1990 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE oil temperature
[x] Cancel search: oil temperaturePage 237 of 391
MANUAL TRANSAXLE <4WD> - Viscous Coupling .(VClJ)21-13In contrast, the inner plates have no such spacer rings, and
each can slide to some extent over the hub spline shaft
between the outer plates.
The space between the housing and outer and inner plates is
filled with mixture of silicone oil and air.
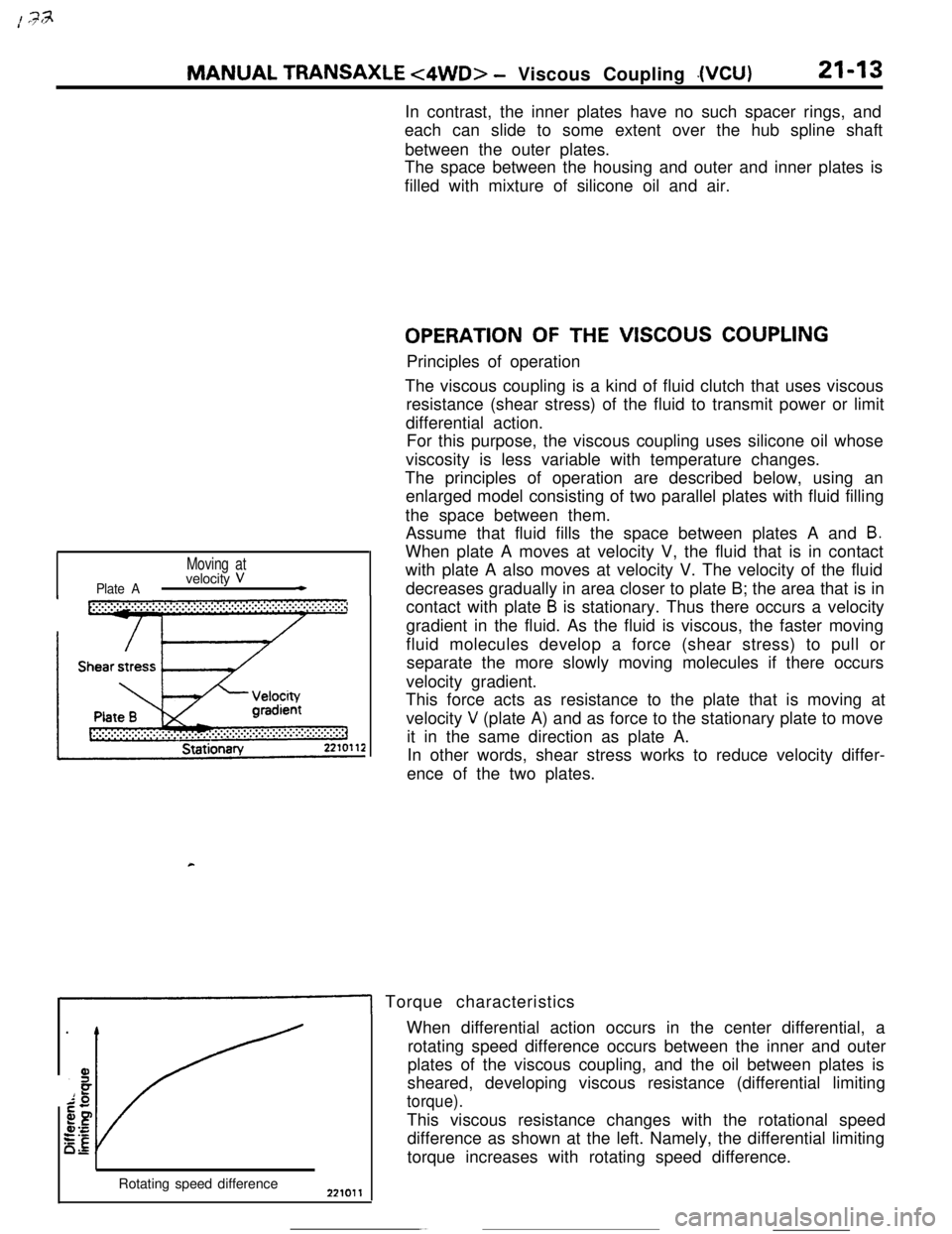
Plate A
Moving atvelocity V*
OPERATION OF THE VISCOUS COUPLINGPrinciples of operation
The viscous coupling is a kind of fluid clutch that uses viscous
resistance (shear stress) of the fluid to transmit power or limit
differential action.
