1995 JEEP XJ warning light
[x] Cancel search: warning lightPage 644 of 2158

READING LAMPS
Circuit M1 from the IOD fuse (fuse F9) in the fuse
block supplies power to the reading lamps. Circuit
M1 is HOT at all times. When the operator depresses
the reading lamp, the reading lamp switch closes and
supplies ground on circuit Z1.
VISOR VANITY MIRROR LAMPS
Circuit M1 from the IOD fuse (fuse F9) in the fuse
block supplies power to the vanity lamps. Circuit M1
is HOT at all times. When the vanity lamps switch
closes, voltage flows to vanity mirror lamps. The van-
ity mirror is case grounded.
UNDERHOOD LAMP
Circuit A6 from fuse 16 in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) supplies battery voltage for the under-
hood lamp. A mercury switch, in series after the
lamp, connects the lamp to ground on circuit Z1.
When the hood is raised, mercury inside the switch
moves to a position where it connects circuit M1 to
ground circuit Z1, illuminating the lamp.
CHIME/BUZZER MODULE
The buzzer or optional chime module sounds an au-
dible warning tone. The tone sounds for seat belt
warning and when the ignition key is in the ignition
switch while the drivers door is open. The tone also
sounds when the ignition key is in the ON position
while the drivers side seat belt is not buckled. Lastly,
the tone sounds when the headlamps are ON when
the ignition is OFF. Refer to Group 8U for system op-
eration.
When the ignition switch is in the RUN or START
position, circuit F87 from fuse 17 in the fuse block
supplies power to the chime/buzzer module. Circuit
A21 from the ignition switch supplies power to fuse
17.
Circuit L7 from fuse 15 in the fuse block also sup-
plies power to the chime/buzzer module. Circuit A3
from fuse 5 in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
powers fuse 15.
When the parking lamps or headlamps are ON, the
headlamp switch connects circuit G26 with the driv-
ers side door jamb switch. Circuit G26 also connects
to the key-in switch. Circuit M11 connects the key-in
switch to the chime/buzzer module and the headlamp
switch.
If the headlamps are ON, and the drivers door
opens, ground for the chime/buzzer is on circuit C26
from the headlamp switch through the door jamb
switch to circuit Z1.
If the headlamps are OFF with the key in the ig-
nition while the drivers side door is open, ground forthe chime/buzzer is supplied through the key-in
switch. The ground path is over circuit M11, through
the closed key-in switch to circuit C26. From circuit
C26, the ground path continues through the drivers
door jamb switch to circuit Z1.
Circuit G11 from the buzzer powers the seat belt
warning lamp in the instrument cluster. Circuit Z1
at the instrument cluster provides ground for the
lamp.
Circuit G10 from the buzzer connects to the seat
belt switch. When the seat belt switch closes a path
to ground is completed on circuit Z1 and the tone
sounds momentarily.
Circuit Z1 also grounds the chime\buzzer module.
HELPFUL INFORMATION
Circuit F87 also powers the instrument cluster and
the headlamp delay module.
