1993 DODGE TRUCK check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 290 of 1502
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7-11
MOUNT.
BOLT
3/8
SQUARE
HOLE
ACCESSORY
DRIVE
BELT AUTOMATIC
BELT
TENSIONER
J9307-59
Fig.
12
Water
Pump—5.91
Diesel
o ~ " o
rSCREW
(2) v '^ov XN
nJ9107-5N
Fig.
13
Pump
Removal/Installation—5.9L
Diesel
O-RING
SEAL
WATER
PUMP
GROOVE
J9107-6
Fig.
14
Pump
O-ring Seal—5.9L
Diesel
(3) Install accessory drive belt. Refer to the Engine
Accessory Drive Belt section of this group.
(4) Fill cooling system. Refer to Refilling Cooling
System in this section.
(5) Connect battery cable. (6) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
WATER PUMP
BYPASS
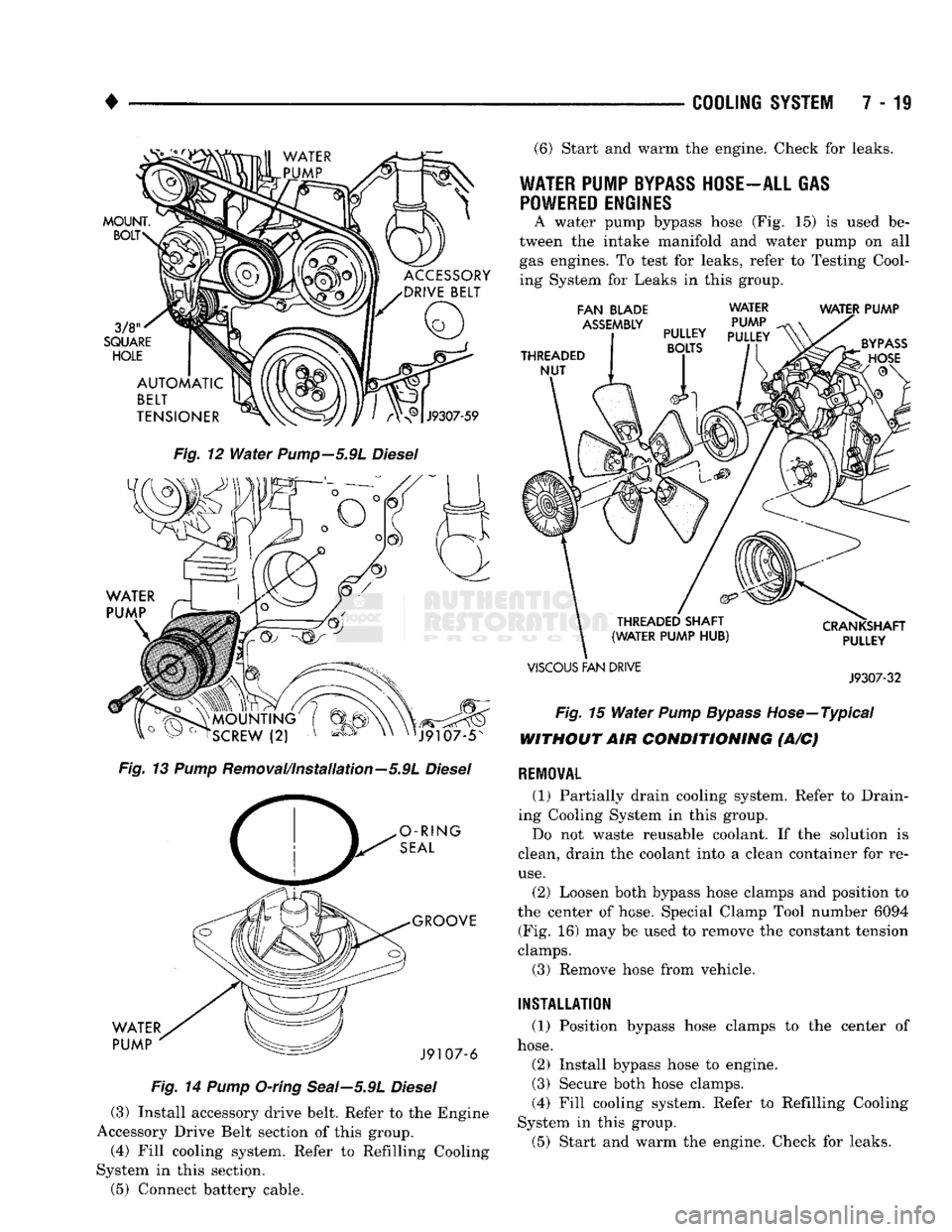
HOSE-ALL GAS POWERED ENGINES
A water pump bypass hose (Fig. 15) is used be
tween the intake manifold and water pump on all gas engines. To test for leaks, refer to Testing Cool
ing System for Leaks in this group.
FAN
BLADE
ASSEMBLY
THREADED
NUT
WATER
PUMP
PULLEY
PULLEY BOLTS WATER PUMP
THREADED SHAFT
(WATER PUMP
HUB)
VISCOUS
FAN DRIVE CRANKSHAFT
PULLEY
J9307-32
Fig.
15
Water
Pump Bypass
Hose—Typical
WITHOUT AIR CONDITIONING (A/C)
RE10WAL
(1) Partially drain cooling system. Refer to Drain
ing Cooling System in this group.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for re
use.
(2) Loosen both bypass hose clamps and position to
the center of hose. Special Clamp Tool number 6094 (Fig. 16) may be used to remove the constant tension
clamps.
(3) Remove hose from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position bypass hose clamps to the center of
hose.
(2) Install bypass hose to engine.
(3) Secure both hose clamps.
(4) Fill cooling system. Refer to Refilling Cooling
System in this group.
(5) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
Page 293 of 1502
7 - 22
COOLING
SYSTEM
•
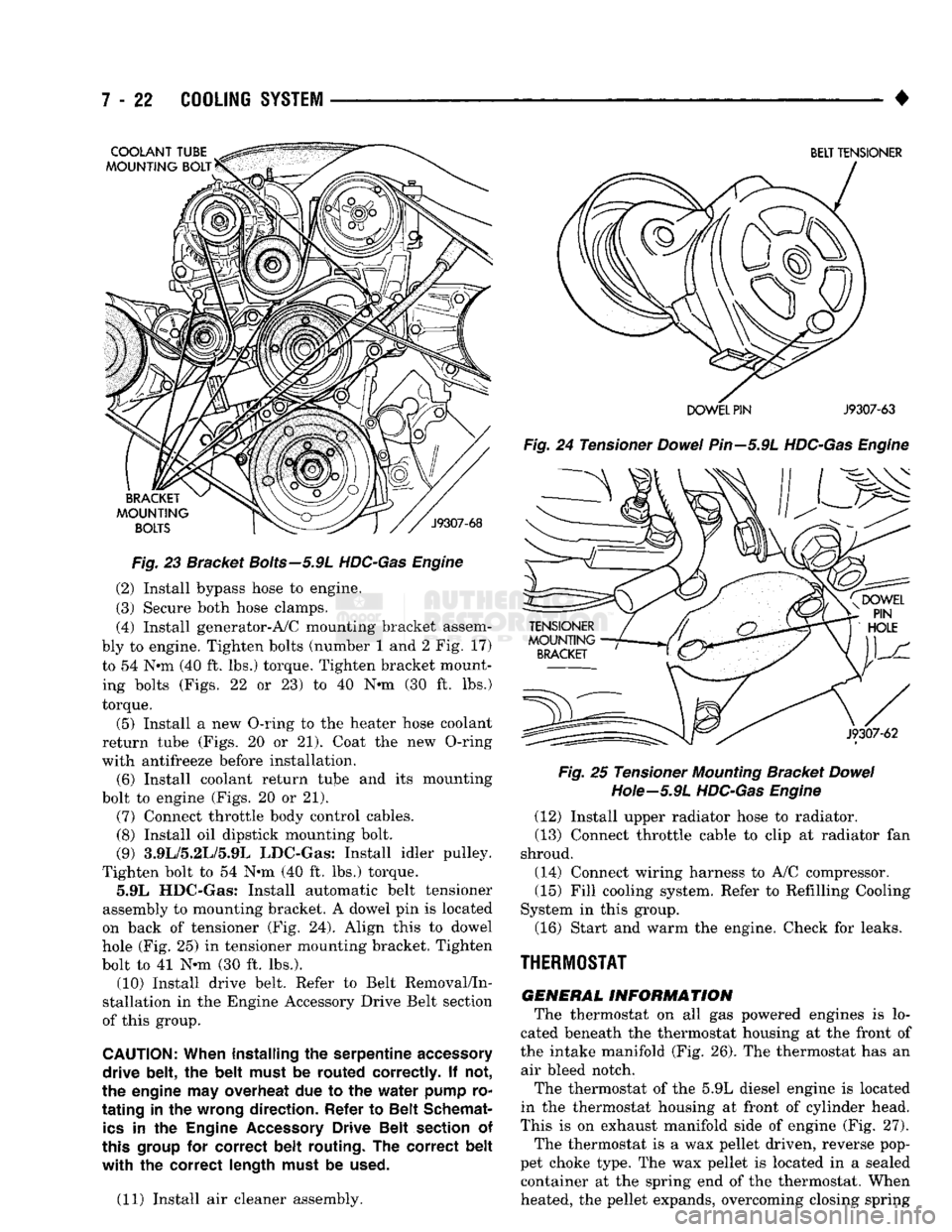
Fig.
23 Bracket
Bolts—5.9L
HDC-Gas Engine
(2) Install bypass hose to engine.
(3) Secure both hose clamps.
(4) Install generator-A/C mounting bracket assem
bly to engine. Tighten bolts (number 1 and 2 Fig. 17)
to 54 Nnn (40 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten bracket mount ing bolts (Figs. 22 or 23) to 40 N-m (30 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Install a new O-ring to the heater hose coolant
return tube (Figs. 20 or 21). Coat the new O-ring
with antifreeze before installation. (6) Install coolant return tube and its mounting
bolt to engine (Figs. 20 or 21). (7) Connect throttle body control cables.
(8) Install oil dipstick mounting bolt.
(9) 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L LDC-Gas: Install idler pulley.
Tighten bolt to 54 Nnn (40 ft. lbs.) torque. 5.9L HDC-Gas: Install automatic belt tensioner
assembly to mounting bracket. A dowel pin is located
on back of tensioner (Fig. 24). Align this to dowel
hole (Fig. 25) in tensioner mounting bracket. Tighten
bolt to 41 N-m (30 ft. lbs.). (10) Install drive belt. Refer to Belt Removal/In
stallation in the Engine Accessory Drive Belt section
of this group.
CAUTION:
When installing
the
serpentine
accessory
drive belt,
the
belt must
be
routed correctly.
If not,
the engine
may
overheat
due to the
water pump
ro
tating
in the
wrong direction. Refer
to
Belt Schemat
ics
in the
Engine
Accessory
Drive Belt section
of
this
group
for
correct belt routing.
The
correct belt
with the
correct length must
be
used.
(11) Install air cleaner assembly.
BELT TENSIONER
DOWEL PIN
J9307-63
Fig.
