1991 BMW 3 SERIES exhaust
[x] Cancel search: exhaustPage 125 of 228

Check
12Warm up the engine, and let it run at idle.
Disconnect the oxygen sensor electrical
connector, and connect the positive probe of
a voltmeter to the oxygen sensor output
connector terminal (refer to the following
table) and the negative probe to earth (see
illustrations).
Note:Most oxygen sensor electrical
connectors are located at the rear of the
engine, near the bulkhead. Look for a large
rubber boot attached to a thick wire harness.
On early 535i models, the connector for the
oxygen sensor heater circuit is under the
vehicle. Look for a small protective cover.
These models should have the updated
oxygen sensor fitted, to make access similar
to other models. Consult your dealer service
department for additional information.
13Increase and then decrease the engine
speed, and monitor the voltage.
14When the speed is increased, the voltage
should increase to 0.5 to 1.0 volts. When the
speed is decreased, the voltage should fall to
about 0 to 0.4 volts.
15Also where applicable, inspect the oxygen
sensor heater (models with multi-wire
sensors). With the ignition on, disconnect the
oxygen sensor electrical connector, and
connect a voltmeter across the terminals
designated in the chart (see below). There
should be battery voltage (approximately
12 volts).
16If the reading is not correct, check the
oxygen sensor heater relay (see Chapter 12).
If the information is not available, check the
owner’s handbook for the exact location of
the oxygen sensor heater relay. The relay
should receive battery voltage.
17If the oxygen sensor fails any of these
tests, renew it.
Renewal
Note: Because it is fitted in the exhaust
manifold, converter or pipe, which contracts
when cool, the oxygen sensor may be very
difficult to loosen when the engine is cold.
Rather than risk damage to the sensor(assuming you are planning to re-use it in
another manifold or pipe), start and run the
engine for a minute or two, then switch it off.
Be careful not to burn yourself during the
following procedure.
18Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
19Raise and support the vehicle.
20Disconnect the electrical connector from
the sensor.
21Carefully unscrew the sensor.
Caution: Excessive force may
damage the threads.
22A high-temperature anti-seize compound
must be used on the threads of the sensor, to
facilitate future removal. The threads of new
sensors will already be coated with this
compound, but if an old sensor is removed
and refitted, recoat the threads.23Refit the sensor and tighten it securely.
24Reconnect the electrical connector of the
pigtail lead to the main engine wiring harness.
25Lower the vehicle, and reconnect the
battery.
Oxygen Sensor Heated power
sensor type output signal supply (12V)
Unheated
(single-wire) black wire (+) Not applicable
Heated terminal 1 (+) terminals
(three-wire) 3 (+) and 2 (-)
Heated terminal 2 (+) terminals
(four-wire) 4 (+) and 3 (-)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
General description
26The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is
located on the end of the throttle shaft on the
throttle body. By monitoring the output
voltage from the TPS, the ECU can determine
fuel delivery based on throttle valve angle
(driver demand). In this system, the TPS acts
as a switch rather than a potentiometer. One
set of throttle valve switch contacts is closed
(continuity) only at idle. A second set of
contacts closes as the engine approaches
full-throttle. Both sets of contacts are open
(no continuity) between these positions. A
broken or loose TPS can cause intermittent
bursts of fuel from the injector and an
unstable idle, because the ECU thinks the
throttle is moving.
27All models (except for early 535i models
with automatic transmission) combine the idle
and full-throttle switch; a separate idle
position switch indicates the closed-throttle
position, while the TPS is used for the full-
throttle position. On 535i models with
automatic transmission, the TPS is connected
directly to the automatic transmission control
unit. With the throttle fully open, the
transmission control unit sends the full-
throttle signal to the Motronic control unit.
All models except early 535i with
automatic transmission
Check
28Remove the electrical connector from the
TPS, and connect an ohmmeter to terminals 2
and 18 (see illustrations). Open the throttle
Engine management and emission control systems 6•3
4.12b These oxygen sensor terminal
designations are for the harness side only.
Use the corresponding terminals on the
sensor side for the testing procedures
(there are three different four-wire oxygen
sensor connectors available - don’t get
them mixed up)4.12a The oxygen sensor, once it is
warmed up (320º C), puts out a very small
voltage signal. To verify it is working,
check for voltage with a digital voltmeter
(the voltage signals usually range from
0.1 to 1.0 volt)
4.28b First check for continuity between
terminals 2 and 18 with the throttle closed
(later Motronic system shown) . . .4.28a The TPS on L-Jetronic systems is
located under the intake manifold
(terminals arrowed)
6
Page 128 of 228
On some models, it will be necessary to
release the retaining clip (see illustration).
13Visually examine the canister for leakage
or damage.
14Renew the canister if you find evidence of
damage or leakage.
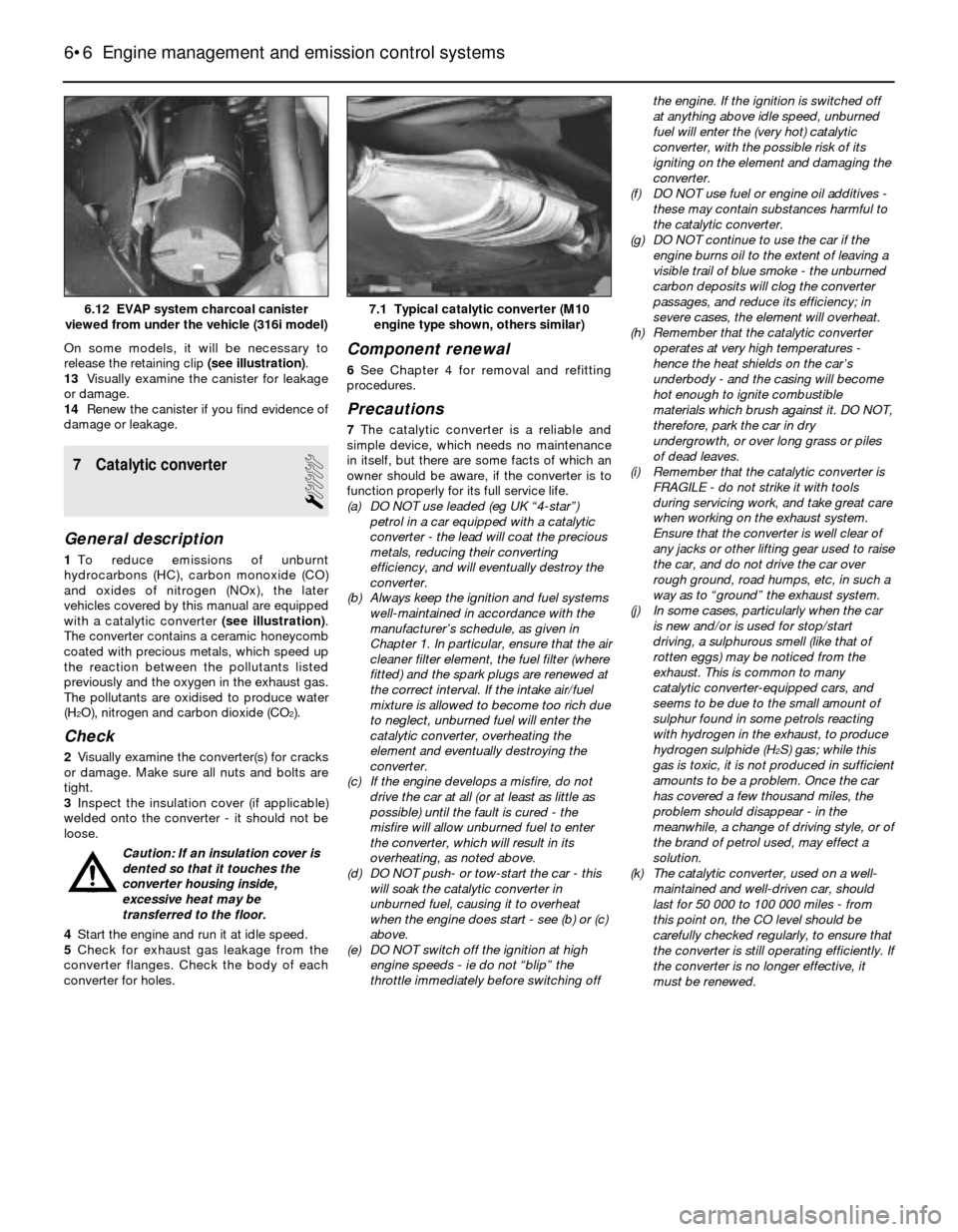
7 Catalytic converter
1
General description
1To reduce emissions of unburnt
hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the later
vehicles covered by this manual are equipped
with a catalytic converter (see illustration).
