1992 HONDA PRELUDE air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 129 of 225

R — Replace I — Inspect After inspection, clean, adjust, repair or replace if necessary.
: Check oil and coolant level at each fuel stop.
: Under severe driving conditions, service these items more often.
* 1 : For cars sold in California, this service is recommended only: other
areas, it is required.
* 2 : Tension adjustment only. *
3 : Thereafter, replace every 2 years or 48,000 km (30,000 miles), which
-
ever comes first.
* 4 : For
cars with Anti-lock brake system.
(US: Si, Si 4WS, Canada
: SR, SR 4WS)
ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 131 of 225

Periodic Checks
You should check the following items at the specified intervals. If
you are unsure of how to perform
any check, turn to the page given. Engine oil level — Check every
time you fill the gas tank. See
page 102.
Engine coolant level — Check
the radiator reserve tank every
time you fill the gas tank. See
page 103.
Windshield washer fluid —
Check the level in the reservoir
monthly. If weather conditions
cause you to use the washers
frequently, check the reservoir each time you stop for gas. See
page 143 .
Automatic transmission — Check the fluid level monthly.
See page 144. Brakes, clutch and power
steering — Check the fluid level
monthly. See page 146.Tires — Check the tire pressure
monthly. Examine the tread for
wear and foreign objects. See
page 159.
Battery — Check its condition
and the terminals for corrosion
monthly. See page 152.
Air conditioner — Check its operation weekly. See page 157.
Lights — Check the operation of
the headlights, parking lights,
taillights, high-mount brake light,
turn signals, brake lights, and
license plate lights monthly. See
page 164.
MaintenanceProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 147 of 225
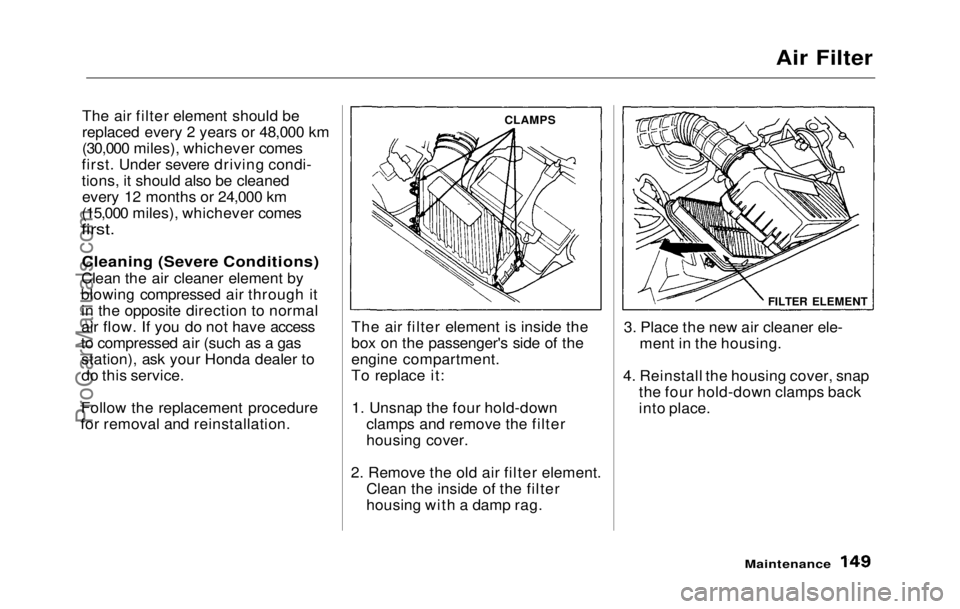
Air Filter
The air filter element should be
replaced every 2 years or 48,000 km
(30,000 miles), whichever comes
first. Under severe driving condi-
tions, it should also be cleaned every 12 months or 24,000 km
(15,000 miles), whichever comes
first.
Cleaning (Severe Conditions)
Clean the air cleaner element by
blowing compressed air through it in the opposite direction to normal
air flow. If you do not have access
to compressed air (such as a gas station), ask your Honda dealer to
do this service.
Follow the replacement procedure
for removal and reinstallation. The air filter element is inside the
box on the passenger's side of the
engine compartment.
To replace it:
1. Unsnap the four hold-down clamps and remove the filter
housing cover.
2. Remove the old air filter element. Clean the inside of the filter
housing with a damp rag. 3. Place the new air cleaner ele-
ment in the housing.
4. Reinstall the housing cover, snap the four hold-down clamps back
into place.
Maintenance
FILTER ELEMENT
CLAMPSProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 155 of 225

Air Conditioner
Optional for S model
Your car's air conditioner is a
sealed system. Any major mainte-
nance, such as recharging, should
be done by a qualified technician. There are a couple of things you
can do to make sure the air condi-
tioner works efficiently. Periodically check the engine's
radiator and air conditioning
condenser for leaves, insects, and
dirt stuck to the front surface.
These block the air flow and
reduce cooling efficiency. Use a light spray from a hose or a soft
brush to remove them.
The condenser and radiator fins
bend easily. Only use a low- pressure spray or soft-bristle brush
to clean them.
Run the air conditioner at least
once a week during the cold
weather months. Run it for at least ten minutes while you are driving
at a steady speed with the engine at
normal operating temperature.
This circulates the lubricating oil contained in the refrigerant. If the air conditioner does not get
as cold as before, it is probably
because some of the refrigerant has
leaked from the system. Have your dealer check the system for leaks
and recharge the system with
Refrigerant 12 (R-12).
Charging quantity: 750 — 800 g (26.5 — 28.3 oz)
Whenever you have the air condi-
tioning system serviced, make sure
the service facility uses a refrige-
rant recycling system. This system captures the refrigerant for reuse.
Releasing refrigerant into the at-
mosphere can damage the environ-
ment.
Maintenance
AIR CONDITIONING
CONDENSER
NOTICE
NOTICEProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 156 of 225

Engine Belts, Tires
Engine Belts
Check the condition of the two
engine belts. Examine the edges of
each belt for cracks or fraying.
Check the tension of each belt by pushing on it with your thumb
midway between the pulleys.
The belts should have the following "play" or deflection.
Alternator belt:
10.0 — 12.0 mm (0.39 — 0.47 in)
Power steering belt:
13.5 — 16.5
mm
(0.53
—
0.65 in)
If you see signs of wear or loose-
ness, have your dealer adjust or
replace the belts. Your dealer will
check these belts as part of the
normal scheduled maintenance.
Tires
Check the inflation and condition
of your car's tires at least once a
month.
Inflation
Check the pressure in the tires
when they are cold. This means the car has been parked for at least
three hours. If you have to drive
the car before checking the tire
pressure, the tires can still be
considered "cold" if you drive less than one mile.
If you check the pressure when the
tires are hot (the car has been
driven several miles), you will see
readings 28 to 41 kPa (0.3 to 0.4
kg/cm2, 4 to 6 psi) higher than the
cold reading. This is normal. Do not
let air out to match the specified
cold pressure. The tire will be
underinflated.
Maintenance
POWER STEERING BELT
ALTERNATOR
BELTProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 159 of 225

Tires
Replacing Tires
The tires that came with your Honda were selected to match the
performance capabilities of the car
and provide the best combination of
handling, ride comfort, and long life.
You should replace them with
radial tires of the same size, load
range, and speed rating. Mixing
radial and bias-ply or bias-belted tires on your car can reduce its
braking ability, traction, and
steering accuracy.
It is best to replace all four tires at
the same time. If that is not possi-
ble or necessary, then replace the two front tires or the two rear tires
as a pair. Replacing just one tire
can seriously affect your car's han-
dling.
If you ever need to replace a wheel,
make sure you use the same wheel
that originally came on your Honda.
Replacement wheels are available
at your Honda dealer. Wheels and Tires
Wheel:
(US: S, Canada: S)
14 x 5.5 JJ
(US: Si, Si 4WS, Canada: SR, SR 4WS)
15
x
6.5 JJ
Tire:
(US: S, Canada: S)
185/70R14 87H
(US: Si, Si 4WS, Canada: SR, SR 4WS)
205/55R15 87V
DOT Tire Quality Grading
(US Cars)
The tires on your car meet all U.S.
Federal Safety Requirements. All
tires are also graded for treadwear,
traction, and temperature perform-
ance according to Department of
Transportation (DOT) standards.
The following explains these
gradings.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a compara-
tive rating based on the wear rate
of the tire when tested under con-
trolled conditions on a specified
government test course. For exam-
ple, a tire graded 150 would wear
one and one half (1-1/2) times as
well on the government course as a
tire graded 100. The relative per-
formance of tires depends upon the
actual conditions of their use, how-
ever, and may depart significantly
from the norm due to variations in
driving habits, service practices
and differences in road character-
istics and climate.
CONTINUED
MaintenanceProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 207 of 225

Emission Controls
The burning of gasoline in your
car's engine produces several by-
products. Some of these are carbon
monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen
(NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC).
Gasoline evaporating from the tank
also produces hydrocarbons. Con-
trolling the production of NOx, CO,
and HC is important to the environ-
ment. Under certain conditions of
sunlight and climate, NOx and HC
react to form photochemical "smog."
Carbon monoxide does not contri-
bute to smog creation, but it is a
poisonous gas.
The Clean Air Act
The United States Clean Air Act*
sets standards for automobile
emissions. It also requires that
automobile manufacturers explain
to owners how their emission
controls work and what to do to
maintain them. This section
summarizes how the emission con-
trols work. Scheduled maintenance
is on page 129 .
* In Canada, Honda vehicles
comply with the Canadian Motor
Vehicle Safety Standards (CMVSS)
for Emissions valid at the time they
are manufactured.
Crankcase Emission Control
System
Your car has a Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) System. This
keeps gasses that build up in the engine's Crankcase from going into
the atmosphere. The PCV valve
routes them from the crankcase
back to the intake manifold. They
are then drawn into the engine and
burned.
Evaporative Emission
Control SystemAs gasoline evaporates in the fuel
tank, a canister filled with charcoal
adsorbs the vapor. It is stored in
this canister while the engine is off.
After the engine is started and
warmed up, the vapor is drawn into the engine and burned during
driving.
Technical Informatio n
ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 208 of 225

Emission Controls
Exhaust Emission Controls
The exhaust emission controls
include four systems: PGM-FI,
Ignition Timing Control, Exhaust
Gas Recirculation and Catalytic
Converter. These four systems
work together to control the engine's combustion and minimize
the amount of HC, CO, and NOx
that comes out the tailpipe. The
exhaust emission control systems
are separate from the crankcase
and evaporative emission control
systems.
PGM-FI System
The PGM-FI System on your car
has three sub systems: Air Intake,
Electronic Control, and Fuel
Control. The Electronic Control
Unit (ECU) uses various sensors to
determine how much air is going
into the engine. It then controls
how much fuel to inject under all
operating conditions. Ignition Timing Control System
This system constantly adjusts the
ignition timing, reducing the
amount of HC, CO and NOx
produced.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
The EGR system takes some of the
exhaust gas and routes it back into
the intake manifold. Adding ex-
haust gas to the air/fuel mixture re-
duces the amount of NOx produced
when the fuel is burned.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is in the exhaust system. Through chemical
reactions, it converts HC, CO, and
NOx in the engine's exhaust to
carbon dioxide (CO 2), dinitrogen
(N 2), and water vapor.
Replacement Parts
The emission control systems are
designed and certified to work to-
gether in reducing emissions to
levels that comply with the Clean
Air Act. To make sure the emis-
sions remain low, you should use
only new genuine Honda replace-
ment parts or their equivalent for
repairs. Using lower quality parts
may increase the emissions from
your car .
The emissions control systems are
covered b y
warranties separate
from the rest of your car. Read
your warranty manual for more
information.
Technical InformationProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t