DIAGRAM INDEX
Component Page
Cargo Lamp............................8W-44-6
Chime/Buzzer Module......................8W-44-3
Courtesy Lamps.........................8W-44-5
Dome Lamp............................8W-44-7
Door Jamb Switches.....................8W-44-10
Fuse 3 (PDC).........................8W-44-4, 6
Fuse 5 (PDC).........................8W-44-3, 8
Fuse 6 (PDC)...........................8W-44-3
Fuse 9 (Fuse Block).....................8W-44-4, 6
Fuse 15 (Fuse Block)....................8W-44-3, 8
Fuse 16 (PDC)........................8W-44-4, 6
Fuse 17 (Fuse Block)......................8W-44-3
Fuse 19 (Fuse Block)......................8W-44-8
Glove Box Lamp and Switch.................8W-44-5
Headlamp Switch...................8W-44-3, 4, 5, 8
Headlamp Delay Module....................8W-44-4
Headlamp Delay Relay.....................8W-44-3
Ignition Switch..........................8W-44-3
Instrument Cluster........................8W-44-3
Instrument Panel Illumination Lamps..........8W-44-8, 9
Intermittent Wiper Control Module.............8W-44-4
Key-In Switch...........................8W-44-4
Liftgate Switch..........................8W-44-6
Reading Lamps..........................8W-44-7
Remote Keyless Entry Module................8W-44-7
Seat Belt Switch.........................8W-44-3
Telltale Connector (Instrument Cluster)...........8W-44-3
Time Delay Relay........................8W-44-4
Underhood Lamp.........................8W-44-4
Vanity Lamps...........................8W-44-7
8W - 44 - 2 8W-44 INTERIOR LIGHTINGÐXJ VEHICLESJ
Page 819 of 2158

WIRING DIAGRAMS
CONTENTS
page page
8W-01 GENERAL INFORMATIONÐWIRING
DIAGRAMS...................... 8W-01-1
8W-10 FUSE/FUSE BLOCK........... 8W-10-1
8W-11 POWER DISTRIBUTION........ 8W-11-1
8W-15 GROUND DISTRIBUTION....... 8W-15-1
8W-20 CHARGING SYSTEM.......... 8W-20-1
8W-21 STARTING SYSTEM........... 8W-21-1
8W-30 FUEL/IGNITION.............. 8W-30-1
8W-31 TRANSMISSION CONTROLS.... 8W-31-1
8W-32 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES........... 8W-32-1
8W-33 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL..... 8W-33-1
8W-40 INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....... 8W-40-1
8W-41 HORN/CIGAR LIGHTER........ 8W-41-1
8W-42 AIR CONDITIONING/HEATER.... 8W-42-1
8W-44 INTERIOR LIGHTING.......... 8W-44-1
8W-47 AUDIO SYSTEM.............. 8W-47-18W-48 HEATED REAR WINDOW....... 8W-48-1
8W-49 OVERHEAD CONSOLE.......... 8W-49-1
8W-50 FRONT LIGHTING............ 8W-50-1
8W-51 REAR LIGHTING............. 8W-51-1
8W-52 TURN SIGNALS.............. 8W-52-1
8W-53 WIPERS.................... 8W-53-1
8W-54 TRAILER TOW................ 8W-54-1
8W-60 POWER WINDOWS............ 8W-60-1
8W-61 POWER DOOR LOCKS......... 8W-61-1
8W-62 POWER MIRRORS............ 8W-62-1
8W-63 POWER SEAT................ 8W-63-1
8W-70 SPLICE INFORMATION........ 8W-70-1
8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN OUTS....... 8W-80-1
8W-90 CONNECTOR LOCATIONS...... 8W-90-1
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS........... 8W-95-1
HOW TO USE THIS GROUP
The purpose of this group is to show the electrical
circuits in a clear, simple fashion and to make trou-
bleshooting easier. Components that work together
are shown together. All electrical components used in
a specific system are shown on one diagram. The feed
for a system is shown at the top of the page. All
wires, connectors, splices, and components are shown
in the flow of current to the bottom of the page. Wir-
ing which is not part of the circuit represented is ref-
erenced to another page/section, where the complete
circuit is shown. In addition, all switches, compo-
nents, and modules are shown in theat rest posi-
tion with the doors closed and the key removed
from the ignition.
If a component is part of several different circuits,
it is shown in the diagram for each. For example, the
headlamp switch is the main part of the exterior
lighting, but it also affects the interior lighting and
the chime warning system.
It is important to realize that no attempt is
made on the diagrams to represent components
and wiring as they appear on the vehicle. For
example, a short piece of wire is treated the
same as a long one. In addition, switches and
other components are shown as simply as pos-
sible, with regard to function only.
The wiring diagram show circuits for all wheel-
bases. If there is a difference in systems or compo-
nents between wheel-bases, an identifier is placed
next to the component.