The converter contains a ceramic honeycomb
coated with precious metals, which speed up
the reaction between the pollutants listed
previously and the oxygen in the exhaust gas.
The pollutants are oxidised to produce water
(H
2O), nitrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Check
2Visually examine the converter(s) for cracks
or damage. Make sure all nuts and bolts are
tight.
3Inspect the insulation cover (if applicable)
welded onto the converter - it should not be
loose.
Caution: If an insulation cover is
dented so that it touches the
converter housing inside,
excessive heat may be
transferred to the floor.
4Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
5Check for exhaust gas leakage from the
converter flanges. Check the body of each
converter for holes.
Component renewal
6See Chapter 4 for removal and refitting
procedures.
Precautions
7The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware, if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded (eg UK “4-star”)
petrol in a car equipped with a catalytic
converter - the lead will coat the precious
metals, reducing their converting
efficiency, and will eventually destroy the
converter.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule, as given in
Chapter 1. In particular, ensure that the air
cleaner filter element, the fuel filter (where
fitted) and the spark plugs are renewed at
the correct interval. If the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, unburned fuel will enter the
catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
(d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see (b) or (c)
above.
(e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - ie do not “blip” the
throttle immediately before switching offthe engine. If the ignition is switched off
at anything above idle speed, unburned
fuel will enter the (very hot) catalytic
converter, with the possible risk of its
igniting on the element and damaging the
converter.
(f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
(g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages, and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry
undergrowth, or over long grass or piles
of dead leaves.
(i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system.
Ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car, and do not drive the car over
rough ground, road humps, etc, in such a
way as to “ground” the exhaust system.
(j) In some cases, particularly when the car
is new and/or is used for stop/start
driving, a sulphurous smell (like that of
rotten eggs) may be noticed from the
exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped cars, and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the car
has covered a few thousand miles, the
problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(k) The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for 50 000 to 100 000 miles - from
this point on, the CO level should be
carefully checked regularly, to ensure that
the converter is still operating efficiently. If
the converter is no longer effective, it
must be renewed.
6•6 Engine management and emission control systems
7.1 Typical catalytic converter (M10
engine type shown, others similar)6.12 EVAP system charcoal canister
viewed from under the vehicle (316i model)
Page 151 of 228

4On some models, working inside the boot,
you can remove the trim to access the upper
mounting nuts; on later models, you’ll have to
remove the rear seat back to get at the upper
mounting nuts. On Touring (Estate) models,
remove the side backrest and rear seat belt
reels, and unscrew the centring shell on the
wheel arch. On Convertibles, simply remove
the top from the recessed well behind the
passenger compartment, and remove the
small rubber access cover. As you remove the
mounting nuts (see illustration), have an
assistant support the shock absorber from
below so it doesn’t fall out.
5Look for oil leaking past the seal in the top
of the shock absorber body. Inspect the
rubber bushings in the shock absorber eye. If
they’re cracked, dried or torn, renew them. To
test the shock absorber, grasp the shock
absorber body firmly with one hand, and push
the damper rod in and out with the other. The
strokes should be smooth and firm. If the rod
goes in and out too easily, or unevenly, the
shock absorber is defective and must be
renewed.
Refitting
6Fit the shock absorbers in the reverse order
of removal, but don’t tighten the mounting
bolts and nuts yet.
