1995 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 152 of 873

12ENGINE
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION The aluminium alloy, tin coated pistons have two
compression and an oil control ring and are secured
to the connecting rods by semi-floating gudgeon pins
which are an interference fit in the small-end bush.
Gudgeon pins are offset towards the thrust side of the
pistons to reduce frictional drag.
Plain, big-end bearing shells are fitted to each
connecting rod.The internally toothed timing belt is driven from a gear
which is keyed to the crankshaft, belt tension being
controlled by a semi-automatic tensioner.
The trochoidal type oil pump is mounted on the front
of the engine and carries the crankshaft front oil seal.
Drive to the pump is via a Woodruff key inserted in the
crankshaft.
Page 209 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Diesel engines operate by compression ignition. The
rapid compression of air in the cylinder during the
compression cycle heats the injected fuel, causing it
to self ignite. During cold starting, automatically
controlled glow plugs assist in raising the temperature
of the compressed air to ignition point.
A cold start advance unit advances the injection timing
to further assist starting. Idle quality is improved by
the high idle setting.
The engine is supplied with pre-compressed air by a
single stage turbocharger.
Exhaust gases passing over a turbine cause it to
rotate, driving a compressor mounted on the turbine
shaft. Air drawn from the cold air intake passes, via
the air cleaner, to the turbocharger where it is
compressed. The compressed air passes to the
cylinders via an intercooler, which reduces the
temperature of the compressed air, increasing its
density.
Fuel is drawn from the tank by a mechanical lift pump
and passes to the injection pump via a filter. In
addition to removing particle contamination from the
fuel, the filter incorporates a water separator, which
removes and stores both bound and unbound water.
The injection pump meters a precisely timed, exact
quantity of fuel to the injectors in response to throttle
variations, injection timing varying with engine speed.
Any excess fuel delivered to the injection pump is not
injected, passing back to the tank via the fuel return
line.
Fuel is injected in a finely atomised form into a
pre-combustion chamber in the cylinder head where it
ignites. The burning fuel expands rapidly into the main
combustion chamber, creating extreme turbulence
which mixes the burning fuel thoroughly with the
compressed air, providing complete combustion.
Cold Starting is assisted by glow plugs, a cold start
advance unit and a high idle setting.Glow plugs
Glow plug operation is controlled by a timer unit, start
relay and resistor. When the ignition is turned on the
timer unit is energised, the glow plugs start to operate
and a warning light on the dashboard illuminates,
remaining illuminated until the glow plugs are
automatically switched off.
The length of time the glow plugs will operate is
dependent on under bonnet temperature, which is
monitored by a sensor located in the timer unit.
Starting the engine results in the power supply to the
glow plugs passing through the resistor, which
reduces their operating temperature. The glow plugs
are cut out either by the temperature sensor in the
timer, or by a microswitch on the injection pump which
operates when the throttle is depressed.
Cold start advance
The cold start advance unit is connected to the engine
cooling system via hoses. It contains a temperature
sensitive element which is retracted when cold and
pulls the advance lever, via cable, towards the rear of
the pump against spring pressure. As coolant
temperature rises, the cold start element expands
releasing tension on the cable and allowing spring
pressure to move the advance lever forwards.
Page 221 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
REPAIR TURBOCHARGER ACTUATOR
Service repair no - 19.42.31
Remove
1.Remove exhaust manifold and turbocharger.
See MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM,
Repair, Exhaust Manifold - Tdi
2.Remove 2 nuts securing the actuator to the
turbocharger bracket.
3.Release clip and disconnect hose from actuator.
4.Remove and discard clip securing control lever
to wastegate spindle.
5.Remove turbocharger actuator.
Refit
6.Fit the replacement actuator and secure with
nuts.
7.Push the control lever as far as possible towards
the actuator and apply pressure to keep the
lever in this position.
8.Pressurise the actuator to 57 - 62 cm Hg and
hold this pressure.
CAUTION: Use only the threaded end of
the lever to make adjustments. Forcing the
complete lever in or out will change the
calibration with the possibility of damaging engine
boost.
9.Screw the lever in either direction until the eye
on the end will locate easily over the wastegate
spindle and secure with a new clip.
10.Release the pressure and tighten the locknut.
11.Refit exhaust manifold and turbocharger.
See
MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair,
Exhaust Manifold - Tdi
TURBOCHARGER AND GASKET
Service repair no - Turbocharger - 19.42.01
Service repair no - Gasket - 19.42.25
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove air cleaner assembly.
See Air Cleaner
3.Remove exhaust manifold assembly.See
MANIFOLD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM, Repair,
Exhaust Manifold - Tdi
4.Remove and discard clip securing control lever
to wastegate spindle.
5.Remove 4 bolts and 2 clamp plates securing
turbocharger to exhaust manifold.
6.Remove turbocharger and discard gaskets.
Refit
7.Clean mating faces of turbocharger and exhaust
manifold.
8.Reverse removal procedure. Use new clip to
secure control lever to wastegate spindle.
Tighten to
45 Nm.
9.Check/top-up engine oil level.
Page 260 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
14
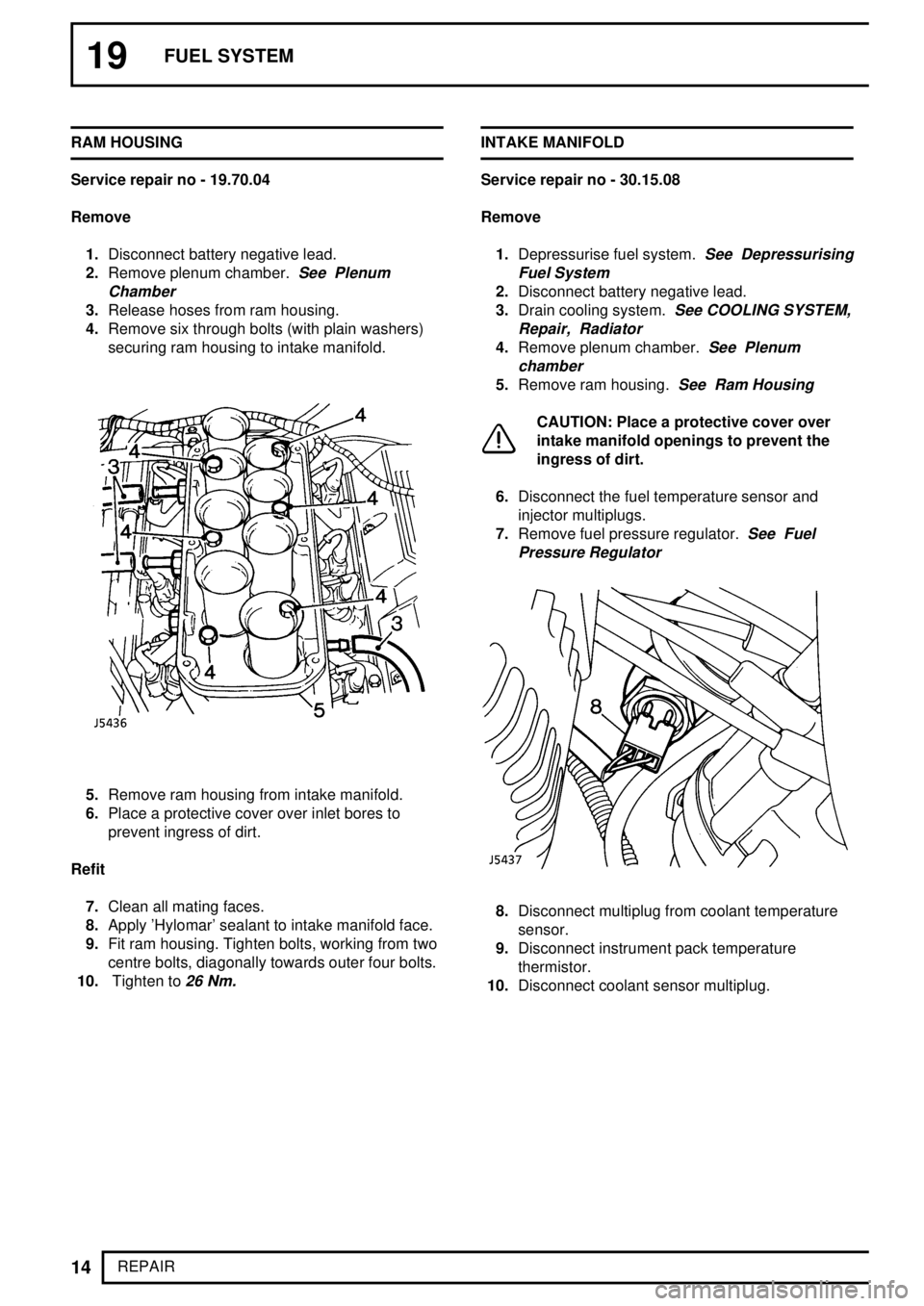
REPAIR RAM HOUSING
Service repair no - 19.70.04
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove plenum chamber.
