1991 FORD FESTIVA battery replacement
[x] Cancel search: battery replacementPage 5 of 454

TURBO BOOST GAUGE & SENSOR (CAPRI)
1. Disconnect 3-pin boost sensor electrical connected located on right side of firewall. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between
Yellow/Green and Black wires. Voltage should be greater than 10 volts. Turn ignition off. If voltage is greater than 10 volts, go t o n e xt
step. If voltage is 10 volts or less, repair Yellow/Green or Black wires as necessary.
2. Remove instrument panel. See INSTRUMENT PANEL
under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Disconnect instrument panel 8-pin
connector. With boost sensor disconnected, measure resistance through White/Black between instrument panel and boost sensor harness
connector. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or more, repair or replace White/Black wire.
3. With 8-pin instrument panel connector disconnected, ground White/Black at boost gauge. Boost gauge should read low. Apply 12 vo l t s
to White/Black wire at boost gauge. Boost gauge should read high. If boost gauge operates as specified, go to next step. If boost gauge
does not operate as specified, replace boost gauge.
4. Reconnect instrument panel connectors (if removed). With ignition on and boost sensor disconnected, install jumper wire between
Yellow/Green and White/Black wires of boost sensor vehicle harness connector. Boost gauge should read high. If boost gauge reads
high, replace boost sensor. If boost gauge does not read high, go to TROUBLE SHOOTING
for other possible causes.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
INSTRUMENT PANEL
Removal & Installation (Capri)
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Pull storage compartment from heater/radio bezel. Pull outward and remove trim covers located on
both sides of steering column. Remove retaining screws and carefully pull instrument panel bezel partially away from dash. Disconnect
electrical connectors from clock and switches in bezel. Remove instrument panel bezel.
2. Disconnect speedometer cable from transaxle. Remove instrument panel retaining screws and slide instrument panel outward. Press lock
tab and release speedometer cable from instrument panel. Remove electrical connectors from rear of instrument panel. Remove
instrument panel. To install instrument panel, reverse removal procedure.
Removal & Installation (Festiva)
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove upper and lower steering column covers. Remove screws from panel bezel and remove bezel.
Disconnect rear wiper switch and rear defogger switch wiring harness connectors (if equipped).
2. Remove instrument panel-to-dash screws. Pull panel from dash. Reach behind panel and release speedometer drive cable lock tab. Lift
lock tabs and disconnect 2 electrical connectors from rear of panel. Remove panel. To install instrument panel, reverse removal
procedure.
INDICATOR LIGHTS
Removal & Installation
Remove instrument panel for access to indicator light bulbs. See INSTRUMENT PANEL under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. To remove
bulb, rotate bulb counterclockwise to disengage locking tabs. When tabs release, pull bulb from printed circuit board. To install bulb, reverse
removal procedure. Install instrument panel and test lights.
SPEEDOMETER R & I
Removal & Installation (Capri)
R e mo ve n e ga t ive b a t t e r y c a b l e . R e mo ve in st r u me n t p a n e l . S e e INSTRUMENT PANEL under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Disassemble
instrument panel and remove speedometer/tachometer/boost gauge assembly from instrument panel. To install, apply a 3/16" (4.6 mm) b al l o f
Silicone Damping Grease (D7AZ-19A331-A) into drive hole of speedometer head. Reverse removal procedure to complete installation.
Removal & Installation (Festiva)
R e mo ve n e ga t ive b a t t e r y c a b l e . R e mo ve in st r u me n t p a n e l . S e e INSTRUMENT PANEL under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Disassemble
instrument panel and remove speedometer head assembly from instrument panel. Speedometer is a separate module and can be removed
independently from gauges. To install, reverse removal procedure.
SPEED SENSOR
On vehicles equipped with speed control, a speed sensor is mounted in speedometer head assembly. If replacement is necessary, speedometer
head assembly must be replaced. See SPEEDOMETER R & I
under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION.
FUEL GAUGE
Removal & Installation
Remo ve in st ru men t p an el . See INSTRUMENT PANEL under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. Disassemble panel and remove fuel gauge.
To install gauge, reverse removal procedure. On Capri, the fuel/volt gauge must be replaced as an assembly.
FUEL SENDING UNIT
Removal & Installation
1. For Festiva, remove rear seat. For Capri, remove rear seat cushion. On Festiva, remove carpet hold-down pins and lift carpet for access
to sending unit access plate. On all models, remove access plate screws. NOTE:Federal law requires that a label stating the odom eter has been repaired or replaced be affixed to any
vehicle that has its odom eter repaired, replaced or set to zero.
Page 4 of 5 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - INSTRUMENT PANEL 1991 ACCESSORIES & SAFETY EQUIPMENT Ford Motor Co. Switches
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B959286D2%2D3A85%2D4BFC%2D9C5C%2D
...
Page 50 of 454
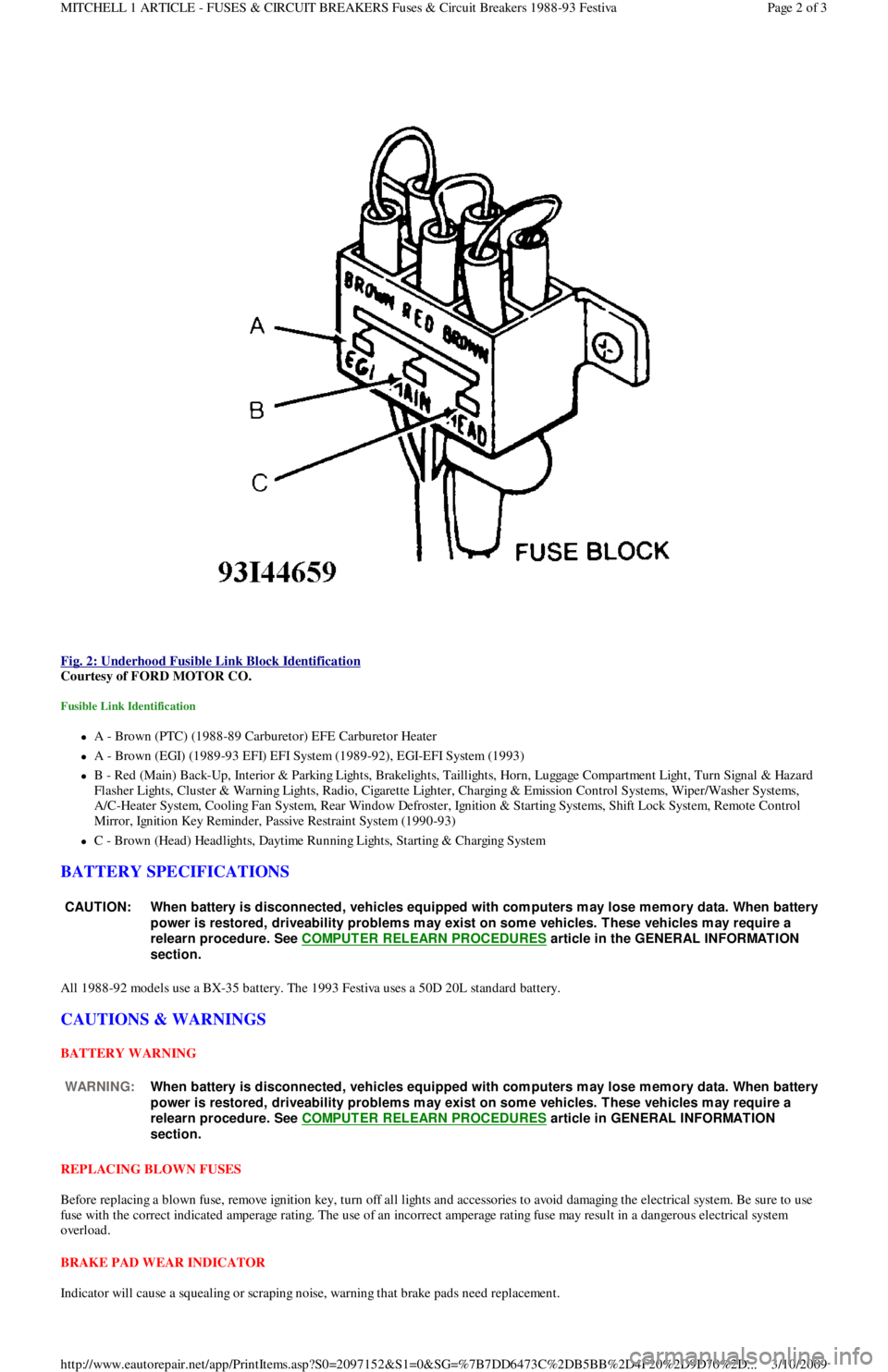
Fig. 2: Underhood Fusible Link Block Identification
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
Fusible Link Identification
A - Brown (PTC) (1988-89 Carburetor) EFE Carburetor Heater
A - Brown (EGI) (1989-93 EFI) EFI System (1989-92), EGI-EFI System (1993)
B - Red (Main) Back-Up, Interior & Parking Lights, Brakelights, Taillights, Horn, Luggage Compartment Light, Turn Signal & Hazard
F l a sh e r Ligh t s, C l u st e r & Wa r n in g Ligh t s, R a d io , C iga r e t t e Ligh t e r , C h a r gin g & E missio n C o n t r o l S yst e ms, Wip e r / Wa sh e r S yst e ms,
A/C-Heater System, Cooling Fan System, Rear Window Defroster, Ignition & Starting Systems, Shift Lock System, Remote Control
Mirror, Ignition Key Reminder, Passive Restraint System (1990-93)
C - Brown (Head) Headlights, Daytime Running Lights, Starting & Charging System
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
All 1988-92 models use a BX-35 battery. The 1993 Festiva uses a 50D 20L standard battery.
CAUTIONS & WARNINGS
BATTERY WARNING
REPLACING BLOWN FUSES
Before replacing a blown fuse, remove ignition key, turn off all lights and accessories to avoid damaging the electrical system. Be sure to use
fuse with the correct indicated amperage rating. The use of an incorrect amperage rating fuse may result in a dangerous electrical system
overload.
BRAKE PAD WEAR INDICATOR
Indicator will cause a squealing or scraping noise, warning that brake pads need replacement.
CAUT ION: When battery is disconnected, vehicles equipped with com puters m ay lose m em ory data. When battery
power is restored, driveability problem s m ay exist on som e vehicles. T hese vehicles m ay require a
relearn procedure. See COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
article in the GENERAL INFORMAT ION
section.
WARNING:When battery is disconnected, vehicles equipped with com puters m ay lose m em ory data. When battery
power is restored, driveability problem s m ay exist on som e vehicles. T hese vehicles m ay require a
relearn procedure. See COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
article in GENERAL INFORMAT ION
section.
Page 2 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - FUSES & CIRCUIT BREAKERS Fuses & Circuit Breakers 1988-93 Festiva
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 153 of 454
Back To Article
C - SPECIFICATIONS
1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury - Service & Adjustm ent Specifications
INTRODUCTION
Use this article to quickly find specifications related to servicing and on-vehicle adjustments. This is a quick-reference article to use when you
are familiar with an adjustment procedure and only need a specification.
CAPACITIES
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS
FLUID CAPACITIES
FLUID CAPACITIES
QUICK-SERVICE
SERVICE INTERVALS & SPECIFICATIONS
REPLACEMENT INTERVALS
BELT ADJUSTMENTS
(1)
BELT ADJUSTMENTS
(1)
MECHANICAL CHECKS
ENGINE COMPRESSION
Check engine compression at specified cranking speed with engine at normal operating temperature, all spark plugs removed and throttle wide
open.