24 Tensioner
Dowel
Pin—5.9L
HDC-Gas Engine Fig.
25 Tensioner
Mounting
Bracket
Dowel
Hote—5.9L
HDC-Gas Engine
(12) Install upper radiator hose to radiator.
(13) Connect throttle cable to clip at radiator fan
shroud.
(14) Connect wiring harness to A/C compressor. (15) Fill cooling system. Refer to Refilling Cooling
System in this group.
(16) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
THERMOSTAT
GENERAL
INFORMATION
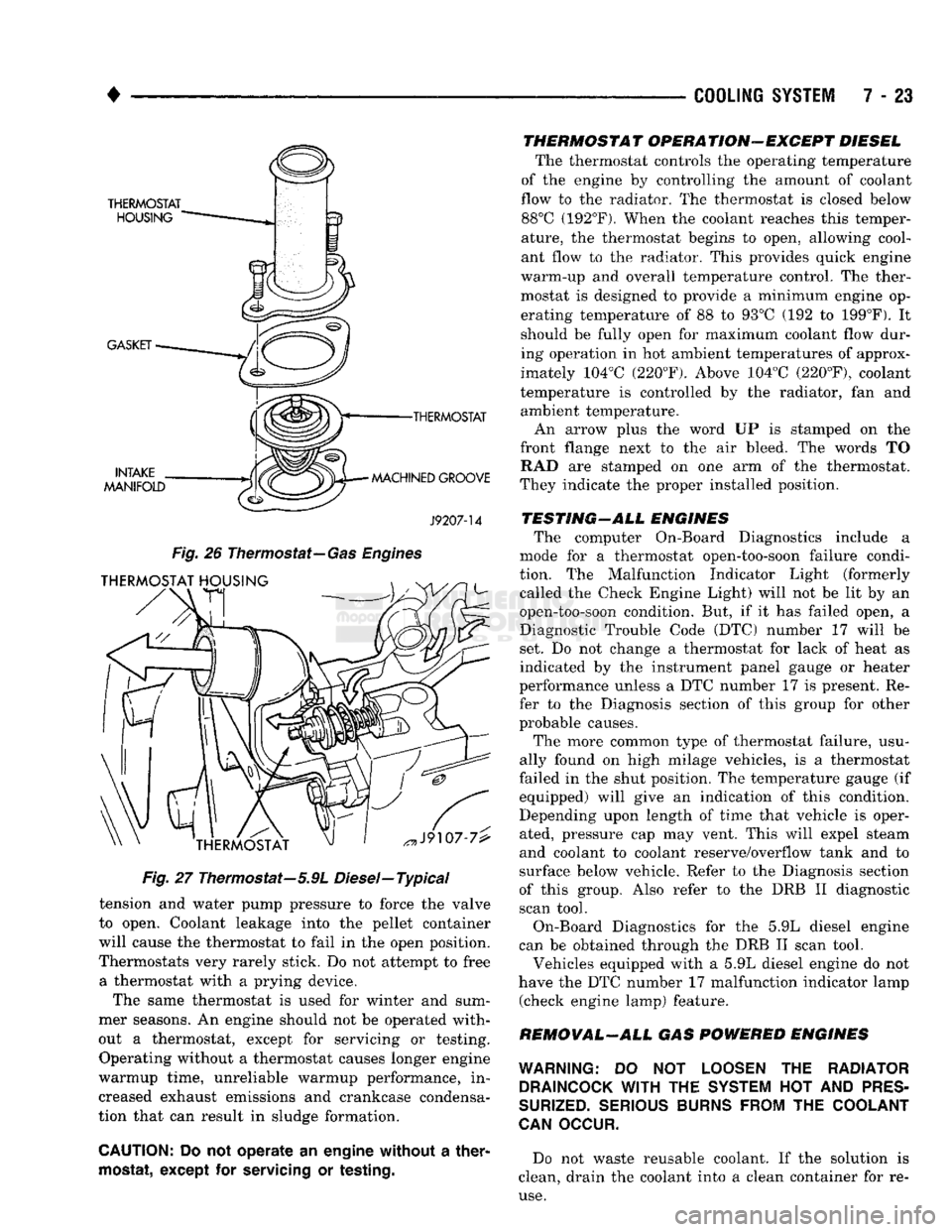
The thermostat on all gas powered engines is lo
cated beneath the thermostat housing at the front of
the intake manifold (Fig. 26). The thermostat has an air bleed notch.
The thermostat of the 5.9L diesel engine is located
in the thermostat housing at front of cylinder head.
This is on exhaust manifold side of engine (Fig. 27). The thermostat is a wax pellet driven, reverse pop
pet choke type. The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at the spring end of the thermostat. When
heated, the pellet expands, overcoming closing spring
Page 294 of 1502
•
COOLING SYSTEM
7 - 23
•THERMOSTAT
MACHINED GROOVE
J9207-14
Fig.
26
Thermostat—
Gas Engines
Fig.
27 Thermostat—5.9L Diesel—Typical
tension and water pump pressure to force the valve
to open. Coolant leakage into the pellet container
will cause the thermostat to fail in the open position.
Thermostats very rarely stick. Do not attempt to free a thermostat with a prying device.
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing. Operating without a thermostat causes longer engine
warmup time, unreliable warmup performance, in
creased exhaust emissions and crankcase condensa
tion that can result in sludge formation.
CAUTION:
Do not operate an engine without a
ther
mostat,
except for
servicing
or
testing.
THERMOSTAT OPERATION-EXCEPT DIESEL
The thermostat controls the operating temperature
of the engine by controlling the amount of coolant
flow to the radiator. The thermostat is closed below 88°C (192°F). When the coolant reaches this temper
ature, the thermostat begins to open, allowing cool
ant flow to the radiator. This provides quick engine
warm-up and overall temperature control. The ther
mostat is designed to provide a minimum engine op erating temperature of 88 to 93°C (192 to 199°F). It
should be fully open for maximum coolant flow dur
ing operation in hot ambient temperatures of approx
imately 104°C (220°F). Above 104°C (220°F), coolant
temperature is controlled by the radiator, fan and ambient temperature.
An arrow plus the word UP is stamped on the
front flange next to the air bleed. The words TO RAD are stamped on one arm of the thermostat.
They indicate the proper installed position.
TESTING-ALL ENGINES The computer On-Board Diagnostics include a
mode for a thermostat open-too-soon failure condi
tion. The Malfunction Indicator Light (formerly called the Check Engine Light) will not be lit by an
open-too-soon condition. But, if it has failed open, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 17 will be
set. Do not change a thermostat for lack of heat as
indicated by the instrument panel gauge or heater
performance unless a DTC number 17 is present. Re
fer to the Diagnosis section of this group for other
probable causes.
The more common type of thermostat failure, usu
ally found on high milage vehicles, is a thermostat
failed in the shut position. The temperature gauge (if equipped) will give an indication of this condition.
Depending upon length of time that vehicle is oper
ated, pressure cap may vent. This will expel steam
and coolant to coolant reserve/overflow tank and to
surface below vehicle. Refer to the Diagnosis section
of this group. Also refer to the DRB II diagnostic
scan tool.
On-Board Diagnostics for the 5.9L diesel engine
can be obtained through the DRB II scan tool.
Vehicles equipped with a 5.9L diesel engine do not
have the DTC number 17 malfunction indicator lamp (check engine lamp) feature.
REMOVAL-ALL GAS POWERED ENGINES
WARNING:
DO NOT
LOOSEN
THE
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH
THE
SYSTEM
HOT AND
PRES
SURIZED.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM
THE
COOLANT
CAN
OCCUR.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for re
use.
Page 296 of 1502
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 25
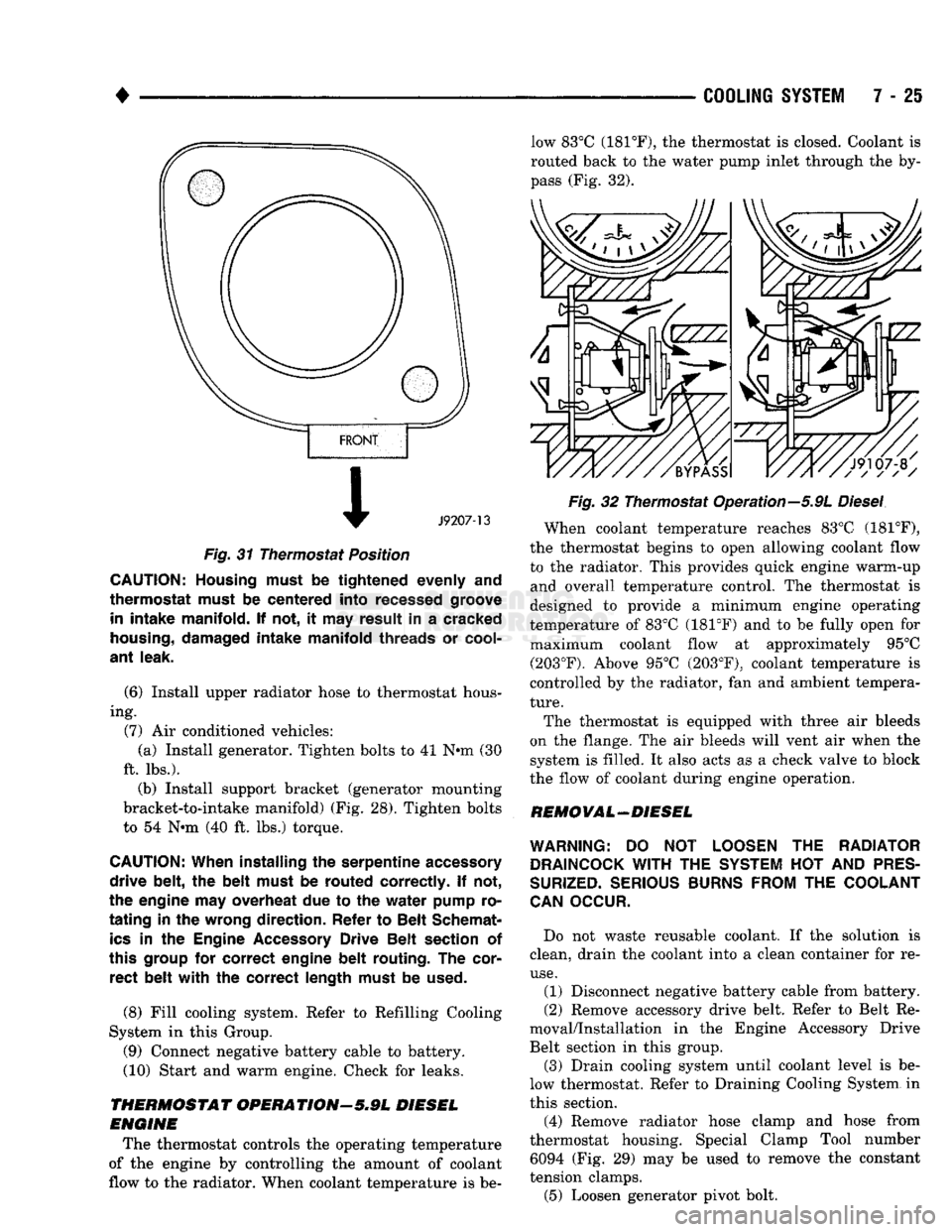
Fig.
31 Thermostat Position
CAUTION; Housing must
be
tightened
evenly and
thermostat must
be
centered into recessed groove in
intake manifold. If not, it may
result
in a
cracked
housing,
damaged intake manifold threads
or
cool
ant
leak.
(6) Install upper radiator hose to thermostat hous
ing. (7) Air conditioned vehicles: (a) Install generator. Tighten bolts to 41 N-m (30
ft. lbs.). (b) Install support bracket (generator mounting
bracket-to-intake manifold) (Fig. 28). Tighten bolts
to 54 N-m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION:
When installing
the
serpentine accessory
drive belt,
the
belt must
be
routed correctly.
If not,
the engine
may overheat due to the
water pump
ro
tating in the
wrong direction. Refer
to
Belt Schemat
ics
in the
Engine
Accessory
Drive Belt section
of
this group
for
correct engine belt routing.
The
cor rect belt with
the
correct length must
be
used.
(8) Fill cooling system. Refer to Refilling Cooling
System in this Group. (9) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(10) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
THERMOSTAT OPERATIONr-5.9L DIESEL
ENGINE
The thermostat controls the operating temperature
of the engine by controlling the amount of coolant
flow to the radiator. When coolant temperature is be low 83°C (181°F), the thermostat is closed. Coolant is
routed back to the water pump inlet through the by
pass (Fig. 32).
Fig.
32 Thermostat Operation—5.9L
Diesel
When coolant temperature reaches 83°C (181°F),
the thermostat begins to open allowing coolant flow
to the radiator. This provides quick engine warm-up and overall temperature control. The thermostat is
designed to provide a minimum engine operating
temperature of 83°C (181°F) and to be fully open for maximum coolant flow at approximately 95°C (203°F). Above 95°C (203°F), coolant temperature is
controlled by the radiator, fan and ambient tempera
ture.
The thermostat is equipped with three air bleeds
on the flange. The air bleeds will vent air when the system is filled. It also acts as a check valve to block
the flow of coolant during engine operation.
REMOVAL-DIESEL
WARNING:
DO NOT
LOOSEN
THE
RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK
WITH
THE
SYSTEM
HOT
AND
PRES
SURIZED.
SERIOUS
BURNS
FROM
THE
COOLANT
CAN
OCCUR.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for re
use.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt. Refer to Belt Re
moval/Installation in the Engine Accessory Drive
Belt section in this group.
(3) Drain cooling system until coolant level is be
low thermostat. Refer to Draining Cooling System in
this section.
(4) Remove radiator hose clamp and hose from
thermostat housing. Special Clamp Tool number 6094 (Fig. 29) may be used to remove the constant
tension clamps.
(5) Loosen generator pivot bolt.
Page 298 of 1502

•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 27 down to -67.7°C (-90°F). A higher percentage will
freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher per centage of antifreeze can cause the engine to over
heat because specific heat of antifreeze is lower than
that of water.
CAUTION:
Richer
antifreeze
mixtures
cannot
be
measured
with
normal
field
equipment
and can
cause
problems
associated
with 100
percent
ethyl
ene-glycol.
COOLANT SELECTION-ADDITIVES The presence of aluminum components in the cool
ing system requires strict corrosion protection. Main
tain coolant at specified level with a mixture of ethylene-glycol based antifreeze and water. Only use an antifreeze containing ALUGARD 340-2
™
such as
Mopar Antifreeze. If coolant becomes contaminated
or looses color, drain and flush cooling system and
fill with correctly mixed solution.
A 0.25 percent emulsifiable oil is added to the ra
diator at the factory to prevent solder corrosion.
CAUTION:
Do not use
coolant
additives
that are
claimed
to
improve
engine
cooling.
COOLANT SERVICE-EXCEPT DIESEL It is recommended that the cooling system be
drained and flushed at 84,000 kilometers (52,500
miles) or 3 years, whichever occurs first. Then every
two years or 48,000 kilometers (30,000 miles), which ever occurs first.
COOLANT SERVICE-DIESEL ENGINE It is recommended that the cooling system be
drained and flushed every 24 months or 38,600 kilo meters (24,000 miles), whichever occurs first.
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK-ROUTINE Do not remove radiator cap for routine coolant
level inspections. The coolant level can be checked at the coolant reserve/overflow tank.
The coolant reserve/overflow system provides a
quick visual method for determining the coolant
level without removing the radiator pressure cap.
With engine idling and at normal operating temper ature, observe coolant level in coolant reserve/over
flow tank. The coolant level should be between the MIN and MAX (diesel engine) or ADD and FULL (gas engines) marks.
ADDING ADDITIONAL COOLANT-ROUTINE Do not remove the radiator cap to add coolant
to the system. When adding coolant to maintain the correct level, do so at the coolant reserve/overflow
tank with a 50/50 mixture of ethylene-glycol anti
freeze (containing Alugard 340-2 ™) and water. Re move the radiator cap only for testing or when
refilling the system after service. Removing cap un necessarily can cause loss of coolant and allow air to
enter system. This produces corrosion.
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK-SERVICE The cooling system is closed and designed to main
tain coolant level to the top of the radiator.
WARNING:
DO
NOT OPEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH
ENGINE RUNNING
OR
WHILE ENGINE
IS HOT
AND COOLING
SYSTEM
IS
UNDER
PRESSURE.
