1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY abs
[x] Cancel search: absPage 230 of 2438

stant velocity joint housings. The rear Tone Wheels
are serviced as an assembly with the rear disc brake
rotor hub. Correct Anti-Lock System operation is dependent
on wheel speed signals from the wheel speed sensors.
The vehicles' wheels and tires must all be the same
size and type to generate accurate signals. In addi-
tion, the tires must be inflated to the recommended
pressures for optimum system operation. Variations
in wheel and tire size or significant variations in in-
flation pressure can produce inaccurate wheel speed
signals.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
The Anti-Lock Brake Controller is a small micro-
processor based device that monitors the brake sys- tem and controls the system while it functions in
Anti-Lock Mode. The CAB is located under the bat-
tery tray and is mounted to the left frame rail (Fig.
7) and uses a 60-way system connector. The power
source for the CAB is through the ignition switch to
pin 60 of the controller. With the ignition in the
RUN or ON position. IF THE (ABS) CONTROL-
LER NEEDS TO BE REPLACED BE SURE THE
CORRECT CONTROLLER IS USED. THE CON-
TROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB) IS NOT
ON THE CCD BUS
Fig. 5 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 4 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 6 Rear Tone Wheel
Fig. 7 Location Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB)
5 - 80 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 231 of 2438
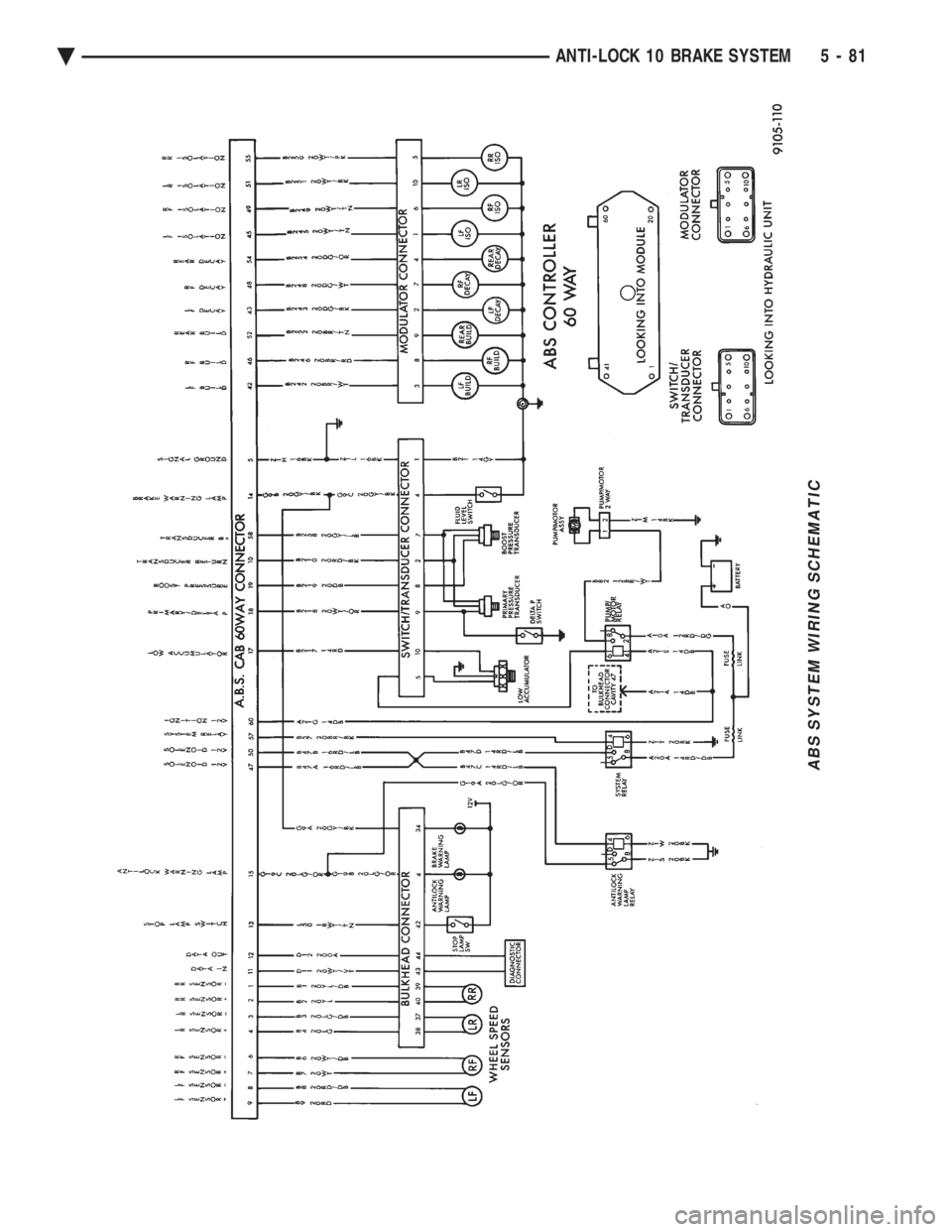
ABS SYSTEM WIRING SCHEMATIC
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 81
Page 232 of 2438

The primary functions of the (CAB) are:
² (1) Detect wheel locking tendencies.
² (2) Control fluid modulation to the brakes while in
Anti-Lock mode.
² (3) Monitor the system for proper operation.
² (4) Provide communication to the DRB II while in
diagnostic mode. The (CAB) continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel, through the signals generated at the Wheel
Speed Sensors, to determine if any wheel is begin-
ning to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is de-
tected, the (CAB) will isolate the master cylinder
from the wheel brakes. This is done by activating the
Isolation Valves. The (CAB) then commands the ap-
propriate Build or Decay valves to modulate brake
fluid pressure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits.
The fluid used for modulation comes from the booster
servo circuit. The (CAB) continues to control pres-
sure in individual hydraulic circuits until a locking
tendency is no longer present. The (ABS) system is constantly monitored by the
(CAB) for proper operation. If the (CAB) detects a
fault, it can disable the Anti-Lock braking function.
Depending on the fault, the (CAB) will light one or
both of the brake warning lamps. The (CAB) contains a System Diagnostic Program
which triggers the brake system warning lamps
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory. There are 19 fault
codes that may be stored in the (CAB) and displayed
through the DRB II. These fault codes will remain in
the (CAB) memory even after the ignition has been
turned off. These fault codes will remain in memory
until they are cleared with the DRB II, or automati-
cally erased from the memory after (50) ignition
switch on/off cycles.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (INPUTS)
² Four wheel speed sensors.
² Boost pressure transducer.
² Primary pressure transducer.
² Low fluid level switch.
² Differential pressure switch.
² Parking brake switch.
² Dual function pressure switch (warning pressure
only)
² Stop lamp switch.
² Ignition switch.
² System relay voltage.
² Ground.
² Low Accumulator
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (OUTPUTS)
²Ten modulator valves-3 decay, 3 build and 4 isola-
tion.
² Red Brake warning lamp.
² Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp.
² System relay actuation. ²
Diagnostic communication.
ABS SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
The Bendix Anti-Lock system diagnostic connector
is located under the lower dash panel or in the area
of the fuse box (Fig. 8). The fuse box is located be-
hind the access panel that is on the bottom portion of
the dash panel, left of the steering column. The diag-
nostics connector is a blue 6 way connector.
ANTI-LOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING
LAMPS
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor relay is located inside the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The relay coil is
energized by a ground from the Dual Function Pres-
sure Switch. See (Fig. 9) for the location of the pump/
motor relay in the (PDC).
SYSTEM RELAY
The (ABS) Modulator Valves and Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp Relay are controlled through a System Re-
lay. The System relay is located on the top left inner
fender behind the headlight (Fig. 10). The system re-
lay provides power to the (CAB) for modulator valve
operation (pins 47 and 50) after the start-up cycle
when the ignition is turned on.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP RELAY
The Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is controlled by the
Yellow Light Relay. See (Fig. 10) for location behind
the left headlight. With the relay de-energized, the
lamp is lit. When the system relay is energized by
Fig. 8 A.B.S. Diagnostic Connector Location
5 - 82 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 233 of 2438

