1997 HONDA CIVIC Air condition
[x] Cancel search: Air conditionPage 270 of 2189

!
Fuel and Emrsslons
SoecialToofs .....,...."..,. 11-2
Component Locations
lndex ....................., ......... 11-3
Svstem Description
Vacuum Connections ................,,..,.. ......... 11-12
Electrical Connections ...............,.,.,... ....... 11-29
System Connectors ........,.,.,.......................... 1 1-51
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures ................. .. 11-81
Engine Control Module/PowertrainControl Module TerminalAfiangement ....,.,..... 11-88
Diagnostic Trouble Code Chart .................,., 11.97
How to Read Flowcharts .,.......................... . 11-103
PGM-Fl System
System Description ...... 11-10,1
Troubleshooting Flowcharts
Engine Control Module/PowertrainContlol Module ........ 11-107
Manitold Absolute Pressure Sensor .....'. . ... 11-115
fntake Air Temperatuie Sensor ..... . . ., . 11'121
Engine Coolant Temperatuae Sensol ........., 11-128
Throttle Position Sensor ...................,........... 11-132
Primary Heated Orygen Sensor (Sensor 1l ... 11-139
Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor(Sensor 21.................................................... 1 1-153
Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater ...................,. 11-157
Fuel Supply System ...... 11-164
Random Mislire ......., ..11-166
Misfire Detected in One Cylindsr ................. 11-167
Knock Sensor .,.,............ 11-170
CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor ................................... 11'172
Vehicle Speed Sensor ...........,......,...,.,........... 1t-176
Barometric Pressure Sensor ...............,......... I 1-178
Electrical Load Detector,.,,............................ 1 1-179
CKF Sensor .................... 11-183
ECM/PCM Internal Circuit ............................. I 1-188
A/T Signal {TMA/TMBI .................................. I 1-189
ldle Control System
System Doscriplion ............ 11-190
Troubleshooting Flowcharts
ldle Control System ...... 11-192
ldle Air Control Va1ve .................................... I 1-19i1
Starter Switch Signal .................................... 1 1'202
Air Conditioning Signal ................................. 11'201
Ahernator FR Signal .................................... . 1 1-208
BrakeSwitch Signal ..................................... f 1"210
Power Sleering Prossure Switch Signal ......11-212
A/T Gear Position Signal ............................... 11-216
Clutch Swiich Signal ................................-.... 11-214
ldte Speed Setting . .............11-220
Fuel Supply System
Fuel Lines .,...................,.,.,.,11-221
Fuef Tube/Ouick-Connect Fittings ..........,.,........ 11 -227
System Description ....'.... 11-230
Fuel Pressure .......,.,,........... 11-230
Fuef fniectors ......................11-232
Fu€f Pressure Regulator .....,.......................'...,. 11-231
Fuef Fifter ............................11-235
Fuel Pump .............'.......'.... 11-236
PGM-FI Main Relay .............11'237
Fuel Tank ................ ....,...'.'.' 11'211
Intake Air System
System Description ....-.-.....11-243
Air Cfeaner ...........,......."". .11-211
Throttle Cable .....................11-211
Throttfe Body ........ ..'... . . .,.11-211
Fuel Iniestion Air Control System ,.,.,....-........... 11-250
Emission Control System
System Description .-..........11-252
Taifpip€ Emission ...............11-252
Three Way Catafytic Convert€r ............,.,,.,.,.,.... 11 -252
Exhaust Gas Racirculaiion System ...,.,,,,.,.,.,.,,. 11'254
Positive Crankcas€ Ventilation System .... . . .. 11-266
Evaoorative Emission Controls ..................,,..,.,. 11 -267
Page 350 of 2189
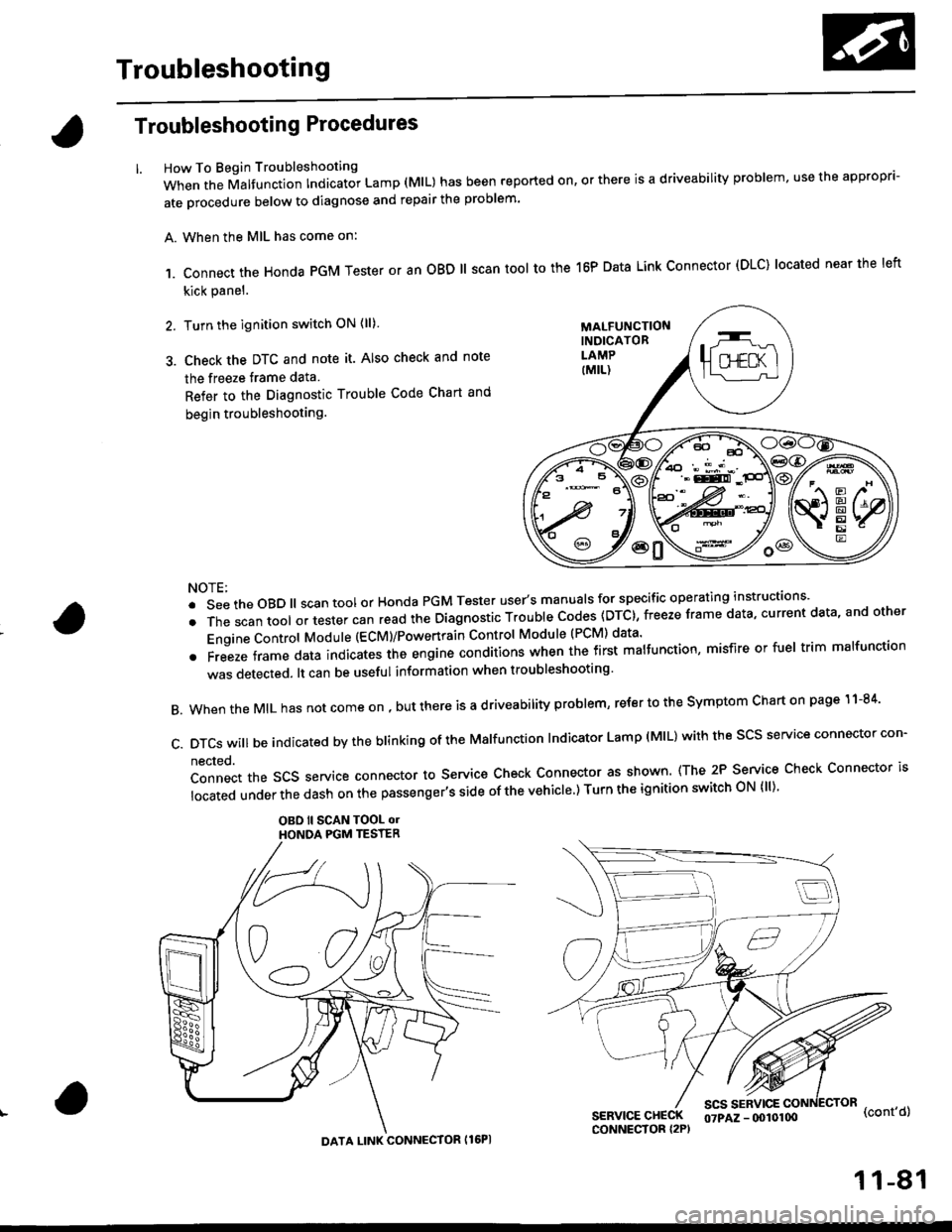
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures
How To Begin Troubleshooting
When the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL) has been reported on, or there is a driveability problem, use the appropr'-
ate orocedure below to diagnose and repair the problem'
A. When the MIL has come on:
,1. connect the Honda PGM Tester or an oBD ll scan tool to the 16P Data Link connector (DLC) located near the left
kick panel.
2. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll)
3. Check the DTC and note it. Also check and note
the freeze trame data
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code Chart and
begin troubleshooting.
NOTE:
.SeetheoBD||scantoolorHondaPGMTesteruser,smanua|sforspecificoperatinginstructions..
.Thescantoo|oltestercanreadtheDiagnosticTroub|ecodes(DTc},freezeframedata,currentdata,andother
Engine Control Module (ECM)/Powertrain Control Module (PCM) data'
oFreezeframedataindicatestheengineconditionswhenthefirstma|function,misfireorfue|trimma|function
was detected. lt can be useful information when troubleshooting'
B. When the MIL has not come on , out there is a d riveability problem, refer to the Symptom Chart on page 1 1-84'
c.DTcswi|lbeindicatedbytheb|inkingoftheMa|function|ndicatorLamp(M|L)withthescsserviceconnectorcon.
nected.
Connect the SCS service connector to Service Check Connector as shown (The 2P Service Check Connector is
|ocatedunderthedashonthepassenger,ssideofthevehic|e')TurntheignitionswitchoN{||)'
OBO ll SCAN TOOL olHONOA PGM TESTER
SERVICE CHECKCONNECTOR I2P)
scs sERvlcE(cont'd)
MALFUNCTIONINDICATORLAMP
DATA LINK CONNECTOR Il6PI
07PAZ - (x)l0100
11-81
Page 356 of 2189
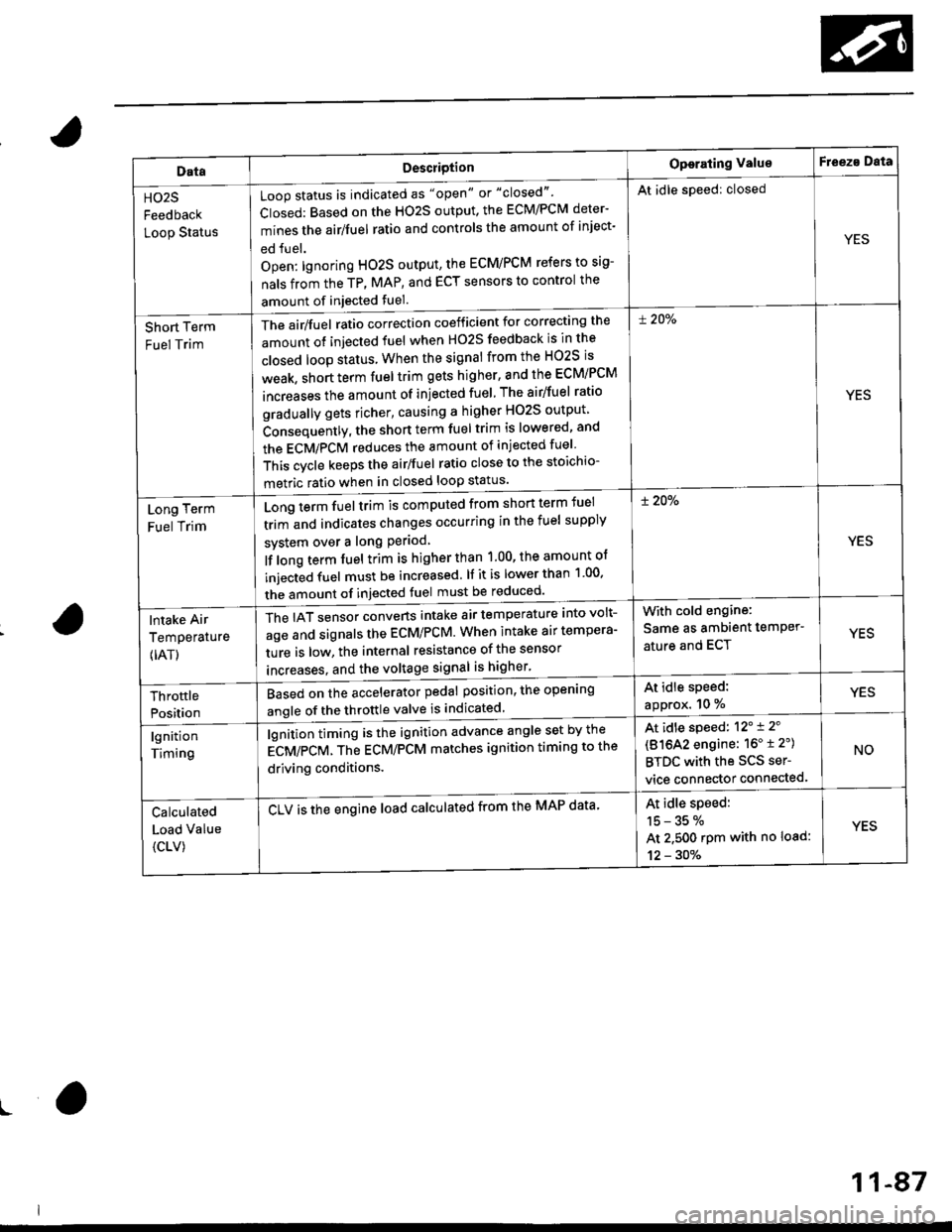
DataDescriotion
Loop status is indicated as "open" or "closed"'
Closed: Based on the HO2S output, the ECM/PCM deter-
mines the airlfuel ratio and controls the amount of inject-
ed fuel.
Open: lgnoring HO2S output, the ECM/PCM refers to sig-
nals from the TP, MAP, and ECT sensors to control the
amount of injected fuel.
The air/fuel ratio correction coefficient for correcting the
amount ot injected fuel when H02S feedback is in the
closed loop status When the signal from the HO2S is
weak, short term fuel trim gets higher, and the ECM/PCM
increases the amount of injected fuel The airlfuel ratio
gradually gets richer, causing a higher HO2S output
Consequently, the short term fuel trim is lowered, and
the ECMiPCM reduces the amount of injected fuel
This cvcle keeps the airlfuel ratio close to the stoichio-
