1993 DODGE TRUCK Transfer case
[x] Cancel search: Transfer casePage 44 of 1502

•
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0 - 25
CAUTION:
Do not
over-tighten
the
drain
and fill
hole
plugs.
Over-tightening
can strip the
hole
threads
and/or crack
the
aluminum housing.
(5) Install the drain hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in
the transfer case. Tighten the drain hole plug to 27 N*m (20 ft-lbs) torque. (6) Fill the transfer case to the bottom edge of the
fill hole (Figs. 4 and 5) with: • MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases
• Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases. (7) Install the fill hole plug (Figs. 4 and 5) in the
transfer case. Tighten the plug to 27 N«m (20 ft-lbs) torque.
(8) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
• MOPAR®ATF PLUS or an equivalent Dexron II®
ATF for NP241 transfer cases • Multi-purpose gear oil (API GL-5) or engine oil (API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE) for NP205 transfer cases
NP20I
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL/ENGINE
OIL
SELECTION
MULTI-PURPOSE GEAR OIL-if the anticipated
minimum temperature will: • Be above 32°C (90°F)-use SAE 140, API GL-5;
• Decrease to as low as -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 90,
API GL-5; and • Be below -23°C (-10°F)-use SAE 80, API GL-5. ENGINE OIL—if the anticipated minimum tem
perature will be: ® Above 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 50, API SG, SG/CD or
SG/CE;
• Below 0°C (32°F)-use SAE 30, API SG, SG/CD or SG/CE.
SHIFT MECHANISM-NP241 AND NP205 The transfer case shift mechanism should be
cleaned and lubricated as necessary.
Lubricate the pivot, the sliding contact areas and
the shift linkage pivot ends with light-weight engine oil (Figs. 6 and 7).
AXLES
INSPECTION/LUBRICANT LEVEL For normal vehicle operation, periodic axle lubri
cant level checks are not necessary. The exterior of
the axle housing should be inspected for leakage. Check the lubricant level to confirm the leakage.
LUBRICANT LEVEL
(1) Raise the vehicle with an axle or wheel type
hoist. Support the vehicle.
(2) The rear axle differential housings have a rub
ber, PRESS-IN type fill plug (Fig. 8). Pry the fill
TRANSMISSION
ASSEMBLY
GEARSHIFT
MECHANISM TRANSFER CASE
SCREWS
(2)
50
FT. LBS.
(68 N*m)
CLAMP
SHIFT
ROD
SCREW
80 IN.
LBS.
(9 N*m)
RP1091
Fig.
6 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP241 Transfer
Case
Fig.
RY682
7 Shift
Mechanism
Lubrication—NP205 Transfer
Case
plug from the differential housing. The front axle (4WD vehicles)*differential housings have a thread
ed-type fill plug (Fig. 9). Un-thread the fill plug from
the differential housing.
(3) The lubricant level should be within 12 mm
(1/2 in) of the fill hole for the 8.25 and 9.25 rear ax
les.
The lubricant level should be between 12mm (1/2
in) and 24mm (1 in.) of the fill hole for the Dana ax
les.
(4) If necessary, add lubricant to raise the level to
the acceptable position.
(5) Install the fill hole plug in the differential
housing (Figs. 8 and 9).
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
Periodic axle lubricant change for normal vehicle
operation is not necessary. Refer to the chart below-
Page 70 of 1502

•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 17
MODEL
44
FRONT
AXLE
INDEX
page
Axle Shaft
and
U-Joint
Service
23
Complete Axle Removal/Installation
31
Differential
Assembly
35
Differential
Disassembly
. 32
Drain
and Refill
19
General
Information
17
Hub,
Spindle
and
Axle Shaft
20
Intermediate
Axle Shaft
30
Lubricant
17
GENERAL
INFORMATION
Model
44
front axles
(Fig. 1)
consists
of an
iron
center casting with axle shaft tubes extending from
either side. The integral type housing, hypoid gear design
has
the centerline
of the
pinion
set
below
the
centerline of
the
ring gear. The axle shaft disconnect housing
is
welded
to the
left axle shaft tube.
A
splined, two-piece axle shaft
is
located
on the
left side
and it is
engaged
or
disen
gaged
by a
shift collar.
The
collar
is
moved
by a
shift
fork controlled
by a
vacuum shift motor.
The
shift motor
is
operated
by
engine vacuum controlled
by a
switch located
at the
transfer case. The axles
are
equipped with full-floating axle
shafts,
meaning that loads
are
supported
by the
spin
dles attached
to the
steering knuckles. The removable, stamped steel cover provides
a
means
for
inspection
and
service without removing
the complete axle from
the
vehicle.
page
Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
and
Adjustment
with
Tool
Set
C-3715-B
40
Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
and
Adjustment
with
Tool
Set
D-115-44
... 38
Pinion Shaft Seal
19
Specifications
48
Steering Knuckle
Arm
31
Steering Knuckle, Upper
and
Lower Ball Studs
. . 24
Vacuum
Shift Motor
26
A small, stamped metal axle gear ratio identifica
tion
tag is
attached
to the
housing cover
via one of
the cover bolts. This
tag
also identifies
the
number
of
ring gear
and
pinion gear teeth.
