Page 738 of 976
HEATING AND VENTILATION
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION HEATING AND VENTILATION UNIT
The heating and ventilation and blower units are
standard on all models. Air conditioning system is an
optional module, which when fitted provides fully
integrated climate control for the vehicle interior.
The heating and ventilation unit controls the air
distribution and heating to the vehicle interior. The
blower unit controls the volume of air supplied, while
the air conditioning module (when fitted) provides
refrigerated and dehumidified air.
1. Fresh air inlet
2. Recirculation air inlet
3. Air outlets screen de-mist
4. Air outlet face level vents
5. Air outlets front footwells
6. Air outlets to rear footwells7. Fresh/recirculation air flap servo
8. Blower motor relay
9. Multiplug connector to main harness
10. Multiplug connector, blower to heater unit
11. Resistor unit - blower speed.
Page 739 of 976
80HEATING AND VENTILATION
2
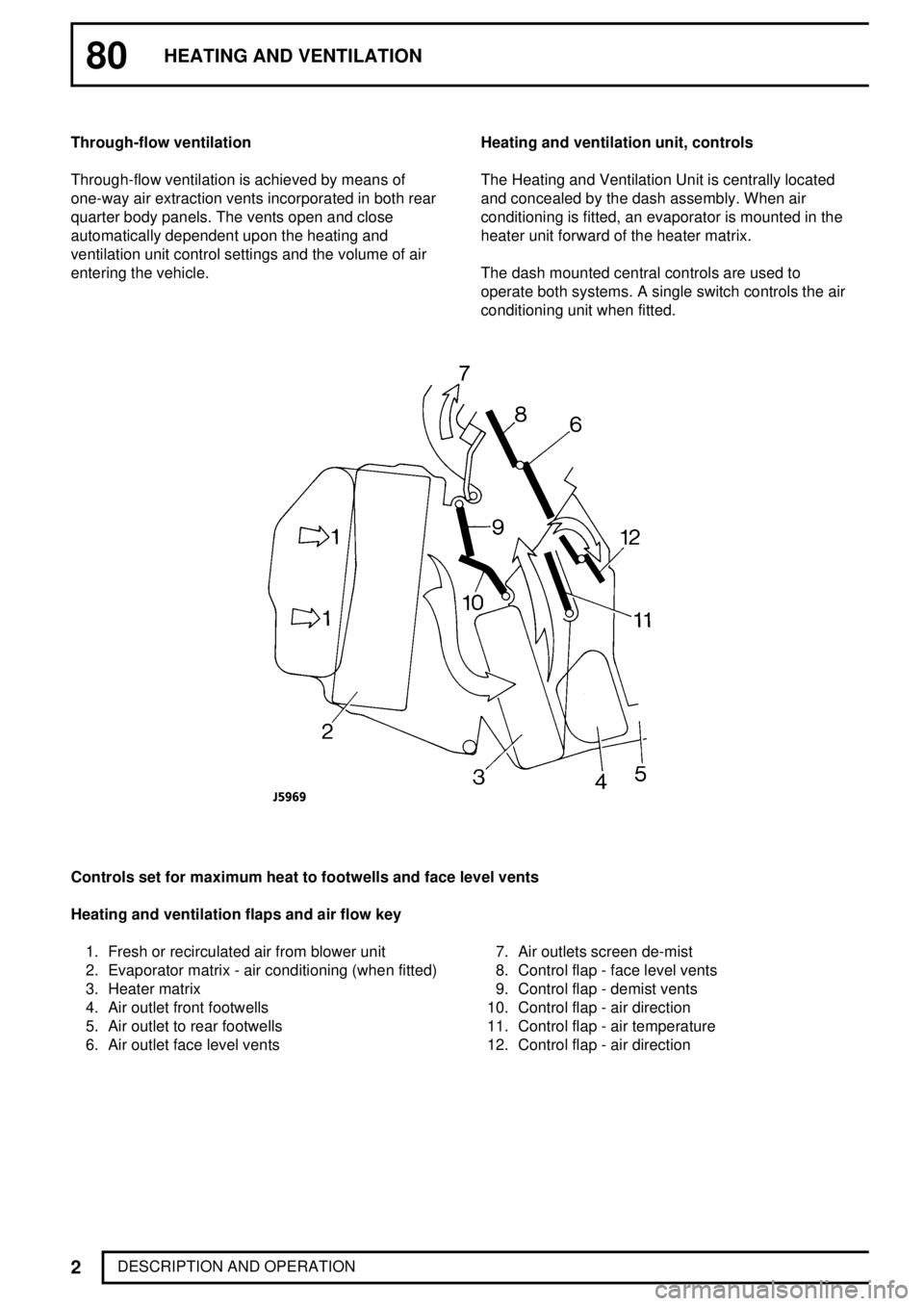
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Through-flow ventilation
Through-flow ventilation is achieved by means of
one-way air extraction vents incorporated in both rear
quarter body panels. The vents open and close
automatically dependent upon the heating and
ventilation unit control settings and the volume of air
entering the vehicle.Heating and ventilation unit, controls
The Heating and Ventilation Unit is centrally located
and concealed by the dash assembly. When air
conditioning is fitted, an evaporator is mounted in the
heater unit forward of the heater matrix.
The dash mounted central controls are used to
operate both systems. A single switch controls the air
conditioning unit when fitted.
Controls set for maximum heat to footwells and face level vents
Heating and ventilation flaps and air flow key
1. Fresh or recirculated air from blower unit
2. Evaporator matrix - air conditioning (when fitted)
3. Heater matrix
4. Air outlet front footwells
5. Air outlet to rear footwells
6. Air outlet face level vents7. Air outlets screen de-mist
8. Control flap - face level vents
9. Control flap - demist vents
10. Control flap - air direction
11. Control flap - air temperature
12. Control flap - air direction
Page 740 of 976

HEATING AND VENTILATION
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Controls set for unheated air to footwells and face level vents
Heater and ventilation operation
The heating and ventilation system contains a heater
matrix, which is connected to the engine cooling
system, and a 4 speed fan for air distribution. Engine
coolant is circulated through the heater matrix
continuously, except when the temperature controls
are set to COLD.
Recirculated air
When the recirculation switch is pressed, an electrical
servo operates and fully closes the fresh air intake
flap.
Fresh air
When the recirculation switch is returned to the OFF
position, the electrical servo returns and fully opens
the fresh air intake flap.Heated air
Temperature output is controlled by the temperature
controls which move the air direction and temperature
flaps independently to increase or decrease the
volume of air flow through the heater matrix.
V8 Engine:When both controls are in the cold
position, the coolant valve is turned off.
Face level vent flap
Control at face level, flap fully open. All other vents
closed.
Control at face and foot level, flaps half open.
Unless an air conditioning unit is fitted, only fresh or
re-circulated air is available from the face level vents.
Demist vent flap
Control at demist, flap fully open. All other vents
closed.
Control at demist and foot level, flaps half open.
Page 741 of 976
80HEATING AND VENTILATION
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Air direction flap
Flap moves across mixing chamber to direct the air
flow away from the heater matrix.
Air temperature flap
Control at HOT, flaps fully closed. All air flow passes
through heater matrix. As control is moved towards
COLD the flaps progressively open directing air flow
away from the heater matrix.
Control at COLD, flaps fully open.
V8 Engine:When both controls are at COLD, 2
micro-switches are closed and operate a vacuum
valve which closes the coolant valve.Air conditioning
When an air conditioning unit is fitted, the mechanical
operation of the heater controls remains unaltered.
However the air conditioning evaporator is positioned
in front of the mixing chamber through which all air
flow passes.
Page 748 of 976
80HEATING AND VENTILATION
6
REPAIR BLOWER MOTOR UNIT - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONING
Service repair no - 80.20.17
Service repair no - 82.25.54.
Remove
1.Move seats to rear most position.
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Remove fascia panel assembly.
See CHASSIS
AND BODY, Repair, Dash Panel Assembly
4.Remove 2 nuts securing lower brackets to
toeboard.
5.Manoeuvre blower unit from heater unit and
remove.
Refit
6.Reverse removal procedure. Ensure seal
between blower and heater unit is tight.BLOWER MOTOR
Service repair no - 80.20.17
Service repair no - 82.25.33.
Remove
1.Remove blower motor unit.
See Blower Motor
Unit - Heater and Air Conditioning
2.Release wiring harness retaining clip.
3.Remove 3 screws securing casing.
4.Remove blower motor assembly.
Page 749 of 976
HEATING AND VENTILATION
7
REPAIR
5.Remove fan retaining clip.
6.Remove fan.
7.Remove 2 screws securing motor to casing.
8.Remove blower motor.
Refit
9.Reverse removal procedure.HEATER MATRIX
Service repair no - 80.20.29
Remove
1.Remove heater unit.
See AIR CONDITIONING,
Repair, Heater and Cooler Unit
2.Remove evaporator.See AIR CONDITIONING,
Repair, Evaporator and Expansion Valve
3.Remove 2 screws and remove RH side footwell
outlet.
4.Remove heater pipe clips.
5.Slide heater matrix from casing.
6.Release 2 clips and remove 2 heater pipes from
matrix.
Refit
7.Reverse removal procedure.
Page 751 of 976
AIR CONDITIONING
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Receiver/drier
4. Evaporator
5. High pressure servicing connection6. Low pressure servicing connection
7. Dual pressure switch
8. Sight glass
9. Rear evaporator/blower motor assembly
Page 752 of 976
82AIR CONDITIONING
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION SCHEMATIC LAYOUT OF THE AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Receiver/drier
4. Thermostatic expansion valve
5. Evaporator
6. Capillary tube
7. Dual pressure switch
8. Cooling fans to maintain air flow
9. Compressor high pressure relief valve
10. Sight glass - refrigerant
11. Drying agent - receiver/drier
12. Blower motorA1 Ambient air flow through condenser
A2 Ambient air flow through fan and evaporator
A3 Cooled air flow to vehicle interior
F1 High pressure high temperature refrigerant
vapour
F2 High pressure slightly subcooled refrigerant
liquid
F3 High pressure slightly subcooled refrigerant
liquid with moisture, vapour bubbles and foreign
matter removed
F4 Low pressure low temperature mixed liquid and
vapour
F5 Low pressure slightly super heated refrigerant
vapour