1993 DODGE TRUCK automatic transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmission fluidPage 1104 of 1502
•
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION—32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
21-103
TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
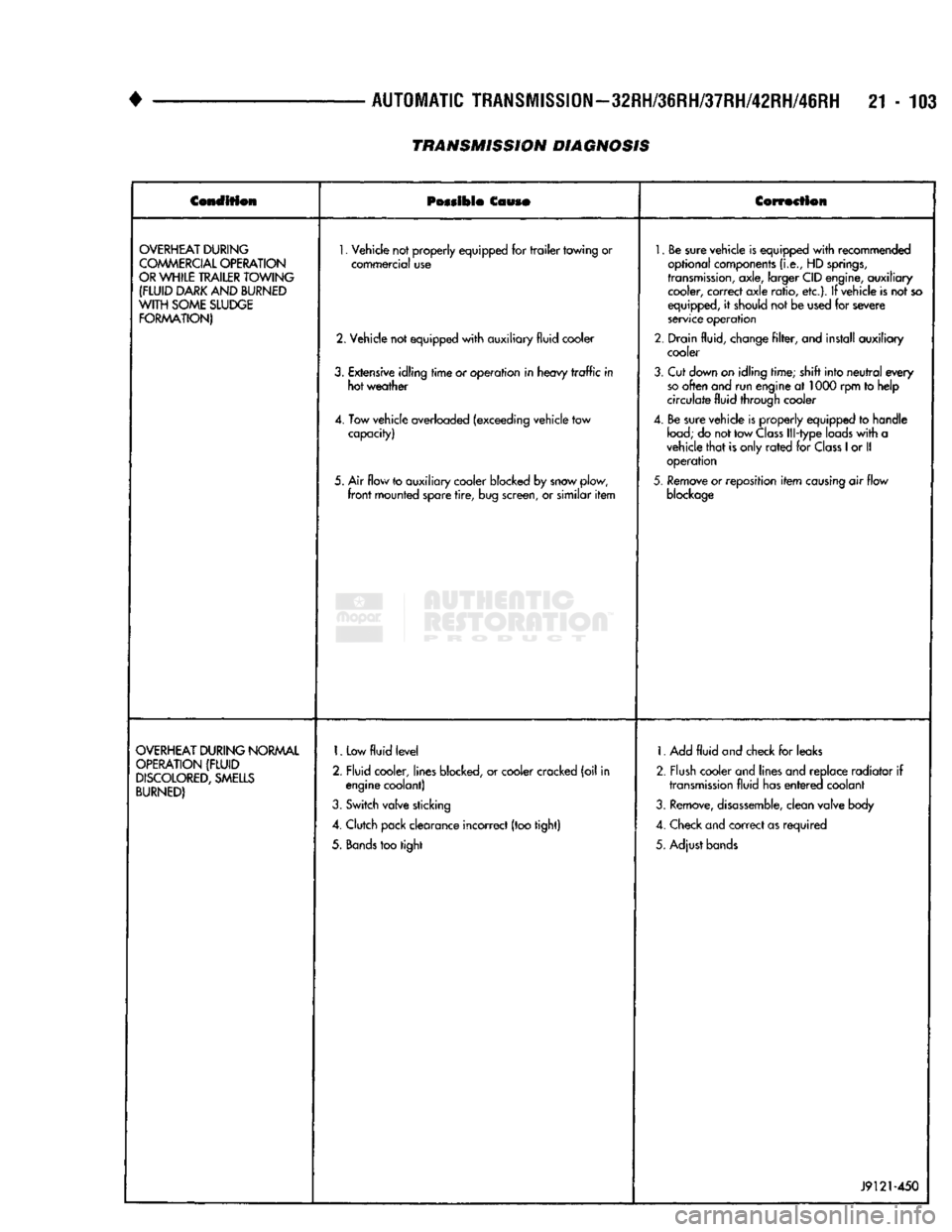
Condition
Possible
Couso
Correction
OVERHEAT
DURING
COMMERCIAL
OPERATION
OR
WHILE
TRAILER
TOWING
(FLUID
DARK
AND
BURNED
WITH
SOME
SLUDGE
FORMATION)
1.
Vehicle not properly equipped for
trailer
towing or
commercial use
2. Vehicle not equipped
with
auxiliary fluid cooler
3.
Extensive idling
time
or operation in heavy
traffic
in hot weather
4. Tow vehicle overloaded (exceeding vehicle tow capacity)
5. Air flow to auxiliary cooler blocked by snow plow,
front
mounted spare
tire,
bug screen, or similar
item
1.
Be sure vehicle is equipped
with
recommended
optional components
(i.e.,
HD
springs,
transmission,
axle, larger CID engine, auxiliary cooler, correct axle ratio, etc.). If vehicle is not so
equipped, it should not be used for severe
service operation
2. Drain fluid, change
filter,
and install auxiliary cooler
3.
Cut down on idling time; shift into
neutral
every
so
often and run engine at 1000 rpm to help
circulate fluid through cooler
4. Be sure vehicle is properly equipped to handle
load;
do not tow
Class
Ill-type loads
with
a
vehicle
that
is only
rated
for
Class
1
or II operation
5.
Remove or reposition
item
causing
air flow
blockage
OVERHEAT
DURING
NORMAL
OPERATION
(FLUID
DISCOLORED,
SMELLS
BURNED)
1.
Low
fluid
level
2. Fluid cooler, lines blocked, or cooler cracked (oil in engine coolant)
3.
Switch valve sticking
4. Clutch pack clearance incorrect (too tight)
5.
Bands
too tight 1. Add
fluid
and check for leaks
2. Flush cooler and lines and replace radiator if
transmission
fluid has
entered
coolant
3.
Remove,
disassemble,
clean valve body
4. Check and correct as required
5. Adjust bands
J9121-450
Page 1105 of 1502
21 - 104
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION—32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
•
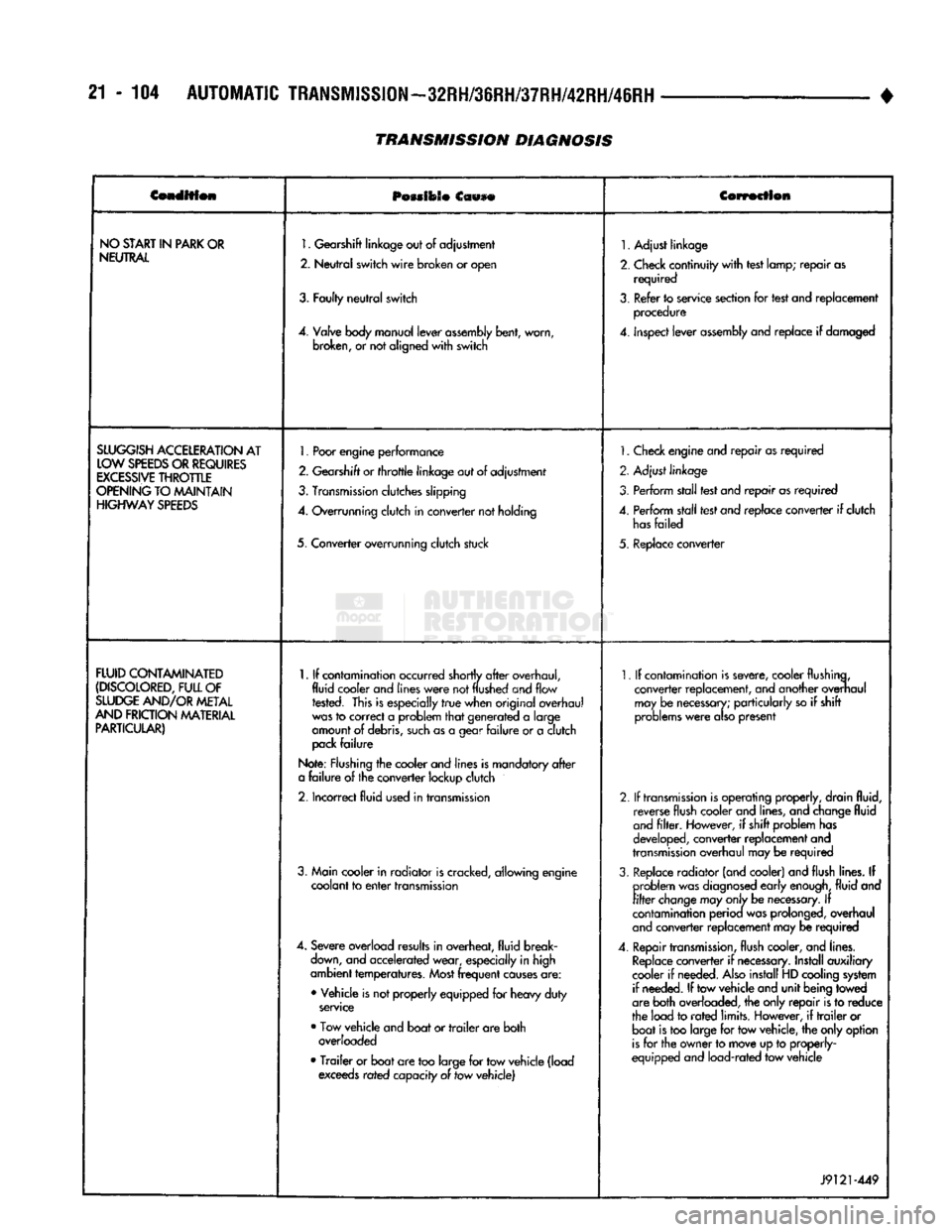
Condition
POMIOSO
Ccwse
Correction
NO
START
IN
PARK
OR
NEUTRAL
1.
Gearshift
linkage
out
of
adjustment
2.
Neutral
switch
wire
broken
or
open
3.
Faulty
neutral
switch
4.
Valve
body
manual
lever
assembly
bent,
worn,
broken,
or not
aligned
with
switch
1.
Adjust linkage
2.
Check continuity
with
test lamp; repair as required
3.
Refer to service section for test and replacement procedure
4.
inspect lever
assembly
and replace if damaged
SLUGGISH
ACCELERATION
AT
LOW
SPEEDS
OR
REQUIRES
EXCESSIVE
THROTTLE
OPENING
TO MAINTAIN
HIGHWAY
SPEEDS
1.
Poor
engine
performance
2.
Gearshift
or
throttle
linkage
out of adjustment
3.
Transmission
clutches slipping
4.
Overrunning clutch in converter not holding
5. Converter overrunning clutch stuck
1.
Check engine and repair as required
2. Adjust linkage
3. Perform stall test and repair as required
4.
Perform stall test and replace converter if clutch
has
failed
5. Replace converter
FLUID
CONTAMINATED
(DISCOLORED,
FULL
OF
SLUDGE
AND/OR
METAL
AND
FRICTION
MATERIAL
PARTICULAR)
1.
If contamination occurred shortly
after
overhaul,
fluid cooler and
lines
were
not
flushed
and flow rested. This is especially
true
when original overhaul
was
to correct a problem
that
generated a large
amount of debris,
such
as a gear
failure
or a clutch
pack
failure
Note: Flushing the cooler and lines is mandatory
after
a
failure
of the converter lockup clutch
2.
Incorrect fluid used in transmission
3. Main cooler in radiator is cracked, allowing engine coolant to
enter
transmission
4.
Severe overload results in overheat, fluid break
down,
and accelerated wear, especially in high
ambient temperatures.
Most
frequent
causes
are:
• Vehicle is not properly equipped for heavy duty
service
• Tow vehicle and boat or
trailer
are both overloaded
•
Trailer
or boat are too large for tow vehicle (load exceeds rated capacity of tow vehicle)
1.
If contamination is severe, cooler flushing,
converter replacement, and another overhaul may be
necessary;
particularly so if shift
problems
were
also
present
2.
If
transmission
is operating properly, drain fluid, reverse flush cooler and lines, and change fluid
and
filter.
However, if shift problem has
developed, converter replacement and
transmission
overhaul may be required
3.
Replace radiator (and cooler) and flush lines. If problem was
diagnosed
early
enough,
fluid and
filter
change
may
only
be
necessary.
If
contamination perioa was prolonged, overhaul
and
converter replacement may be required
4.
Repair
transmission,
flush cooler, and lines.
Replace
converter if
necessary.
Install auxiliary
cooler if needed.
Also
install HD cooling system if needed. If tow vehicle and unit being towed
are both overloaded, the only repair is to reduce
the load to
rated
limits. However, if
trailer
or boat is too large for tow vehicle, the only option
is
for the owner to move up to properly-
equipped and load-rated tow vehicle
J9121-449
TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
Page 1106 of 1502
•
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION—32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
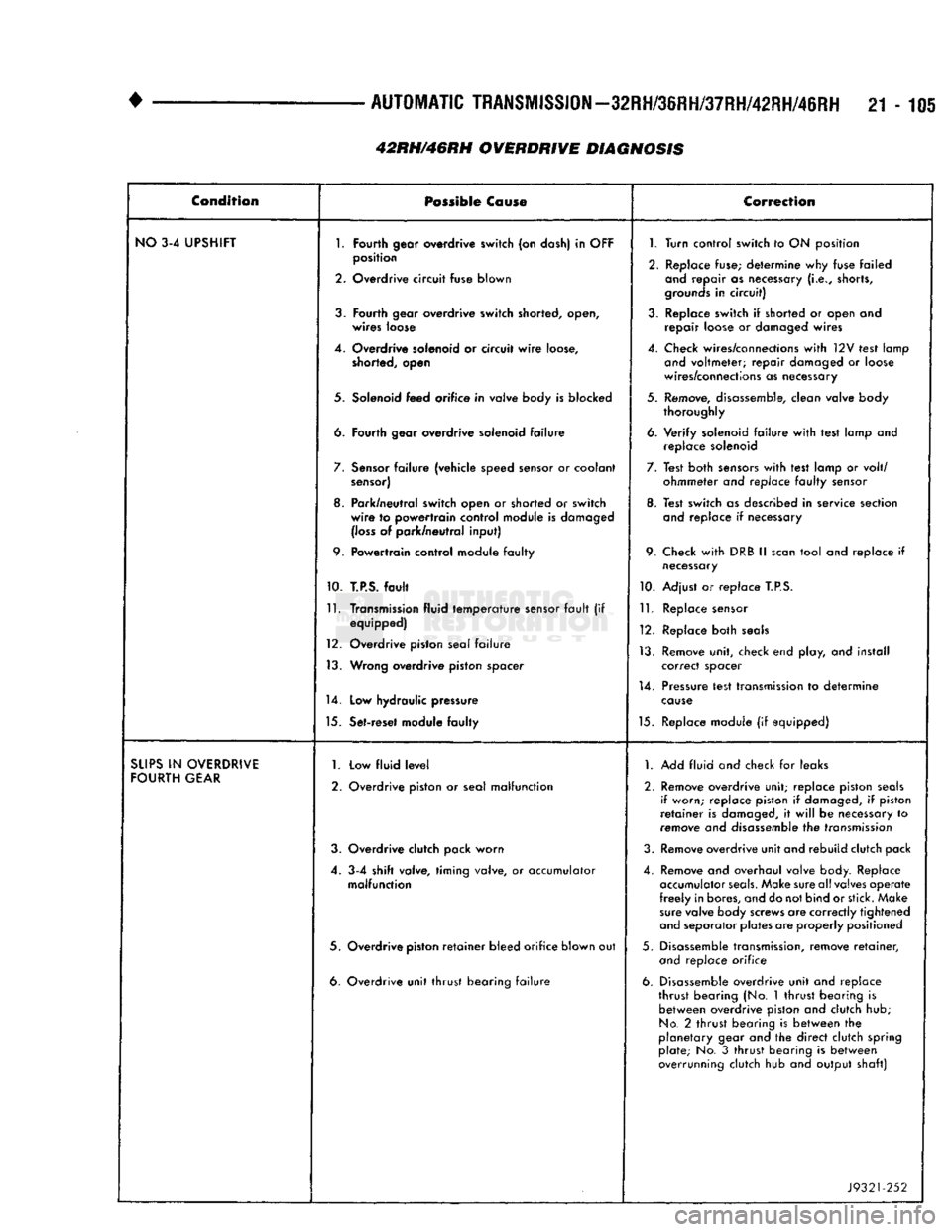
21-105 Condition
Possible
Co
use
Correction
NO
3-4 UPSHIFT
1.
Fourth
gear overdrive
switch
(on dash) in
OFF
1.
Turn control
switch
to ON position
2.
position
Overdrive
circuit
fuse
blown
2. Replace fuse; determine why fuse failed
and
repair as necessary
(i.e.,
shorts,
grounds
in
circuit)
3.
Fourth
gear
overdrive
switch
shorted, open,
wires
loose 3. Replace switch if shorted or open and
repair loose or damaged wires
4. Overdrive solenoid or circuit
wire
loose,
shorted, open 4. Check wires/connections
with
12V test lamp
and
voltmeter; repair damaged or loose
wires/connections as necessary
5. Solenoid
feed
orifice
in valve body is
blocked
5. Remove, disassemble, clean valve body
thoroughly
6.
Fourth
gear
overdrive
solenoid
failure
6. Verify solenoid
failure
with
test lamp and
replace solenoid
7.
Sensor
failure
(vehicle speed sensor or coolant
sensor)
7. Test both
sensors
with
test lamp or volt/
ohmmeter and replace
faulty
sensor
8. Park/neutral switch open or
shorted
or
switch
wire
to
powertrain
control
module is damaged
(loss
of park/neutral
input)
8. Test switch as described in service section
and
replace if necessary
9.
Powertrain
control module
faulty
9. Check
with
DRB II
scan
tool and replace if
necessary
10.
T.P.S.
fault
10. Adjust or replace
T.P.S.
11.
Transmission fluid
temperature
sensor
fault
(if equipped)
12. Overdrive piston seal
failure
13. Wrong
overdrive
piston
spacer
11.
Replace sensor
12. Replace both
seals
13. Remove unit, check end play, and install correct spacer
14.
Low
hydraulic pressure 14. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause
15. Set-reset module
faulty
15. Replace module (if equipped)
SUPS
IN
OVERDRIVE
FOURTH
GEAR
1.
2. Low
fluid
level
Overdrive piston or seal
malfunction
1.
