1993 BUICK LESABRE warning lights
[x] Cancel search: warning lightsPage 14 of 324
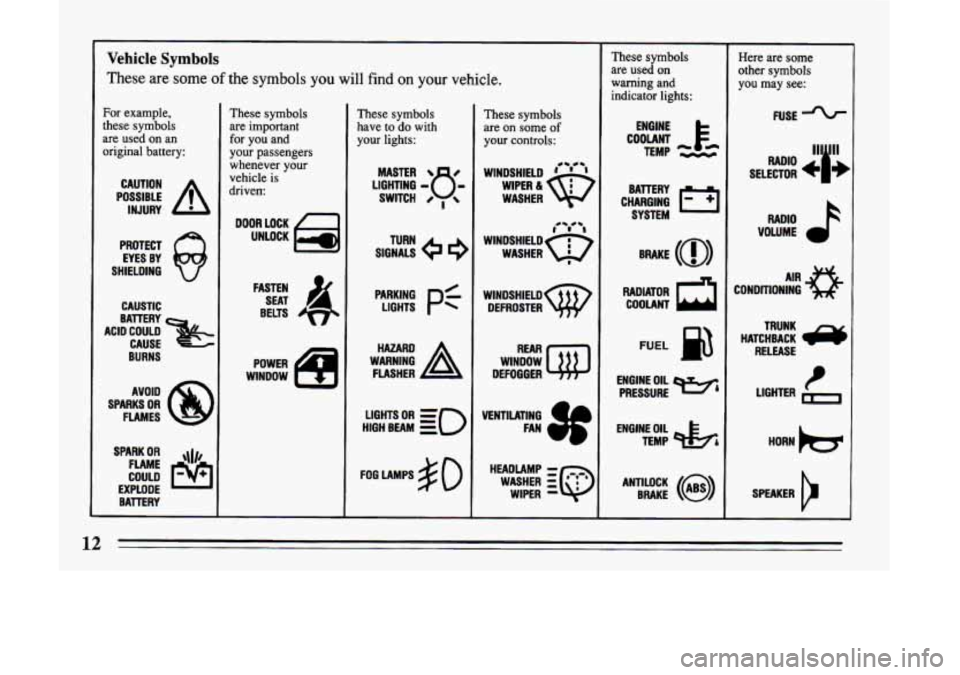
Vehicle Symbols
These
are some of the symbols you will find on your vehicle.
For example,
these symbols
are used on an
original battery:
POSSIBLE A
CAUTION
INJURY
PROTECT EYES BY
SHIELDING
Q
CAUSTIC
BURNS AVOID
SPARKS
OR
FLAMES
SPARK
OR ,\I/,
COULD FLAME
EXPLODE BATTERY
These symbols
are important
for you and
your passengers
whenever your
vehicle is
driven
DOOR LOCK
UNLOCK
FASTEN SEAT
4
BELTS
WINDOW POWER
These symbols
have
to do with
your lights:
LIGHTING - 8 -
MASTER 8
SWITCH 0 ,
SIGNALS e 9
TURN
LIGHTS
Pf
HIGH BEAM OR = =o
FOG LAMPS # 0
These symbols
are on some
of
your controls:
WINDSHIELD ' ' ' 4- e-
WASHER
wlNDsHIELDw DEFROSTER
WINDOW
DEFOGGER
HEADLAMP
- r~.c.r
WASHER :Q
WIPER -
These symbols
are used on
warning and
indicator lights:
COOLANT F*
TEMP -.--
ENGINE
CHARGING
I-1
BATTERY SYSTEM
RADIATOR
a
COOLANT
FUEL
ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
TEMP OIL
&
ANTILOCK (@)
BRAKE
Here are some
other symbols
you
may see:
FUSE
RADIO >
VOLUME
CONDITIONING
AIR 33
HATCHBACK /y
TRUNK
RELEASE
t LIGHTER
Page 59 of 324

@ Part 2 Features & Controls I
I
L-
Here you can learn about the many standard and optional features on your Buick. and information on starting. shifting
and braking
. Also explained are the instrument panel and the warning systems that tell you if everything is working
properly
.. and what to do if you have a problem .
Part 2 includes:
Keys
........................................................................\
.... 58
DoorLocks ....................................................................... \
59
NewVehicleBreak-In .............................................................. 68
StartingtheEngine ................................................................. 70
ShiftingtheTransaxle .............................................................. 73
Windows ........................................................................\
. 82
Tilt Steering Wheel ................................................................ 84
Multi-Function Lever ............................................................... 85
TunrandLaneChangeSignals ................................................... 85
Headlight High-Low Beam Changer .............................................. 87
Windshield Wipermasher ...................................................... 87
CruiseControl ................................................................ 89
Instrumentpanel ................................................................... 104
Speedometer and Odometer ..................................................... 105
Warning Lights and Gages ...................................................... 106
57
Page 98 of 324

Press the PARK switch to turn the parking lights on.
Press it again to
turn them off. (If the parking lights
were turned on with the PARK switch, they must be
turned
off with that switch).
Lights 660N’Z Warning
If the parking light or headlight switch is left on you’ll
hear a warning tone when you turn the ignition
off and
open the driver’s door.
Panel Lights
c
The instrument panel intensity can be adjusted by
I
moving this lever between
“LO” and “HI”. The
interior courtesy lights can
be turned
on by sliding the
lever all the way to the
right.
Time Out Feature (Option)
The interior lights will automatically shut off after a
10 minute period if a door is left ajar. This feature is
designed to help eliminate battery wear down.
Page 108 of 324

Warning Lights, Gages and
Indicators
This section describes the warning lights and gages that
may be on your vehicle. The pictures will help you
locate them.
Warning lights and gages can signal that something is
wrong before it becomes serious enough to cause an
expensive repair or replacement. Paying attention to
your warning lights and gages could also save
you or
others from injury.
Warning lights go on when there may be or
is a problem
with
one of your vehicle’s functions. As you will see in
the details
on the next few pages, some warning lights
come on briefly when
you turn the ignition key just to
let you know they’re working. If you are familiar with
this section, you should not be alarmed when this
happens.
Gages can indicate when there may be or is a problem
with one of your vehicle’s functions. Often gages and
warning lights work together to
let you how when
there’s a problem with your vehicle. When
one
of the warning lights comes on and stays on
when you are driving,
or when one of the gages shows
there may be
a problem, check the section that tells you
what to do about it. Please follow the manual’s advice.
Waiting to do repairs can be costly
-- and even
dangerous.
So please get to know your warning lights
and gages. They’re a big help.
Fuel Gage
r
F
”
I//,
0
ONLY E F F
106
Page 155 of 324

Pavement Markings
NO
PASSING
ZONE
Pavement markings add to traffic signs and signals.
They give information to drivers without taking
attention from the roadway. A solid yellow line on your
side
of the road or lane means “don’t cross.’’
Your Own Signals
Drivers signal to others, too. It’s not only more polite,
it’s safer to let other drivers know what
you are doing.
And in some places the law requires driver signals.
Turn and
lane change signals. Always signal when you
plan to turn or change lanes.
If necessary, you can use hand signals
out the window:
Left arm straight out for a left turn, down for slow or
about-to-stop, and
up for a right turn.
Slowinn down. If time allows, tap the brake pedal once
or twice in advance of slowing or stopping. This warns
the driver behind
you.
Disabled. Your four-way flashers signal that your
vehicle is disabled
or is a hazard. See “Hazard Warning
Flashers” in the Index.
Traffic Officer
The traffic police officer is also a source of important
information. The officer’s signals govern, no matter
what the traffic lights or other signs say.
The next section discusses some
of the road conditions
you may encounter.
153
Page 171 of 324

vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning clues -
such as enough water, ice or packed snow on the road to
make a “mirrored surface”
- and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock braking system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid. Steer the way
you want to go.
Driving at Night
Night driving is more dangerous than day driving. One
reason is that some drivers are likely
to be impaired -- by
alcohol or drugs, with night vision problems, or by
fatigue.
Here are some tips on night driving.
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Drive defensively. Remember, this is the most
dangerous time.
Don’t drink and drive, (See “Drunken Driving’’ in
the Index for more
on this problem.)
Adjust your inside rearview mirror to reduce the
glare from headlights behind you.
Since you can’t see as well,
you may need to slow
down and keep more space between you and other
vehicles. It’s hard to tell
how fast the vehicle ahead
is going just by looking at its taillights.
Slow down, especially on higher speed roads. Your
headlights can light up only
so much road ahead.
In remote areas, watch for animals.
If you’re tired, pull off the road in a safe place and
rest.
169
Page 177 of 324

lights on, start your hazard warning flashers, and sound
your horn at intervals or when you hear approaching
traffic.
Pass other vehicles in fog only if you can see far enough
ahead to pass safely. Even then, be prepared
to delay
your pass if you suspect the fog is worse up ahead. If
other vehicles try
to pass you, make it easy for them.
City Driving
I
One of the biggest problems with city streets is the
amount
of traffic on them. You’ll want to watch out for
what the other drivers are doing and pay attention to
traffic signals.
Here are ways
to increase your safety in city driving:
0
0
0
0
Know the best way to get to where you are going.
Try not to drive around trying to pick out a familiar
street or landmark. Get a city map and plan your trip
into an unknown part of the city just
as you would
for a cross-country trip.
Try
to use the freeways that rim and crisscross most
large cities. You’ll save time and energy. (See the
next section, “Freeway Driving.”)
Treat a green light as a warning signal.
A traffic light
is there because the corner is busy enough to need it.
When a light turns green, and just before you start to
move, check both ways for vehicles that have not
cleared
the intersection or may be running the red
light.
Obey all posted speed limits. But remember that they
are for ideal road, weather and visibility conditions.
You may need to drive below the posted limit in bad
weather or when visibility is especially poor.
Page 179 of 324

If you are on a three-lane freeway, treat the right lane as
the slower-speed through lane, the middle lane as the
higher-speed through lane, and the left lane
as the
passing lane.
Before changing lanes, check your rearview mirrors.
Then use your turn signal.
Just before
you leave the lane, glance quickly over your
shoulder to make sure there isn’t another vehicle in your
“blind” spot.
If you are moving from an outside
to a center lane on a
freeway having more than two lanes, make sure another
vehicle isn’t about to move into the same spot. Look at
the vehicles two lanes over and watch for telltale signs:
turn signals flashing, an increase in speed, or moving
toward the edge of the lane. Be prepared
to delay your
move.
Once
you are moving on the freeway, make certain you
allow
a reasonable following distance. Expect to move
slightly slower at night.
Leaving the Freeway
When you want to leave the freeway, move to the proper
lane well in advance. Dashing across lanes at the last
minute
is dangerous. If you miss your exit do not, under any circumstances, stop
and back up. Drive
on to the
next exit.
AI each exit point is a deceleration lane. Ideally it
should
be long enough for you to enter it at freeway
speed (after signaling,
of course) and then do your
braking before moving onto the exit ramp.
Unfortunately,
not all deceleration lanes are long enough
-- some are too short for all the braking. Decide when to
start braking. If you must brake on the through lane, and
if there is traffic close behind you, you can allow a little
extra time and flash your brake lights
(in addition to
your turn signal) as extra warning that
you are about to
slow down and exit.
The exit ramp can be curved, sometimes quite sharply.
I ne exit speed is usually posted. Reduce your speed
according to your speedometer, not
to your sense of
motion. After driving for any distance at higher speeds,
you may tend
to think you are going slower than you
actually are.
For example, 40 mph (65 km/h) might
seem like only
20 mph (30 km/h). Obviously, this could
lead to serious trouble on a ramp designed for
20 mph
(30 km/h)!
177