7Bounce the rear of the vehicle a couple of
times to settle the bushings, then tighten the
nuts and bolts to the torque values listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications.
10 Rear coil springs (3-Series)-
removal and refitting
4
Note: Although coil springs don’t always wear
out simultaneously, renew both left and right
springs at the same time, to prevent handling
peculiarities or abnormal ride quality.
Removal
1Loosen the wheel bolts. Chock the front
wheels, then raise the rear of the vehicle andsupport it securely on axle stands. Make sure
the stands don’t interfere with the rear
suspension when it’s lowered and raised
during this procedure. Remove the wheels.
2Disconnect the mountings and brackets
which support the rear portion of the exhaust
system, and temporarily lower the exhaust
system (see Chapter 4). Lower the exhaust
system only enough to lower the suspension
and remove the springs. Suspend the exhaust
with a piece of wire.
3Support the differential with a trolley jack,
then remove the differential rear mounting
bolt. Push the differential down, and wedge it
into this lowered position with a block of
wood. This reduces the drive angle,
preventing damage to the CV joints when the
trailing arms are lowered to remove the
springs.
4Place a trolley jack under the trailing arm.
5If the vehicle has a rear anti-roll bar,
disconnect the bar from its connecting links,
or disconnect the links from the trailing arms
(see Section 12).
6Loop a chain through the coil spring, and
bolt the chain together, to prevent the coil
spring from popping out when the trailing arm
is lowered. Be sure to leave enough slack in
the chain to allow the spring to extend
completely.
7Disconnect the shock absorber lower
mounting bolt (see Section 9), carefully lower
the trailing arm and remove the coil spring.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. As the
trailing arm is raised back up, make sure the
spring seats properly.
11 Rear shock absorber/coil
spring assembly (5-Series)-
removal and refitting
4
Removal
Note:Although shock absorbers don’t always
wear out simultaneously, renew both left and
right shock absorbers at the same time, to
prevent handling peculiarities or abnormal ride
quality.1Loosen the wheel bolts, then chock the
front wheels. Raise the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands. Remove the wheels.
2Remove the shock absorber lower
mounting bolt (see illustration).
3On early models, peel back the trim inside
the luggage compartment far enough to
access the upper mounting nuts. To get at the
upper mounting nuts on later models, first
remove the rear seat cushion (see Chap-
ter 11), then remove the two bolts holding the
rear seat backrest, and remove the backrest.
Support the trailing arm with a jack, and
remove the upper mounting nuts (see
illustration). Lower the jack, and remove the
shock absorber and the gasket. To separate
the shock absorber and spring, refer to
Section 6.
Refitting
4Refitting is the reverse of removal. Don’t
forget to fit the gasket between the upper end
of the shock absorber and the body. Tighten
the upper nuts to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Don’t tighten the
lower bolt until the vehicle is lowered.
5Lower the vehicle, and with it sitting at the
normal ride height, tighten the lower bolt to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.
12 Rear anti-roll bar-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
Note:The rear anti-roll bar is mounted
basically the same way on all models. Follow
these general removal and refitting
procedures, keeping in mind any variations.
1Chock the front wheels, then raise the rear
of the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands.
2Remove the anti-roll bar bracket bolts or
nuts (see illustration).
3Disconnect the anti-roll bar from the link at
each end of the bar (see illustrations)and
detach the anti-roll bar.
Suspension and steering systems 10•9
11.3 Shock absorber upper mounting nuts
(arrowed) on a later (E34) 5-Series model11.2 Remove the shock absorber lower
mounting bolt (arrowed)9.4 Shock absorber upper mounting nuts
(arrowed) - late-model convertible shown.
On other early models, upper nuts are
accessible from the luggage compartment;
on later models, they’re behind the back of
the rear seat, up under the parcel shelf
10
Page 202 of 228

REF•1
REF
MOT Test Checks
This is a guide to getting your vehicle through the MOT test.
Obviously it will not be possible to examine the vehicle to the same
standard as the professional MOT tester. However, working through
the following checks will enable you to identify any problem areas
before submitting the vehicle for the test.