Add fluid and check for leaks
2. Remove overdrive unit; replace piston
seals
if worn; replace piston if damaged, if piston
retainer
is damaged, it
will
be necessary to
remove and disassemble the transmission
3. Overdrive clutch pack
worn
3. Remove overdrive unit and rebuild clutch pack
4. 3-4
shift
valve,
timing
valve, or accumulator
malfunction
4. Remove and overhaul valve body. Replace
accumulator
seals.
Make sure all valves operate
freely
in bores, and do not bind or stick. Make
sure
valve body screws are correctly tightened
and
separator plates are properly positioned
5. Overdrive
piston
retainer
bleed
orifice
blown out 5. Disassemble transmission, remove
retainer,
and
replace orifice
6. Overdrive
unit
thrust
bearing
failure
6. Disassemble overdrive unit and replace
thrust bearing (No. 1 thrust bearing is between overdrive piston and clutch hub;
No.
2 thrust bearing is between the
planetary gear and the direct clutch spring plate; No. 3
thrust
bearing is between
overrunning clutch hub and output shaft)
J9321-252
42RH/46RH OVERDRIVE DIAGNOSIS
Page 1107 of 1502
21-106
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION—32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
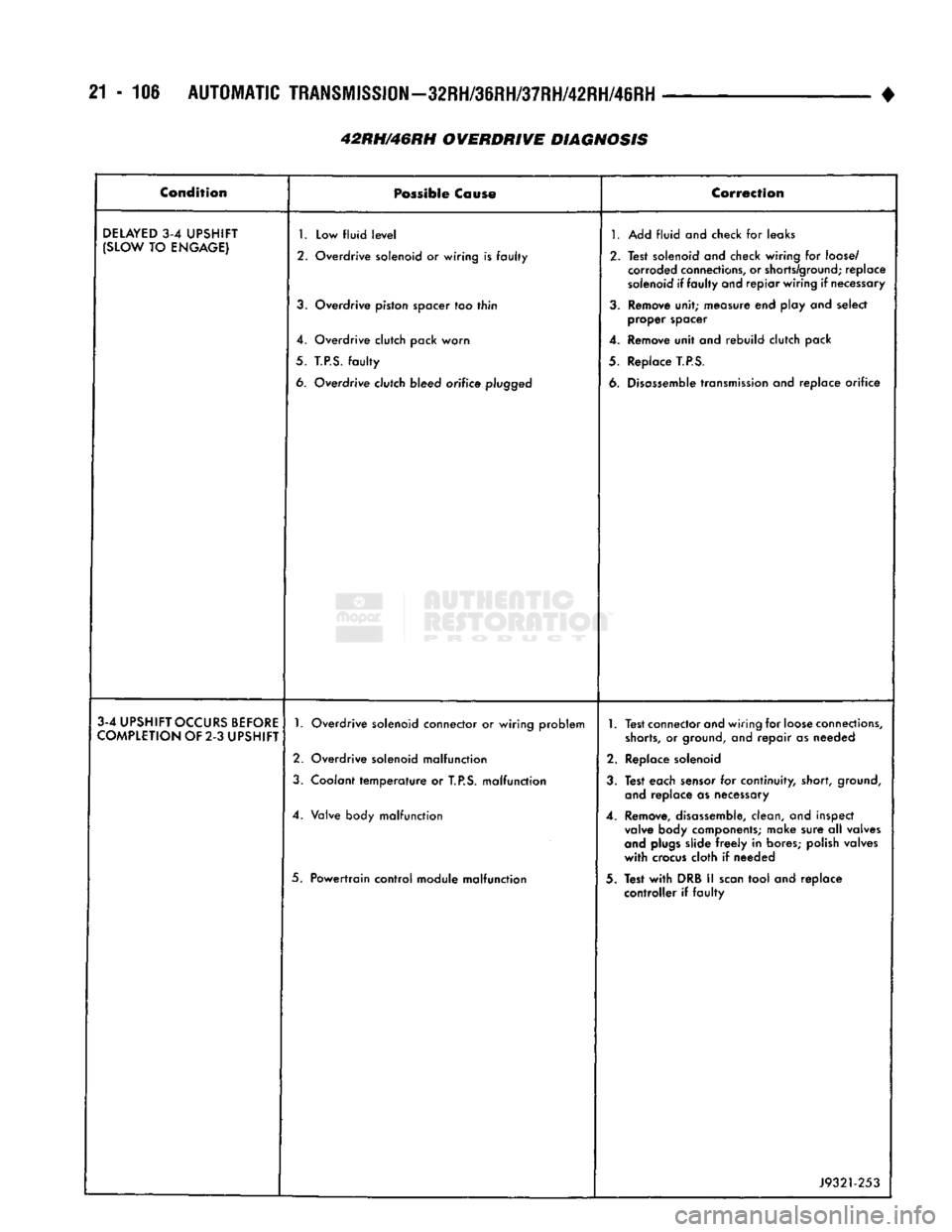
42RH/46RH OVERDRIVE DIAGNOSIS •
Condition
Possible
Cause
Correction
DELAYED
3-4
UPSHIFT
(SLOW
TO
ENGAGE)
1.
Low fluid
level
2. Overdrive solenoid or wiring is faulty
3.
Overdrive piston spacer too thin
4. Overdrive clutch pack worn
5.
T.P.S.
faulty
6. Overdrive clutch bleed orifice
plugged
1.
Add fluid and check for leaks
2. Test solenoid and check wiring for
loose/
corroded
connections,
or
shorts/ground;
replace
solenoid
if faulty and repiar wiring if
necessary
3.
Remove unit; measure end play and select proper spacer
4. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack
5. Replace
T.P.S.
6.
Disassemble
transmission
and replace orifice
3-4
UPSHIFT
OCCURS
BEFORE
COMPLETION
OF 2-3
UPSHIFT
1.
Overdrive solenoid connector or wiring problem
2. Overdrive solenoid malfunction
3.
Coolant temperature or
T.P.S.
malfunction
4. Valve body malfunction
5. Powertrain control module malfunction
1.
Test connector and wiring for
loose
connections,
shorts,
or
ground,
and repair as needed
2. Replace solenoid
3.
Test each
sensor
for continuity, short,
ground,
and
replace as necessary
4. Remove,
disassemble,
clean, and inspect
valve
body components; make sure all valves
and
plugs
slide
freely
in bores; polish valves
with
crocus
cloth if needed
3. Test
with
DRB II
scan
tool and replace controller if faulty
J9321-253
Page 1131 of 1502

21
-
130
IN-VEHICLE
SERVICE-~32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/4iRH
•
IN-VEHICLE
SERVICE-32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
INDEX
page
Aluminum Thread Repair
141
Checking
Fluid
Level
130
Extension Housing Bushing
and
Output
Shaft
Bearing
Service-32RH/36RH/37RH
... .
135
Extension Housing Yoke Seal Replacement
....
135
Fluid
and Filter
Change
130
Front
Band
Adjustment
133
Gearshift Linkage
Adjustment
130
Governor
and
Park Gear Service—
32RH/36RH/37RH
137
Governor
and
Park Lock Service—42RH/46RH
.
138
CHECKING
FLUID LEVEL
(1) Position vehicle
on
level surface. This
is ex
tremely important
for
accurate check.
(2)
Apply parking brakes
and run
engine
at
curb
idle speed.
(3)
Shift transmission momentarily into
all
gear
ranges. Then shift back
to
Neutral.
(4)
Clean
top of
filler tube
and
dipstick
(to
avoid
dirt entry)
and
check fluid level. Correct level
is as
follows:
(5)
Be
sure fluid
is at
normal operating tempera
ture (180°F). Correct level
is
between "Maximum Level
Hot"
and
"Add"
marks (crosshatched area)
on
dipstick. (6)
If
fluid level
is
low,
add
only enough fluid
to
correct level.
CAUTION:
Do not
overfill
the
transmission. Overfilling
will
force fluid
out
the
pump vent which
can
be
mistaken
for
a
pump seal leak. Overfilling
will
also
cause
fluid aeration
and foaming
when
the
excess
fluid
is
picked
up
and
churned
by
the
gear train. Aeration
will
reduce fluid
life
significantly.
FLUID
AND
FILTER
CHANGE
Normal Change
Interval
The fluid
and
filter should
be
changed
(and the
bands adjusted)
at
recommended maintenance inter
vals.
Or
whenever
the
transmission
has
been disassembled
for
any
reason.
Recommended Fluid
The recommended
(and
preferred) fluid
for
Chrysler automatic transmissions
is
Mopar
ATF
Plus,
type
7176.
Use
Mopar Dexron
II
only when
ATF Plus
is not
readily available.
page
Park Lock
Service-32RH/36RH/37RH
. 138
Park/Neutral Position Switch
134
Rear
Band
Adjustment
133
Speedometer Service
134
Transmission Cooler Service
140
Transmission
Throttle
Cable
Adjustment-
Cummins Diesel Engine
132
Transmission
Throttle
Cable
Adjustment-
Gas
Engines
131
Valve Body
Control
Pressure Adjustments
.....
140
Valve Body Service
138
Severe Usage Change
Interval
Under severe usage,
the
fluid
and
filter should
be
changed
and the
bands adjusted
at
12,000 mile (19,000
km)
intervals.
Severe usage
is
defined
as:
• More than half
of
vehicle operation occurs
in
heavy city traffic during
hot
weather
at
ambient
temperatures above
90°
F.
• Vehicle
is
used
for
Taxi, Police, Limousine,
or
sim
ilar commercial operations.
• Vehicle
is
used
for
trailer/boat towing
or
heavy
load hauling. When
the
factory fluid
is
drained, refill
the
trans
mission with Mopar
ATF
Plus, type
7176
fluid.
Mo
par Dexron
II
can
be
used
if
ATF
Plus
is
not
readily available.
FLUID
AND
FILTER
REPLACEMENT
PROCEDURE
(1) Raise vehicle, remove
oil pan
and
drain fluid.
(2) Remove filter screws
and
remove filter.
(3) Position
new
filter
on
valve body
and
install fil
ter screws finger tight. (4) Tighten filter screws
to 4
N*m (35
in.
lbs.)
with
torque wrench.
(5) Position
new
gasket
on oil pan
and
install
pan
on transmission. Tighten
pan
bolts
to 17
N»m
(150
in.
lbs.)
torque. (6) Lower vehicle
and
refill transmission with rec
ommended fluid.
GEARSHIFT LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Check linkage adjustment
by
starting
the
engine
in Park
and
Neutral. Adjustment
is
OK
if
the
engine starts only
in
park
and Neutral. Adjustment
is
incorrect
if
the
engine starts
in one
but
not
both positions. If
the
engine starts
in
any
position other than Park
or Neutral,
or if
the
engine will
not
start
at
all,
the
park/neutral position switch
may
be
faulty.
Page 1142 of 1502
•
IN-VEHICLE
SERVICE-32RH/36RH/37RH/42RH/46RH
21 - 141 (2) Position drain pan under cooler pressure line to
catch material flushed through cooler and lines. (3) Reverse flush cooler using hand operated suc
tion gun filled with mineral spirits. Insert gun nozzle (or hose) into cooler return line. Then force mineral
spirits into line and through cooler. (4) Continue reverse flushing until fluid exiting
cooler pressure line is clear and free from debris. Re
place cooler if fluid cannot be pumped through. (5) Clear flushing materials from cooler and lines
with short pulses of compressed air. Insert air gun nozzle into cooler return line and continue short air pulses until all fluid is cleared from cooler and lines. (6) Pump one quart of fresh automatic transmission
fluid through cooler and lines before reconnecting lines.
CHECKING COOLER FLUID FLOW Cooler flow is checked, by measuring the amount of
fluid pumped through the cooler in a specified time
by the transmission oil pump. (1) Disconnect cooler return line from transmission
and place it in one quart test container.
(2) Add extra quart of fluid to transmission.
(3) Use stopwatch to check test time.
(4) Shift into Neutral.
(5) Start and run engine at curb idle speed and
note cooler flow. A minimum of one quart (0.9 liter)
of fluid should flow into test container in 20 seconds. (6) If fluid flow is intermittent, flows less than one
quart in 20 seconds, or fails to flow at all, cooler is
plugged or damaged and should be replaced.
MAIN COOLER REPLACEMENT The main transmission cooler is located in the ra
diator lower tank. The cooler is not a serviceable component. If the cooler is damaged in any way, the
radiator will have to be replaced.
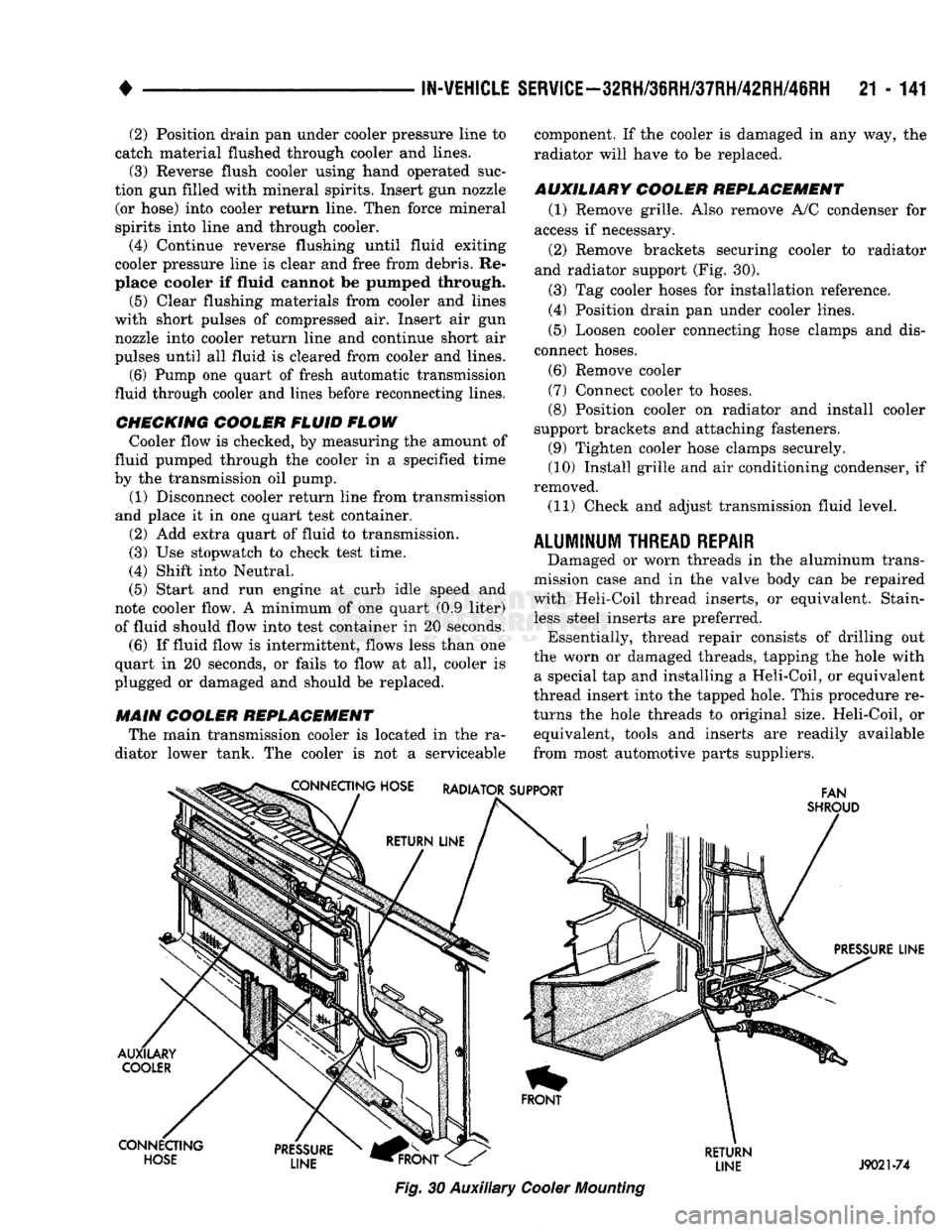
AUXILIARY COOLER REPLACEMENT (1) Remove grille. Also remove A/C condenser for
access if necessary.
(2) Remove brackets securing cooler to radiator
and radiator support (Fig. 30).
(3) Tag cooler hoses for installation reference.
(4) Position drain pan under cooler lines.
(5) Loosen cooler connecting hose clamps and dis
connect hoses.
(6) Remove cooler
(7) Connect cooler to hoses.
(8) Position cooler on radiator and install cooler
support brackets and attaching fasteners. (9) Tighten cooler hose clamps securely.
(10) Install grille and air conditioning condenser, if
removed.
(11) Check and adjust transmission fluid level.
ALUMINUM
THREAD
REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans
mission case and in the valve body can be repaired
with Heli-Coil thread inserts, or equivalent. Stain less steel inserts are preferred. Essentially, thread repair consists of drilling out
the worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with a special tap and installing a Heli-Coil, or equivalent
thread insert into the tapped hole. This procedure re
turns the hole threads to original size. Heli-Coil, or equivalent, tools and inserts are readily available
from most automotive parts suppliers. CONNECTING HOSE RADIATOR SUPPORT
FAN
SHROUD
PRESSURE LINE
AUXILARY COOLER
CONNECTING HOSE PRESSURE
LINE
HFRONT
Fig.
30 Auxiliary
Cooler
Mounting
RETURN
LINE J9021-74
Page 1143 of 1502
!1
- 142
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
• AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION REMOWAL AND INSTALLATION
INDEX
page
Dverdrlve
Unit
Installation
150
Overdrive
Unit
Removal-42RH/46RH
........ 149
Pump
Oil
Seal
146
Starter
Ring Gear Replacement
144
Torque Converter
and
Drive
Plate
Service
..... 144
Transmission
and
Torque Converter
Installation—
2-Wheel Drive
146
page
Transmission
and
Torque Converter
Installation—
4-Wheel Drive
. . .' 148
Transmission
and
Torque Converter Removal— 2-Wheel Drive
142
Transmission
and
Torque Converter Removal
—
4-Wheel Drive
143
TRANSMISSION
AND
TORQUE CONVERTER REMOVAL—2-WHEEL DRIVE The
transmission and torque converter should
be removed as an assembly to avoid component damage. The converter drive plate, pump bush
ing, or oil seal can be damaged if the converter
is left attached to the driveplate during removal. Be sure to remove the transmission and con
verter as an assembly.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect or remove exhaust components as
needed for service access.