For this purpose, the viscous coupling uses silicone oil whose
viscosity is less variable with temperature changes.
The principles of operation are described below, using an
enlarged model consisting of two parallel plates with fluid filling
the space between them.
Assume that fluid fills the space between plates A and
B.When plate A moves at velocity V, the fluid that is in contact
with plate A also moves at velocity V. The velocity of the fluid
decreases gradually in area closer to plate B; the area that is in
contact with plate
B is stationary. Thus there occurs a velocity
gradient in the fluid. As the fluid is viscous, the faster moving
fluid molecules develop a force (shear stress) to pull or
separate the more slowly moving molecules if there occurs
velocity gradient.
This force acts as resistance to the plate that is moving at
velocity
V (plate A) and as force to the stationary plate to move
it in the same direction as plate A.
In other words, shear stress works to reduce velocity differ-
ence of the two plates.
1 Torque characteristics
Rotating speed differenceWhen differential action occurs in the center differential, a
rotating speed difference occurs between the inner and outer
plates of the viscous coupling, and the oil between plates is
sheared, developing viscous resistance (differential limiting
torque).This viscous resistance changes with the rotational speed
difference as shown at the left. Namely, the differential limiting
torque increases with rotating speed difference.
Page 238 of 391

21-14MANUAL TRANSAXLE t4WD> - Viscous Coupling (VCU)
Rotating speed difference
Transmitted
torque
TemperatureII I
t
/
IIc
P&e surface‘II I
preTYl-LLL
Hump mode2210llrHump phenomenon specific to viscous couplings
Hump is a phenomenon specific to viscous couplings
althob,, Iit does not occur under normal operating conditions.
This phenomenon occurs when the silicone oil temperature has
risen due to sustained differential action. Normally silicone oil
fills the space between the inner and outer plates, preventing
their direct coupling. When silicone oil expands at a high
temperature to such a degree as to develop abnormally high
pressure between the plates (normal thermal expansion is
absorbed by compression of air mixed in silicone oil), silicone oilescapes from between the plates. As a result, the plates
couple directly, causing abrupt torque transmission. When the
viscous coupling is directly coupled in this way, a rotating
speed difference does not exist, and then silicone oil tempera-
ture drops and normal function is restored.
Hump mode2210115
Page 266 of 391
21-42AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control
ELECTRONIC CONTROL DEVICE
DAMPER CLUTCH CONTROL
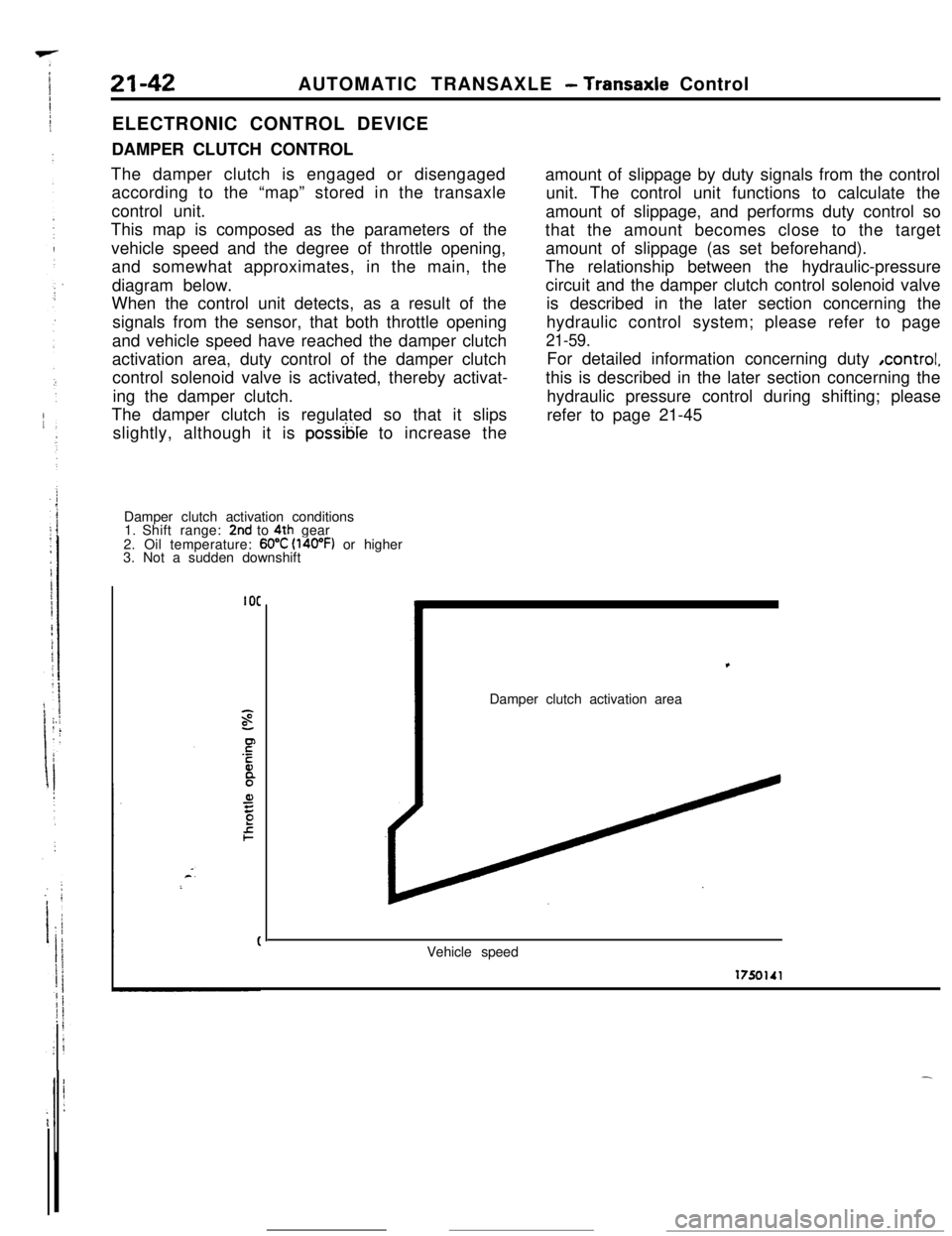
The damper clutch is engaged or disengaged
according to the “map” stored in the transaxle
control unit.
This map is composed as the parameters of the
vehicle speed and the degree of throttle opening,
and somewhat approximates, in the main, the
diagram below.
When the control unit detects, as a result of the
signals from the sensor, that both throttle opening
and vehicle speed have reached the damper clutch
activation area, duty control of the damper clutch
control solenoid valve is activated, thereby activat-
ing the damper clutch.
The damper clutch is regulated so that it slips
slightly, although it is
possible to increase the
Damper clutch activation conditions
1. Shift range:
2nd to 4th gear
2. Oil temperature: 60°C (l4oOF) or higher
3. Not a sudden downshift
IOCamount of slippage by duty signals from the control
unit. The control unit functions to calculate the
amount of slippage, and performs duty control so
that the amount becomes close to the target
amount of slippage (as set beforehand).
The relationship between the hydraulic-pressure
circuit and the damper clutch control solenoid valve
is described in the later section concerning the
hydraulic control system; please refer to page
21-59.For detailed information concerning duty ,control,
this is described in the later section concerning the
hydraulic pressure control during shifting; please
refer to page 21-45,
Damper clutch activation area
Vehicle speed
Page 267 of 391
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control21-43
“YIR PAllERN CONTROL
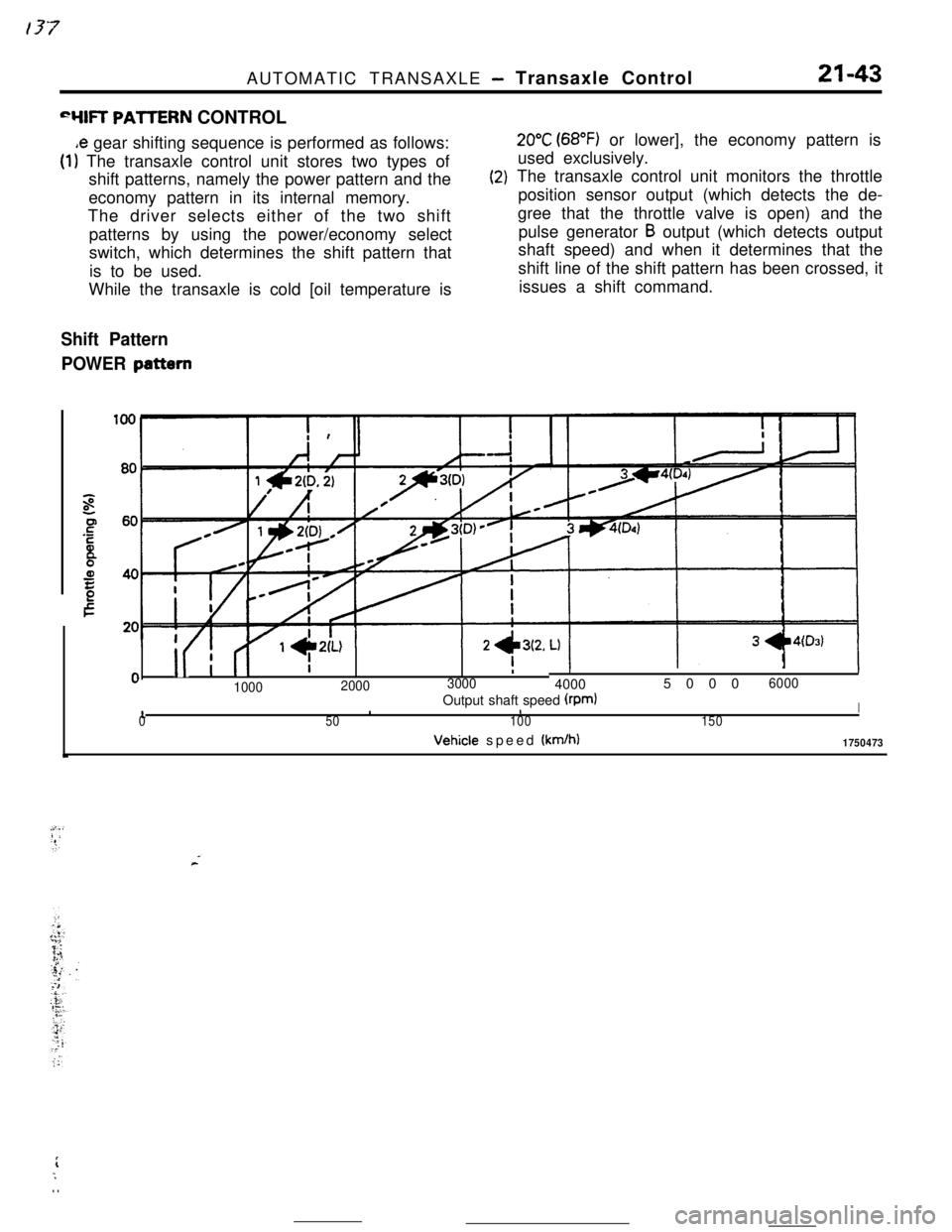
,e gear shifting sequence is performed as follows:
(1) The transaxle control unit stores two types of
shift patterns, namely the power pattern and the
economy pattern in its internal memory.
The driver selects either of the two shift
patterns by using the power/economy select
switch, which determines the shift pattern that
is to be used.
While the transaxle is cold [oil temperature is
(2)
Shift Pattern
POWER
pattern
20°C (68°F) or lower], the economy pattern is
used exclusively.
The transaxle control unit monitors the throttle
position sensor output (which detects the de-
gree that the throttle valve is open) and the
pulse generator
B output (which detects output
shaft speed) and when it determines that the
shift line of the shift pattern has been crossed, it
issues a shift command.
i
II I (I
I -L\LI1- --‘-0
II
0I
100020003000
II400050006000
10Output shaft speed (rpmlIII50100150Vehicle speed
(km/h)1750473
rL;. .
Page 269 of 391
‘4) Once the operation is step (2) is completed, the
hydraulic control device functions by hydraulic
pressure force to change the state of the
clutches and brakes to accomplish the gear
shifting. To minimize the shock that would
otherwise be produced during gear shifting,
hydraulic pressure is controlled during the gear
shifting period by the “duty control” of the
pressure control solenoid valve. The duty control
is explained later.
‘HYDRAULIC PRESSURE CONTROL DURING
SHFIING(1) The hydraulic pressure that functions during
gear shifting to engage the clutches and apply
the brakes is regulated by the pressure control
valve, The hydraulic pressure that works on the
pressure control valve is further regulated by the
pressure control solenoid valve which functions
under the control of the transaxle control unit.
The transaxle control unit controls the solenoid
valve through the duty control, thus providing
appropriate regulation of the hydraulic pressure.
(2)
(3)
(4)The transaxle control unit decides the timing of
the gear shifting period (during which ‘it per-
forms hydraulic pressure control for gear shift-
ing) according to the change in the kickdown
drum rotating speed that it detects. The unit
identifies the time just before the kickdown
brake is applied and uses that as the timing for
initiating control of the hydraulic pressure which
is to be applied to the kickdown brake.
When the transaxle is cold, the fluid viscosity is
high, causing slower oil pressure response. in
such conditions, the transaxle control unit pro-
vides a correction for the oil pressure by
changing the control duty of the pressure control
solenoid valve.
This control is performed when the fluid temper-
atures as indicated by the oil temperature
sensor is lower than
60°C (140°F).After the engine has been started and the
vehicle is inmotion, the transaxle
continues torefine its performance
est possiblegear shifting.control unit
for smooth-
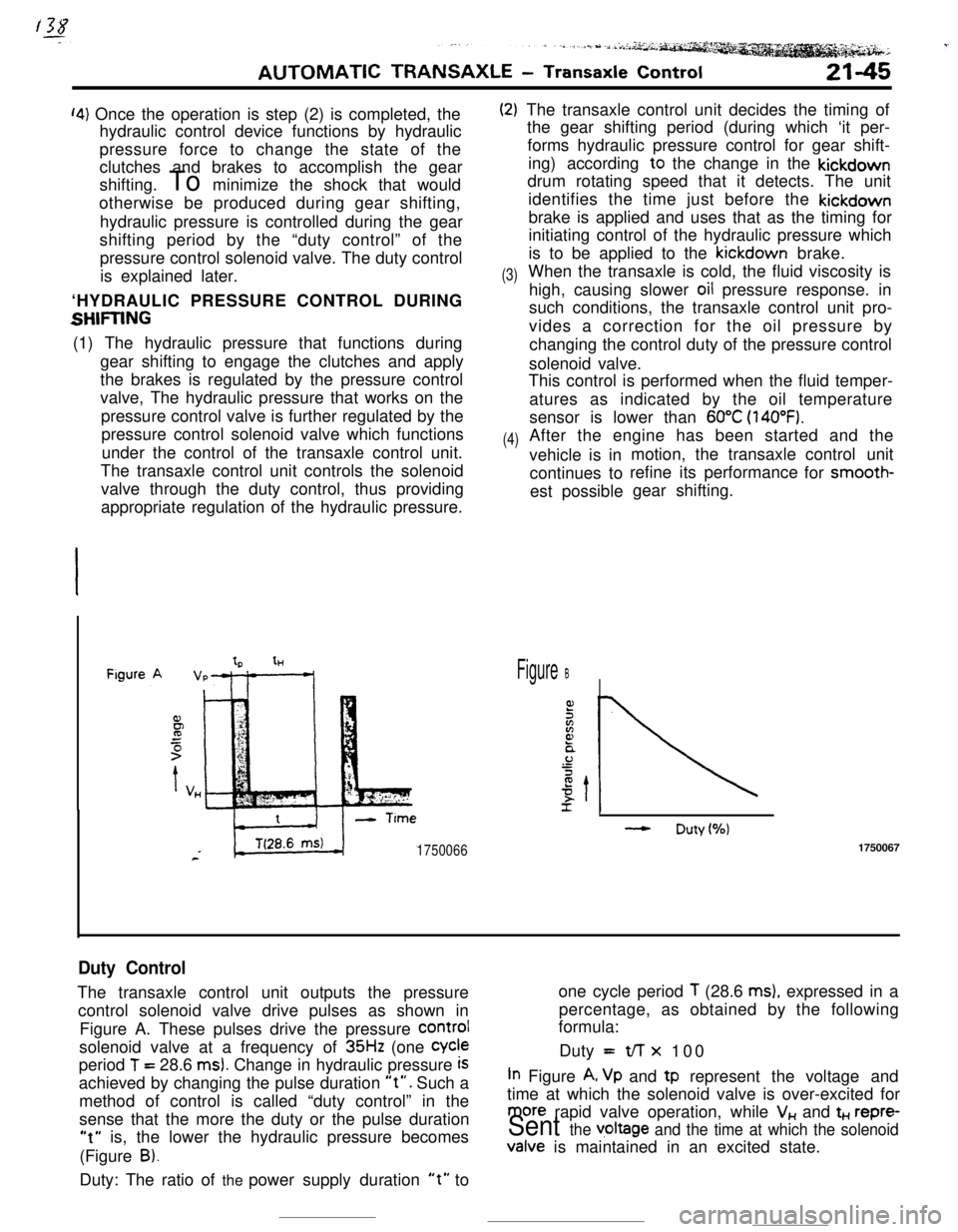
tHFigure B
- Duty(%)
17500661750067
Duty ControlThe transaxle control unit outputs the pressureone cycle period
T (28.6 ms), expressed in a
control solenoid valve drive pulses as shown inpercentage, as obtained by the following
formula:
Figure A. These pulses drive the pressure
COrmIsolenoid valve at a frequency of
35Hz (one Cycleperiod
T = 28.6 ms). Change in hydraulic pressure iSDuty =t/-r x 100
achieved by changing the pulse duration
“t”. Such aIn Figure A, Vp and tp represent the voltage and
method of control is called “duty control” in thetime at which the solenoid valve is over-excited for
sense that the more the duty or the pulse duration
more rapid valve operation, while V,, and t+., repre-
“t” is, the lower the hydraulic pressure becomesSent the v,oltage and the time at which the solenoid(Figure
B).Valve is maintained in an excited state.
Duty: The ratio of the power supply duration
“t” to
Page 271 of 391
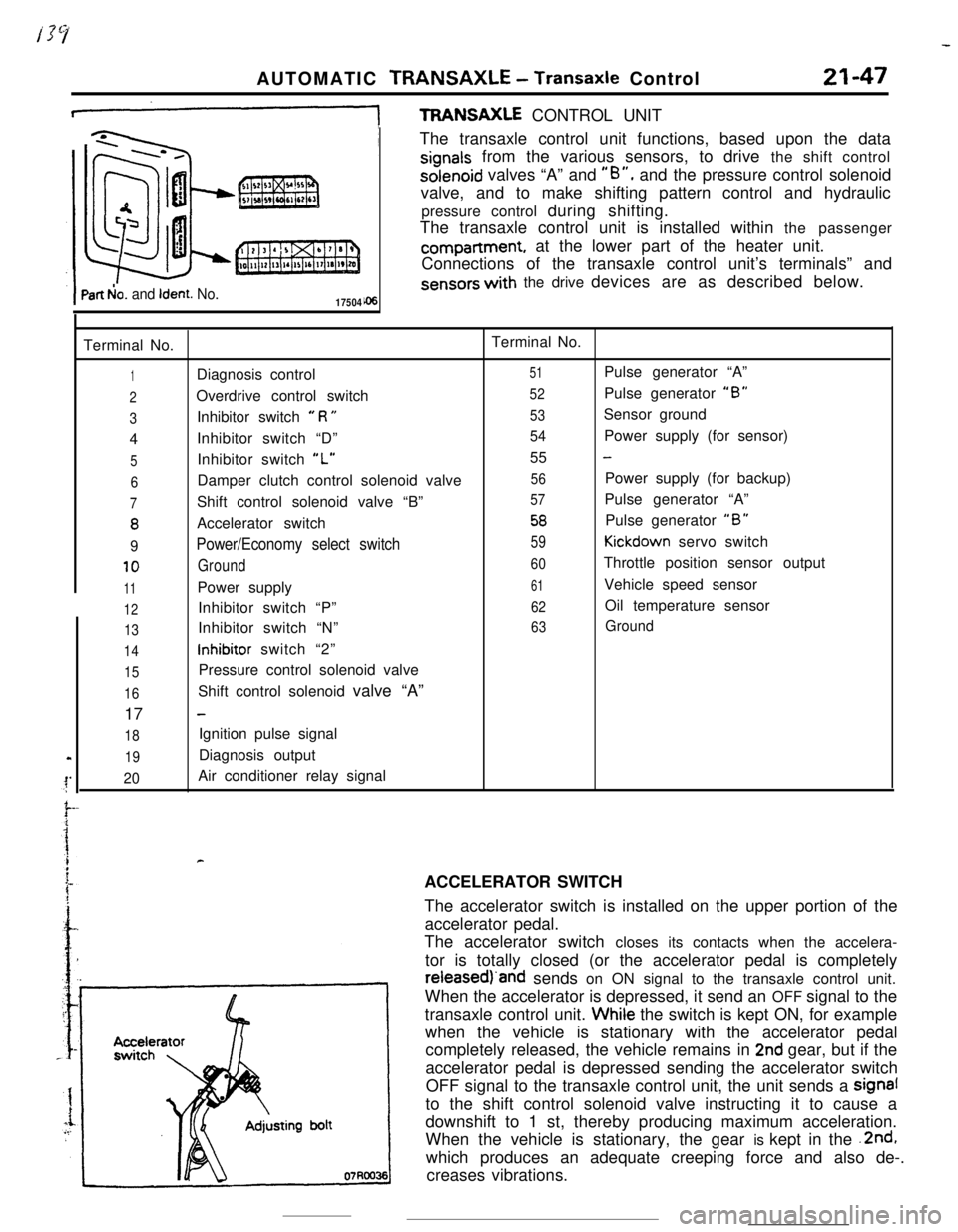
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control21-47
+TFWNSAXLE CONTROL UNIT
Part b!o. and Ident. No.17504The transaxle control unit functions, based upon the data
signals from the various sensors, to drive the shift controlsolenoid valves “A” and
“B”, and the pressure control solenoid
valve, and to make shifting pattern control and hydraulic
pressure control during shifting.
The transaxle control unit is installed within the passengercompartment, at the lower part of the heater unit.
Connections of the transaxle control unit’s terminals” and
sensors with the drive devices are as described below.
Terminal No.Terminal No.
1Diagnosis control51Pulse generator “A”
2Overdrive control switch52Pulse generator “B”
3Inhibitor switch e R U53Sensor ground
4Inhibitor switch “D”
54Power supply (for sensor)
5Inhibitor switch “L”55 -
6Damper clutch control solenoid valve56Power supply (for backup)
7Shift control solenoid valve “B”57Pulse generator “A”
8Accelerator switch58Pulse generator “B”
9Power/Economy select switch59Kickdown servo switch
10Ground60Throttle position sensor output
11Power supply61Vehicle speed sensor
12Inhibitor switch “P”62Oil temperature sensor
13Inhibitor switch “N”63Ground
14inhibitor switch “2”
15Pressure control solenoid valve
16Shift control solenoid valve “A”
17
-
18Ignition pulse signal
19Diagnosis output
20Air conditioner relay signal
rACCELERATOR SWITCH
The accelerator switch is installed on the upper portion of the
accelerator pedal.
The accelerator switch closes its contacts when the accelera-
tor is totally closed (or the accelerator pedal is completelyreieasedj‘and sends on ON signal to the transaxle control unit.
When the accelerator is depressed, it send an OFF signal to the
transaxle control unit. Whiie the switch is kept ON, for example
when the vehicle is stationary with the accelerator pedal
completely released, the vehicle remains in
2nd gear, but if the
accelerator pedal is depressed sending the accelerator switch
OFF signal to the transaxle control unit, the unit sends a signal
to the shift control solenoid valve instructing it to cause a
downshift to 1 st, thereby producing maximum acceleration.
When the vehicle is stationary, the gear is kept in the .2nd,
which produces an adequate creeping force and also de-.
creases vibrations.
Page 274 of 391
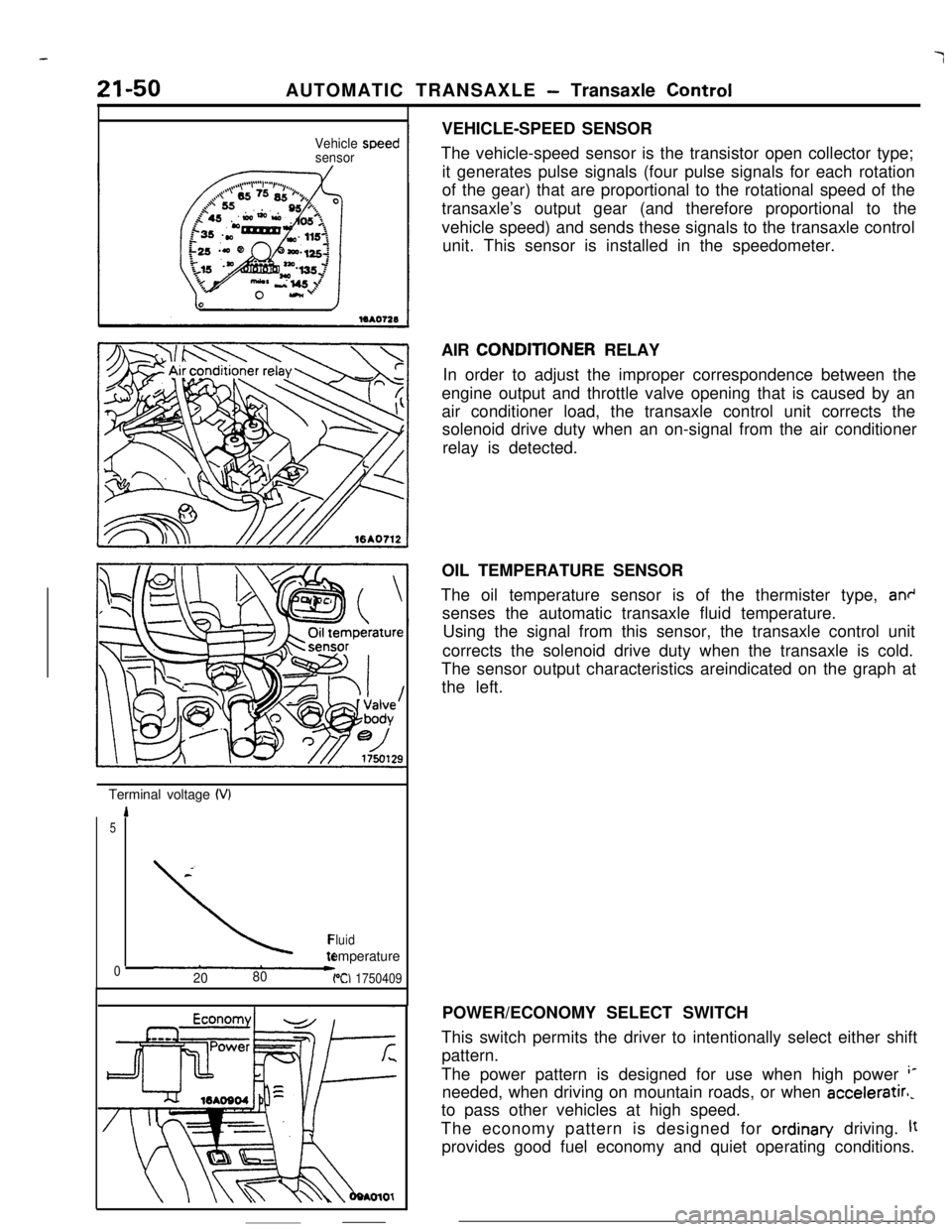
21-50AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle Control
Vehicle
sensorspeedTerminal voltage
(VI
1
5
\*Fluidtemperature
02080PCI 1750409VEHICLE-SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle-speed sensor is the transistor open collector type;
it generates pulse signals (four pulse signals for each rotation
of the gear) that are proportional to the rotational speed of the
transaxle’s output gear (and therefore proportional to the
vehicle speed) and sends these signals to the transaxle control
unit. This sensor is installed in the speedometer.
AIR CONDlTlONER RELAY
In order to adjust the improper correspondence between the
engine output and throttle valve opening that is caused by an
air conditioner load, the transaxle control unit corrects the
solenoid drive duty when an on-signal from the air conditioner
relay is detected.
OIL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The oil temperature sensor is of the thermister type,
an+senses the automatic transaxle fluid temperature.
Using the signal from this sensor, the transaxle control unit
corrects the solenoid drive duty when the transaxle is cold.
The sensor output characteristics areindicated on the graph at
the left.
POWER/ECONOMY SELECT SWITCH
This switch permits the driver to intentionally select either shift
pattern.
The power pattern is designed for use when high power
‘*needed, when driving on mountain roads, or when acceleratirl,
to pass other vehicles at high speed.
The economy pattern is designed for ordinan/ driving.
ltprovides good fuel economy and quiet operating conditions.
Page 276 of 391

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Transaxle ControlSELF-DIAGNOStS SYSTEM
The transaxle control unit has self-diagnosis function.
Self-diagnosis codes can be read by connecting a voltmeter to the
diagnosis connector on the side of the junction block.
0: Ground
6%: ELC-MIT
Self-diagnosisThere are 25 diagnosis items, including those items
indicating normal conditions; a maximum of
10items can be stored in memory in the order that
they occur. The memory is supported by a power
supply directly connected to the battery so that it isretained even after the Ignition switch is turned to
the off position.
To clear the memory once an inspection has been
completed. keep negative
(-) terminal of the
battery disconnected for
10 seconds or longer.
r
No.
23
24
Output code
Display pattern
TDiagnosis itemRemarks
NormalAbnormal increases of throttle position
sensor output
Abnormal decrease of throttle position
sensor output
Poor adjustment of throttle position sen-
sorOpen circuit in oil temperature sensor
Once this occurs, output is re-
garded as 2.5 V.Once this occurs, output is re-
garded as 2.5 VOnce this occurs,
oil temperature isregarded as 80°C (176°F).