metric ratio when in closed loop status'
Operating ValueF eeza Data
HO2S
Feedback
Loop Status
At idle speed: closed
YES
Short Term
Fuel Trim
! 20%
YES
Long Term
Fuel Trim
Long term fuel trim is computed from shon term fuel
trim and indicates changes occurring in the fuel supply
svstem over a long Period
lf long term fuel trim is higher than 1.00, the amount of
injecGd fuel must be increased. lf it is lower than 1 00'
the amount of injected fuel must be reduced'
! 20%
YES
lntake Air
Temperature
{IAT)
The IAT sensor converts intake air temperature into volt-
age and signals the ECM/PCM. When intake air tempera-
ture is low, the internal resistance of the sensor
increases. and the voltaqe signal is higher'
With cold engine:
Same as ambient temPer'
ature and ECTYES
At idle speed:
approx. 10 %YESThrottle
Position
Based on the accelerator pedal position, the open'ng
angle of the throttle valve is indicated
lgnition
Timing
lgnition timing is the ignition advance angle set by the
gCV/eCV. tn" gCU/PCM matches ignition timing to the
driving conditions.
CLV is the engine load calculated from the MAP data'
At idle speed: 12'i 2'
(81642 engine: 16" t 2")
BTDC with the SCS ser-
vice connector connected.
NO
Calculated
Load Value
{CLV)
At idle speed:
15-35%
At 2.500 rpm with no load:
12 - 30%
YES
ro
11-87
Page 372 of 2189

How to Read Flowcharts
A flowchart is designed to be used from start to final repair. lt's like a map showing you the shortest distance. But beware:
lf you go off the "map" anywhere but a "stop" symbol, you can easily get lost.
tSrARTl(bold type)
FanoNl
@
tsroP I
{bold type)
Describes the conditions or situation to start a troubleshooting flowchart.
Asks you to do something; perform a test, set up a condition etc.
Asks you about the result of an action, then sends you in the appropriate troubleshooting direction.
The end of a series of actions and decisions. describes a final repair action and sometimes directs you to
an earlier part of the flowchart to confirm your repair,
NOTE:
. The term "lntermittent Failure" is used in these charts, lt simply means a system may have had a failure. but it checks
out OK at this time. lf the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL) on the dash does not come on, check for poor connections
or loose wires at all connectors related to the circuit that you are troubleshooting (see illustration below)'
. Most of the troubleshooting flowcharts have you reset the Engine Control Moduls (ECM)/Powertrain Control Module
(pCM) and try to duplicate the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). lf the problem is intermittent and you can't duplicate the
code, do not continue though the flowchart. To do so will only result in confusion and, possibly, a needlessly replaced
ECM/PCM.
. ,,Open" and "Short" are common electrical terms. An open is a break in a wire or at a connection. A short is an acci-
dental connection of a wire to ground or to another wire. In simple electronics, this usually means something won't
work at all. In complex electronics (like ECM's/PCM'sl. this can sometim€s mean something works, but not the way it's
suDDosed to.
toosE
1 1-103
Page 373 of 2189

PGM-FI System
System Description
CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor
MAP Sensor
IAT SensorTP SensorEGR Valve Lift Sensor*'Primary H02SSecondary HO2SVSSBARO SensorELD*'KS€Starter SignalALT FR SignalAir Conditioning SignalA/T Gear Position SignalBattery Voltage {lGN.1}Erake Switch SignalPSP Switch SignalFuel Tank Pressure Sensor*iVTEC Pressure Switch*5Clutch Switch Signal*6Countershaft Speed SensornBMainshaft Speed Sensorrs
-\
----t /
F;ilrr j"-----fi-tri-'r.;l
Fb"t."'i" d" c;;il
F,h"'c;;tr*".io";-l
@."r.l"sc;;ll
EaM/PcM B""k-p F"""till
r\
-:/
Fuel IniectorsPGM-Fl Main Belay {Fuel Pump)MILIAC Valve!y'C Compressor Clutch RelayRadiator Fan Relay*,Condenser Fan RelayALT*'lcMEVAP Purge Control Solenoid
Primary HO2S HeaterSecondary H02S HeaterEGR Control Solenoid Valve*rEGR valve*6EVAP Bypass Solenoid Valve*'EVAP Control Canister Vent Shut
VTEC Solenoid Valve*5DLCLock-up Control Solenoid Valve*aShift Control Solenoid Valve*3Linear Solenoid Valve*3
*1: Dl6Y5 engine*2: USA model*3: CW (D16Y5 ensine), D16Y8 engine and 81642 ensine*4: '96 D16Y8 engine lcoupe),'97 Dl6Y7 engine (coupe: KL model, sedan: KL (LX) model),'97 D16Y8 engine {coupe: all models, sedan: KLmodel),'98-all models,'99'all models,'00-all models+5: D16Y5, D16Y8,816A2 engine*6: M/T (D16Y5 enginei*7: CVT 1D'l6Y5 engine)+8: A/T (D16Y7, D16Y8 engine)*9: '96 D16Y5 engine,'96 D16Y7 engine,'96 Dl6Y8 engine (sedan),'97 D16Y5 engine,'97 Dl6Y7 engine (coupe: KA, KC models, sedan:KA, KC, KL (LX) models, hatchback: all models),'97 D16Y8 engine (sedan: KA, KC modelsi
PGM-FI Sy3lem
The PGM-Fl system on this model is a sequential multipon fuel injection system.
Fuel iniector Timing and Duration
The ECM/PCM contains memories for the basic discharge durations at various engine speeds and manifold air flow rates.
The basic discharge duration, after being read out from the memory. is further modified by signals sent from various sen-
sors to obtain the final discharge duration.
ldle Air Control
ldle Air Control Valve llAC Valve)
When the engine is cold. the A,/C compressor is on, the transmission is in gear, the brake pedal is depressed, the P/S load
is high, or the alternator is charging, the ECM/PCM controls current to the IAC Valve to maintain the correct idle speed.
lgnition Timing Control
. The ECM/PCM contains memories for basic ignition timing at various engine speeds and manifold air flow rates.
lgnition timing is also adjusted for engine coolant temperature.
. Aknockcontrol system was adopted which sets the ideal ignition timing for the octane rating ofthegasoline used.*3
Othgr Control Funqtions
1. Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECM/PCM provides a rich mixture by increasing fuel injector duration.
2. Fuel Pump Control
. When the ignition switch is initially turned on, the ECM/PCM supplies ground to the PGM-Fl main relay that sup-plies current to the fuel pump for two seconds to pressurize the fuel system.. When the engine is running, the ECI\4PCM supplies ground to the PGM-FI majn relay that supplies current to the fuel
oumo.
. When the engine is not running and the ignition is on, the ECM/PCM cuts ground to the PGM-FI main relay which
cuts current to the fuel pump.
11-104
INPUTS
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECMY
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM) OUTPUTS
Page 374 of 2189

3.
5.
6.
1.
Fuel Cut-off Control
. During deceleration with the throttle valve closed, current to the fuel injectors is cut off to improve fuel economy at
speeds over the following rpm:. D16Y5 engine (M/T):850 rpm. D]6Y5 engine (CVT), D'16Y8 engine (USA M/T): 920 rpm
. Dl6Y8 engine (USA A,/I), D16Y7 engine (USA A,/T);910 rpm
. D16Y8 engine (Canada M/T), D16Y7 engine (canada): 990 rpm
' D16Y8 engine (Canada M/T): 1,000 rpm
. 816A2 engine: 970 rpm
. Fuel cut-off action also takes place when engine speed exceeds 6,900 rpm (D16Y5, D16Y7 engine; D'16Y8 engine:
7,000 rpm. 816A2 engine: 8.100 rpm), regardless of the position of the throttle valve, to protect the engine from
over-rewing. With '99 Dl6Y7 engine (A,/T) and '99 D16Y8 engine (A./T), the PCM cuts the fuel at engine speeds over
5,000 rpm when the vehicle is not moving.
IVC Compressor Clutch Relay
When the ECM/PCM receives a demand for cooling from the air conditioning system, it delays the compressor from
being energized, and enriches the mixture to assure smooth transition to the A,/C mode
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge Control Solenoid Valve*'
When the engine coolant temperature is above 154'F (68'C). the ECM/PCM controls the EVAP purge control solenoid
valve which controls vacuum to the EVAP purge control canister.
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge Control Solenoid Valve*a
When the engine coolant temperature above 154"F (68"C), intake air temperature above 32"F (0'C) and vehicle speed
above 0 mile (0 km/h) or [Ay'C compressor clutch on and intake air temperature above 160"F (41'C)], the ECM/PCM
controls the EVAP purge control solenoid valve which controls vacuum to the EVAP purge control canister.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Control Solenoid Valve*?
When EGR is required for control of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions. the ECM controls the EGR control solenoid
valve which supplies regulated vacuum to the EGR valve
Alternator Control
The system controls the voltage generated at the alternator in accordance with the electrical load and driving mode,
which reduces the engine load to improve the fuel economy.
ECM/PCM Fail-safe/Back-up Functions
1. Fail safe Function
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM/PCM ignores that signal and assumes a pre-pro-
grammed value for that sensor that allows the engine to continue to run.
2. Back-uD Function
When an abnormality occurs in the ECM/PCM itself, the fuel injectors are controlled by a back-up circuit independent
of the system in order to permit minimal driving.
3. Self diagnosis Function lMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL)l
When an abnormality occurs in a signal from a sensor, the ECM/PCM supplies ground for the lvllL and stores the DTC
in erasable memory. When the ignition is initially turned on, the ECM/PCM supplies ground for the MIL for two sec-
onds to check the MIL bulb condition.
4. Two Trip Detection Method
To prevent false indications, the Two Trip Detection Method is used for the HO2S, fuel metering-related. idle control
system, ECT sensor, EGR system and EVAP control system self-diagnostic functions. When an abnormality occurs,
the ECM/PCM stores it in its memory. When the same abnormality recurs after the ignition switch is turned OFF and
ON 0l) again, the ECM/PCM informs the driver by lighting the MlL. However, to ease troubleshooting, this function is
cancelled when you jump the service check connector. The MIL will then blink immediately when an abnormality
occurs,
5. Two (or Three) Driving Cycle Detection Method
A "Driving Cycle" consists ot starting the engine. beginning closed loop operation, and stopping the engine. lf misfir-
ing that increases emissions is detected during two consecutive driving cycles, or TWC deterioration is detected dur-
ing three consecutive driving cycles, the ECM/PCM turns the MIL on. However, to ease troubleshooting, this function
is cancelled when you jump the service check connector. The MIL will then blink immediately when an abnormality
occurs.
(cont'd)
1 1-1 05
.1.
Page 414 of 2189

Primary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Primary HO2S) (Sensor 1l
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0133: A slow response problem in the Primary Heated
Oxygen Sensor {Primary H02S) (Sensor 1) circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble code (DTC) Pl163: A slow response problem in the Primary Heated
Oxygen Sensor (Primary HO2S) (Sensor 1)circuit
Description
By controlling the airlfuel ratio with a Primary Ho2S {Sensor 1) and a secondary HO2S {Sensor 2), the deterioration of the
primary HO2S (Sensor 1) can be evaluated by its feedback period. when the feedback period of the Ho2s exceeds a cer-
tain value during stable driving conditions, the sensor will be judged as deteriorated
when deterioration has been detected during two consecutive trips. the MIL comes on and DTC P0133 or P1163* will be stored'
NOTE: tf DTC P0131, P0132 and/or P0135 are stored at the same time as DTC P0133, troubleshoot those DTCS first' then
troubleshoot DTC P0133. lf DTC Pl 162, P1168 and/or P1169 are stored at the same time as DTC P1163, troubleshoot those
DTCS first, then recheck for DTC Pl163.
Possible Cause
o Primary HO2S (Sensor 'l) Deterioration
o Primary HO2S Heater (Sensor 1)Deterioration
. Exhaust system leakage
Troublsshooting Flowchart
tFol3al
I P1163
- The MIL has been reported on- DTC P0133 and/or Pl163* is
stored,
Problem Verilication:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Pro
cedure-2. Connect the scan tool
3. Start the engine. Hold the
engine at 3,000 rpm with no
load (in Park or neutral) until
the radiator fan comes on
4. Connect the SCS service con-
nector.5. Test-drive u nder Iollowing
conditions.- 55 mph (88 km/h) steadyspeed- A/f in D position {M/T in
5th gear)
Until readiness code comes
lntermittent failure, 3Y3tem i3 OK
at thi3 time. Ch.ck lol Poor con-
ncctions or loosc wiros at C123
{C145)! lPrimary HO2S, Sensor 1l
and ECM/PCM.
Replace th6 Prim.ry HO2S (Sen'
sor 11.
*: P'l163 (D16Y5 engine with M/T)
11-145
Page 437 of 2189
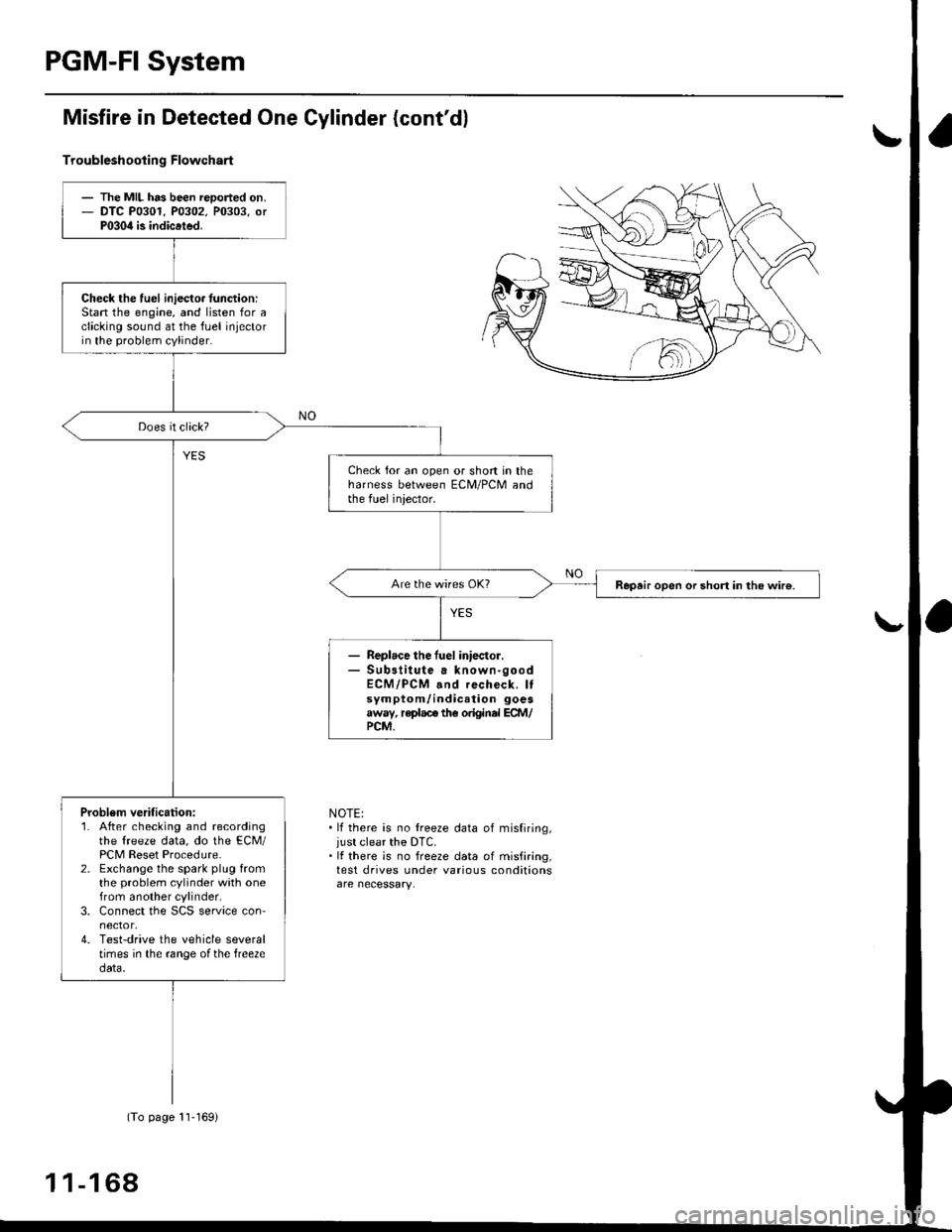
PGM-FI System
Misfire in Detected One Gylinder (cont'dl
Troubleshootin g Flowchart
NOTE:. lf there is no treeze data of misfiring,just clear the DTC.. It there is no freeze data of misfiring,test drives under various conditions
- The MIL has been reoorted on.- DTC P0301. P0302. P0303, orP030il is indicated.
Check the fuel iniecto. lunction:Stan the engine, and listen for aclicking sound at the fuel injectorin the problem cylinder.
Check for an open or short in theharness between ECM/PCM andthe fuel iniector.
Repair open or short in the wir€.
Replace the fuel iniector.Sub3titute a known-goodECM/PCM and recheck. Itsymptom/indication goesaway, replace the original ECM/PCM.
Problem verification:1. After checking and recordingthe freeze data, do the ECM/PCM Reset Procedure.2. Exchange the spark plug fromthe problem cylinder with onefrom another cylinder,3. Connect the SCS service con'nector,4. Test-drive the vehicle severaltimes in the range ofthe free2edata.
(To page 11-169)
1 1-1 68