When vehicle servicing requires a coolant level
check in the radiator, drain several ounces of coolant
from the radiator drain cock. Do this while observing
the coolant reserve/overflow system tank. The cool ant level in the reserve/overflow tank should drop
slightly. If not, inspect for a leak between radiator and coolant reserve/overflow system connection. Re
move radiator cap. The coolant level should be to the
top of the radiator. If not and if coolant level in re serve/overflow tank is at the ADD (gas engines) or
MIN (5.9L diesel engine) mark, check for:
• An air leak in the coolant reserve/overflow tank
• An air leak in the radiator filler neck
• Leak in the pressure cap seal to the radiator filler
neck
LOW COOLANT LEVEL-AERATION If the coolant level in the radiator drops below the
top of the radiator core tubes, air will enter the sys
tem. Low coolant level can cause the thermostat pellet
to be suspended in air instead of coolant. This will cause the thermostat to open later, which in turn causes higher coolant temperature. Air trapped in
cooling system also reduces the amount of coolant
circulating in the heater core. This may result in low
heat output.
DEAERATION As the engine operates, air trapped in the cooling
system gathers under the radiator cap. The next time
engine is operated, thermal expansion of coolant will
push trapped air past radiator cap into coolant re serve/overflow tank. Here it escapes to atmosphere in
the tank. When engine cools down the coolant, it will
be drawn from reserve/overflow tank into radiator to replace removed air.
DRAINING
COOLING
SYSTEM
WARNING:
DO NOT
REMOVE
THE
CYLINDER BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS
OR
LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN PLUG
WITH
SYSTEM
HOT AND
UNDER
PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS
FROM
COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Page 300 of 1502
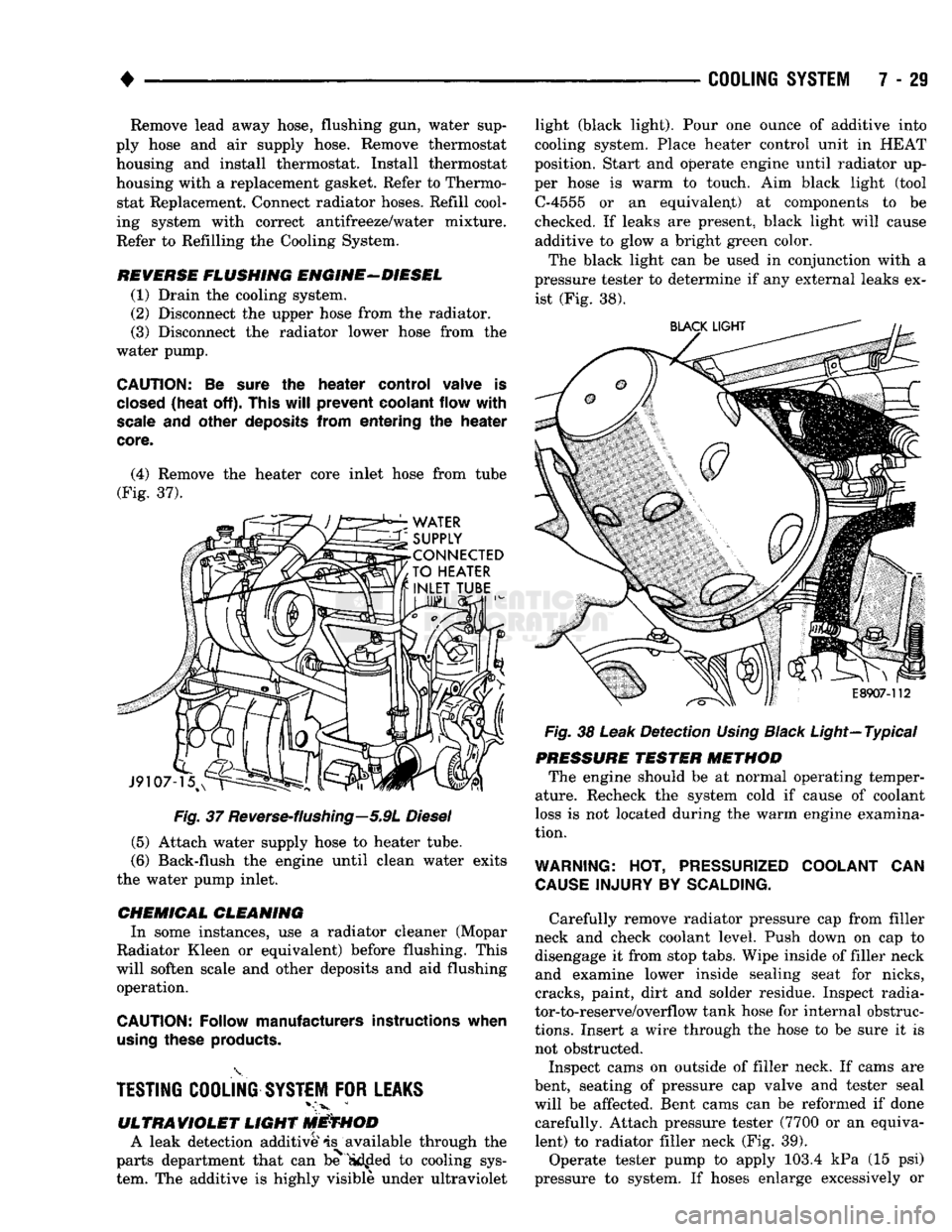
+
Fig.
37
Reverse-flushing—5.9L
Diesel
(5) Attach water supply hose to heater tube.
(6) Back-flush the engine until clean water exits
the water pump inlet.
CHEMICAL
CLEANING
In some instances, use a radiator cleaner (Mopar
Radiator Kleen or equivalent) before flushing. This
will soften scale and other deposits and aid flushing operation.
CAUTION;
Follow manufacturers instructions when
using
these
products.
TESTING
COOLING
SYSTEM
FOR
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET
LIGHT
METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be Sidfled to cooling sys
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 29
Fig.
38
Leak
Detection
Using
Black
Light—Typical
PRESSURE
TESTER
METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina
tion.
WARNING:
HOT,
PRESSURIZED
COOLANT
CAN
CAUSE
INJURY
BY
SCALDING.
Carefully remove radiator pressure cap from filler
neck and check coolant level. Push down on cap to
disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of filler neck and examine lower inside sealing seat for nicks,
cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect radia
tor-to-reserve/overflow tank hose for internal obstruc
tions.
Insert a wire through the hose to be sure it is
not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of filler neck. If cams are
bent, seating of pressure cap valve and tester seal
will be affected. Bent cams can be reformed if done carefully. Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to radiator filler neck (Fig. 39).
Operate tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
pressure to system. If hoses enlarge excessively or
Remove lead away hose, flushing gun, water sup
ply hose and air supply hose. Remove thermostat housing and install thermostat. Install thermostat
housing with a replacement gasket. Refer to Thermo stat Replacement. Connect radiator hoses. Refill cool
ing system with correct antifreeze/water mixture.
Refer to Refilling the Cooling System.
REVERSE
FLUSHING
ENGINE-DIESEL
(1) Drain the cooling system. (2) Disconnect the upper hose from the radiator.
(3) Disconnect the radiator lower hose from the
water pump.
CAUTION;
Be
sure
the
heater
control valve is
closed
(heat
off).
This
will
prevent coolant flow
with
scale
and other
deposits
from entering the
heater
core.
(4) Remove the heater core inlet hose from tube
(Fig. 37). light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator up
per hose is warm to touch. Aim black light (tool C-4555 or an equivalent) at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks ex ist (Fig. 38).
Page 301 of 1502

7 - 30
COOLING
SYSTEM
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
Fig.
39
Pressure
Testing
Cooling
System—Typical bulges while testing, replace as necessary. Observe
gauge pointer and determine condition of cooling sys
tem according to following criteria:
Holds Steady: If pointer remains steady for two
minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in sys
tem. However, there could be an internal leak that does not appear with normal system test pressure. If
it is certain that coolant is being lost and leaks can
not be detected, inspect for interior leakage or per
form Internal Leakage Test.
Drops Slowly: Indicates a small leak or seepage is
occurring. Examine all connections for seepage or
slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect radiator,
hoses,
gasket edges and heater. Seal small leak holes
with a Sealer Lubricant (or equivalent). Repair leak
holes and inspect system again with pressure ap
plied.
Drops Quickly: Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine system for external leakage. If
leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.
INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION Remove engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil.
An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done, re
move engine dipstick and inspect for water globules.
Also inspect transmission dipstick for water globules and transmission fluid cooler for leakage.
WARNING:
WITH
PRESSURE TESTER TOOL
7700
INSTALLED
ON
RADIATOR,
DO
NOT ALLOW
PRES
SURE
TO
EXCEED
110 KPA (20
PSI). PRESSURE
WILL
BUILD
UP
QUICKLY
IF A
COMBUSTION LEAK
IS
PRESENT.
TO
RELEASE
PRESSURE,
ROCK
TESTER
FROM SIDE
TO
SIDE. WHEN REMOVING
TESTER,
DO NOT
TURN TESTER MORE THAN
1/2
TURN
IF
SYSTEM
IS
UNDER
PRESSURE.
Operate engine without pressure cap on radiator
until thermostat opens. Attach a Pressure Tester to
filler neck. If pressure builds up quickly it indicates a combustion leak exists. This is usually the result of
a cylinder head gasket leak or crack in engine. Re
pair as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi). Fluctuation of gauge pointer indicates compression or
combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter, do not remove spark plug cables or short
out cylinders (non-diesel engines) to isolate compres
sion leak.
If the needle on dial of pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an ab normal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
exhaust pipe may indicate a faulty cylinder head
gasket, cracked engine cylinder block or cylinder
head. A convenient check for exhaust gas leakage into
cooling system is provided by a commercially avail able Block Leak Check tool. Follow manufacturers
instructions when using this product.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST-WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING:
DO NOT
REMOVE CYLINDER BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS
OR
LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK
WITH
SYSTEM
HOT AND
UNDER PRES
SURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN
OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow thermostat re
moval. Refer to Thermostat Replacement. Disconnect
water pump drive belt. Add coolant to radiator to bring level to within 6.3
mm (1/4 in) of top of thermostat housing.
CAUTION:
Avoid
overheating.
Do not
operate
en
gine
for an
excessive
period
of
time.
Open
drain-
cock
immediately
after
test
to
eliminate
boil
over.
Start engine and accelerate rapidly three times, to
approximately 3000 rpm while observing coolant. If
internal engine combustion gases% are leaking into
cooling system, bubbles will appear in coolant. If
bubbles do not appear, internal combustion gas leak age is not present.
COOLANT
RESERVE/0WERFL0W
SYSTEM
The coolant reserve/overflow system (Fig. 40 or 41)
works in conjunction with the radiator pressure cap.
Page 302 of 1502
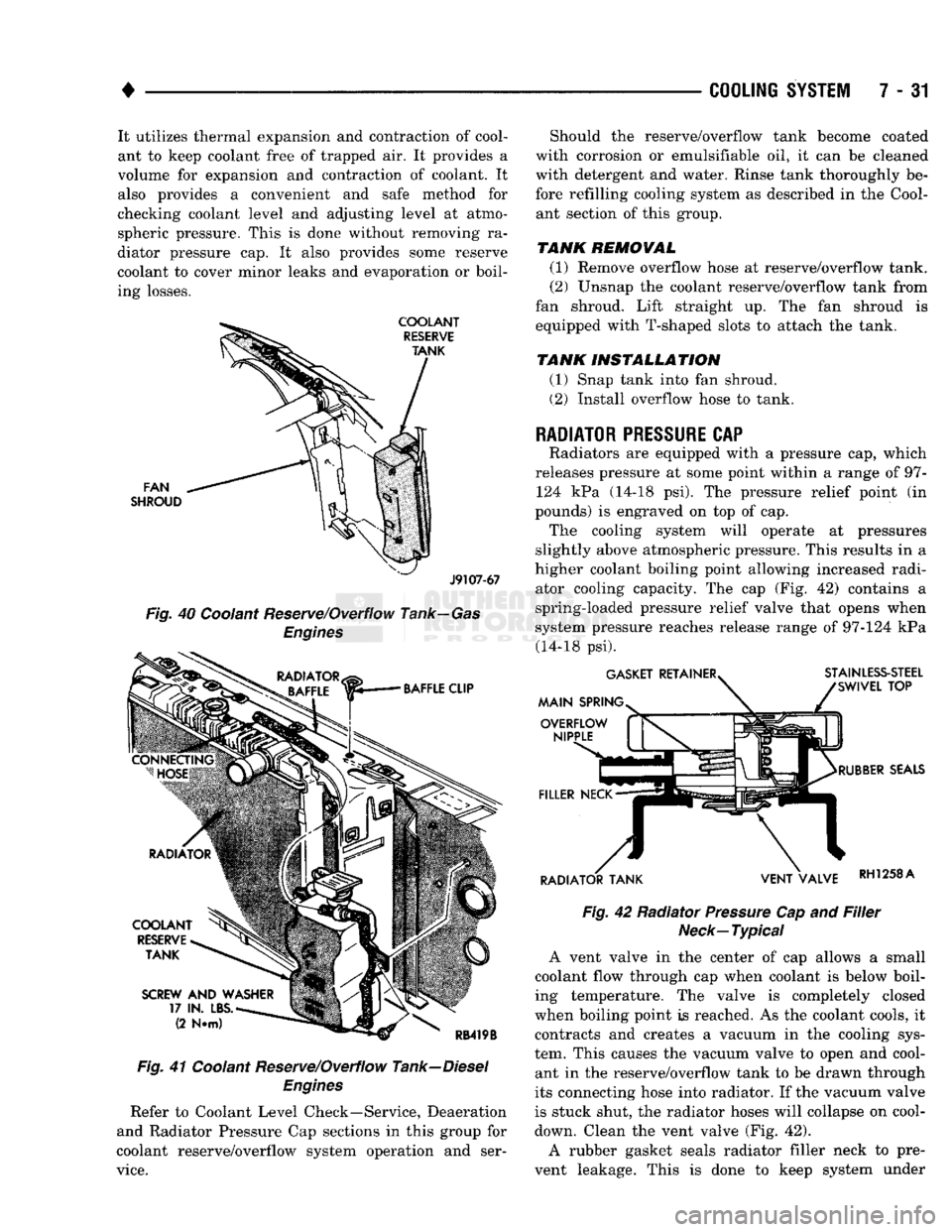
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 31 It utilizes thermal expansion and contraction of cool
ant to keep coolant free of trapped air. It provides a
volume for expansion and contraction of coolant. It
also provides a convenient and safe method for
checking coolant level and adjusting level at atmo
spheric pressure. This is done without removing ra
diator pressure cap. It also provides some reserve
coolant to cover minor leaks and evaporation or boil
ing losses.
FAN
SHROUD
J9107-67
Fig.
40 Coolant Reserve/Overflow Tank—Gas
Engines
Fig.
41 Coolant Reserve/Overflow Tank—Diesel
Engines
Refer to Coolant Level Check—Service, Deaeration
and Radiator Pressure Cap sections in this group for
coolant reserve/overflow system operation and ser
vice.
Should the reserve/overflow tank become coated
with corrosion or emulsifiable oil, it can be cleaned
with detergent and water. Rinse tank thoroughly be
fore refilling cooling system as described in the Cool ant section of this group.
TANK REMOVAL
(1) Remove overflow hose at reserve/overflow tank.
(2) Unsnap the coolant reserve/overflow tank from
fan shroud. Lift straight up. The fan shroud is
equipped with T-shaped slots to attach the tank.
TANK INSTALLATION
(1) Snap tank into fan shroud.
(2) Install overflow hose to tank.
RADIATOR
PRESSURE
CAP
Radiators are equipped with a pressure cap, which
releases pressure at some point within a range of 97- 124 kPa (14-18 psi). The pressure relief point (in
pounds) is engraved on top of cap. The cooling system will operate at pressures
slightly above atmospheric pressure. This results in a
higher coolant boiling point allowing increased radi ator cooling capacity. The cap (Fig. 42) contains a
spring-loaded pressure relief valve that opens when
system pressure reaches release range of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
Fig.
42 Radiator
Pressure
Cap and
Filler
Neck—Typical
A vent valve in the center of cap allows a small
coolant flow through cap when coolant is below boil
ing temperature. The valve is completely closed
when boiling point is reached. As the coolant cools, it contracts and creates a vacuum in the cooling sys
tem. This causes the vacuum valve to open and cool ant in the reserve/overflow tank to be drawn through
its connecting hose into radiator. If the vacuum valve
is stuck shut, the radiator hoses will collapse on cool-
down. Clean the vent valve (Fig. 42).
A rubber gasket seals radiator filler neck to pre
vent leakage. This is done to keep system under