The differential case
is a
one-piece design.
The dif
ferential pinion mate shaft
is
retained with
a
roll
pin. Differential bearing preload
and
ring gear back lash
are
adjusted
by the use of
shims located between
the differential bearing cones
and
case.
LUBRICANT
Multi-purpose
API GL 5
quality hypoid gear lubri
cant should
be
used
for
Model
44
axles. MOPAR
Hy
poid Gear Lubricant conforms with these specifications
and is
recommended.
CAUTION:
If a
front axle
is
submerged
in
water,
the
axle lubricant must
be
replaced immediately.
Page 79 of 1502
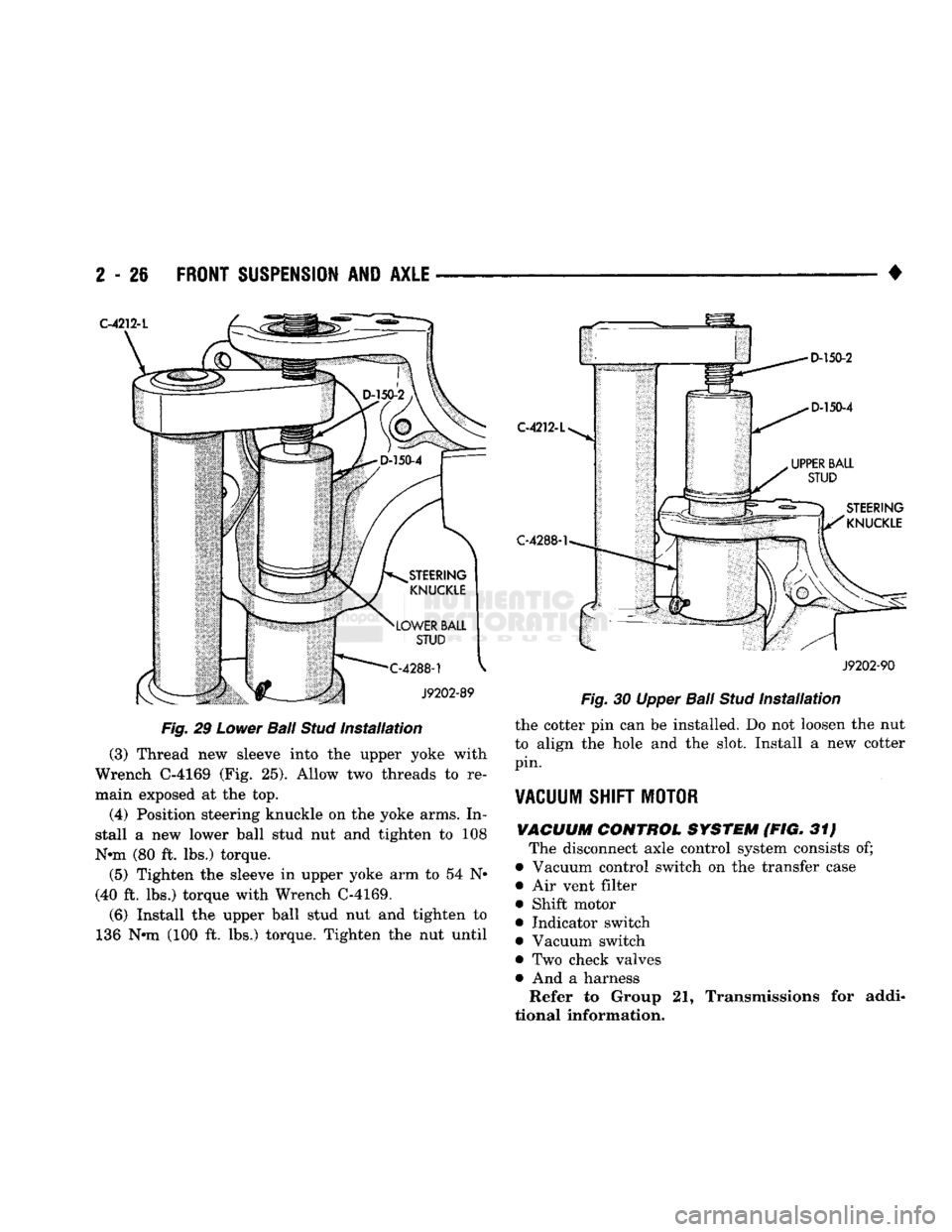
2
- 26
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
•
Fig.
29
Lower
Ball
Stud
Installation
(3) Thread new sleeve into the upper yoke with
Wrench C-4169 (Fig. 25). Allow two threads to re
main exposed at the top.
(4) Position steering knuckle on the yoke arms. In
stall a new lower ball stud nut and tighten to 108
Nnn (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Tighten the sleeve in upper yoke arm to 54 N*
(40 ft. lbs.) torque with Wrench C-4169.
(6) Install the upper ball stud nut and tighten to
136 Nnn (100 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the nut until C-4212-L
C-4288-1
J9202-90
Fig.
30 Upper
Ball
Stud
Installation
the cotter pin can be installed. Do not loosen the nut
to align the hole and the slot. Install a new cotter
pin.
VACUUM
SHIFT
MOTOR
VACUUM
CONTROL
SYSTEM
(FIG. 31) The disconnect axle control system consists of;
• Vacuum control switch on the transfer case • Air vent filter
• Shift motor
• Indicator switch
• Vacuum switch
• Two check valves • And a harness Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for addi
tional information.
Page 81 of 1502
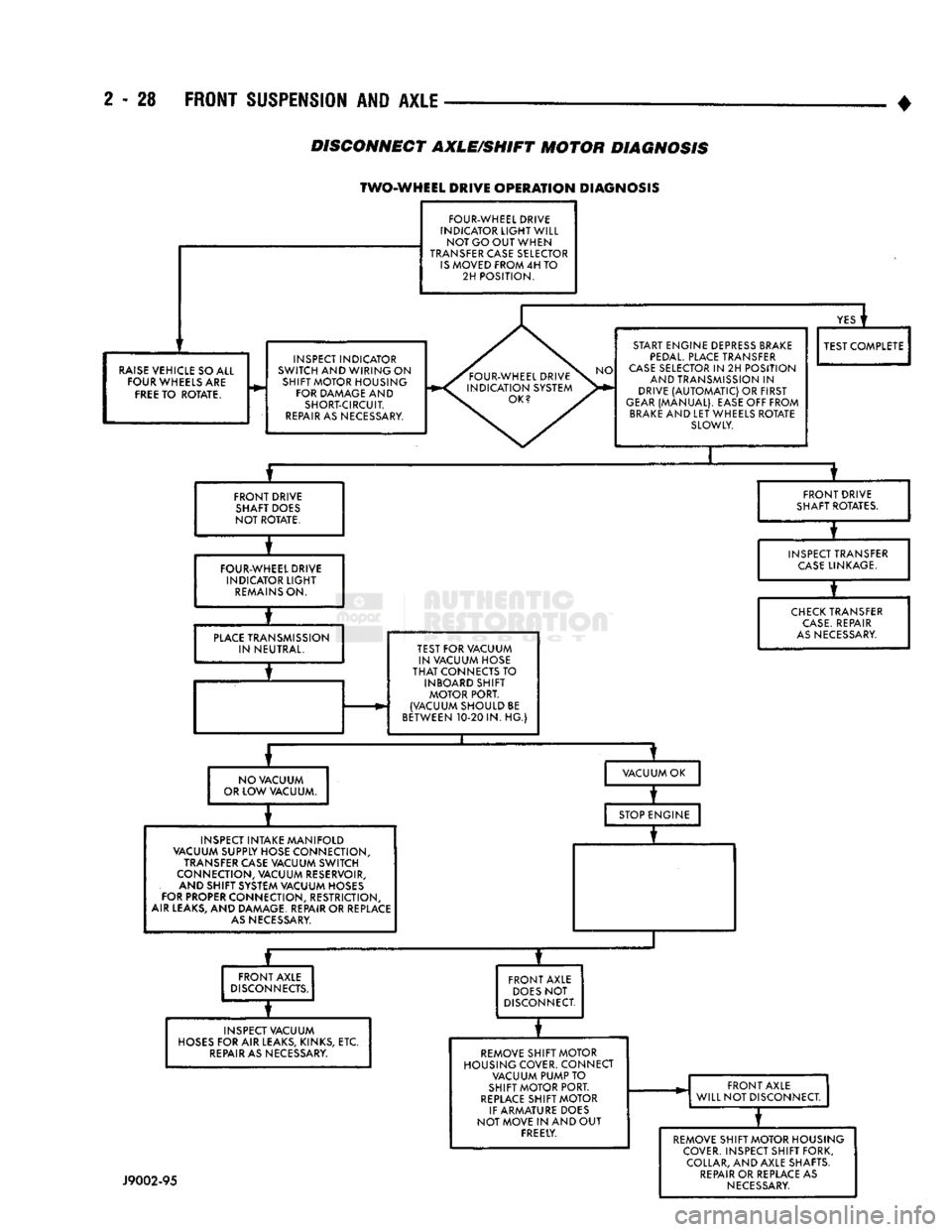
2 - 28
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
DISCONNECT
AXLE/SHIFT
MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS
TWO-WHEEL DRIVE
OPERATION
DIAGNOSIS
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE
INDICATOR
LIGHT
WILL NOT GO OUT WHEN
TRANSFER CASE SELECTOR
IS
MOVED FROM 4H TO 2H POSITION.
RAISE
VEHICLE SO ALL FOUR WHEELS ARE
FREE
TO ROTATE. INSPECT INDICATOR
SWITCH AND WIRING ON SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING FOR DAMAGE AND SHORT-CIRCUIT.
REPAIR
AS NECESSARY.
YES
i
START ENGINE DEPRESS BRAKE
PEDAL.
PLACE TRANSFER
CASE
SELECTOR IN 2H POSITION AND TRANSMISSION IN
DRIVE
(AUTOMATIC)
OR FIRST
GEAR
(MANUAL). EASE OFF FROM
BRAKE
AND LET WHEELS ROTATE SLOWLY. TEST COMPLETE
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT DOES
NOT ROTATE. FRONT DRIVE
SHAFT ROTATES.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE INDICATOR
LIGHT
REMAINS
ON. INSPECT TRANSFER
CASE
LINKAGE.
PLACE
TRANSMISSION IN NEUTRAL. TEST FOR VACUUM
IN VACUUM HOSE
THAT
CONNECTS TO INBOARD SHIFT MOTOR PORT.
(VACUUM SHOULD BE
BETWEEN 10-20 IN. HG.)
CHECK
TRANSFER
CASE.
REPAIR
AS
NECESSARY.
NO VACUUM
OR LOW VACUUM. VACUUM OK
INSPECT INTAKE MANIFOLD
VACUUM SUPPLY HOSE CONNECTION,
TRANSFER CASE VACUUM SWITCH
CONNECTION, VACUUM RESERVOIR, AND SHIFT SYSTEM VACUUM HOSES
FOR PROPER CONNECTION, RESTRICTION,
AIR LEAKS, AND DAMAGE. REPAIR OR REPLACE
AS
NECESSARY. STOP ENGINE
—r~
FRONT AXLE
DISCONNECTS.
INSPECT VACUUM
HOSES
FOR AIR LEAKS, KINKS, ETC.
REPAIR
AS NECESSARY. FRONT AXLE
DOES
NOT
DISCONNECT.
REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR
HOUSING COVER. CONNECT VACUUM PUMP TO
SHIFT MOTOR PORT.
REPLACE
SHIFT MOTOR
IF ARMATURE DOES
NOT MOVE IN AND OUT FREELY. FRONT AXLE
WILL NOT DISCONNECT.
J9002-95
REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING
COVER. INSPECT SHIFT FORK, COLLAR, AND AXLE SHAFTS.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS
NECESSARY
Page 82 of 1502
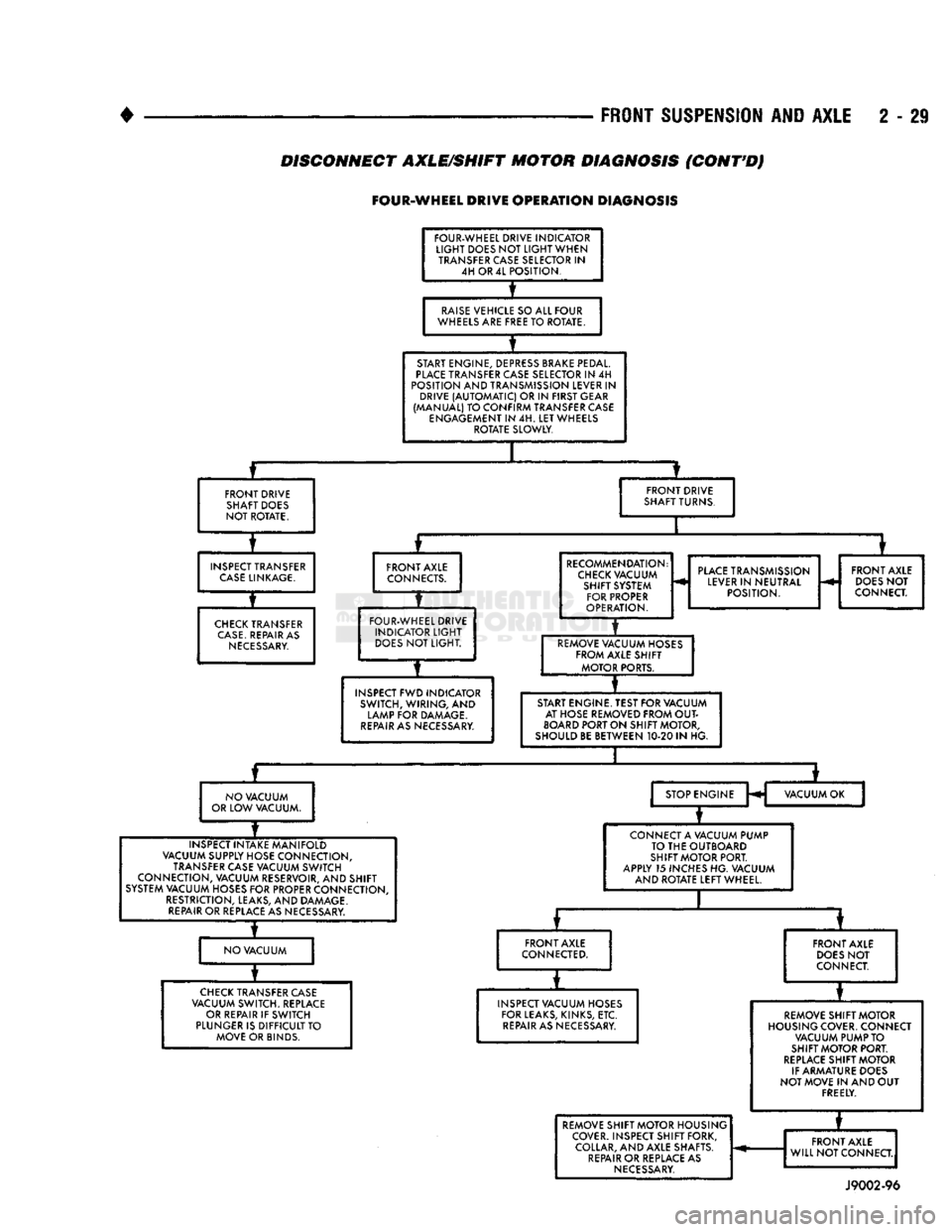
FRONT
SUSPENSION AND
AXLE
2 - 29
DISCONNECT AXLE/SHIFT MOTOR DIAGNOSIS
(CONT'D)
FOUR-WHEEL
DRIVE
OPERATION
DIAGNOSIS
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE INDICATOR
LIGHT
DOES NOT
LIGHT
WHEN TRANSFER CASE SELECTOR IN 4H OR 4L POSITION.
RAISE
VEHICLE SO ALL FOUR
WHEELS ARE FREE TO ROTATE.
START ENGINE, DEPRESS BRAKE PEDAL.
PLACE
TRANSFER CASE SELECTOR IN 4H
POSITION AND TRANSMISSION LEVER IN DRIVE
(AUTOMATIC)
OR IN FIRST GEAR