Where a testable component is in borderline condition, the tester
has discretion in deciding whether to pass or fail it. The basis of such
discretion is whether the tester would be happy for a close relative or
friend to use the vehicle with the component in that condition. If the
vehicle presented is clean and evidently well cared for, the tester may
be more inclined to pass a borderline component than if the vehicle is
scruffy and apparently neglected.
It has only been possible to summarise the test requirements here,
based on the regulations in force at the time of printing. Test standards
are becoming increasingly stringent, although there are some
exemptions for older vehicles. For full details obtain a copy of the Haynes
publication Pass the MOT! (available from stockists of Haynes manuals).
An assistant will be needed to help carry out some of these checks.
The checks have been sub-divided into four categories, as follows:
HandbrakeMTest the operation of the handbrake.
Excessive travel (too many clicks) indicates
incorrect brake or cable adjustment.
MCheck that the handbrake cannot be
released by tapping the lever sideways. Check
the security of the lever mountings.
Footbrake
MDepress the brake pedal and check that it
does not creep down to the floor, indicating a
master cylinder fault. Release the pedal, wait
a few seconds, then depress it again. If the
pedal travels nearly to the floor before firm
resistance is felt, brake adjustment or repair is
necessary. If the pedal feels spongy, there is
air in the hydraulic system which must be
removed by bleeding.MCheck that the brake pedal is secure and in
good condition. Check also for signs of fluid
leaks on the pedal, floor or carpets, which
would indicate failed seals in the brake master
cylinder.
MCheck the servo unit (when applicable) by
operating the brake pedal several times, then
keeping the pedal depressed and starting the
engine. As the engine starts, the pedal will
move down slightly. If not, the vacuum hose or
the servo itself may be faulty.
Steering wheel and column
MExamine the steering wheel for fractures or
looseness of the hub, spokes or rim.
MMove the steering wheel from side to side
and then up and down. Check that the
steering wheel is not loose on the column,
indicating wear or a loose retaining nut.
Continue moving the steering wheel as before,
but also turn it slightly from left to right.
MCheck that the steering wheel is not loose
on the column, and that there is no abnormalmovement of the steering wheel, indicating
wear in the column support bearings or
couplings.
Windscreen and mirrors
MThe windscreen must be free of cracks or
other significant damage within the driver’s
field of view. (Small stone chips are
acceptable.) Rear view mirrors must be
secure, intact, and capable of being adjusted.
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S SEAT
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S
SEAT2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
ON THE GROUND3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
RAISED AND THE
WHEELS FREE TO
TURN4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S
EXHAUST EMISSION
SYSTEM
Page 204 of 228

REF•3
REF
MOT Test Checks
Exhaust system
MStart the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
MHave your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
MExamine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
MStarting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
MNow grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
MIf excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
MCarry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
MExamine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
MIf coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
MIf leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.MThe same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
MInspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
MRotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
MIf possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
MExamine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
MLook for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
MSlowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN
Page 205 of 228

REF•4MOT Test Checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 218 of 228

REF•18Automotive chemicals and lubricants
A number of automotive chemicals and
lubricants are available for use during vehicle
maintenance and repair. They include a wide
variety of products ranging from cleaning
solvents and degreasers to lubricants and
protective sprays for rubber, plastic and
vinyl.
Cleaners
Carburettor cleaner and choke cleaner
is a strong solvent for gum, varnish and
carbon. Most carburettor cleaners leave a
dry-type lubricant film which will not harden or
gum up. Because of this film, it is not
recommended for use on electrical
components.
Brake system cleaneris used to remove
grease and brake fluid from the brake system,
where clean surfaces are absolutely
necessary. It leaves no residue, and often
eliminates brake squeal caused by
contaminants.
Electrical cleaner removes oxidation,
corrosion and carbon deposits from electrical
contacts, restoring full current flow. It can also
be used to clean spark plugs, carburettor jets,
voltage regulators and other parts where an
oil-free surface is desired.
Moisture dispersantsremove water and
moisture from electrical components such as
alternators, voltage regulators, electrical
connectors and fuse blocks. They are non-
conductive and non-corrosive.
Degreasersare heavy-duty solvents used
to remove grease from the outside of the
engine and from chassis components. They
can be sprayed or brushed on, and are usually
rinsed off with water.
Lubricants
Engine oilis the lubricant formulated for
use in engines. It normally contains a wide
variety of additives to prevent corrosion and
reduce foaming and wear. Engine oil comes in
various weights (viscosity ratings) from 5 to
60. The recommended weight of the oil
depends on the season, temperature and the
demands on the engine. Light oil is used in
cold climates and under light load conditions.
Heavy oil is used in hot climates, and where
high loads are encountered. Multi-viscosity
(multigrade) oils are designed to have
characteristics of both light and heavy oils,
and are available in a number of weights from
5W-20 to 20W-50.
Gear oilis designed to be used in
differentials, manual transmissions and other
areas where high-temperature lubrication is
required.
Chassis and wheel bearing greaseis a
heavy grease used where increased loads and
friction are encountered, such as for wheel
bearings, balljoints, tie-rod ends and universal
joints.High-temperature wheel bearing grease
is designed to withstand the extreme
temperatures encountered by wheel bearings
in disc brake-equipped vehicles. It usually
contains molybdenum disulphide (moly),
which is a dry-type lubricant.
White greaseis a heavy grease for metal-
to-metal applications where water is a
problem. White grease stays soft at both low
and high temperatures, and will not wash off
or dilute in the presence of water.
Assembly lubeis a special extreme-
pressure lubricant, usually containing moly,
used to lubricate high-load parts (such as
main and rod bearings and cam lobes) for
initial start-up of a new engine. The assembly
lube lubricates the parts without being
squeezed out or washed away until the engine
oiling system begins to function.
Silicone lubricants are used to protect
rubber, plastic, vinyl and nylon parts.
Graphite lubricantsare used where oils
cannot be used due to contamination
problems, such as in locks. The dry graphite
will lubricate metal parts while remaining
uncontaminated by dirt, water, oil or acids. It
is electrically conductive, and will not foul
electrical contacts in locks such as the
ignition switch.
Penetrating oilsloosen and lubricate
frozen, rusted and corroded fasteners and
prevent future rusting or freezing.
Heat-sink greaseis a special electrically
non-conductive grease that is used for
mounting electronic ignition modules where it
is essential that heat is transferred away from
the module.
Sealants
RTV sealantis one of the most widely-
used gasket compounds. Made from silicone,
RTV is air-curing; it seals, bonds, waterproofs,
fills surface irregularities, remains flexible,
doesn’t shrink, is relatively easy to remove,
and is used as a supplementary sealer with
almost all low- and medium-temperature
gaskets.
Anaerobic sealantis much like RTV in that
it can be used either to seal gaskets or to form
gaskets by itself. It remains flexible, is solvent-
resistant, and fills surface imperfections. The
difference between an anaerobic sealant and
an RTV-type sealant is in the curing. RTV
cures when exposed to air, while an anaerobic
sealant cures only in the absence of air. This
means that an anaerobic sealant cures only
after the assembly of parts, sealing them
together.
Thread and pipe sealant is used for
sealing hydraulic and pneumatic fittings and
vacuum lines. It is usually made from a Teflon
compound, and comes in a spray, a paint-on
liquid and as a wrap-around tape.
Chemicals
Anti-seize compoundprevents seizing,
chafing, cold welding, rust and corrosion in
fasteners. High-temperature anti-seize,
usually made with copper and graphite
lubricants, is used for exhaust system and
exhaust manifold bolts.
Anaerobic locking compoundsare used
to keep fasteners from vibrating or working
loose, and cure only after installation, in the
absence of air. Medium-strength locking
compound is used for small nuts, bolts and
screws that may be removed later. High-
strength locking compound is for large nuts,
bolts and studs which aren’t removed on a
regular basis.
Oil additivesrange from viscosity index
improvers to chemical treatments that claim
to reduce internal engine friction. It should be
noted that most oil manufacturers caution
against using additives with their oils.
Fuel additivesperform several functions,
depending on their chemical make-up. They
usually contain solvents that help dissolve
gum and varnish that build up on carburettor,
fuel injection and intake parts. They also serve
to break down carbon deposits that form on
the inside surfaces of the combustion
chambers. Some additives contain upper
cylinder lubricants for valves and piston rings,
and others contain chemicals to remove
condensation from the fuel tank.
Miscellaneous
Brake fluidis specially-formulated
hydraulic fluid that can withstand the heat and
pressure encountered in brake systems. It is
poisonous and inflammable. Care must be
taken so this fluid does not come in contact
with painted surfaces or plastics. An opened
container should always be resealed, to
prevent contamination by water or dirt. Brake
fluid absorbs moisture from the air, if left in an
unsealed container.
Weatherstrip adhesiveis used to bond
weatherstripping around doors, windows and
boot lids. It is sometimes used to attach trim
pieces.
Undersealis a petroleum-based, tar-like
substance that is designed to protect metal
surfaces on the underside of the vehicle from
corrosion. It also acts as a sound-deadening
agent by insulating the bottom of the vehicle.
Waxes and polishesare used to help
protect painted and plated surfaces from the
weather. Different types of paint may require
the use of different types of wax and polish.
Some polishes utilise a chemical or abrasive
cleaner to help remove the top layer of
oxidised (dull) paint on older vehicles. In
recent years, many non-wax polishes
containing a wide variety of chemicals such as
polymers and silicones have been introduced.
These non-wax polishes are usually easier to
apply, and last longer than conventional
waxes and polishes.
Page 219 of 228

REF•19
REF
Buying spare parts & vehicle identification numbers
Buying spare parts
Spare parts are available from many
sources; for example, BMW garages, other
garages and accessory shops, and motor
factors. Our advice regarding spare part
sources is as follows.
Officially-appointed BMW garages- This is
the best source for parts which are peculiar to
your vehicle, and which are not generally
available (eg complete cylinder heads, internal
transmission components, badges, interior
trim etc). It is also the only place at which you
should buy parts if the vehicle is still under
warranty. To be sure of obtaining the correct
parts, it will be necessary to give the storeman
the full Vehicle Identification Number, and if
possible, to take the old parts along for
positive identification. Many parts are
available under a factory exchange scheme -
any parts returned should always be clean. It
obviously makes good sense to go straight to
the specialists on your vehicle for this type of
part, as they are best equipped to supply you.
Other garages and accessory shops- These
are often very good places to buy materials
and components needed for the maintenance
of your vehicle (eg oil filters, spark plugs,
bulbs, drivebelts, oils and greases, touch-up
paint, filler paste, etc). They also sell general
accessories, usually have convenient opening
hours, charge lower prices, and can often be
found not far from home.
Motor factors- Good factors will stock all
the more important components which wearout comparatively quickly (eg exhaust
systems, brake pads, seals and hydraulic
parts, clutch components, bearing shells,
pistons, valves etc). Motor factors will often
provide new or reconditioned components on
a part-exchange basis - this can save a
considerable amount of money.
Vehicle identification
numbers
Modifications are a continuing and
unpublicised process in vehicle manufacture,
quite apart from major model changes. Spare
parts manuals and lists are compiled upon a
numerical basis, the appropriate identification
number or code being essential to correct
identification of the component concerned.When ordering spare parts, always give as
much information as possible. Quote the
vehicle model, year of manufacture, Vehicle
Identification Number and engine numbers, as
appropriate.
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)is
located on the right-hand front wheel arch
next to the front suspension strut upper
mounting, on the driver’s door, and on a plate
on top of the facia, just inside the windscreen
(see illustrations).
The engine number is stamped on a
machined face on the left-hand side of the
cylinder block, near the base of the oil level
dipstick tube.
The body numberis located on the seam
between the left-hand front wing and inner
panel.
The VIN (arrowed) is stamped on the
bulkheadThe VIN is also present on the edge of the
driver’s door