See Plenum
Chamber
3.Release hoses from ram housing.
4.Remove six through bolts (with plain washers)
securing ram housing to intake manifold.
5.Remove ram housing from intake manifold.
6.Place a protective cover over inlet bores to
prevent ingress of dirt.
Refit
7.Clean all mating faces.
8.Apply 'Hylomar' sealant to intake manifold face.
9.Fit ram housing. Tighten bolts, working from two
centre bolts, diagonally towards outer four bolts.
10.Tighten to
26 Nm.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
Service repair no - 30.15.08
Remove
1.Depressurise fuel system.
See Depressurising
Fuel System
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Drain cooling system.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Radiator
4.Remove plenum chamber.See Plenum
chamber
5.Remove ram housing.See Ram Housing
CAUTION: Place a protective cover over
intake manifold openings to prevent the
ingress of dirt.
6.Disconnect the fuel temperature sensor and
injector multiplugs.
7.Remove fuel pressure regulator.
See Fuel
Pressure Regulator
8.Disconnect multiplug from coolant temperature
sensor.
9.Disconnect instrument pack temperature
thermistor.
10.Disconnect coolant sensor multiplug.
Page 291 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
8
REPAIR IGNITION COILS
Service repair no - 18.20.45 - Set
Service repair no - 18.20.43 - Each
Service repair no - 18.20.44 - Extra - Each
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect H.T. leads from ignition coils. Note
positions of leads.
3.Place H.T. leads aside.
4.Disconnect ignition coil multiplug.
5.Remove 4 nuts securing coil bracket.
6.Release ignition coil bracket from inlet manifold
studs.
7.Manoeuvre coil/bracket assembly from behind
plenum chamber and remove.
8.Remove terminal cover. Note lead positions.
9.Remove 2 nuts securing leads to coil terminals.
10.Remove leads from terminals.
11.Remove 3 Torx screws securing ignition coil to
bracket and remove coil.Refit
12.Fit ignition coil to bracket. Secure with screws.
13.Connect leads to terminals. Secure with nuts.
14.Fit terminal cover.
15.Position ignition coil bracket on inlet manifold
studs.
16.Secure fuel rail and ignition coil bracket with
nuts. Tighten to
8 Nm.
17.Connect multiplug.
18.Connect H.T. leads to respective coil towers.
19.Reconnect battery negative lead.
Page 347 of 873

Tdi
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING
Description
The Tdi engine uses a pressurized cooling system
and cross flow radiator which is supplied from a
separate header tank. The radiator assembly is in
three sections. The largest section is for engine
coolant and the other two sections which are cast in
aluminium, are the engine oil cooler and the turbo
charger intercooler.
A belt driven viscous fan and centrifugal water pump
is located in the front of the cylinder block. Hot coolant
is supplied to the heater through hoses. Two small
diameter air purge hoses connect the top of the
radiator and cylinder head water gallery, to the header
tank.
Coolant circulation (engine cold)
1. Cross flow radiator
2. Header tank
3. Viscous fan
4. Heater hoses
5. By pass hose and engine thermostat
6. Air purge hoses
7. Coolant pumpCOOLANT CIRCULATION
Operation
When the engine is started from cold the thermostat
prevents any coolant circulation through the radiator
by closing off the top hose. During the engine warm
up period, the water pump, pumps coolant towards
the rear of the cylinder block around each of the
cylinders. Coolant as it is heated rises through ports in
the cylinder block and head gasket, into the cylinder
head.The coolant flows forwards to the thermostat,
by-pass port and radiator top hose connection.
Start from cold (thermostat closed)
While the thermostat is closed, coolant circulates
around the cylinder block and cylinder head via the
by-pass.
Engine warm (thermostat open)
When the engine reaches normal running temperature
the thermostat closes off the by-pass and opens the
flow to the top of the radiator.
Page 350 of 873

Tdi
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE OVERHEATING
Before conducting any cooling system diagnosis:
See
Description and operation, Engine Cooling
1.Is coolant level correct?
NO - Allow engine to cool, top up level to
expansion tank seam.
YES - Continue.
2.Is drive belt tension correct?
NO -
See ENGINE, Repair, Compressor
Drive Belt
YES - Continue.
3.Is coolant in radiator frozen?
YES - Slowly thaw and drain system.
See
Adjustment, Coolant
NO - Continue.
4.Is air flow through radiator restricted or blocked?
YES - Apply air pressure from engine side of
radiator to clear obstruction.
NO - Continue.
5.Are there any external leaks, from water pump,
engine gaskets, fast idle thermostat or the heater
unit?
YES - Investigate and rectify.
See Adjustment,
Coolant
NO - Continue.
6.Are fan blades fitted correct way round, concave
side towards engine?
NO - Rectify.
YES - Continue
7.Is viscous unit operating correctly?
See
Description and operation, Viscous Fan
NO - Renew.See Repair, Viscous
Coupling, Fan Blades, Pulley and Fan
Cowl
YES - Carry out a pressure test on radiator cap
and system. Check thermostat type,
operation and correct fitting.
See Repair,
Thermostat
If pressure test leads you to suspect coolant
leakage across gaskets, go to check 10,
otherwise: Continue.8.Are the air conditioning fans operating correctly?
See Electrical Trouble Shooting Manual.
NO - Rectify.
YES - Continue.
9.Is temperature sender and gauge giving
accurate readings?
NO - Sustitute parts and compare readings.
YES - Continue.
10.Carry out cylinder pressure test to determine if
pressure is leaking into cooling system causing
over pressurising and loss of coolant.
If problem is not diagnosed, check the coolant system
for engine oil contamination and engine lubrication
system for coolant contamination.
If only the coolant system is contaminated suspect a
cylinder head gasket.
If both systems are contaminated, suspect the
radiator.
If only the lubrication system is contaminated with
coolant, suspect leakage past cylinder liner seals or
cylinder head gasket.
Page 360 of 873

V8i
1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS ENGINE OVERHEATING
Before conducting any cooling system diagnosis:
See
Description and operation, Engine Cooling
1.Is coolant level correct?
NO - Allow engine to cool, top up level to
expansion tank seam.
YES - Continue.
2.Is drive belt tension correct?
NO -
See ENGINE, Repair, Drive Belt -
Check Tension
YES - Continue.
3.Is ignition timing correct?
NO -
See ELECTRICAL, Adjustment,
Ignition Timing
YES - Continue.
4.Is coolant in radiator frozen?
YES - Slowly thaw and drain system.
See
Adjustment, Coolant Requirements
NO - Continue.
5.Is air flow through radiator restricted or blocked?
YES - Apply air pressure from engine side of
radiator to clear obstruction.
NO - Continue.
6.Are there any external leaks, from water pump,
engine gaskets or the heater unit?
YES - Investigate and rectify.
See Adjustment,
Coolant Requirements
NO - Continue.
7.Are fan blades fitted correct way round, concave
side towards engine?
NO - Rectify.
YES - Continue.8.Is viscous unit operating correctly?
See
Description and operation, Viscous Fan
NO - Renew.See Repair, Viscous
Coupling, Fan Blades, Pulley and Fan
Cowl
YES - Carry out a pressure test on radiator cap
and system. Check thermostat type,
operation and correct fitting
See Repair,
Thermostat
If pressure test leads you to suspect coolant
leakage across gaskets, go to check 11,
otherwise: Continue.
9.Are the air conditioning fans operating correctly?
See Electrical Trouble Shooting Manual.K5
NO - Rectify.
YES - Continue.
10.Is temperature sender and gauge giving
accurate readings?
NO - Substitute parts and compare readings.
YES - Continue.
11.Carry out cylinder pressure test to determine if
pressure is leaking into cooling system causing
over pressurising and loss of coolant.
If problem is not diagnosed, check the coolant system
for engine oil contamination and engine lubrication
system for coolant contamination.
If the coolant only, or both systems are contaminated,
suspect cylinder head gaskets or radiator.
If only the lubrication stystem is contaminated with
coolant, suspect inlet manifold or front cover gaskets.