(3) Remove engine-to-transmission struts, if
equipped. (4) Disconnect fluid cooler lines at transmission.
(5) Remove starter motor and cooler line bracket.
(6) Remove torque converter bolt access cover.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan, drain fluid and
reinstall pan. (8) Remove transmission fill tube bracket bolts and
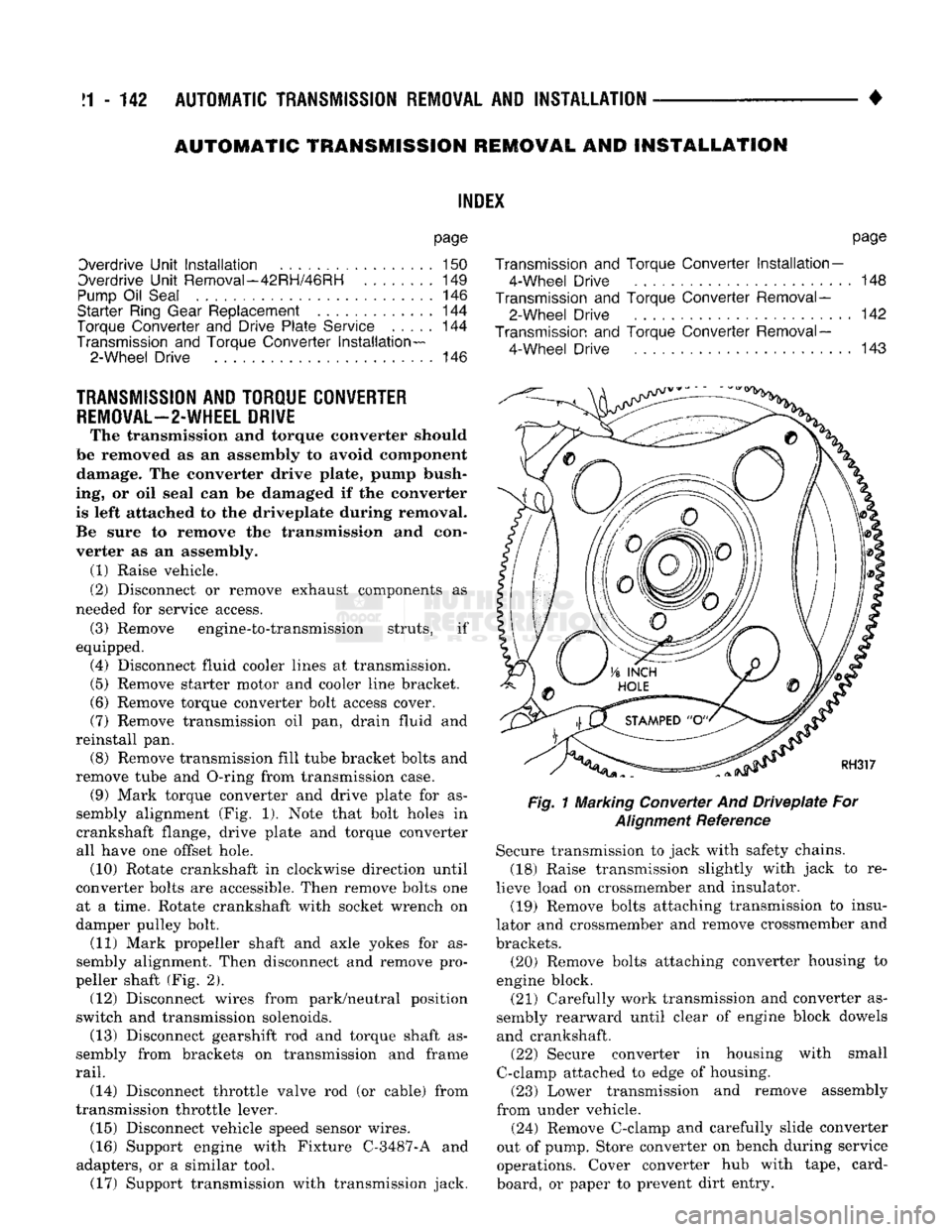
remove tube and O-ring from transmission case. (9) Mark torque converter and drive plate for as
sembly alignment (Fig. 1). Note that bolt holes in
crankshaft flange, drive plate and torque converter
all have one offset hole. (10) Rotate crankshaft in clockwise direction until
converter bolts are accessible. Then remove bolts one at a time. Rotate crankshaft with socket wrench on
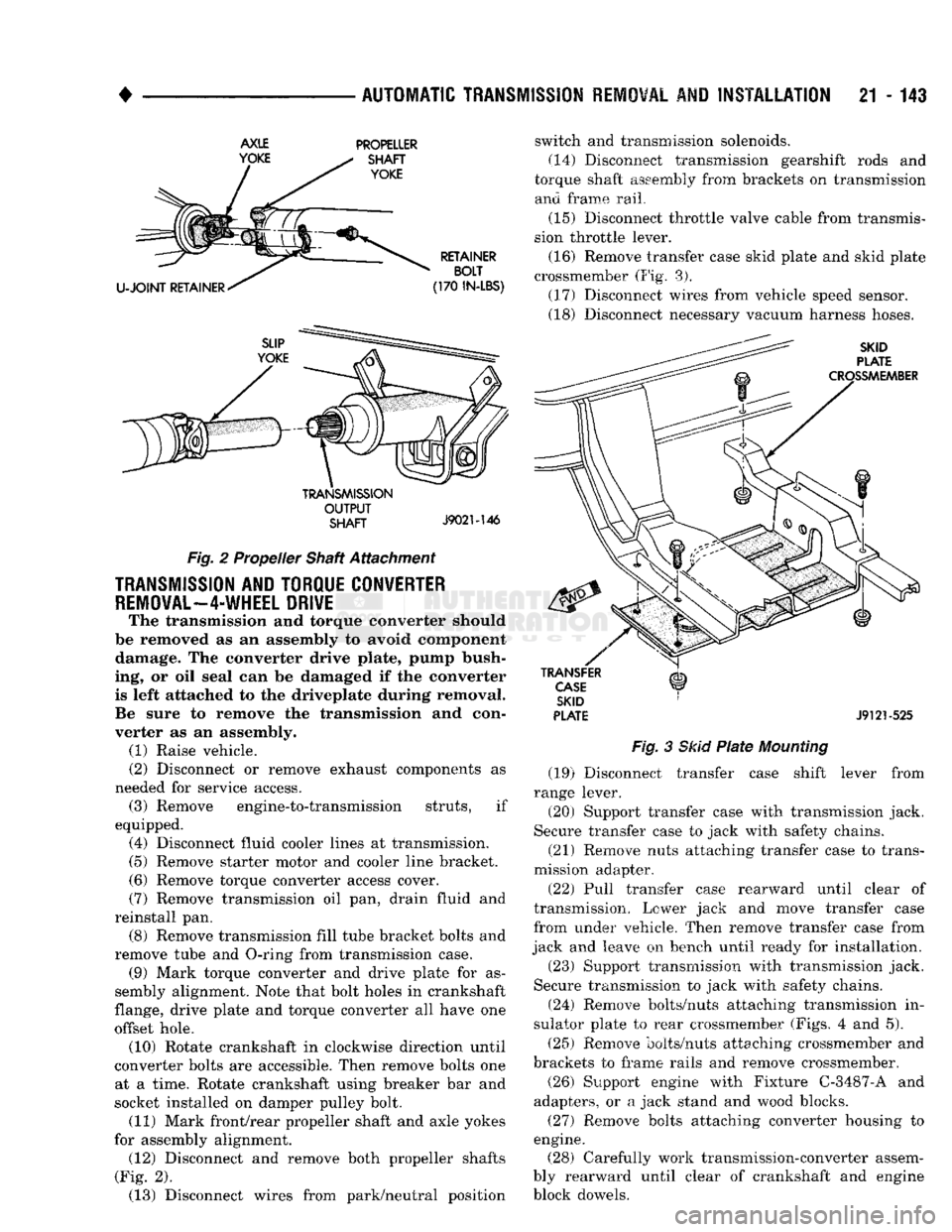
damper pulley bolt. (11) Mark propeller shaft and axle yokes for as
sembly alignment. Then disconnect and remove pro
peller shaft (Fig. 2). (12) Disconnect wires from park/neutral position
switch and transmission solenoids. (13) Disconnect gearshift rod and torque shaft as
sembly from brackets on transmission and frame
rail.
(14) Disconnect throttle valve rod (or cable) from
transmission throttle lever. (15) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor wires.
(16) Support engine with Fixture C-3487-A and
adapters, or a similar tool. (17) Support transmission with transmission jack.
Fig.
1 Marking Converter And
Driveplate
For
Alignment
Reference Secure transmission to jack with safety chains.
(18) Raise transmission slightly with jack to re
lieve load on crossmember and insulator. (19) Remove bolts attaching transmission to insu
lator and crossmember and remove crossmember and
brackets. (20) Remove bolts attaching converter housing to
engine block.
(21) Carefully work transmission and converter as
sembly rearward until clear of engine block dowels and crankshaft. (22) Secure converter in housing with small
C-clamp attached to edge of housing. (23) Lower transmission and remove assembly
from under vehicle.
(24) Remove C-clamp and carefully slide converter
out of pump. Store converter on bench during service
operations. Cover converter hub with tape, card
board, or paper to prevent dirt entry.
Page 1144 of 1502
•
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
21 - 143
AXLE
YOKE PROPELLER
SHAFT
YOKE
U-JOINT
RETAINER RETAINER
BOLT
(170
IN-LBS)
TRANSMISSION
OUTPUT
SHAFT
J9021-146
Fig.
2 Propeller Shaft Attachment
TRANSMISSION
AND TORQUE CONVERTER
REMOVAL—4-WHEEL
DRIVE
The transmission and torque converter should
be removed as an assembly to avoid component damage. The converter drive plate, pump bush