(MANUAL) TO CONFIRM TRANSFER CASE ENGAGEMENT IN 4H. LET WHEELS ROTATE SLOWLY.
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT DOES
NOT ROTATE. FRONT DRIVE
SHAFT TURNS.
INSPECT TRANSFER
CASE
LINKAGE.
CHECK
TRANSFER
CASE.
REPAIR AS
NECESSARY.
FRONT AXLE
CONNECTS.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE INDICATOR
LIGHT
DOES
NOT LIGHT.
INSPECT FWD INDICATOR SWITCH, WIRING, AND
LAMP FOR DAMAGE.
REPAIR
AS NECESSARY. RECOMMENDATION:
CHECK
VACUUM SHIFT SYSTEM FOR PROPER
OPERATION.
PLACE
TRANSMISSION
LEVER IN NEUTRAL POSITION. FRONT AXLE
DOES
NOT
CONNECT.
REMOVE VACUUM HOSES FROM AXLE SHIFT MOTOR PORTS.
START ENGINE. TEST FOR VACUUM AT HOSE REMOVED FROM
OUT
BOARD
PORT ON SHIFT MOTOR,
SHOULD BE BETWEEN 10-20 IN HG.
NO VACUUM
OR LOW VACUUM. STOP ENGINE
H VACUUM OK
INSPECT INTAKE MANIFOLD
VACUUM SUPPLY HOSE CONNECTION, TRANSFER CASE VACUUM SWITCH
CONNECTION, VACUUM RESERVOIR, AND SHIFT
SYSTEM VACUUM HOSES FOR PROPER CONNECTION, RESTRICTION, LEAKS, AND DAMAGE.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS NECESSARY. CONNECT A VACUUM PUMP
TO THE OUTBOARD
SHIFT MOTOR PORT.
APPLY 15 INCHES HG. VACUUM AND ROTATE LEFT WHEEL.
NO VACUUM FRONT AXLE
CONNECTED.
CHECK
TRANSFER CASE
VACUUM SWITCH. REPLACE OR REPAIR IF SWITCH
PLUNGER IS DIFFICULT TO MOVE OR BINDS. FRONT AXLE
DOES
NOT
CONNECT.
INSPECT VACUUM HOSES FOR LEAKS, KINKS, ETC.
REPAIR
AS NECESSARY. REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR
HOUSING COVER. CONNECT VACUUM PUMP TO
SHIFT MOTOR PORT.
REPLACE
SHIFT MOTOR
IF ARMATURE DOES
NOT MOVE IN AND OUT FREELY. REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING
COVER. INSPECT SHIFT FORK, COLLAR, AND AXLE SHAFTS.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS
NECESSARY.
*
REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING
COVER. INSPECT SHIFT FORK, COLLAR, AND AXLE SHAFTS.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS
NECESSARY.
FRONT AXLE
WILL NOT CONNECT.
REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING
COVER. INSPECT SHIFT FORK, COLLAR, AND AXLE SHAFTS.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS
NECESSARY.
FRONT AXLE
WILL NOT CONNECT.
REMOVE SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING
COVER. INSPECT SHIFT FORK, COLLAR, AND AXLE SHAFTS.
REPAIR
OR REPLACE AS
NECESSARY.
J9002-96
Page 98 of 1502
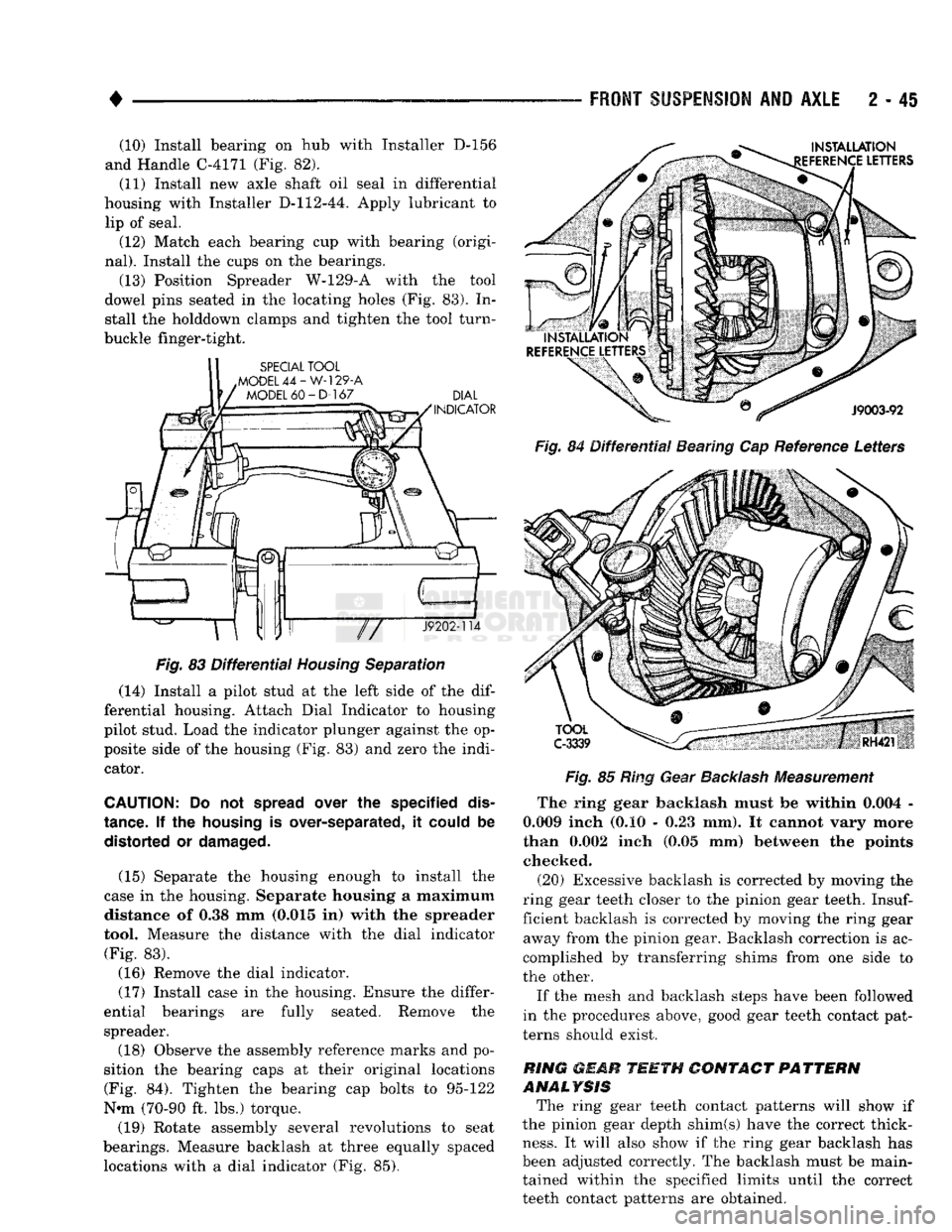
4
____________
(10) Install bearing
on hub
with Installer
D-156
and Handle C-4171
(Fig. 82).
(11) Install
new
axle shaft
oil
seal
in
differential
housing with Installer D-112-44. Apply lubricant
to
lip
of
seal. (12) Match each bearing
cup
with bearing (origi
nal).
Install
the
cups
on the
bearings.
(13) Position Spreader W-129-A with
the
tool
dowel pins seated
in the
locating holes
(Fig. 83). In
stall
the
holddown clamps
and
tighten
the
tool turn-
buckle finger-tight.
Fig.
83
Differential
Housing
Separation
(14) Install
a
pilot stud
at the
left side
of the dif
ferential housing. Attach Dial Indicator
to
housing
pilot stud. Load
the
indicator plunger against
the op
posite side
of the
housing
(Fig. 83) and
zero
the
indi cator.
CAUTION:
Do not
spread
over
the
specified
dis
tance.