COMPRESSION SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationAmp Hr. Rating
1.3L & 1.6L50
ApplicationQts. (L)
Crankcase (Includes Filter)3.6 (3.4)
Cooling System (Includes Heater)5.3 (5.0)
Manual Transaxle (Mercon)2.6 (2.5)
Automatic Transaxle (Mercon)6.0 (5.7)
ApplicationQts. (L)
Crankcase (Includes Filter)
Non-Turbo3.5 (3.3)
Turbo3.7 (3.5)
Cooling System (Includes Heater)
Non-Turbo5.3 (5.0)
Turbo6.3 (6.0)
Manual Transaxle (Mercon)3.4 (3.2)
Automatic Transaxle (Mercon)6.0 (5.7)
ComponentInterval (Miles)
Air Filter30,000
Camsh aft Timin g Bel t60,000
Coolant30,000
Oil & Filter3000
Spark Plugs30,000
ApplicationNew BeltUsed Belt
A/C Belt110-125 (50-57)92-110 (42-50)
Alternator Belt110-132 (50-60)95-110 (43-50)
(1)Tension in Lbs. (Kg) Using Strand Tension Gauge
ApplicationNew BeltUsed Belt
A/C Belt110-132 (50-60)110-132 (50-60)
Alternator Belt110-132 (50-60)110-132 (50-60)
(1)Tension in Lbs. (Kg) Using Strand Tension Gauge.
ApplicationSpecification
Compression Ratio
1.3L9.7:1
1.6L(1)
Compression Pressure(2)
Page 1 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - C - SPECIFICATIONS 1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury - Service & Adjustment Spe
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 215 of 454
IGNITION SYSTEM TROUBLE SHOOTING
connections
Defective alternator or regulatorSee Bench Tests and On-
Vehicle Tests in
ALTERNATOR article
Defective ammeter, or improper ammeter wiring connectionSee Testing in STANDARD
INSTRUMENTS in the
ACCESSORIES &
EQUIPMENT section
Noisy Alternator
Loose drive pulleyTighten drive pulley attaching
nut
Loose mounting boltsTighten all alternator mounting
bolts
Worn or dirty bearingsSee Bearing Replacement
ALTERNATOR article
Defective diodes or statorSee Bench Test in
ALTERNATOR article
Battery Does Stay Charged
Loose or worn drive beltCheck alternator drive belt
tension and condition. See Belt
Adjustment in appropriate
TUNE-UP article in the TUNE-
UP section
Loose or corroded battery connectionsCheck all charging system
connections
Loose alternator connectionsCheck all charging system
connections
Defective alternator or batterySee On-Vehicle Tests and
Bench Tests in ALTERNATOR
article
Add-on electrical accessories exceeding alternator capacityInstall larger alternator
Battery Overcharged-Uses Too Much Water
Defective batteryCheck alternator output and
repair as necessary
Defective alternatorSee On-Vehicle Test and Bench
Tests in ALTERNATOR article
Excessive alternator voltageCheck alternator output and
repair as necessary
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. T he purpose of this T rouble Shooting inform ation is to provide a list
of com m on causes to problem sym ptom s. For m odel-specific T rouble Shooting, refer to SUBJECT ,
DIAGNOST IC, or T EST ING articles available in the section(s) you are accessing.
Page 2 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 284 of 454

Since DVOMs update their display roughly two to five times a second, all measurements in between are averaged. Because a potential voltage
drop is visible for such a small amount of time, it ge t s "a ve r a ge d o u t ", c a u sin g yo u t o miss it .
Only a DVOM that has a "min-max" function that checks EVERY MILLISECOND will catch this fault consistently (if used in that mode). The
Fluke 87 among others has this capability.
A "min-max" DVOM with a lower frequency of checking (100 millisecond) can miss the fault because it will probably check when the injector
is not on. This is especially true with current controlled driver circuits. The Fluke 88, among others fall into this category.
Outside of using a Fluke 87 (or equivalent) in the 1 mS "min-max" mode, the only way to catch a voltage drop fault is with a lab scope. You
will be able to see a voltage drop as it happens.
One final note. It is important to be aware that an injector circuit with a solenoid resistor will always show a voltage drop when the circuit is
energized. This is somewhat obvious and normal; it is a designed-in voltage drop. What can be unexpected is what we already covered--a
voltage drop disappears when the circuit is unloaded. The unloaded injector circuit will show normal battery voltage at the injector.
Remember this and do not get confused.
Checking Injector On-Time With Built-In Function
Several DVOMs have a feature that allows them to measure injector on-time (mS pulse width). While they are accurate and fast to hookup,
they have three limitations you should be aware of:
They only work on voltage controlled injector drivers (e.g "Saturated Switch"), NOT on current controlled injector drivers (e.g. "Peak &
Hold").
A few unusual conditions can cause inaccurate readings.
Varying engine speeds can result in inaccurate readings.
Regarding the first limitation, DVOMs need a well-defined injector pulse in order to determine when the injector turns ON and OFF. Voltage
controlled drivers provide this because of their simple switch-like operation. They completely close the circuit for the entire duration of the
pulse. This is easy for the DVOM to interpret.
The other type of driver, the current controlled type, start off well by completely closing the circuit (until the injector pintle opens), but then
they throttle back the voltage/current for the duration of the pulse. The DVOM understands the beginning of the pulse but it cannot figure out
the throttling action. In other words, it cannot distinguish the throttling from an open circuit (de-energized) condition.
Yet current controlled injectors will still yield a millisecond on-time reading on these DVOMs. You will find it is also always the same,
regardless of the operating conditions. This is because it is only measuring the initial completely-closed circuit on-time, which always takes the
same amount of time (to lift the injector pintle off its seat). So even though you get a reading, it is useless.
The second limitation is that a few erratic conditions can cause inaccurate readings. This is because of a DVOM's slow display rate; roughly
two to five times a second. As we covered earlier, measurements in between display updates get averaged. So conditions like skipped injector
pulses or intermittent long/short injector pulses tend to get "averaged out", which will cause you to miss important details.
The last limitation is that varying engine speeds can result in inaccurate readings. This is caused by the quickly shifting injector on-time as the
engine load varies, or the RPM moves from a state of acceleration to stabilization, or similar situations. It too is caused by the averaging of all
measurements in between DVOM display periods. You can avoid this by checking on-time when there are no RPM or load changes.
A lab scope allows you to overcome each one of these limitations.
Checking Injector On-Time With Dwell Or Duty
If no tool is available to directly measure injector millisecond on-time measurement, some techs use a simple DVOM dwell or duty cycle
functions as a replacement.
While this is an approach of last resort, it does provide benefits. We will discuss the strengths and weaknesses in a moment, but first we will
look at how a duty cycle meter and dwell meter work.
How A Duty Cycle Meter and Dwell Meter Work
All readings are obtained by comparing how long something has been OFF to how long it has been ON in a fixed time period. A dwell meter
and duty cycle meter actually come up with the same answers using different scales. You can convert freely between them. See
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DWELL & DUTY CYCLE READINGS TABLE
.
The DVOM display updates roughly one time a second, although some DVOMs can be a little faster or slower. All measurements during this
update period are tallied inside the DVOM as ON time or OFF time, and then the total ratio is displayed as either a percentage (duty cycle) or
degrees (dwell meter).
For example, let's say a DVOM had an update rate of exactly 1 second (1000 milliseconds). Let's also say that it has been measuring/tallying
an injector circuit that had been ON a total of 250 mS out of the 1000 mS. That is a ratio of one-quarter, which would be displayed as 25%
duty cycle or 15° dwell (six-cylinder scale). Note that most duty cycle meters can reverse the readings by selecting the positive o r n e ga t ive
slope to trigger on. If this reading were reversed, a duty cycle meter would display 75%.
Strengths of Dwell/Duty Meter
The obvious strength of a dwell/duty meter is that you can compare injector on-time against a known-good reading. This is the only practical
way to use a dwell/duty meter, but requires you to have known-good values to compare against.
Another strength is that you can roughly convert injector mS on-time into dwell reading with some computations.
A final strength is that because the meter averages everything together it does not miss anything (though this is also a severe weakness that we
will look at later). If an injector has a fault where it occasionally skips a pulse, the meter registers it and the reading changes accordingly.
Page 3 of 19 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Waveforms - Injector Pattern Tutorial
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...