1990 BMW 5 SERIES gas type
[x] Cancel search: gas typePage 105 of 228

gauge to the pressure regulator vacuum hose,
and check for vacuum (engine idling).
11If there is vacuum present, renew the fuel
pressure regulator.
12If there isn’t any reading on the gauge,
check the hose and its port for a leak or a
restriction.
Renewal
13Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
14Detach the battery negative cable.
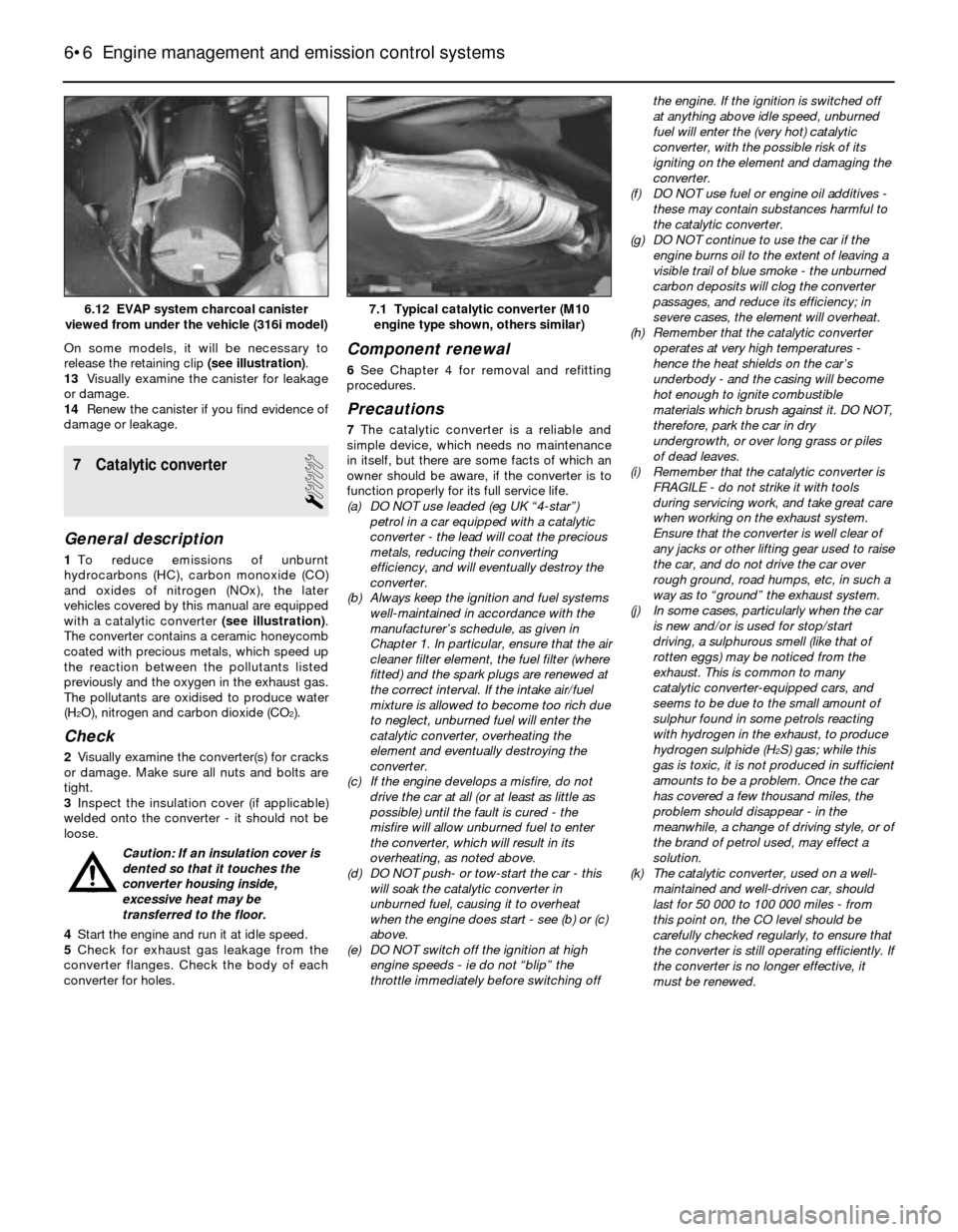
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
15Detach the vacuum hose and fuel return
hose from the pressure regulator, then
unscrew the mounting bolts (see illustration).
16Remove the pressure regulator.
17Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to use a new O-ring. Coat the O-ring with a
light film of engine oil prior to refitting.
18Check for fuel leaks after refitting the
pressure regulator.
19 Cold start injector and
thermotime switch- check
and renewal
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you performany kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
Check
Cold start injector
1The engine coolant should be below 30ºC
for this check. Preferably, the engine should
have been switched off for several hours.
Disconnect the electrical connector from the
cold start injector (see illustration)and move
it aside, away from the work area - there will
be fuel vapour present. Remove the two
screws holding the injector to the air intake
plenum, and take the injector out. The fuel line
must be left connected. Wipe the injector
nozzle. Disable the ignition system by
detaching the coil wire from the centre
terminal of the distributor cap, and earthing it
on the engine block with a jumper wire. Run
the fuel pump for 1 minute by bridging the
appropriate relay terminals (see Section 3).
There must be no fuel dripping from the
nozzle. If there is, the injector is faulty and
must be renewed. Switch off the ignition and
remake the original fuel pump relay
connections.
2Now direct the nozzle of the injector into a
can or jar. Reconnect the electrical connector
to the injector. Have an assistant switch on
the ignition and operate the starter. The
injector should squirt a conical-shaped sprayinto the jar (see illustration). If the spray
pattern is good, the injector is working
properly. If the spray pattern is irregular, the
injector is fouled or damaged, and should be
cleaned or renewed.
3If the cold start injector does not spray any
fuel, check for a voltage signal at the electrical
connector for the cold start injector when the
starter motor is operated (see illustration). If
there is no voltage, check the thermotime
switch.
Thermotime switch
4The thermotime switch detects the
temperature of the engine, and controls the
action of the cold start injector. It is usually
located up front, near the coolant temperature
sensor. The engine coolant should be below
30ºC for this check. Preferably, the engine
should have been switched off for several
hours. Disable the ignition system by detaching
the coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap, and earthing it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Pull back the rubber
boot from the thermotime switch (see
illustration)and probe the black/yellow wire
connector terminal with a voltmeter.
5Have an assistant switch on the ignition and
operate the starter. The voltmeter should
register a voltage signal the moment the
starter engages. This signal should last
approximately 6 to 10 seconds, depending on
the temperature of the engine.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•17
19.2 Watch for a steady, conical-shaped
spray of fuel when the starter motor is
operated19.1 Cold start injector electrical
connector (arrowed) on the M10 engine.
Most cold start injectors are mounted in
the intake manifold18.15 Remove the two bolts (arrowed) and
remove the fuel pressure regulator from
the fuel rail
19.4 Check for a voltage signal on the
black/yellow wire of the thermotime switch
when the ignition is on19.3 Check for a voltage signal (about
12 volts) at the cold start injector connector
when the starter motor is operated
4
Page 106 of 228

6If the voltage is correct, unplug the
electrical connector and, using an ohmmeter,
check for continuity between the terminals of
the thermotime switch (see illustration).
Continuity should exist.
7Reconnect the coil lead, start the engine
and warm it up above 41ºC. When the engine
is warm, there should be no continuity
between the terminals. If there is, the switch is
faulty and must be renewed. Note: On 5-
Series models, there are several types of
thermotime switch. Each one is stamped with
an opening temperature and maximum
duration.
Renewal
Cold start injector
8Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
9Disconnect the electrical connector from
the cold start injector.
10Where applicable, using a ring spanner or
deep socket, remove the fuel line fitting
connected to the cold start injector. On other
models, simply loosen the hose clamp and
detach the hose from the injector.
11Remove the cold start injector securing
bolts, and remove the injector.
12Refitting is the reverse of removal. Clean
the mating surfaces, and use a new gasket.
Thermotime switch
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure. Also, remove the
cap from the expansion tank or
radiator to relieve any residual pressure in
the cooling system.
13Prepare the new thermotime switch for
fitting by applying a light coat of thread
sealant to the threads.
14Disconnect the electrical connector from
the old thermotime switch.
15Using a deep socket, or a ring spanner,
unscrew the switch. Once the switch is
removed coolant will start to leak out, so
insert the new switch as quickly as possible.
Tighten the switch securely, and plug in the
electrical connector.
20 Fuel injectors-
check and renewal
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
Check
In-vehicle check
1Using a mechanic’s stethoscope (available
at most car accessory shops), check for a
clicking sound at each of the injectors while
the engine is idling (see illustration 15.7).
2The injectors should make a steady clicking
sound if they are operating properly.
3Increase the engine speed above 3500 rpm.
The frequency of the clicking sound should
rise with engine speed.
4If an injector isn’t functioning (not clicking),
purchase a special injector test light (a car
accessory shop or fuel injection specialist
may be able to help) and connect it to the
injector electrical connector. Start the engine
and make sure the light flashes. If it does, the
injector is receiving the proper voltage, so the
injector itself must be faulty.
5Unplug each injector connector, and checkthe resistance of the injector (see
illustration). Check your readings with the
values listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
Renew any that do not give the correct
resistance reading.
Volume test
6Because a special injection checker is
required to test injector volume, this
procedure is beyond the scope of the home
mechanic. Have the injector volume test
performed by a BMW dealer or other
specialist.
Renewal
7Unplug the main electrical connector for the
fuel injector wiring harness. Remove the
intake manifold (see Chapter 2A).
8Detach the fuel hoses from the fuel rail, and
remove the fuel rail mounting bolts (see
illustration).
9Lift the fuel rail/injector assembly from the
intake manifold.
10Unplug the electrical connectors from the
fuel injectors. Detach the injectors from the
fuel rail.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to renew all O-rings. Coat the O-rings with a
light film of engine oil to prevent damage
during refitting. Pressurise the fuel system
(refit the fuel pump fuse and switch on the
ignition) and check for leaks before starting
the engine.
21 Idle air stabiliser valve-
check, adjustment and
renewal
4
1The idle air stabiliser system works to
maintain engine idle speed within a 200 rpm
range, regardless of varying engine loads at
idle. An electrically-operated valve allows a
small amount of air to bypass the throttle
plate, to raise the idle speed whenever the idle
speed drops below approximately 750 rpm. If
the idle speed rises above approximately
950 rpm, the idle air stabiliser valve closes
and stops extra air from bypassing the throttle
plate, reducing the idle speed.
4•18 Fuel and exhaust systems
20.8 Remove the bolts (arrowed) and
separate the fuel rail and injectors from
the intake manifold20.5 Check the resistance of each of the
fuel injectors19.6 Check the resistance of the
thermotime switch with the engine coolant
temperature below 30º C. There should be
continuity
If you don’t have a
mechanic’s stethoscope, a
screwdriver can be used to
check for a clicking sound at
the injectors. Place the tip of the
screwdriver against the injector, and
press your ear against the handle.
Page 124 of 228

4 Information sensors
2
Note:Refer to Chapters 4 and 5 for additional
information on the location and diagnosis of
the information sensors that are not covered in
this Section.
Coolant temperature sensor
General description
1The coolant temperature sensor (see
illustration)is a thermistor (a resistor which
varies its resistance value in accordance with
temperature changes). The change in the
resistance value regulates the amount of
voltage that can pass through the sensor. At
low temperatures, the sensor’s resistance is
high. As the sensor temperature increases, its
resistance will decrease. Any failure in this
sensor circuit will in most cases be due to a
loose or shorted-out wire; if no wiring
problems are evident, check the sensor as
described below.
Check
2To check the sensor, first check its
resistance (see illustration)when it is
completely cold (typically 2100 to 2900 ohms).
Next, start the engine and warm it up until it
reaches operating temperature. The resistance
should be lower (typically 270 to 400 ohms).
Note: If restricted access to the coolant
temperature sensor makes it difficult to attach
electrical probes to the terminals, remove the
sensor as described below, and perform the
tests in a container of heated water to simulate
the conditions.
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
Renewal
3To remove the sensor, depress the spring
lock, unplug the electrical connector, then
carefully unscrew the sensor. Be prepared for
some coolant spillage; to reduce this, have
the new sensor ready for fitting as quickly as
possible.Caution: Handle the coolant
sensor with care. Damage to this
sensor will affect the operation of
the entire fuel injection system.
Note: It may be necessary to drain a small
amount of coolant from the radiator before
removing the sensor.
4Before the sensor is fitted, ensure its
threads are clean, and apply a little sealant to
them.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Oxygen sensor
General description
Note:Oxygen sensors are normally only fitted
to those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter. Most oxygen sensors are located in
the exhaust pipe, downstream from the
exhaust manifold. On 535 models, the oxygen
sensor is mounted in the catalytic converter.
The sensor’s electrical connector is located
near the bulkhead (left side) for easy access.
6The oxygen sensor, which is located in the
exhaust system (see illustration), monitors
the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
oxygen content in the exhaust reacts with the
oxygen sensor, to produce a voltage output
which varies from 0.1 volts (high oxygen, lean
mixture) to 0.9 volts (low oxygen, rich
mixture). The ECU constantly monitors this
variable voltage output to determine the ratio
of oxygen to fuel in the mixture. The ECU
alters the air/fuel mixture ratio by controlling
the pulse width (open time) of the fuel
injectors. A mixture ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1
part fuel is the ideal mixture ratio for
minimising exhaust emissions, thus allowing
the catalytic converter to operate at maximum
efficiency. It is this ratio of 14.7 to 1 which the
ECU and the oxygen sensor attempt to
maintain at all times.
7The oxygen sensor produces no voltage
when it is below its normal operating
temperature of about 320º C. During this initial
period before warm-up, the ECU operates in
“open-loop” mode (ie without the information
from the sensor).
8If the engine reaches normal operating
temperature and/or has been running for two
or more minutes, and if the oxygen sensor is
producing a steady signal voltage below 0.45 volts at 1500 rpm or greater, the ECU
fault code memory will be activated.
9When there is a problem with the oxygen
sensor or its circuit, the ECU operates in the
“open-loop” mode - that is, it controls fuel
delivery in accordance with a programmed
default value instead of with feedback
information from the oxygen sensor.
10The proper operation of the oxygen
sensor depends on four conditions:
a) Electrical - The low voltages generated by
the sensor depend upon good, clean
connections, which should be checked
whenever a malfunction of the sensor is
suspected or indicated.
b) Outside air supply - The sensor is
designed to allow air circulation to the
internal portion of the sensor. Whenever
the sensor is disturbed, make sure the air
passages are not restricted.
c) Proper operating temperature - The ECU
will not react to the sensor signal until the
sensor reaches approximately 320º C.
This factor must be taken into
consideration when evaluating the
performance of the sensor.
d) Unleaded fuel - The use of unleaded fuel
is essential for proper operation of the
sensor. Make sure the fuel you are using
is of this type.
11In addition to observing the above
conditions, special care must be taken
whenever the sensor is serviced.
a) The oxygen sensor has a permanently-
attached pigtail and electrical connector,
which should not be removed from the
sensor. Damage or removal of the pigtail
or electrical connector can adversely
affect operation of the sensor.
b) Grease, dirt and other contaminants
should be kept away from the electrical
connector and the louvered end of the
sensor.
c) Do not use cleaning solvents of any kind
on the oxygen sensor.
d) Do not drop or roughly handle the sensor.
e) The silicone boot must be fitted in the
correct position, to prevent the boot from
being melted and to allow the sensor to
operate properly.
6•2 Engine management and emission control systems
4.6 The oxygen sensor (arrowed) is usually
located in the exhaust pipe, downstream
from the exhaust manifold4.2 Check the resistance of the coolant
temperature sensor at different
temperatures4.1 The coolant temperature sensor
(arrowed) is usually located next to the
temperature sender unit, near the fuel
pressure regulator
Page 127 of 228

filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block
Page 128 of 228
On some models, it will be necessary to
release the retaining clip (see illustration).
13Visually examine the canister for leakage
or damage.
14Renew the canister if you find evidence of
damage or leakage.
7 Catalytic converter
1
General description
1To reduce emissions of unburnt
hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), the later
vehicles covered by this manual are equipped
with a catalytic converter (see illustration).
The converter contains a ceramic honeycomb
coated with precious metals, which speed up
the reaction between the pollutants listed
previously and the oxygen in the exhaust gas.
The pollutants are oxidised to produce water
(H
2O), nitrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Check
2Visually examine the converter(s) for cracks
or damage. Make sure all nuts and bolts are
tight.
3Inspect the insulation cover (if applicable)
welded onto the converter - it should not be
loose.
Caution: If an insulation cover is
dented so that it touches the
converter housing inside,
excessive heat may be
transferred to the floor.
4Start the engine and run it at idle speed.
5Check for exhaust gas leakage from the
converter flanges. Check the body of each
converter for holes.
Component renewal
6See Chapter 4 for removal and refitting
procedures.
Precautions
7The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device, which needs no maintenance
in itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware, if the converter is to
function properly for its full service life.
(a) DO NOT use leaded (eg UK “4-star”)
petrol in a car equipped with a catalytic
converter - the lead will coat the precious
metals, reducing their converting
efficiency, and will eventually destroy the
converter.
(b) Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule, as given in
Chapter 1. In particular, ensure that the air
cleaner filter element, the fuel filter (where
fitted) and the spark plugs are renewed at
the correct interval. If the intake air/fuel
mixture is allowed to become too rich due
to neglect, unburned fuel will enter the
catalytic converter, overheating the
element and eventually destroying the
converter.
(c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
(d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see (b) or (c)
above.
(e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - ie do not “blip” the
throttle immediately before switching offthe engine. If the ignition is switched off
at anything above idle speed, unburned
fuel will enter the (very hot) catalytic
converter, with the possible risk of its
igniting on the element and damaging the
converter.
(f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
(g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages, and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases, the element will overheat.
(h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody - and the casing will become
hot enough to ignite combustible
materials which brush against it. DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry
undergrowth, or over long grass or piles
of dead leaves.
(i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, and take great care
when working on the exhaust system.
Ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car, and do not drive the car over
rough ground, road humps, etc, in such a
way as to “ground” the exhaust system.
(j) In some cases, particularly when the car
is new and/or is used for stop/start
driving, a sulphurous smell (like that of
rotten eggs) may be noticed from the
exhaust. This is common to many
catalytic converter-equipped cars, and
seems to be due to the small amount of
sulphur found in some petrols reacting
with hydrogen in the exhaust, to produce
hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) gas; while this
gas is toxic, it is not produced in sufficient
amounts to be a problem. Once the car
has covered a few thousand miles, the
problem should disappear - in the
meanwhile, a change of driving style, or of
the brand of petrol used, may effect a
solution.
(k) The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for 50 000 to 100 000 miles - from
this point on, the CO level should be
carefully checked regularly, to ensure that
the converter is still operating efficiently. If
the converter is no longer effective, it
must be renewed.
6•6 Engine management and emission control systems
7.1 Typical catalytic converter (M10
engine type shown, others similar)6.12 EVAP system charcoal canister
viewed from under the vehicle (316i model)
Page 162 of 228

it to the approximate size and shape required,
then pull off the backing paper (if used) and
stick the tape over the hole; it can be
overlapped if the thickness of one piece is
insufficient. Burnish down the edges of the
tape with the handle of a screwdriver or
similar, to ensure that the tape is securely
attached to the metal underneath.
Bodywork repairs - filling and
respraying
Before using this Section, see the Sections
on dent, deep scratch, rust holes and gash
repairs.
Many types of bodyfiller are available, but
generally speaking, those proprietary kits
which contain a tin of filler paste and a tube of
resin hardener are best for this type of repair. A
wide, flexible plastic or nylon applicator will be
found invaluable for imparting a smooth and
well-contoured finish to the surface of the filler.
Mix up a little filler on a clean piece of card
or board - measure the hardener carefully
(follow the maker’s instructions on the pack),
otherwise the filler will set too rapidly or too
slowly. Using the applicator, apply the filler
paste to the prepared area; draw the
applicator across the surface of the filler to
achieve the correct contour and to level the
surface. As soon as a contour that
approximates to the correct one is achieved,
stop working the paste - if you carry on too
long, the paste will become sticky and begin
to “pick-up” on the applicator. Continue to
add thin layers of filler paste at 20-minute
intervals, until the level of the filler is just
proud of the surrounding bodywork.
Once the filler has hardened, the excess
can be removed using a metal plane or file.
From then on, progressively-finer grades of
abrasive paper should be used, starting with a
40-grade production paper, and finishing with
a 400-grade wet-and-dry paper. Always wrap
the abrasive paper around a flat rubber, cork,
or wooden block - otherwise the surface of
the filler will not be completely flat. During the
smoothing of the filler surface, the wet-and-
dry paper should be periodically rinsed in
water. This will ensure that a very smooth
finish is imparted to the filler at the final stage.
At this stage, the “dent” should be
surrounded by a ring of bare metal, which in
turn should be encircled by the finely
“feathered” edge of the good paintwork.
Rinse the repair area with clean water, until all
of the dust produced by the rubbing-down
operation has gone.
Spray the whole area with a light coat of
primer - this will show up any imperfections in
the surface of the filler. Repair these
imperfections with fresh filler paste or
bodystopper, and once more smooth the
surface with abrasive paper. Repeat this
spray-and-repair procedure until you are
satisfied that the surface of the filler, and the
feathered edge of the paintwork, are perfect.
Clean the repair area with clean water, and
allow to dry fully.The repair area is now ready for final
spraying. Paint spraying must be carried out
in a warm, dry, windless and dust-free
atmosphere. This condition can be created
artificially if you have access to a large indoor
working area, but if you are forced to work in
the open, you will have to pick your day very
carefully. If you are working indoors, dousing
the floor in the work area with water will help
to settle the dust which would otherwise be in
the atmosphere. If the repair area is confined
to one body panel, mask off the surrounding
panels; this will help to minimise the effects of
a slight mis-match in paint colours. Bodywork
fittings (eg chrome strips, door handles etc)
will also need to be masked off. Use genuine
masking tape, and several thicknesses of
newspaper, for the masking operations.
Before commencing to spray, agitate the
aerosol can thoroughly, then spray a test area
(an old tin, or similar) until the technique is
mastered. Cover the repair area with a thick
coat of primer; the thickness should be built
up using several thin layers of paint, rather
than one thick one. Using 400-grade wet-and-
dry paper, rub down the surface of the primer
until it is really smooth. While doing this, the
work area should be thoroughly doused with
water, and the wet-and-dry paper periodically
rinsed in water. Allow to dry before spraying
on more paint.
Spray on the top coat, again building up the
thickness by using several thin layers of paint.
Start spraying at one edge of the repair area,
and then, using a side-to-side motion, work
until the whole repair area and about 2 inches
of the surrounding original paintwork is
covered. Remove all masking material 10 to
15 minutes after spraying on the final coat of
paint.
Allow the new paint at least two weeks to
harden, then, using a paintwork renovator, or
a very fine cutting paste, blend the edges of
the paint into the existing paintwork. Finally,
apply wax polish.
Plastic components
With the use of more and more plastic body
components by the vehicle manufacturers (eg
bumpers. spoilers, and in some cases major
body panels), rectification of more serious
damage to such items has become a matter
of either entrusting repair work to a specialist
in this field, or renewing complete
components. Repair of such damage by the
DIY owner is not really feasible, owing to the
cost of the equipment and materials required
for effecting such repairs. The basic technique
involves making a groove along the line of the
crack in the plastic, using a rotary burr in a
power drill. The damaged part is then weldedback together, using a hot-air gun to heat up
and fuse a plastic filler rod into the groove.
Any excess plastic is then removed, and the
area rubbed down to a smooth finish. It is
important that a filler rod of the correct plastic
is used, as body components can be made of
a variety of different types (eg polycarbonate,
ABS, polypropylene).
Damage of a less serious nature (abrasions,
minor cracks etc) can be repaired by the DIY
owner using a two-part epoxy filler repair
material. Once mixed in equal proportions,
this is used in similar fashion to the bodywork
filler used on metal panels. The filler is usually
cured in twenty to thirty minutes, ready for
sanding and painting.
If the owner is renewing a complete
component himself, or if he has repaired it
with epoxy filler, he will be left with the
problem of finding a suitable paint for finishing
which is compatible with the type of plastic
used. At one time, the use of a universal paint
was not possible, owing to the complex range
of plastics encountered in body component
applications. Standard paints, generally
speaking, will not bond to plastic or rubber
satisfactorily. However, it is now possible to
obtain a plastic body parts finishing kit which
consists of a pre-primer treatment, a primer
and coloured top coat. Full instructions are
normally supplied with a kit, but basically, the
method of use is to first apply the pre-primer
to the component concerned, and allow it to
dry for up to 30 minutes. Then the primer is
applied, and left to dry for about an hour
before finally applying the special-coloured
top coat. The result is a correctly-coloured
component, where the paint will flex with the
plastic or rubber, a property that standard
paint does not normally possess.
6 Bodywork repair-
major damage
5
1Major damage must be repaired by a
qualified bodywork repair specialist, or
preferably by a BMW dealer. Specialised
equipment is required to do the job properly.
2If the damage is extensive, the bodyshell
must be checked for proper alignment, or the
vehicle’s handling characteristics may be
adversely affected and other components
may wear at an accelerated rate.
3Due to the fact that all of the major body
components (bonnet, wings, etc.) are
separate units, any seriously damaged
components should be replaced with new
ones rather than repaired.
Bodywork and fittings 11•3
11
If bodystopper is used, it can
be mixed with cellulose
thinners to form a really thin
paste which is ideal for filling
small holes
Sometimes bodywork
components can be found in
a scrapyard that specialises
in used vehicle components,
often at a considerable saving over the
cost of new parts.
Page 173 of 228

SI board is a self-contained computer which
includes a chip and batteries.
The rechargeable SI board nickel cadmium
(nicad) batteries maintain power to the
computer memory in the event of a power
drop (such as during starting) or complete
power loss (such as a dead or disconnected
battery) (see illustration). This assures power
so the computer can continue to keep track of
mileage and turn the lights on at the proper
interval.
The batteries have a life of approximately
six years, at which time they must be replaced
with new ones. Also, since they are recharged
by the engine charging system, they can run
down prematurely if power is cut off for some
reason (such as a blown fuse, a fault in the
wiring, or extended storage of the vehicle).
Excessive heat or cold can also shorten
battery life, with heat the greatest enemy.
Extreme heat can cause the batteries to
actually split open, allowing acid to drip into
the instrument cluster.
Several instruments controlled by the SI
board can be affected by low or discharged
batteries. Symptoms of low or dead SI board
batteries can include inconsistent tachometer
and temperature gauge readings, background
radio noise, and the inability to turn the
service lights off with the special tool.
Although only complete SI boards are
available from the manufacturer, batteries are
available separately from aftermarket sources.
While it is possible for the home mechanic to
renew the batteries, they are soldered to the
board, so unless you are skilled at this and
have the proper tools, this job should be left
to an experienced electronics technician.
Considerable savings can be realised by
removing the instrument cluster (see
Section 10) and taking it to an electronics
specialist.
Caution: the instrument cluster
and components are very
susceptible to damage from
static electricity. Make sure you
are earthed and have discharged any
static electricity (by touching an object
such as a metal water pipe) before
touching the cluster components.12 Headlights- bulb renewal
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Sealed-beam type
2Remove the grille (see Chapter 11).
3Remove the headlight retainer screws,
taking care not to disturb the adjustment
screws.
4Remove the retainer and pull the headlight
out enough to allow the connector to be
unplugged.
5Remove the headlight.
6To refit the headlight, plug the connector in,
place the headlight in position, and refit the
retainer and screws. Tighten the screws
securely.7Refit the grille. Connect the battery negative
cable.
Halogen bulb type
Warning: Halogen gas-filled bulbs
are under pressure, and may
shatter if the surface is scratched
or the bulb is dropped. Wear eye
protection, and handle the bulbs carefully,
grasping only the base whenever possible.
Do not touch the surface of the bulb with
your fingers, because the oil from your
skin could cause it to overheat and fail
prematurely.
8From behind the headlight assembly,
remove the outer cover (see illustration).
9Twist and release the inner cover from the
rear of the headlight (see illustration).
10Disconnect the wire from the rear of the
headlight bulb (see illustration).
11Release the clips, and withdraw the bulb
from the headlight unit (see illustration).
12Fit the new bulb using a reversal of the
removal procedure. Make sure that the clips
engage the bulb correctly.
13Connect the battery negative cable.
Body electrical systems 12•5
12.9 Twist and release the headlight inner
cover12.8 Removing the headlight rear outer
cover (3-Series shown)11.2 These batteries (arrowed) power the
Service Indicator (SI) board
12.11 Removing the headlight bulb (do not
touch the surface of the bulb with your
fingers)12.10 Disconnecting the wire from the rear
of the headlight bulb
12
If you do touch the headlamp
bulb surface, clean it with
methylated spirit.
Page 176 of 228

12Refitting is a reversal of removal. When
fitting the motor, if necessary plug in the
connector and run the motor briefly until it is
in the “neutral” (wiper parked) position.
17 Heated rear window-
check and repair
2
1The heated rear window consists of a
number of horizontal elements on the glass
surface.
2Small breaks in the element can be repaired
without removing the rear window.
Check
3Switch on the ignition and the heated rear
window.
4Place the positive lead of a voltmeter to the
heater element nearest to the incoming power
source.
5Wrap a piece of aluminium foil around the
negative lead of the voltmeter on the positive
side of the suspected broken element, and
slide it slowly towards the negative side.
Watch the voltmeter needle - when it moves
from zero, you have located the break.
Repair
6Repair the break in the line using a repair kit
recommended specifically for this purpose,
such as BMW repair kit No. 81 22 9 (or
equivalent). Included in this kit is plastic
conductive epoxy. The following paragraphs
give general instructions for this type of repair;
follow the instructions supplied with the repair
kit if they are different.
7Prior to repairing a break, switch off the
circuit and allow it to cool down for a few
minutes.
8Lightly buff the element area with fine steel
wool, then clean it thoroughly.
9Use masking tape to mask off the area of
repair, leaving a slit to which the epoxy can be
applied.
10Mix the epoxy thoroughly, according to
the instructions on the package.
11Apply the epoxy material to the slit in the
masking tape, overlapping the undamaged
area about 20 mm on each end.12Allow the repair to cure for 24 hours
before removing the tape and using the
heated rear window.
18 Supplemental Restraint
System (SRS)- general
information
Later models are equipped with a
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS),
incorporating an airbag. This system is
designed to protect the driver from serious
injury in the event of a head-on or frontal
collision. It consists of an airbag module in the
centre of the steering wheel, two crash
sensors mounted on the front inner wing
panels, and a crash safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment.
The airbag module contains a housing
incorporating the airbag and the inflator units.
The inflator assembly is mounted on the back
of the housing over a hole through which gas
is expelled, inflating the bag almost instanta-
neously when an electrical signal is sent from
the system. This signal is carried by a wire
which is specially wound with several turns,
so the signal will be transmitted regardless of
the steering wheel position.
The SRS system has three sensors: two at
the front, mounted on the inner wing panels
(see illustration), and a safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment. The crash
sensors are basically pressure-sensitive
switches, which complete an electrical circuit
during an impact of sufficient force. The
electrical signal from the crash sensors is sent
to a third sensor, which then completes the
circuit and inflates the airbag.
The module containing the safety switch
monitors the system operation. It checks the
system every time the vehicle is started,
causing the AIRBAG warning light to come on,
then go out if the system is operating
correctly. If there is a fault in the system, the
light will stay on. If the AIRBAG warning light
does stay on, or if it comes on while driving,
take the vehicle to your dealer immediately.
19 Cruise control system-
description and check
1
The cruise control system maintains vehicle
speed using a vacuum-actuated servo motor
located in the engine compartment, which is
connected to the throttle linkage by a cable.
The system consists of the servo motor,
clutch switch, brake switch, control switches,
a relay, and associated vacuum hoses.
Because of the complexity of the cruise
control system, repair should be left to a
dealer service department. However, it is
possible for the home mechanic to make
simple checks of the wiring and vacuum
connections for minor faults which can be
easily repaired. These include:
a) Inspect the cruise control actuating switches
for broken wires and loose connections.
b) Check the cruise control fuse.
c) The cruise control system is operated by
vacuum, so it’s critical that all vacuum
switches, hoses and connections are
secure. Check the hoses in the engine
compartment for loose connections,
cracks, or obvious vacuum leaks.
20 Central locking system-
description and check
2
The central door locking system operates
the door lock actuators mounted in each
door. The system consists of the switches,
actuators and associated wiring. Diagnosis is
limited to simple checks of the wiring
connections and actuators for minor faults
which can be easily repaired. These include:
a) Check the system fuse and/or circuit
breaker (where applicable).
b) Check the switch wires for damage and
loose connections. Check the switches
for continuity.
c) Remove the door trim panel(s), and check
the actuator wiring connections to see if
they’re loose or damaged. Inspect the
actuator rods to make sure they aren’t
12•8 Body electrical systems
18.3 The SRS system crash sensors
(arrowed) are located in the engine
compartment - check the wiring regularly
for damage16.11b Tailgate wiper motor (5-Series)16.11c Wiper blade and pivot mechanism
on the rear window (5-Series)