If the
housing
is
over-separated,
it
could
be
distorted
or
damaged.
(15) Separate
the
housing enough
to
install
the
case
in the
housing. Separate housing
a
maximum distance
of 0.38 mm
(0.015
in)
with
the
spreader
tool. Measure
the
distance with
the
dial indicator (Fig.
83).
(16) Remove
the
dial indicator.
(17) Install case
in the
housing. Ensure
the
differ
ential bearings
are
fully seated. Remove
the
spreader.
(18) Observe
the
assembly reference marks
and po
sition
the
bearing caps
at
their original locations (Fig.
84).
Tighten
the
bearing
cap
bolts
to
95-122
N-m (70-90
ft. lbs.)
torque.
(19) Rotate assembly several revolutions
to
seat
bearings. Measure backlash
at
three equally spaced locations with
a
dial indicator
(Fig. 85).
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 45
Fig.
84
Differential
Bearing
Cap
Reference Letters
Fig.
85
Ring Gear
Backlash
Measurement
The ring gear backlash must
be
within 0.004
-
0.009 inch
(0.10 - 0.23 mm). It
cannot vary more
than 0.002 inch
(0.05 mm)
between
the
points checked.
(20) Excessive backlash
is
corrected
by
moving
the
ring gear teeth closer
to the
pinion gear teeth.
Insuf
ficient backlash
is
corrected
by
moving
the
ring gear away from
the
pinion gear. Backlash correction
is ac
complished
by
transferring shims from
one
side
to
the other.
If
the
mesh
and
backlash steps have been followed
in
the
procedures above, good gear teeth contact pat
terns should exist.
RING
mMR
TEETH
CONTACT
PATTERN
ANALYSIS The ring gear teeth contact patterns will show
if
the pinion gear depth shim(s) have
the
correct thick
ness.
It
will also show
if the
ring gear backlash
has
been adjusted correctly.
The
backlash must
be
main tained within
the
specified limits until
the
correct
teeth contact patterns
are
obtained.
Page 126 of 1502
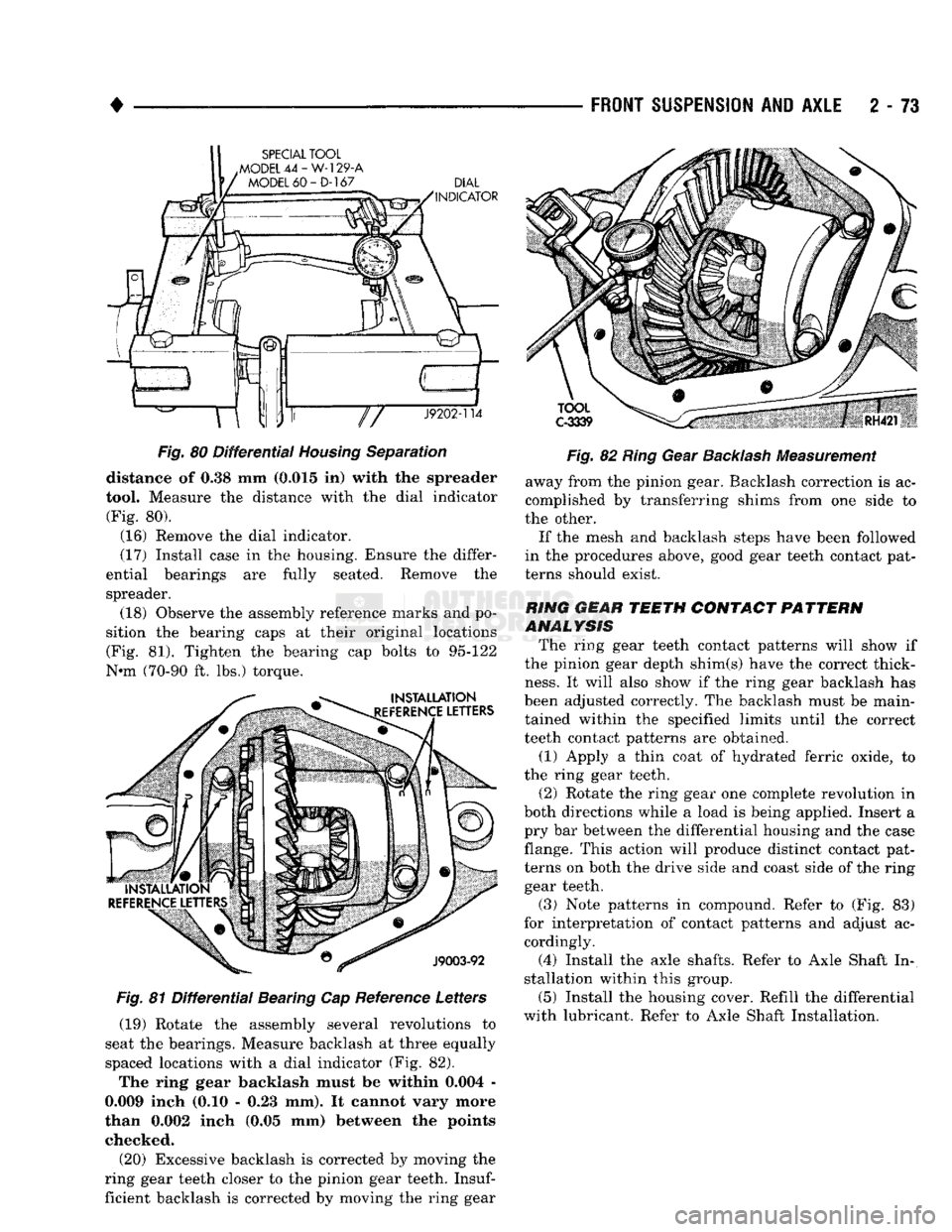
•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 73
SPECIAL TOOL
.MODEL
44-W-129-A
MODEL
60 - D-167
DIAL
INDICATOR
J9202-114
TOOL
C-3339
Fig.