SECTION IDENTIFICATION
Sections in Group 8W are organized by sub-sys-
tems. The sections contain circuit operation descrip-
tions, helpful information, and system diagrams. The
intention is to organize information by system, con-
sistently from year to year.
CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
Section 8W-90 contains Connector Location illus-
trations. The illustrations contain the connector
number and component identification. Connector Lo-
cation charts in Section 8W-90 reference the illustra-
tion number for components and connectors.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the number on the Diagram
pages.
SPLICE LOCATIONS
Splice Location charts in Section 8W-70 show the
entire splice, and provide references to other sections
the splice serves.
Section 8W-95 contains illustrations that show the
general location of the splices in each harness. The
illustrations show the splice by number, and provide
a written location.
JWIRING DIAGRAMSÐXJ-RHD 8W - 1 - 1
Page 914 of 2158

CHIME/BUZZER MODULE
The buzzer or optional chime module sounds an au-
dible warning tone. The tone sounds for seat belt
warning and when the ignition key is in the ignition
switch while the drivers door is open. The tone also
sounds when the ignition key is in the ON position
while the drivers side seat belt is not buckled. Lastly,
the tone sounds when the headlamps are ON when
the ignition is OFF. Refer to Group 8U for system op-
eration.
When the ignition switch is in the RUN or START
position, fuse F87 from fuse 26 in the fuse block sup-
plies power to the chime/buzzer module. Circuit A21
from the ignition switch supplies power to fuse 26.
Circuit L7 from fuse 9 in the fuse block also sup-
plies power to the chime/buzzer module. Circuit A3
from fuse 5 in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
powers fuse 9.
When the parking lamps or headlamps are ON, the
headlamp switch connects circuit G26 with the driv-
ers side door jamb switch. Circuit G26 also connects
to the key-in switch. Circuit M11 connects the key-in
switch to the chime module and the headlamp
switch.
If the headlamps are ON, and the drivers door
opens, ground for the chime/buzzer is on circuit C26
from the headlamp switch through the door jamb
switch to circuit Z1.
If the headlamps are OFF with the key in the ig-
nition while the drivers side door is open, ground for
the chime/buzzer is supplied through the key-in
switch. The ground path is over circuit M11, through
the closed key-in switch to circuit C26. From circuit
C26, the ground path continues through the drivers
door jamb switch to circuit Z1.
Circuit G11 from the buzzer powers the seat belt
warning lamp in the instrument cluster. Circuit Z1
at the instrument cluster provides ground for the
lamp.Circuit G10 from the buzzer connects to the seat
belt switch. When the seat belt switch closes a path
to ground is completed on circuit Z1 and the tone
sounds momentarily.
Circuit Z1 also grounds the chime buzzer module.
HELPFUL INFORMATION
Circuit F87 also powers the instrument cluster and
the headlamp delay module.
DIAGRAM INDEX
Component Page
Cargo Lamp............................8W-44-6
Chime/Buzzer Module......................8W-44-3
Courtesy Lamps.........................8W-44-5
Dome Lamp............................8W-44-6
Door Jamb Switches......................8W-44-7
Fuse 3 (PDC)...........................8W-44-6
Fuse 5 (PDC).........................8W-44-5, 8
Fuse 6 (PDC)...........................8W-44-6
Fuse 9 (Fuse Block).....................8W-44-3, 8
Fuse 16 (PDC)........................8W-44-4, 6
Fuse 25 (Fuse Block)......................8W-44-8
Fuse 26 (Fuse Block)......................8W-44-3
Glove Box Lamp and Switch.................8W-44-5
Headlamp Switch....................8W-44-3, thru 8
Headlamp Delay Module....................8W-44-3
Ignition Switch..........................8W-44-3
Instrument Cluster......................8W-44-3, 9
Instrument Panel Illumination Lamps..........8W-44-8, 9
Key-In Switch...........................8W-44-4
Liftgate Switch..........................8W-44-6
Reading Lamps..........................8W-44-6
Seat Belt Switch.........................8W-44-3
Telltale Connector (Instrument Cluster)...........8W-44-3
Time Delay Relay........................8W-44-4
Underhood Lamp.........................8W-44-4
8W - 44 - 2 8W-44 INTERIOR LIGHTINGÐXJ-RHDJ
Page 1094 of 2158
WIRING DIAGRAMS
CONTENTS
page page
8W-01 GENERAL INFORMATIONÐWIRING
DIAGRAMS...................... 8W-01-1
8W-10 FUSE/FUSE BLOCK........... 8W-10-1
8W-11 POWER DISTRIBUTION........ 8W-11-1
8W-15 GROUND DISTRIBUTION....... 8W-15-1
8W-20 CHARGING SYSTEM.......... 8W-20-1
8W-21 STARTING SYSTEM........... 8W-21-1
8W-30 FUEL/IGNITION.............. 8W-30-1
8W-31 TRANSMISSION CONTROLS.... 8W-31-1
8W-32 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES.......... 8W-32-1
8W-40 INSTRUMENT CLUSTER....... 8W-40-1
8W-41 HORN/CIGAR LIGHTER........ 8W-41-18W-42 AIR CONDITIONING/HEATER.... 8W-42-1
8W-44 INTERIOR LIGHTING.......... 8W-44-1
8W-47 AUDIO SYSTEM.............. 8W-47-1
8W-48 HEATED REAR WINDOW....... 8W-48-1
8W-50 FRONT LIGHTING............ 8W-50-1
8W-51 REAR LIGHTING............. 8W-51-1
8W-52 TURN SIGNALS.............. 8W-52-1
8W-53 WIPERS.................... 8W-53-1
8W-70 SPLICE INFORMATION........ 8W-70-1
8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN OUTS....... 8W-80-1
8W-90 CONNECTOR LOCATIONS...... 8W-90-1
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS........... 8W-95-1
HOW TO USE THIS GROUP
The purpose of this group is to show the electrical
circuits in a clear, simple fashion and to make trou-
bleshooting easier. Components that work together
are shown together. All electrical components used in
a specific system are shown on one diagram. The feed
for a system is shown at the top of the page. All
wires, connectors, splices, and components are shown
in the flow of current to the bottom of the page. Wir-
ing which is not part of the circuit represented is ref-
erenced to another page/section, where the complete
circuit is shown. In addition, all switches, compo-
nents, and modules are shown in theat rest posi-
tion with the doors closed and the key removed
from the ignition.
If a component is part of several different circuits,
it is shown in the diagram for each. For example, the
headlamp switch is the main part of the exterior
lighting, but it also affects the interior lighting and
the chime warning system.
It is important to realize that no attempt is
made on the diagrams to represent components
and wiring as they appear on the vehicle. For
example, a short piece of wire is treated the
same as a long one. In addition, switches and
other components are shown as simply as pos-
sible, with regard to function only.
The wiring diagram show circuits for all wheel-
bases. If there is a difference in systems or compo-
nents between wheel-bases, an identifier is placed
next to the component.
SECTION IDENTIFICATION
Sections in Group 8W are organized by sub-sys-
tems. The sections contain circuit operation descrip-
tions, helpful information, and system diagrams. The
intention is to organize information by system, con-
sistently from year to year.
CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
Section 8W-90 contains Connector Location illus-
trations. The illustrations contain the connector
number and component identification. Connector Lo-
cation charts in Section 8W-90 reference the illustra-
tion number for components and connectors.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the number on the Diagram
pages.
SPLICE LOCATIONS
Splice Location charts in Section 8W-70 show the
entire splice, and provide references to other sections
the splice serves.
Section 8W-95 contains illustrations that show the
general location of the splices in each harness. The
illustrations show the splice by number, and provide
a written location.
JWIRING DIAGRAMSÐÐYJ VEHICLES 8W - 1 - 1
Page 1174 of 2158

INTERIOR LIGHTING
INDEX
page page
Accessory Lamp and Heater Control Panel Lamp . . 1
Combination Buzzer........................ 1
Courtesy Lamps and Dome Lamps............. 1
Diagram Index............................ 2General Information........................ 1
Transmission Range Lamp................... 1
Underhood Lamp.......................... 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Circuit M1 supplies power to the underhood lamp,
dome lamp, right courtesy lamp and left courtesy
lamp. Fuse 12 in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) protects circuit M1. Circuit A4 from fuse 8 in
the PDC supplies voltage to fuse 12 and circuit M1.
Fuse 12 is referred to as the Ignition Off Draw (IOD)
fuse.
COURTESY LAMPS AND DOME LAMPS
Circuit M1 supplies battery voltage to the dome
lamps and the right and left courtesy lamps. Circuit
M2 provides ground for the lamps through either the
case grounded door jamb switches or through the
dimmer switch to circuit Z1.
In the ON position, the dimmer switch connects
circuit M2 to ground on circuit Z1. When a door
opens, the case grounded door jamb switch closes and
provides ground for the lamps on circuit M2.
HELPFUL INFORMATION
²Circuit M1 also supplies voltage for radio memory,
underhood lamp and the ABS data link connector.
UNDERHOOD LAMP
Circuit M1 supplies battery voltage for the under-
hood lamp. A mercury switch in series after the lamp
connects the lamp to ground on circuit Z1. When the
hood is raised, mercury inside the switch moves to a
position where it connects circuit M1 to circuit Z1, il-
luminating the lamp. The underhood lamp is wired
in parallel with other components on circuit M1.
ACCESSORY LAMP AND HEATER CONTROL PANEL
LAMP
Circuit E1 from the dimmer switch supplies bat-
tery voltage to fuse 10 in the fuse block when the
dimmer switch is in the LOW or ON position. Fuse
10 protects circuit E2 which supplies power to the
heater control panel lamp and the accessory lamp.
Circuit Z1 provides ground for each lamp.
TRANSMISSION RANGE LAMP
Circuit E1 from the dimmer switch supplies bat-
tery voltage to fuse 10 in the fuse block when thedimmer switch is in the LOW or ON positions. Fuse
10 protects circuit E2 which supplies power to the
transmission range lamp. The lamp is case grounded.
COMBINATION BUZZER
The combination buzzer module sounds an audible
warning tone. The tone sounds for seat belt warning
and when the key is in the ignition switch while the
drivers door is open. The tone also sounds when the
ignition switch is in the ON position while the driv-
ers side seat belt is not buckled. Refer to Group 8U
for buzzer operation.
Fuses 3 and 9 in the fuse block protect the combi-
nation buzzer. Fuse 3 powers circuit F32 which con-
nects to the buzzer. Circuit A6 from fuse 3 in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) supplies power to
the fuse block for circuit F32.
Circuit G5 from fuse 9 also provides voltage to the
combination buzzer when the ignition switch is in
the START or RUN position. The ignition switch con-
nects circuit A1 from fuse 4 in the PDC to circuit
A21. Circuit A21 connects to the fuse block.
When the key-in switch closes, it connects circuit
G26 to circuit G16. Circuit G16 connects to the driv-
ers side door jamb switch. When the drivers side door
is open and the key-in switch is closed, the case
grounded door jamb switch closes and supplies
ground for the buzzer. Circuit G26 from the combina-
tion buzzer connects to the key-in switch.
Circuit G13 form the buzzer powers the seat belt
warning lamp in the instrument cluster. Circuit Z1
at the instrument cluster provides ground for the
lamp.
Circuit G10 from the buzzer connects to the seat
belt switch. When the seat belt is unlatched, the seat
belt switch closes providing ground on circuit Z1.
Circuit Z1 also grounds the combination buzzer
module.
HELPFUL INFORMATION
²Circuit F32 also powers the stop lamp switch.
²Circuit G5 also provides power for the instrument
cluster gauges and warning lamps, heated rear win-
dow relay and A/C compressor clutch relay. On Cana-
J8W-44 INTERIOR LIGHTINGÐYJ VEHICLES 8W - 44 - 1
Page 1285 of 2158

CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder ac-
cording to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to the Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leak-
age Test Diagnosis chart.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the en-
gine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak. If
an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the fol-
lowing steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for ap-
proximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified, re-
pair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat step (3).
If the oil leak source is not positively identi-
fied at this time, proceed with the air leak detec-
tion test method as follows:
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is de-
tected and identified, repair per service manual pro-
cedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps. In-
stall the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to step 7.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the en-
gine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The fol-
lowing steps should be followed to help pinpoint the
source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
9 - 6 ENGINESJ
Page 1417 of 2158
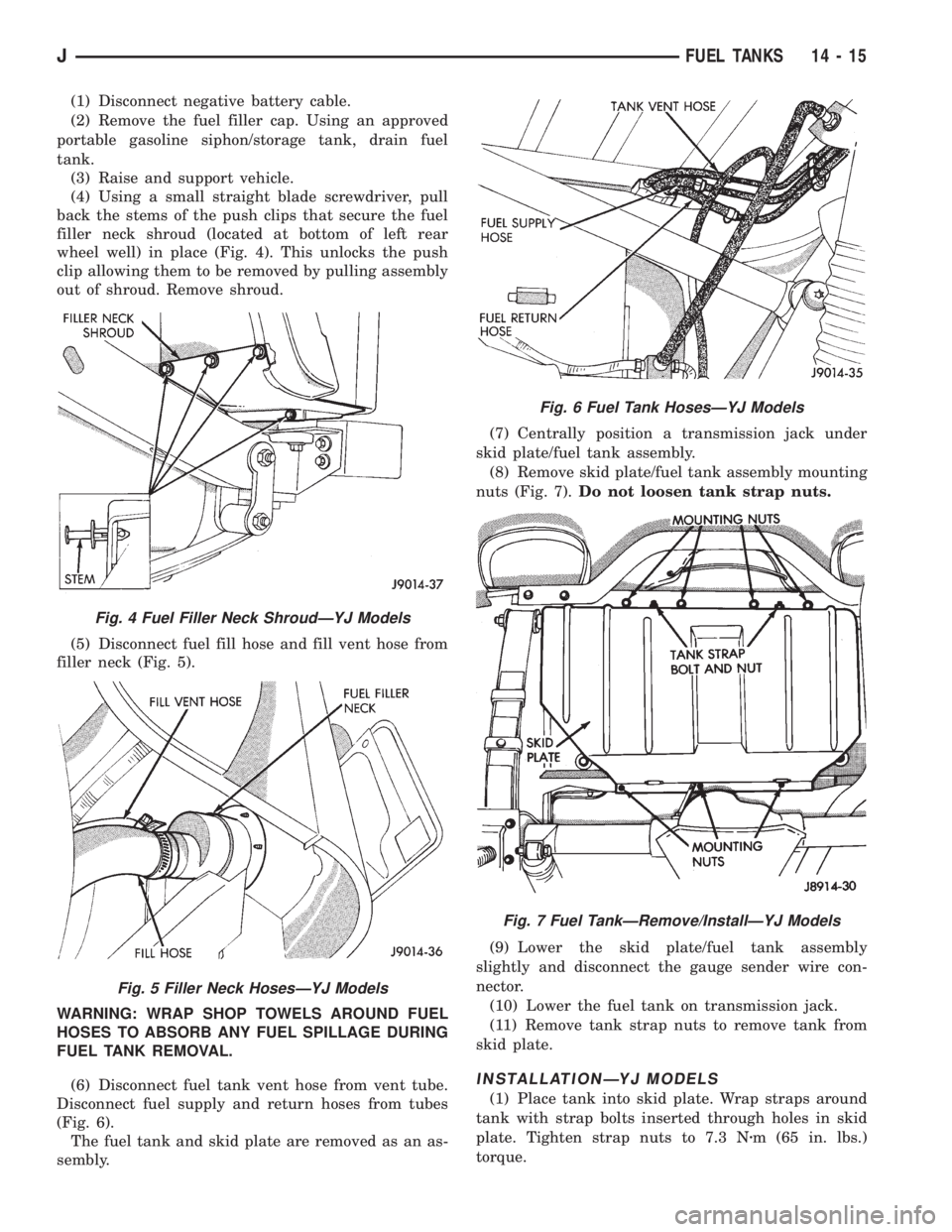
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the fuel filler cap. Using an approved
portable gasoline siphon/storage tank, drain fuel
tank.
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) Using a small straight blade screwdriver, pull
back the stems of the push clips that secure the fuel
filler neck shroud (located at bottom of left rear
wheel well) in place (Fig. 4). This unlocks the push
clip allowing them to be removed by pulling assembly
out of shroud. Remove shroud.
(5) Disconnect fuel fill hose and fill vent hose from
filler neck (Fig. 5).
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND FUEL
HOSES TO ABSORB ANY FUEL SPILLAGE DURING
FUEL TANK REMOVAL.
(6) Disconnect fuel tank vent hose from vent tube.
Disconnect fuel supply and return hoses from tubes
(Fig. 6).
The fuel tank and skid plate are removed as an as-
sembly.(7) Centrally position a transmission jack under
skid plate/fuel tank assembly.
(8) Remove skid plate/fuel tank assembly mounting
nuts (Fig. 7).Do not loosen tank strap nuts.
(9) Lower the skid plate/fuel tank assembly
slightly and disconnect the gauge sender wire con-
nector.
(10) Lower the fuel tank on transmission jack.
(11) Remove tank strap nuts to remove tank from
skid plate.
INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS
(1) Place tank into skid plate. Wrap straps around
tank with strap bolts inserted through holes in skid
plate. Tighten strap nuts to 7.3 Nzm (65 in. lbs.)
torque.
Fig. 4 Fuel Filler Neck ShroudÐYJ Models
Fig. 5 Filler Neck HosesÐYJ Models
Fig. 6 Fuel Tank HosesÐYJ Models
Fig. 7 Fuel TankÐRemove/InstallÐYJ Models
JFUEL TANKS 14 - 15
Page 1517 of 2158

CLEAN AND INSPECTION
(1) Wash all components in clean solvent and dry
with compressed air.
(2) Check for scores, nicks or burrs on the rack pis-
ton finished surface. Slight wear is normal on the
worm gear surfaces.
ASSEMBLE
(1) Install O-ring seal and teflon ring and lubricate
with power steering fluid.
(2) Install worm shaft to rack piston outside of
housing. Fully seat worm shaft to rack piston and
align worm shaft spiral groove with rack piston ball
guide hole (Fig. 33).
WARNING: MAKE SURE ALL RACK PISTON BALLS
ARE REINSTALLED IN THE RACK PISTON. IM-
PROPER INSTALLATION MAY RESULT IN PER-
SONAL INJURY.There are 24 balls in the rack piston circuit,
12 are black and 12 are silver (Chrome). The
black rack piston balls are smaller than the sil-
ver balls. THE BLACK AND SILVER BALLS
MUST BE INSTALLED ALTERNATELY INTO
THE RACK PISTON AND BALL GUIDE. This
procedure will maintain worm shaft preload.
(3) Lubricate and install rack piston balls through
return guide hole while turning wormshaft COUN-
TERCLOCKWISE.
(4) Install remaining balls to guide using grease or
petroleum jelly at each end to hold in place (Fig. 34).
(5) Install guide onto rack piston and return with
clamp and screws. Tighten screws to 58 Nzm (43 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Insert Arbor C-4175 into bore of rack piston.
Hold tool tightly against worm shaft while turning
Fig. 31 Remove and Install Rack Piston
Fig. 32 Remove and Install Seal on Rack Piston
Fig. 33 Installing Balls in Rack Piston
Fig. 34 Balls in the Return Guide
JSTEERING 19 - 33