the (CAB), the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp relay is en-
ergized, and the lamp is turned off. Thus, the lamp
will be lit if the (CAB) is disconnected or if a system
fault causes (ABS) function to be turned off, or if the
system relay fails open.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay (normally open) and Yellow
Light Relay (normally closed) Energized. When the (CAB) energizes the system relay by pro-
viding 12 volts to pin 57. The voltage flow in the coil
closes the system relay. Electrical current is then
provided to pins 47 and 50 of the (CAB) to provide
power to the modulator valves. This voltage also en-
ergizes the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay Switch.
This breaks the ground path to the Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp and the lamp is turned off. The (CAB) by itself, also can turn on the Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp. The (CAB) can turn on the Anti-
Lock Warning Lamp by providing a ground at pin
15.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP ON
System Relay and Anti-Lock Warning Lamp
Relay De-Energized. When the Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is on,
there is no current flow from the (CAB) at pin 57.
The system relay coil is NOT energized. No electrical
current flows to pins 47 and 50 (modulator valve
power), or to the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp relay coil.
Thus, the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay is not en-
ergized. The Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is grounded
through the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp relay contacts.
The Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is illuminated.
Fig. 9 Pump/Motor
Fig. 10 ABS System Relay And Yellow Lamp Relay Location
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 83
Page 235 of 2438

ABS HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE
OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions and
diagrams. The function of the various hydraulic con-
trol valves in the ABS system will be described. The
fluid control valves mentioned below, control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of Anti-Lock Braking.
NORMAL BRAKING
ISOLATION VALVES
Open to primary and secondary master cylinder
brake fluid supply (Fig. 11)
DECAY AND BUILD VALVES
Closed, not allowing for the build-up or release of
brake fluid supply (Fig. 11). The brake pedal is applied. The travel of the brake
pedal closes primary, secondary and booster servo
circuits from fluid supply at the fluid reservoir.
Brake fluid from the primary and secondary circuits
flows through the open isolation valves and applies
the wheel brakes. Fluid from the booster servo cir- cuit does not flow to the wheel brakes. The fluid flow
is blocked by the closed build valves and check
valves.
POWER ASSIST
The boost control valve shuttles between its three
positions to provide power assisted braking (Fig. 11).
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE
ISOLATION VALVES
Closed, isolating wheel brakes from master cylin-
der primary and secondary fluid supplies and open to
booster servo circuit pressure through open build
valves (Fig. 12)
DECAY VALVES
Closed, not allowing the escape of pressurized fluid
supply from the hydraulic system (Fig. 12).
BUILD VALVES
Open, allowing booster servo circuit pressure to
flow to the wheel brakes through the isolation valves
(Fig. 12).
Fig. 11 Normal Braking - Hydraulic Control
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 85
Page 236 of 2438

POWER ASSIST The boost control valve shuttles between its three
positions to provide power assisted braking (Fig. 12).
ABS BRAKING-HOLD PRESSURE
For explanation purposes we will assume all speed
sensors are sending the same wheel speed informa-
tion, requiring the same modulation at the same
rate.
ISOLATION VALVES Closed, isolating the wheel brakes from the master
cylinder primary and secondary fluid supplies. Build
and decay valves are closed preventing any fluid
from reaching the open isolation valves (Fig. 13).
DECAY AND BUILD VALVES Closed, not allowing fluid supply to reach the open
isolation valves (Fig. 13).
ABS BRAKING-DECAY PRESSURE
ISOLATION VALVES
Closed, isolating the wheel brakes from the master
cylinder primary and secondary fluid supplies (Fig.
14)
DECAY VALVES Open, allowing release of fluid pressure through
decay valve to the fluid reservoir (Fig. 14)
BUILD VALVE Closed, blocking booster servo circuit fluid to wheel
brakes (Fig. 14).
Fig. 12 Build Pressure - Hydraulic Control
5 - 86 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 237 of 2438

ABS BRAKING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
WARNING: SOME OPERATIONS IN THIS SECTION
REQUIRE THAT HYDRAULIC TUBES, HOSES AND
FITTINGS BE DISCONNECTED FOR INSPECTION
OR TESTING PURPOSES. THIS BRAKE SYSTEM
USES A HYDRAULIC ACCUMULATOR THAT, WHEN
FULLY CHARGED, CONTAINS BRAKE FLUID AT
HIGH PRESSURE. BEFORE DISCONNECTING ANY
HYDRAULIC TUBE, HOSE OR FITTING. BE SURE
THAT THE ACCUMULATOR IS FULLY DE-PRES-
SURIZED AS DESCRIBED IN THIS SECTION. FAIL-
URE TO DE-PRESSURIZE THE ACCUMULATOR
MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR DAM-
AGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
CAUTION: Certain components of the Anti-Lock
Brake System (ABS) are not intended to be serviced
individually. Attempting to remove or disconnect
certain system components, may result in personal
injury and/or improper system operation. Only
those components with approved removal, service
and installation procedures described in this man-
ual should be serviced.
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section contains information necessary to di-
agnosis mechanical conditions that can affect opera-
tion of the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System.
Specifically, this section should be used to help diag-
nose mechanical conditions that result in any of the
following:
CAUTION: Review this entire section before per-
forming any mechanical work on a vehicle equipped
with the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 brake system. For in-
formation on precautions pertaining to potential
component damage, vehicle damage and personal
injury.
(1) Anti-Lock warning lamp illuminated
(2) BRAKE warning lamp on
(3) Lack of Power Assist or Excessive Pedal Travel
(4) Brakes Lock on Hard Application
Diagnosis of conditions that are obviously mechan-
ical in nature. Such as brake noise, brake pulsation,
or vehicle vibration during normal braking. Should
be directed to Group 5 Brakes in the service manual.
This also pertains to problems involving the parking
brake system.
Fig. 13 Hold Pressure - Hydraulic Control
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 87
Page 238 of 2438

In order to effectively diagnose an Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) condition. It is important to read Sec-
tion 1 of this manual, Anti-Lock Brake System De-
scription. This section will give you information on
the function of the ABS components. Then follow the
diagnostic procedures outlined in this section. Many conditions that generate customer com-
plaints of the ABS system may be normal operating
conditions. These conditions though are judged to be
a problem due to unfamiliarity with the ABS system.
These conditions can be recognized without perform-
ing extensive diagnostic work, given adequate under-
standing of operating principles and performance
characteristics of the ABS system. See Section 1 of
this manual to familiarize yourself with the operat-
ing principles of the ABS system.
DEFINITIONS
Several abbreviations are used in this manual.
They are presented here for reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
² PSIÐPounds per Square Inch (pressure)
² WSSÐWheel Speed Sensor
ABS CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB) SER-
VICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS system uses an electronic control module,
the (CAB). This module is designed to withstand nor-
mal current draws associated with vehicle operation.
However care must be taken to avoid overloading the
(CAB) circuits. In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the circuits unless
instructed to do so by the appropriate diagnostic pro-
cedure. These circuits should only be tested using a
high impedance multi-meter, special tools or the DRB
II tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module with
the ignition in the ON position. Before removing or
connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors, always
turn the ignition to the OFF position.
ABS SYSTEM GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive as a
part of the diagnostic procedure. The purpose of the
test drive is to duplicate the condition. Before test driving a brake complaint vehicle,
especially if the Red Brake Warning Lamp is on.
Test the brake function at low speed to be sure
that the car will stop normally. Remember that
conditions that result in illumination of the Red
Fig. 14 Decay Pressure - Hydraulic Control
5 - 88 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä