1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Shifting
[x] Cancel search: ShiftingPage 302 of 2627

CLUTCH
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CLUTCH
WARNING.............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................1
SPECIFICATIONS........................5
CLUTCH DISC
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
CLUTCH HOUSING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................7
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION.........................10
FLYWHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................10REMOVAL.............................11
DISASSEMBLY.........................11
ASSEMBLY............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
PILOT BEARING
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
LINKAGE
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................13
CLUTCH
WARNING
WARNING: Exercise care when servicing clutch
components. Factory installed clutch discs do not
contain asbestos fibers. Dust and dirt on clutch
parts may contain asbestos fibers from aftermarket
components. Breathing excessive concentrations of
these fibers can cause serious bodily harm. Wear a
respirator during service and never clean clutch
components with compressed air or with a dry
brush. Either clean the components with water
dampened rags or use a vacuum cleaner specifi-
cally designed to remove asbestos fibers and dust.
Do not create dust by sanding a clutch discs.
Replace the disc if the friction material is damaged.
Dispose of all dust and dirt containing asbestos
fibers in sealed bags or containers. This will mini-
mize exposure to yourself and to others. Follow all
recommended safety practices prescribed by the
occupational safety and health administration
(OSHA) and the environmental safety agency (EPA),
for the handling and disposal of products contain-
ing asbestos. Failure to follow these instructions
may result in personal injury or death
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Road test and inspect components to determine a
clutch problem. Road test the vehicle at normalspeeds. Shift the transmission through all gear
ranges and observe clutch action. If clutch chatters,
grabs, slips or does not release properly, remove and
inspect clutch components. If problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed to the
transmission and driveline component.
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Contamination is a frequent cause of clutch mal-
functions. Oil, water or clutch fluid on the clutch disc
and pressure plate surfaces will cause chatter, slip
and grab. Oil contamination indicates a leak at
either the rear main seal or transmission input shaft.
Clutch fluid leaks are usually from damaged slave
cylinder push rod seals. Heat buildup caused by slip-
page between the pressure plate, disc and flywheel
can bake the oil residue onto the components. The
glaze-like residue ranges in color from amber to
black.
Road splash contamination is dirt/water entering
the clutch housing due to loose bolts, housing cracks.
Driving through deep water puddles can force water/
road splash into the housing through such openings.
IMPROPER RELEASE OR CLUTCH ENGAGEMENT
Clutch release or engagement problems can be
caused by worn or damage clutch components.
Release problems can cause hard shifting and
noise. Look for leaks at clutch cylinders, connecting
line and loose slave cylinder bolts. Also worn/loose
release fork, pivot stud, clutch disc, pressure plate or
release bearing.
DRCLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 308 of 2627

(11) Wipe pilot bearing surface clean.
(12) Install release lever and bearing in clutch
housing. Verify spring clips that retain fork on pivot
ball and release bearing on fork are installed prop-
erly (Fig. 5).
NOTE: If release lever is installed correctly, the
lever part number will be toward the bottom of the
transmission and right side up. There is also a
stamped ªIº in the lever which goes to the pivot ball
side of the transmission.
(13) Install transmission and transfer case if
equipped.
(14) Check fluid level in clutch master cylinder.
CLUTCH HOUSING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
The clutch housing maintains alignment between
the crankshaft and transmission input shaft. Mis-
alignment can cause clutch noise, hard shifting,
incomplete release and chatter. Also premature pilot
bearing, cover release fingers and clutch disc wear.
In severe cases, it can cause premature wear of the
transmission input shaft and front bearing.
NOTE: Only the NV4500 clutch housing can be
checked using the following bore and face runout
procedures. The NV5600 clutch housing is a inte-
gral part of the transmission and can only be
checked off the vehicle.
CLUTCH HOUSING BORE RUNOUT
CAUTION: On diesel engines if housing bore runout
exceeds 0.015 inch, the clutch housing/transmis-
sion adapter plate must be replaced. On gas
engines if housing bore runout exceeds 0.053 in.
the clutch housing must be replaced.
NOTE: Offset dowels are available for gas engines
to correct housing bore runout. They are not avail-
able for diesel engines.
(1) Remove the clutch housing.
(2) Remove the clutch cover and disc.
(3) Replace one of the flywheel bolts with an
appropriate size threaded rod that is 10 in. (25.4 cm)
long (Fig. 6). The rod will be used to mount the dial
indicator.
(4) Remove release fork from the clutch housing.
(5) Install clutch housing. Tighten the housing
bolts nearest the alignment dowels first.
(6) Mount dial indicator on the threaded rod and
position indicator plunger on the clutch housing bore
(Fig. 7).
(7) Rotate crankshaft until indicator plunger is at
the topof the housing bore. Zero the indicator at this
point.
(8) Rotate crankshaft and record indicator read-
ings at eight points (45É apart) around the bore (Fig.
8). Take measurement at least twice for accuracy.
(9) Subtract each reading from the one 180É oppo-
site to determine runout and direction. Bore runout
example (Fig. 8):
²0.000 ± (±0.007) = 0.007 in.
²+0.002 ± (±0.010) = 0.012 in.
²+0.004 ± (±0.005) = 0.009 in.
²±0.001 ± (+0.001) = ±0.002 in.
Fig. 5 FORK, BEARING AND SPRING CLIPS
1 - FORK
2 - SPRING CLIP
3 - BEARING
4 - SPRING CLIP
Fig. 6 DIAL INDICATOR MOUNTING STUD
1 - 7/16 - 20 THREAD
2 - NUT
3 - STUD OR THREADED ROD
4 - 10 INCHES LONG
DRCLUTCH 6 - 7
CLUTCH DISC (Continued)
Page 425 of 2627

SHIFT OUT OF NEUTRAL
The following steps describe the process for a shift
out of NEUTRAL.
²Extinguish the Neutral LED.
²Engage the shift motor for a maximum of 1 sec-
ond 100 msec toward the transfer case 4H mode
position while monitoring the mode sensor channel
transitions.
²Disengage the shift motor when the correct
mode sensor code is recognized.
²Extinguish the Neutral LED.
²Transmit a bus message that the transfer case
shift is complete.
²If the desired mode sensor code is not received
after the shift timer expires (ie. a blocked or other
condition exists), stop driving the motor and wait for
200 msec 50 msec. The shift motor is then reversed
in the direction back toward the source gear for up to
1.0 seconds 100 msec. The TCCM waits for 2.0 sec-
onds 50 msec. and repeats the attempt to shift to
the desired position.
²When the Neutral button is released, if the 4H
position is the desired position, the shift is complete.
Illuminate the 4H LED.
²Otherwise when the Neutral button is released,
if all of the shift requirements are being met then
engage the shift motor towards the desired position
for 1 second 100 msec per 'D' channel. (if require-
ments for shifting are not met, illuminate the 4H
LED and flash the destination LED as an indication
to the driver that all of the driver controllable shift
conditions are not being met). If this requires
another range or mode shift, begin the range/mode
shift process.
²If the desired mode sensor code is not received
after the shift timer expires (i.e. a blocked or other
condition exists), refer to the section on Blocked Shift
Strategy.
BLOCKED SHIFT STRATEGY
When a shift is commanded, the shift motor will be
driven towards its destination position, except in the
case of shifting out of Neutral if 4L was selected (the
transfer case will shift to the 4H position first, before
proceeding to 4L). If the shift is blocked on the way
to the destination, the TCCM may attempt to drivethe motor back to the original position. This process
will be allowed to occur 5 times. If the transfer case
has reached a non-NEUTRAL 'D' channel during the
shift re-attempts, the LED for the achieved gear posi-
tion is illuminated and the shift attempts are
stopped. To re-attempt the desired shift, the selector
switch will need to be rotated to the current position
until the switch debounce timer expires then a shift
will need to be requested again.
At the end of the 5th blocked attempt, the shift
motor is driven towards the last known 'D' channel
position. If this motor drive allows the transfer case
to reach the 2WD/AWD 'D' channel, or the 2WD/AWD
between gear position on the 4H side of 2WD/AWD,
the shift is considered complete and the shift
attempts are ended.
If the mode sensor is in the NEUTRAL region at
the expiration of the shift timer, the TCCM will con-
tinue to make the shift attempts according to the
blocked shift strategy independent of whether or not
the driver controlled conditions are met.
For shifts from NEUTRAL, if all 5 attempts fail to
reach the desired position (which by default is 4H),
the motor will be driven to stall in the direction of
4H or 4L, depending on the achieved position. If the
transfer case has reached the 2WD/AWD or 4L
between gear position nearest the NEUTRAL posi-
tions and the shift conditions are no longer being
met, the transfer case will be driven toward the cor-
responding 'D' channel. Otherwise, the transfer case
will be driven in the direction opposite the last
attempt with the desired target being 4H or 4L.
If the transfer case reaches the 2WD/AWD 'D'
channel when being driven in the 4H direction, then
one final 1.0 second drive toward 4H is attempted. If
the transfer case then reaches any of the 4H posi-
tions, the shift is considered complete and the 4H
LED is illuminated. If the transfer case is still the
2WD/AWD position, the shift is considered complete
and the 2WD/AWD LED is illuminated.
NOTE: If after the 5th blocked shift and reversal
attempt, if the transfer case position is in the NEU-
TRAL region, shift attempts will continue until a
non-NEUTRAL 'D' channel is reached.
8E - 18 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 426 of 2627

SHIFT REVERSAL TARGETS
If the shift timer expires (1 second per 'D' channel)
and the transfer case has not reached the desired
position, all shifts will attempt to return to their
original position with the exceptions of:
²If the intended shift is going to the High rail
from Low and can't make it, but it can make the
2WD/AWD position, the motor stops at that position.
The TCCM will not attempt to cross back over NEU-
TRAL if it does not have to. This means that there
was a block on the first attempt to go to 4H and the
transfer case has made it through NEUTRAL to a
known good position, then the motor will go back
only to the 2WD/4WD position and execute the
remainder of the attempts from there.
²For shifts out of NEUTRAL, any time a shift is
commanded out of NEUTRAL, the system needs to
get out. The TCCM should never go to NEUTRAL
unless the driver is commanding it and all required
conditions are being met
ENCODER DRIFT CORRECTION
Whenever a shift is completed, the TCCM stores
the position in memory as the transfer case's
intended position. The TCCM continuously monitors
the mode sensor and if the mode sensor drifts toward
into a NEUTRAL region sensor position for 2.0 sec-
onds, the TCCM will perform a motor drive to correct
the drift. The transfer case will be driven toward the
intended position for 1.0 seconds 100 msec. The
TCCM will wait for 2.0 seconds 50 msec. and repeat
the attempt to shift to the desired position. This will
continue until the intended position is reached.
SHIFT MOTOR BRAKING
Two modes of shift motor braking are employed to
improve shift performance, static and dynamic. Static
shift motor braking is utilized under the following
conditions:
²Whenever the transfer case is in the 2WD/AWD
or 4L 'D' channel position.²Whenever an invalid mode sensor code is
present.
Static motor braking is achieved by applying +12V
on both shift motor wires.
NOTE: Static Shift Motor Braking is independent of
ignition key position.
SHIFT ATTEMPT LIMIT
To protect the transfer case system, the TCCM will
impose a limit on the number of shifts that can occur
over a calibrated time period. The system will moni-
tor the number of 'D' channel segment transitions
that occur in any 30 second time period. If the num-
ber of segment transitions is 30 or greater, the sys-
tem will go into a default mode. The default mode of
operation for shifting is that the number of allowed
'D' channel transitions permitted to occur will be 3
over each 15 second 100 msec calibrated window of
time. After 5 minutes 100 msec, the motor can be
assumed to have cooled down and the system will
revert to normal operation. The following rules also
apply to the shift limit:
²The attempt limit will not prevent shifts coming
out of NEUTRAL, they will be allowed regardless of
the counter/timer.
²Any shift that is in progress when the counter
reaches a maximum count in time will be allowed to
complete before the default mode is entered. D-chan-
nel transitions during this period will not be counted
towards the default mode limit.
²A block, regardless of the direction, whether
towards destination or back towards reversal target
(shift timer expiring), will count as a value of 2 tran-
sitions towards the 30 segment transitions to go into
default mode as defined above. Current attempt limit
values are 30 transitions in 30 seconds and default
mode values are 3 transitions every 15 seconds for 5
minutes.
DRELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 19
TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1704 of 2627

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500..........1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500..........43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600..........88
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE........130
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE.311
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII...........415TRANSFER CASE - NV271................447
TRANSFER CASE - NV243................482
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII...........512
TRANSFER CASE - NV273................542
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................3
REMOVAL.............................3
DISASSEMBLY..........................4CLEANING............................15
INSPECTION..........................16
ASSEMBLY............................17
INSTALLATION.........................39
SPECIFICATIONS.......................40
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................40
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
NV3500
DESCRIPTION
The transmission is a medium-duty 5-speed, con-
stant mesh fully synchronized manual transmission
with fifth gear overdrive range. The transmission is
available in two and four-wheel drive configurations.
The transmission gear case consists of two aluminum
housings (Fig. 1). The clutch housing is an integral
part of the transmission front housing.
A combination of roller and ball bearings are used
to support the transmission shafts in the two hous-
ings. The transmission gears all rotate on caged type
needle bearings. A roller bearing is used between the
input and output shaft.
The transmission has a single shaft shift mecha-
nism with three shift forks all mounted on the shaft.
The shaft is supported in the front and rear housings
by bushings and one linear ball bearing. Internal
shift components consist of the forks, shaft, shift
lever socket and detent components
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through the
clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc issplined to the transmission input shaft and is turned at
engine speed at all times that the clutch is engaged.
The input shaft is connected to the transmission coun-
tershaft through the mesh of fourth speed gear on the
input shaft and the fourth countershaft gear. At this
point, all the transmission gears are spinning.
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This movement
moves the internal transmission shift components to
begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever moves the
selected shift rail, the shift fork attached to that rail
begins to move. The fork is positioned in a groove in the
outer circumference of the synchronizer sleeve. As the
shift fork moves the synchronizer sleeve, the synchro-
nizer begins to speed-up or slow down the selected gear
(depending on whether we are up-shifting or down-shift-
ing). The synchronizer does this by having the synchro-
nizer hub splined to the mainshaft and moving the
blocker ring into contact with the gear's friction cone. As
the blocker ring and friction cone come together, the
gear speed is brought up or down to the speed of the
synchronizer. As the two speeds match, the splines on
the inside of the synchronizer sleeve become aligned
with the teeth on the blocker ring and the friction cone
and eventually will slide over the teeth, locking the gear
to the mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchro-
nizer.
DRTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1706 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. Leaks can occur at the
mating surfaces of the gear case, adaptor or exten-
sion housing, or from the front/rear seals. A sus-
pected leak could also be the result of an overfill
condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Shift component damage or damaged clutch pres-
sure plate or disc are additional probable causes of
increased shift effort. Worn/damaged pressure plate
or disc can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem
is advanced, gear clash during shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear and bearing
damage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot bezel screws and slide boot
upward on shift lever extension.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(7) Drain lubricant if transmission will be disas-
sembled for service.
(8) Mark propeller shaft/shafts and companion
flange yoke/yokes for installation reference and
remove propeller shaft/shafts.
(9) Disconnect harness from clips on transmission
housing.
(10) Remove transfer case linkage if equipped.
(11) Remove transfer case mounting nuts and
remove transfer case if equipped.
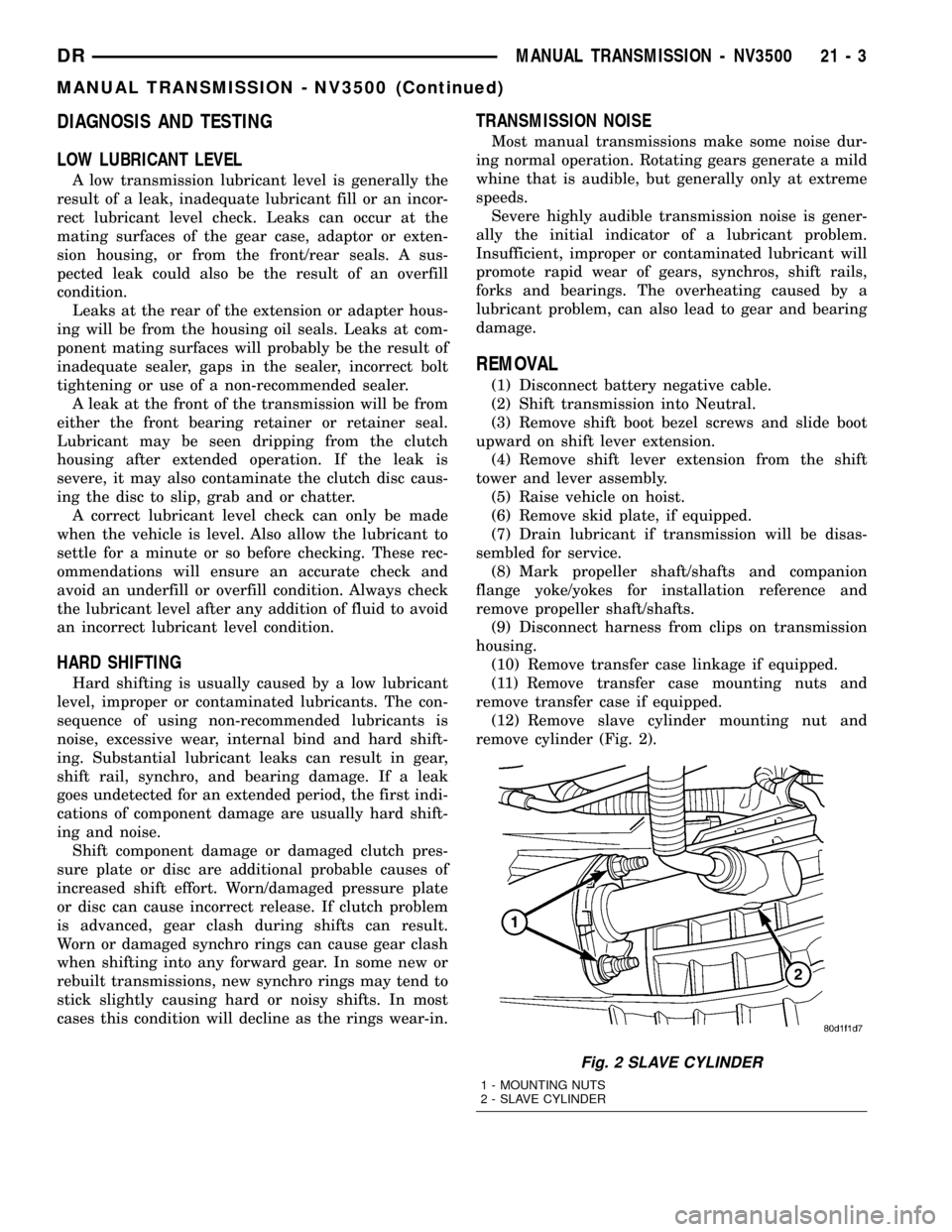
(12) Remove slave cylinder mounting nut and
remove cylinder (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SLAVE CYLINDER
1 - MOUNTING NUTS
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2627

The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether the
driver is up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchro-
nizer does this by having the synchronizer hub
splined to the mainshaft, or the countershaft in some
cases, and moving the blocker ring into contact with
the gear's friction cone. As the blocker ring and fric-
tion cone come together, the gear speed is brought up
or down to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two
speeds match, the splines on the inside of the syn-
chronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on
the blocker ring and the friction cone and eventually
will slide over the teeth, locking the gear to the
mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants isnoise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds. Severe highly audible transmission noise is
generally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant
will promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift
rails, forks and bearings. The overheating caused by
a lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Remove shift boot screws from floorpan and
slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(3) Remove shift lever extension from shift tower
and lever assembly.
(4) Remove shift tower bolts (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - SHIFTER
3 - BOLTS
21 - 44 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1781 of 2627

(8) Assemble and install fifth synchro clutch gear
and stop ring in fifth gear hub (Fig. 124). Verify
parts are seated in fifth gear hub.
(9) Install clutch gear snap ring (Fig. 125).
(10) Align roll pin holes in shift fork with notches
in shift lug rail. Then install roll pins from top side
of fork (Fig. 122).
NOTE: Roll pins only fit one way due to small
shoulder at one end of each pin.
FIFTH GEAR NUT
(1) Install belleville washer onto the mainshaft.
(2) Install fifth gear nut over the mainshaft.
(3) Tighten the clamp bolt until the gap in the
clamp nut assembly is closed.
(4) Back the clamp bolt off one full turn.(5) Place 10-15 drops of Loctite 272 onto the main-
shaft threads where the fifth gear nut will be
engaged.
(6) Install fifth gear nut on mainshaft (Fig. 126).
(7) Hold mainshaft Socket 6993 4X2 or Socket
6984 4X4 while installing the fifth gear nut.
(8) Tighten fifth gear nut as much as possible with
Wrench 6743, long handle ratchet, breaker bar and
applicable socket wrench (Fig. 127).
(9) Lock mainshaft gears by shifting all synchro
sleeves into engaged position.
Fig. 124 FIFTH SYNCHRO CLUTCH GEAR AND
STOP RING
1 - STOP RING
2 - CLUTCH GEAR
Fig. 125 FIFTH SYNCHRO CLUTCH SNAP RING
1 - CLUTCH GEAR RING
2 - FIFTH SYNCHRO CLUTCH GEAR
Fig. 126 FIFTH GEAR NUT
1 - FIFTH GEAR
2 - FIFTH GEAR NUT
Fig. 127 FIFTH GEAR NUT
1 - WRENCH
2 - FIFTH GEAR NUT
3 - SOCKET
21 - 78 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 (Continued)