ing, or oil seal can be damaged if the converter
is left attached to the driveplate during removal.
Be sure to remove the transmission and con
verter as an assembly. (1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect or remove exhaust components as
needed for service access. (3) Remove engine-to-transmission struts, if
equipped. (4) Disconnect fluid cooler lines at transmission. (5) Remove starter motor and cooler line bracket.
(6) Remove torque converter access cover.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan, drain fluid and
reinstall pan. (8) Remove transmission fill tube bracket bolts and
remove tube and O-ring from transmission case. (9) Mark torque converter and drive plate for as
sembly alignment. Note that bolt holes in crankshaft
flange, drive plate and torque converter all have one
offset hole. (10) Rotate crankshaft in clockwise direction until
converter bolts are accessible. Then remove bolts one at a time. Rotate crankshaft using breaker bar and
socket installed on damper pulley bolt. (11) Mark front/rear propeller shaft and axle yokes
for assembly alignment. (12) Disconnect and remove both propeller shafts
(Fig. 2). (13) Disconnect wires from park/neutral position switch and transmission solenoids.
(14)
Disconnect transmission gearshift rods and
torque shaft assembly from brackets on transmission and frame rail.
(15) Disconnect throttle valve cable from transmis
sion throttle lever.
(16) Remove transfer case skid plate and skid plate
crossmember (Fig. 3). (17) Disconnect wires from vehicle speed sensor.
(18) Disconnect necessary vacuum harness hoses.
SKID
PLATE
CROSSMEMBER
TRANSFER
CASE
SKID
PLATE
J9121-525
Fig.
3
Skid
Plate
Mounting
(19) Disconnect transfer case shift lever from
range lever.
(20) Support transfer case with transmission jack.
Secure transfer case to jack with safety chains.
(21) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans
mission adapter.
(22) Pull transfer case rearward until clear of
transmission. Lower jack and move transfer case
from under vehicle. Then remove transfer case from
jack and leave on bench until ready for installation.
(23) Support transmission with transmission jack.
Secure transmission to jack with safety chains.
(24) Remove bolts/nuts attaching transmission in
sulator plate to rear crossmember (Figs. 4 and 5).
(25) Remove bolts/nuts attaching crossmember and
brackets to frame rails and remove crossmember.
(26) Support engine with Fixture C-3487-A and
adapters, or a jack stand and wood blocks.
(27) Remove bolts attaching converter housing to
engine. (28) Carefully work transmission-converter assem
bly rearward until clear of crankshaft and engine
block dowels.