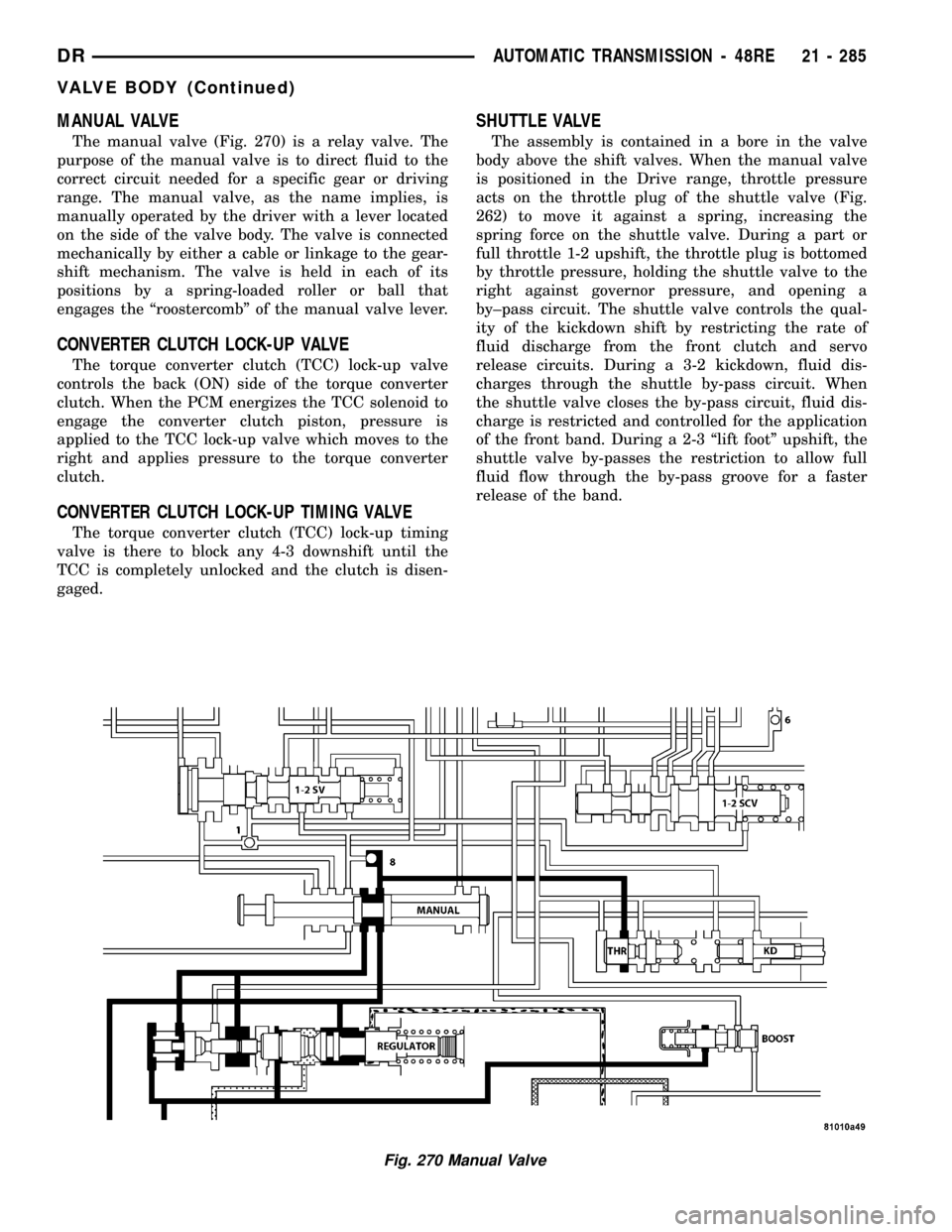
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1989 of 2627
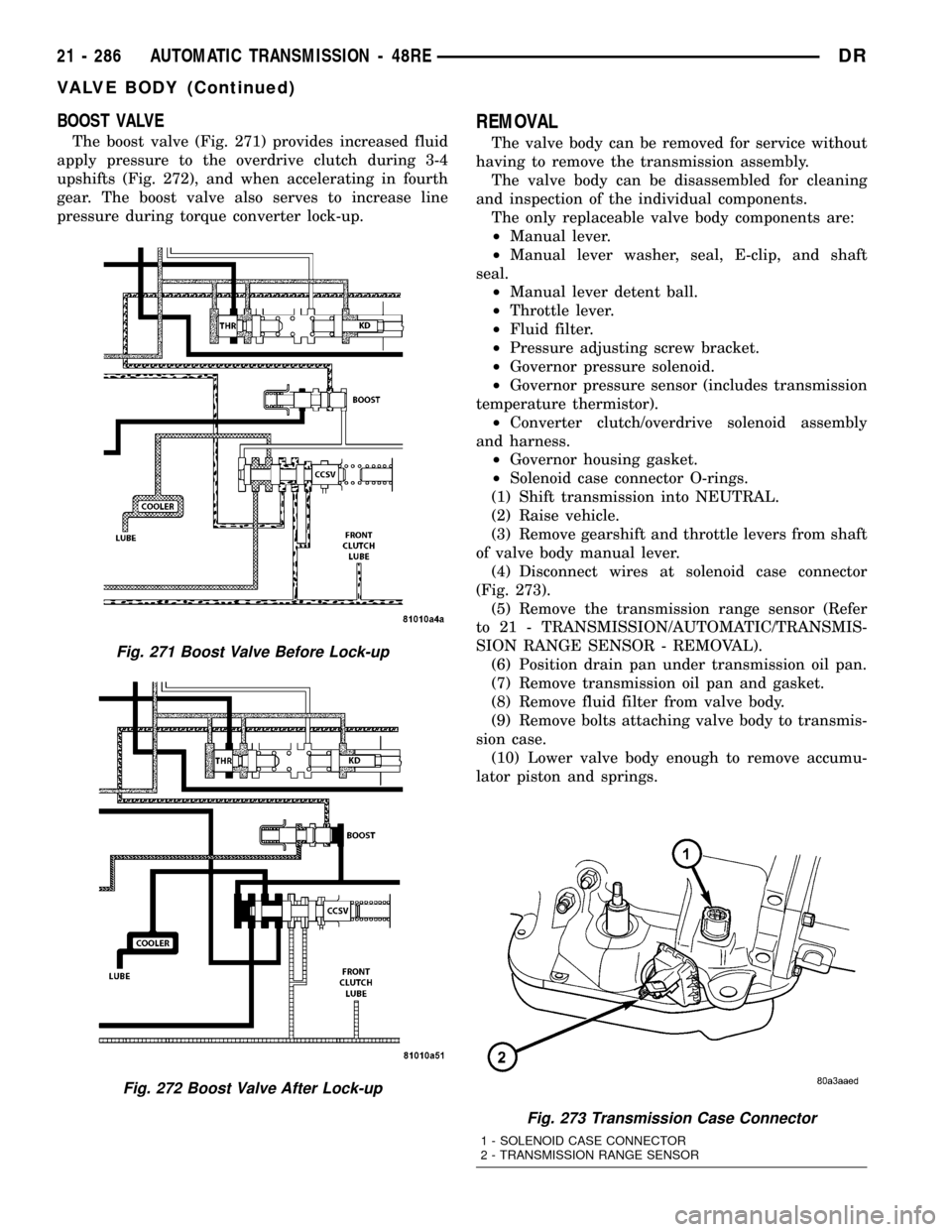
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 271) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 272), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 273).
(5) Remove the transmission range sensor (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/TRANSMIS-
SION RANGE SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(8) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(9) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(10) Lower valve body enough to remove accumu-
lator piston and springs.
Fig. 273 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 271 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 272 Boost Valve After Lock-up
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)