80
Differential
Housing
Separation
distance
of 0.38 mm
(0.015
in)
with
the
spreader
tool. Measure
the
distance with
the
dial indicator
(Fig.
80).
(16) Remove
the
dial indicator.
(17) Install case
in the
housing. Ensure
the
differ
ential bearings
are
fully seated. Remove
the
spreader.
(18) Observe
the
assembly reference marks
and po
sition
the
bearing caps
at
their original locations (Fig.
81).
Tighten
the
bearing
cap
bolts
to
95-122
Nnn (70-90
ft. lbs.)
torque.
Fig.
81
Differential
Bearing
Cap
Reference Letters (19) Rotate
the
assembly several revolutions
to
seat
the
bearings. Measure backlash
at
three equally
spaced locations with
a
dial indicator
(Fig. 82).
The ring gear backlash must
be
within 0.004
-
0.009 inch
(0.10 - 0.23 mm). It
cannot vary more
than 0.002 inch
(0.05 mm)
between
the
points checked.
(20) Excessive backlash
is
corrected
by
moving
the
ring gear teeth closer
to the
pinion gear teeth.
Insuf
ficient backlash
is
corrected
by
moving
the
ring gear
Fig.
82
Ring
Gear
Backlash
Measurement
away from
the
pinion gear. Backlash correction
is ac
complished
by
transferring shims from
one
side
to
the other.
If
the
mesh
and
backlash steps have been followed
in
the
procedures above, good gear teeth contact pat
terns should exist.
RING GEAR TEETH CONTACT PATTERN
ANALYSIS
The ring gear teeth contact patterns will show
if
the pinion gear depth shim(s) have
the
correct thick
ness.
It
will also show
if the
ring gear backlash
has
been adjusted correctly.
The
backlash must
be
main
tained within
the
specified limits until
the
correct
teeth contact patterns
are
obtained.
(1) Apply
a
thin coat
of
hydrated ferric oxide,
to
the ring gear teeth. (2) Rotate
the
ring gear
one
complete revolution
in
both directions while
a
load
is
being applied. Insert
a
pry
bar
between
the
differential housing
and the
case
flange. This action will produce distinct contact pat terns
on
both
the
drive side
and
coast side
of the
ring gear teeth.
(3) Note patterns
in
compound. Refer
to (Fig. 83)
for interpretation
of
contact patterns
and
adjust
ac
cordingly.
(4) Install
the
axle shafts. Refer
to
Axle Shaft
In
stallation within this group.
(5) Install
the
housing cover. Refill
the
differential
with lubricant. Refer
to
Axle Shaft Installation.
Page 137 of 1502

3
- 8
REAR SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
• level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion gear shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
• Damaged drive shaft
• Missing drive shaft balance weight
• Worn, out-of-balance wheel and tires
• Loose wheel lug nuts
• Worn U-joint • Loose spring U-bolts
• Loose/broken rear springs or shackles
• Damaged axle shaft bearings
• Loose pinion gear nut
• Excessive pinion yoke run out
• Bent axle shaft Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end vi
bration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets and drive belts. All driveline components should be examined be
fore starting any repair. Refer to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for additional
information.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by: • High engine idle speed
• Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts
9
Worn U-joints
• Loose spring shackles or U-bolts
• Loose pinion gear nut and yoke
• Excessive ring gear backlash
• Excessive differential side gear-to-case clearance A worn bushing in the transmission extension
housing can also cause noise. The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the ve
hicle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is
helpful in isolating the source of a noise.
LIMITED
SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
Under normal traction conditions, engine torque is
divided evenly. With low-traction surfaces, engine
torque is transferred to the wheel with the most tire
traction. When diagnosing a limited-slip differential
problem condition, the wheel with the least traction can continue spinning. The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Check for incorrect or contaminated lubricant. Replace the gear lubricant if necessary.
• With Sure-Grip differentials add a container of
MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Additive This will correct the condition in most instances. If
the chatter persists, clutch damage could have oc curred. After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches.