1996 CHEVROLET BLAZER ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 210 of 392

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Maintenance When Trailer Towing
Your vehicle will need service more often when you’re
pulling
a trailer. See the Maintenance Schedule for more
on this. Things that are especially important in trailer
operation are automatic transmission fluid (don’t
overfill), engine oil, axle lubricant, belt, cooling system
and brake adjustment. Each of these is covered
in this
manual, and the Index will help you find them quickly.
If you’re trailering, it’s a good idea to review these
sections before you start your trip.
Check periodically to see that all hitch nuts and bolts
are tight.
Trailer Wiring Harness
The light duty trailer wiring is a six-wire harness
assembly. The heavy duty trailer wiring is an eight-wire
harness assembly. The harnesses are stored under
the
vehicle, along the passenger-side frame crossmember on
two-door vehicles or on the driver’s side corner frame
crossmember
on four-door vehicles. The heavy duty
trailer wiring has a 30-amp feed wire with an inline fuse
located by the junction block. See “Fuses and Circuit
Breakers” in
the Index. Both harnesses have no
connector and should be wired
by a qualified electrical technician. The technician can
use the following color code chart when connecting the
wiring harness
to your trailer.
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
DARK BLUE: Use for electric trailer brakes or
auxiliary wiring.
RED: Use for battery charging; it connects to the
starter solenoid (eight-wire harness
only).
LIGHT GREEN: Back-up lamps (eight-wire
harness only).
BROWN: Taillamps and parking lamps.
YELLOW Left stoplamp and turn signal.
DARK GREEN: Right stoplamp and turn signal.
WHITE (Heavy Gage): Ground wire.
WHITE (Light Gage): Auxiliary stoplamp.
Securely attach the harness
to the trailer, then tape or
strap it to your vehicle’s frame rail. Be sure you leave
it loose enough
so the wiring doesn’t bend or break,
but
not so loose that it drags on the ground. Store the
harness in its original place. Wrap the harness together
and
tie it neatly so it won’t be damaged.
4-56
Page 232 of 392

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Fan Noise
This vehicle has a clutched engine cooling fan. When
the
clutch is engaged, the fan spins faster to provide
more air to cool the engine. In most every day driving
conditions, the clutch is
not engaged. This improves
fuel economy and reduces fan noise. Under heavy
vehicle loading, trailer towing and/or high outside
temperatures, the’ fan speed increases when
the clutch
engages.
So you may hear an increase in fan noise.
This is normal and should not be mistaken as
the
transmission slipping or making extra shifts. It is
merely the cooling system functioning properly. The
fan will slow down when additional cooling
is not
required and the clutch disengages.
You may also hear this fan noise when you start the
engine. It will go away as the fan clutch disengages.
If a Tire Goes Flat
It’s unusual for a tire to “blow out” while you’re driving,
especially
if you maintain your tires properly. If air goes
out of a tire, it’s much more likely
to leak out slowly.
But
if you should ever have a “blowout,” here are a few
tips about what to expect and what
to do:
If a front tire fails, the flat tire will create a drag that
pulls
the vehicle toward that side. Take your foot off the
accelerator pedal and grip
the steering wheel firmly.
Steer
to maintain lane position, and then gently brake to
a stop well out of the traffic lane.
A rear blowout, particularly on a curve, acts much like
a skid and may require the same correction you’d use in
a skid. In any rear blowout, remove your
foot from the
accelerator pedal. Get
the vehicle under control by
steering the way you want the vehicle
to go. It may be
very bumpy and noisy, but you can
still steer. Gently
brake to a stop
-- well off the road if possible.
If a tire goes flat, the next part shows how to use your
jacking equipment
to change a flat tire safely.
5-20
Page 262 of 392

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine .. Automatic Transmission Fluid
When to Check and Change
A good time to check your automatic transmission fluid
level
is when the engine oil is changed.
Change both
the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles
(83 000 km) if the vehicle is mainly driven under one or
more
of these conditions:
In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature
regularly reaches
90°F (32°C) or higher.
0 In hilly or mountainous terrain.
When doing frequent trailer towing.
0 Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
If you do not use your vehicle under any of these
conditions, the fluid and filter
do not require changing.
See “Scheduled Maintenance Services” in the Index.
How to Check
Because this operation can be a little difficult, you
may choose to have this done at your GM dealer
Service Department.
If you do it yourself, be sure to follow all the instructions
here, or you could get
a false reading on the dipstick.
I NOTICE:
Too much or too little fluid can damage your
transmission.
Too much can mean that some of
the fluid could come out and fall on hot engine
parts or exhaust system parts, starting a fire. Be
sure to get an accurate reading if you check your
transmission fluid.
Wait at least 30 minutes before checking the
transmission fluid level
if you have been driving:
When outside temperatures are above 90°F (32°C).
At high speed for quite a while.
In heavy traffic -- especially in hot weather.
While pulling a trailer.
To get the right reading, the fluid should be at normal
operating temperature, which is
180°F to 200°F
(82°C to 93°C).
. 6-14
Page 264 of 392
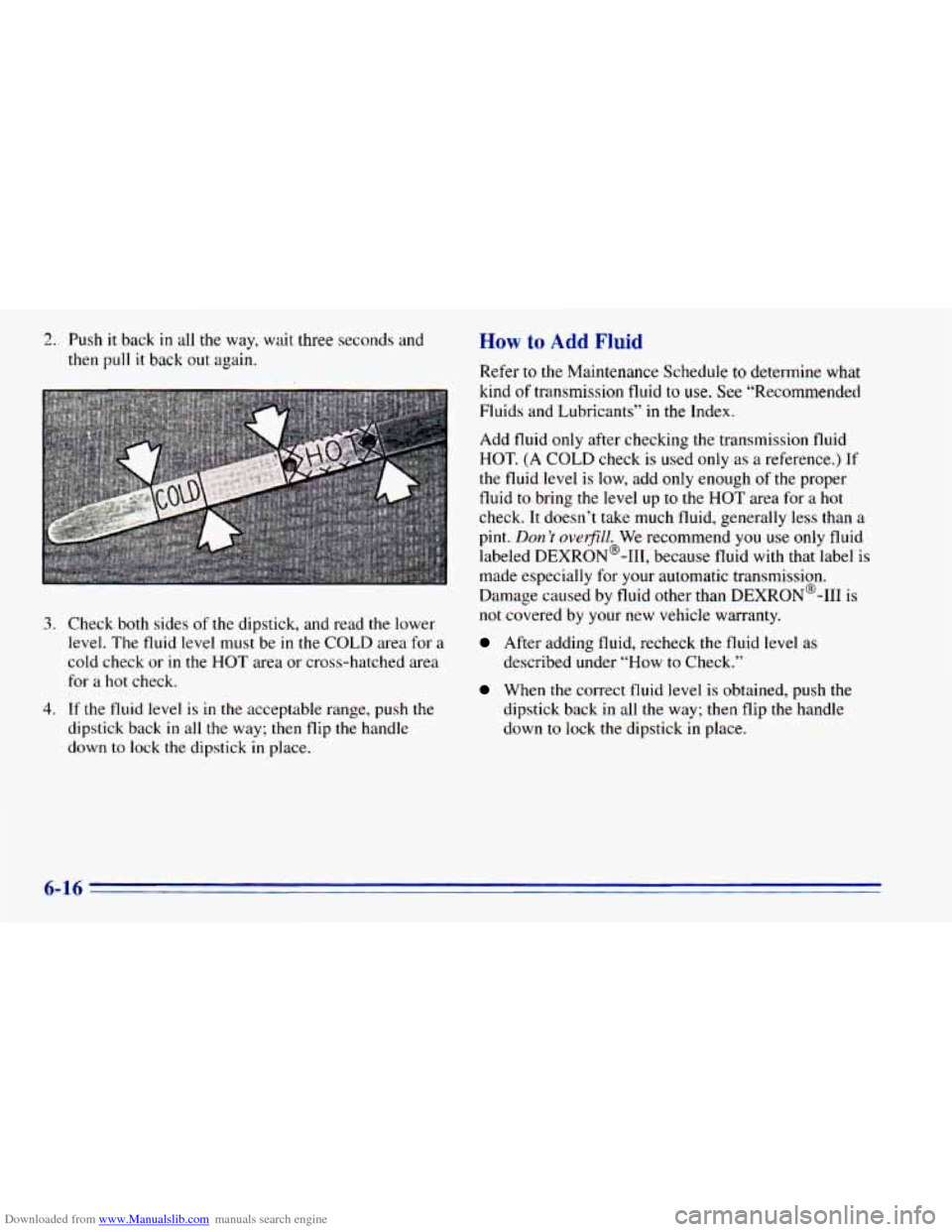
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2. Push it back in all the way, wait three seconds and
then
pull it back out again,
3. Check both sides of the dipstick, and read the lower
level. The fluid level must be in the COLD area for a
cold check or in the HOT area or cross-hatched area
for a hot check.
4. If the fluid level is in the acceptable range, push the
dipstick back in all
the way; then flip the handle
down
to lock the dipstick in place.
How to Add Fluid
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule to determine what
kind
of transmission fluid to use. See “Recommended
Fluids and Lubricants”
in the Index.
Add fluid only after checking the transmission fluid
HOT. (A COLD check is used only as
a reference.) If
the fluid level is low, add only enough
of the proper
fluid to bring the level up
to the HOT area for a hot
check. It doesn’t take much fluid, generally less than a
pint. Don ’t overfill. We recommend you use only fluid
labeled DEXR0N’-111, because fluid with that label is
made especially
for your automatic transmission.
Damage caused by fluid other than DEXRON@-I11 is
not covered by your new vehicle warranty.
After adding fluid, recheck the fluid level as
described under “How to Check.”
When the correct fluid level is obtained, push the
dipstick back in all the way; then flip the handle
down to lock the dipstick in place.
Page 293 of 392

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while
driving.
If you mix tires of different sizes or types
(radial and bias-belted tires), the vehicle may not
handle properly, and you could have a crash.
Using tires
of different sizes may also cause
damage to your vehicle. Be sure
to use the same
size and type tires
on all wheels.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system
developed by the United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration, which grades tires by
treadwear, traction and temperature performance. (This
applies only to vehicles sold
in the United States.) The
grades are molded on the sidewalls of most passenger
car tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading system does
not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires,
space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with
nominal rim diameters of
10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm),
or to some limited-production tires. While the tires
available on General Motors passenger
cars and light trucks may vary with respect to these
grades, they must also conform to Federal safety
requirements and additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC) standards.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course. For
example, a tire graded
150 would wear one and a half
(1 1/2) times as well on the government course as a tire
graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends
upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and
may depart significantly from the norm due to variations
in driving habits, service practices and differences in
road characteristics and climate.
Traction - A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are A, B,
and C, and they represent the tire’s ability to stop
on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces
of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have
poor traction performance.
6-45
Page 294 of 392

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire is based
on braking (straightahead) traction tests and does not
include cornering (turning) traction.
Temperature - A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under
controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the
material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and
excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure.
The grade
C corresponds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades
B and A represent higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced
carefully
at the factory to give you the longest tire life
and best overall performance.
In most cases, you will not need to have your wheels
aligned again. However, if you notice
unusual tire wear
or your vehicle pulling one way or the other, the
alignment may need to be reset. If you notice your
vehicle vibrating when driving
on a smooth road, your
wheels
may need to be rebalanced.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked, or badly rusted
or corroded.
If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the wheel,
wheel bolts and wheel
nuts should be replaced. If the
wheel leaks
air, replace it (except some aluminum
wheels, which can sometimes be repaired). See your
GM dealer if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer
will know the kind of wheel you need.
6-46