Page 3362 of 4087
Cold Start Injector Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
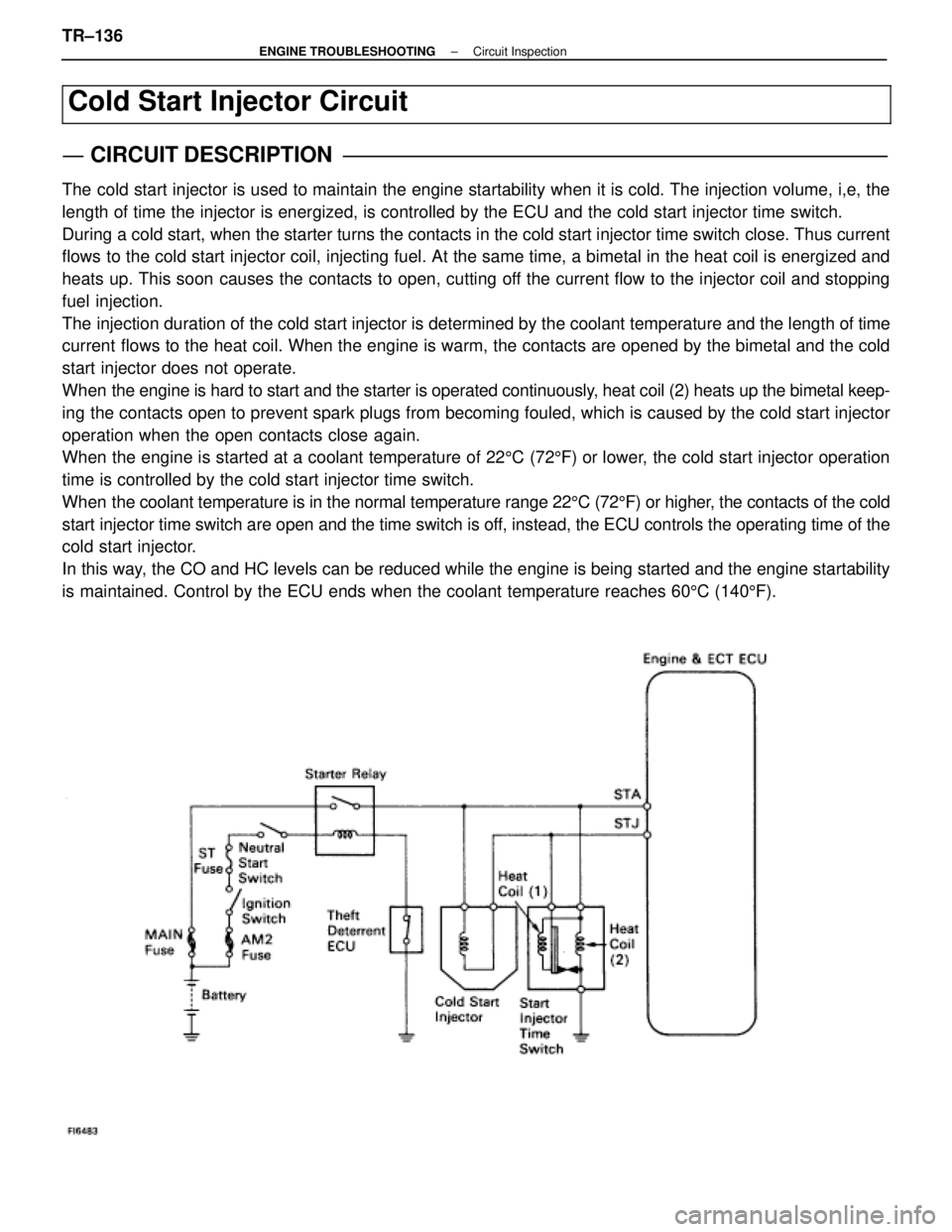
The cold start injector is used to maintain the engine startability when it\
is cold. The injection volume, i,e, the
length of time the injector is energized, is controlled by the ECU and t\
he cold start injector time switch.
During a cold start, when the starter turns the contacts in the cold start inj\
ector time switch close. Thus current
flows to the cold start injector coil, injecting fuel. At the same time, a bi\
metal in the heat coil is energized and
heats up. This soon causes the contacts to open, cutting off the current flow to the injector coil and stopping
fuel injection.
The injection duration of the cold start injector is determined by the cool\
ant temperature and the length of time
current flows to the heat coil. When the engine is warm, the contacts are opened by the bimetal and the cold
start injector does not operate.
When the engine is hard to start and the starter is operated continuously, heat coil (2) heats up the bimetal keep-
ing the contacts open to prevent spark plugs from becoming fouled, which is\
caused by the cold start injector
operation when the open contacts close again.
When the engine is started at a coolant temperature of 225C (72 5F) or lower, the cold start injector operation
time is controlled by the cold start injector time switch.
When the coolant temperature is in the normal temperature range 22 5C (72 5F) or higher, the contacts of the cold
start injector time switch are open and the time switch is off, instead, the ECU controls the operating time of the
cold start injector.
In this way, the CO and HC levels can be reduced while the engine is being started \
and the engine startability
is maintained. Control by the ECU ends when the coolant temperature reac\
hes 60 5C (140 5F).
TR±136±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3574 of 4087
Cold Start Injector Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
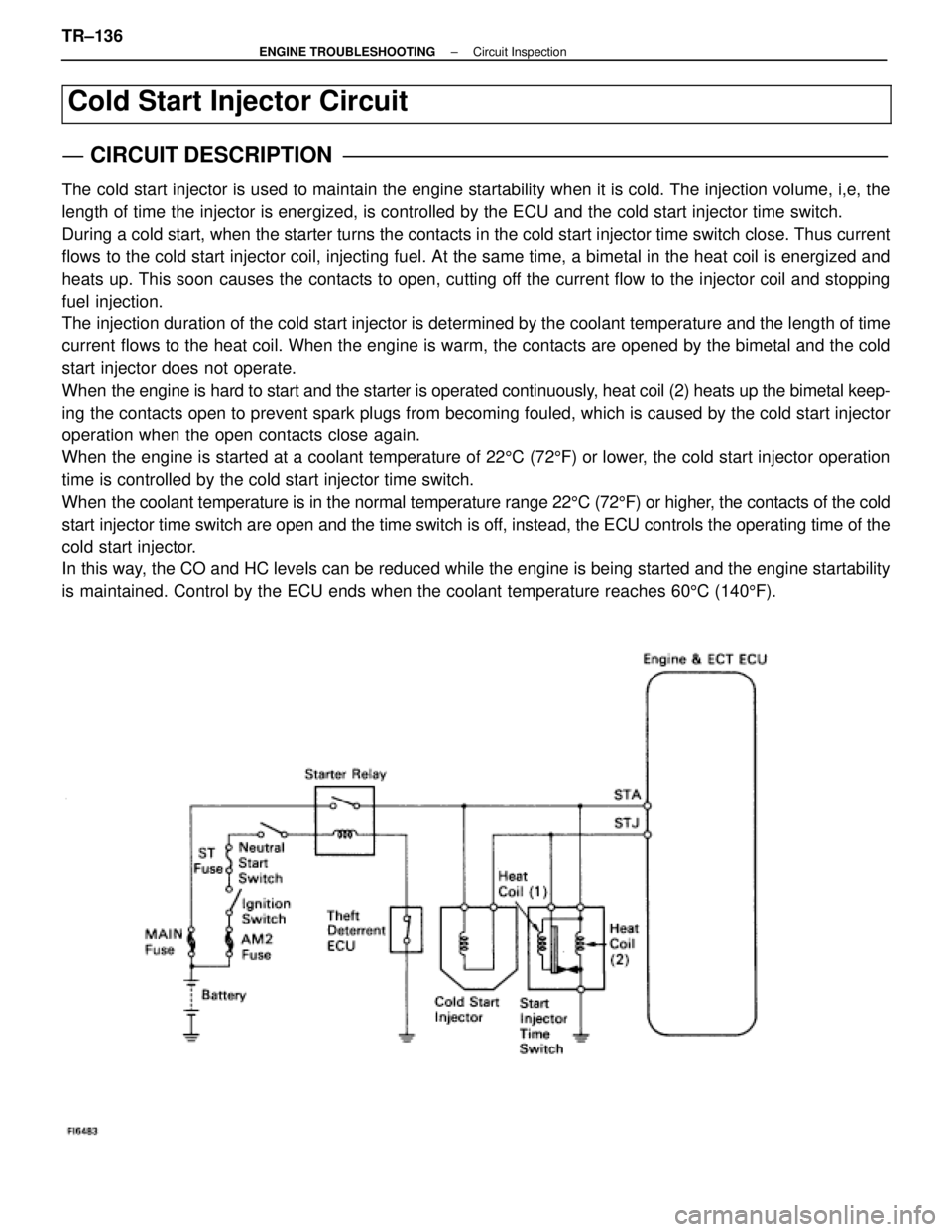
The cold start injector is used to maintain the engine startability when it\
is cold. The injection volume, i,e, the
length of time the injector is energized, is controlled by the ECU and t\
he cold start injector time switch.
During a cold start, when the starter turns the contacts in the cold start inj\
ector time switch close. Thus current
flows to the cold start injector coil, injecting fuel. At the same time, a bi\
metal in the heat coil is energized and
heats up. This soon causes the contacts to open, cutting off the current flow to the injector coil and stopping
fuel injection.
The injection duration of the cold start injector is determined by the cool\
ant temperature and the length of time
current flows to the heat coil. When the engine is warm, the contacts are opened by the bimetal and the cold
start injector does not operate.
When the engine is hard to start and the starter is operated continuously, heat coil (2) heats up the bimetal keep-
ing the contacts open to prevent spark plugs from becoming fouled, which is\
caused by the cold start injector
operation when the open contacts close again.
When the engine is started at a coolant temperature of 225C (72 5F) or lower, the cold start injector operation
time is controlled by the cold start injector time switch.
When the coolant temperature is in the normal temperature range 22 5C (72 5F) or higher, the contacts of the cold
start injector time switch are open and the time switch is off, instead, the ECU controls the operating time of the
cold start injector.
In this way, the CO and HC levels can be reduced while the engine is being started \
and the engine startability
is maintained. Control by the ECU ends when the coolant temperature reac\
hes 60 5C (140 5F).
TR±136±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3917 of 4087

METER, ANALOGCurrent flow activates a magnetic
coil which causes a needle to
move, thereby providing a relative
display against a background
calibration.
LED (LIGHT EMITTING DIODE)
Upon current flow, these diodes
emit light without producing the
heat of a comparable light.
IGNITION COIL
Converts low±voltage DC current
into high±voltage ignition current
for firing the spark plugs.
1. SINGLE
FILAMENT
GROUND
The point at which wiring attaches
to the Body, thereby providing a
return path for an electrical circuit;
without a ground, current cannot
flow. Current flow causes a headlight
filament to heat up and emit light.
A headlight may have either a
single (1) filament or a double (2)
filament.
BATTERY
Stores chemical energy and
converts it into electrical energy.
Provides DC current for the auto's
various electrical circuits.
CAPACITOR (Condenser) A small holding unit for temporary
storage of electrical voltage.
CIRCUIT BREAKER Basically a reusable fuse, a circuit
breaker will heat and open if too
much current flows through it. Some
units automatically reset when cool,
others must be manually reset.
DIODE A semiconductor which allows
current flow in only one direction.
DIODE, ZENER A diode which allows current flow
in one direction but blocks reverse
flow only up to a specific voltage.
Above that potential, it passes the
excess voltage. This acts as a
simple voltage regulator.
FUSE A thin metal strip which burns
through when too much current
flows through it, thereby stopping
current flow and protecting a
circuit from damage.
FUSIBLE LINK A heavy±gauge wire placed in
high amperage circuits which
burns through on overloads,
thereby protecting the circuit.
The numbers indicate the cross±
section surface area of the wires. HORN
An electric device which sounds a
loud audible signal.
LIGHT Current flow through a filament
causes the filament to heat up
and emit light.
METER, DIGITAL Current flow activates one or
many LED's, LCD's, or fluorescent
displays, which provide a relative
or digital display.
MOTOR A power unit which converts
electrical energy into mechanical
energy, especially rotary motion.
CIGARETTE LIGHTER
An electric resistance heating
element.
DISTRIBUTOR, IIA Channels high±voltage current
from the ignition coil to the
individual spark plugs. 2. DOUBLE
FILAMENT
HEADLIGHTS
FUEL
(for High Current Fuse or
Fusible Link)
(for Medium Current Fuse)
M
16
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND SYMBOLS
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName