1989 Citroen BX HATCHBACK air suspension
[x] Cancel search: air suspensionPage 3 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine REPAIRS & OVERHAUL
Engine and Associated Systems
150 engine repair procedures Page2A•1
171 and 159 engine repair procedures Page2B•1
K1G engine repair procedures Page2C•1
D6C engine repair procedures Page2D•1
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems Page3•1
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models Page4A•1
Fuel and exhaust systems - Bosch LE3 Jetronic injection Page4B•1
Fuel and exhaust systems - Motronic injection Page4C•1
Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Page4D•1
Ignition system - carburettor models Page5A•1
Ignition system - fuel injection models Page5B•1
Starting and charging systems Page5C•1
Transmission
ClutchPage6•1
Manual gearboxPage7A•1
Automatic transmission Page7B•1
DriveshaftsPage8•1
Brakes and Suspension
Hydraulic systemPage9•1
Braking systemPage10•1
Suspension and steering Page11•1
Body Equipment
Bodywork and fittingsPage12•1
Body electrical systems Page13•1
Wiring DiagramsPage13•16
REFERENCEDimensions and weights PageREF•1
Conversion factorsPageREF•2
Buying spare partsPageREF•3
Vehicle Identification PageREF•3
General repair procedures PageREF•4
Jacking and vehicle support PageREF•5
Tools and working facilities PageREF•6
MOT test checksPageREF•8
Fault findingPageREF•12
Glossary of technical terms PageREF•19
IndexPageREF•23
Contents
Page 13 of 16
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Weekly checks0•13
Tyre condition and pressure
It is very important that tyres are in good
condition, and at the correct pressure - having
a tyre failure at any speed is highly dangerous.
Tyre wear is influenced by driving style - harsh
braking and acceleration, or fast cornering,
will all produce more rapid tyre wear. As a
general rule, the front tyres wear out faster
than the rears. Interchanging the tyres from
front to rear ("rotating" the tyres) may result in
more even wear. However, if this is
completely effective, you may have the
expense of replacing all four tyres at once!
Remove any nails or stones embedded in the
tread before they penetrate the tyre to cause
deflation. If removal of a nail does reveal thatthe tyre has been punctured, refit the nail so
that its point of penetration is marked. Then
immediately change the wheel, and have the
tyre repaired by a tyre dealer.
Regularly check the tyres for damage in the
form of cuts or bulges, especially in the
sidewalls. Periodically remove the wheels,
and clean any dirt or mud from the inside and
outside surfaces. Examine the wheel rims for
signs of rusting, corrosion or other damage.
Light alloy wheels are easily damaged by
"kerbing" whilst parking; steel wheels may
also become dented or buckled. A new wheel
is very often the only way to overcome severe
damage.New tyres should be balanced when they are
fitted, but it may become necessary to re-
balance them as they wear, or if the balance
weights fitted to the wheel rim should fall off.
Unbalanced tyres will wear more quickly, as
will the steering and suspension components.
Wheel imbalance is normally signified by
vibration, particularly at a certain speed
(typically around 50 mph). If this vibration is
felt only through the steering, then it is likely
that just the front wheels need balancing. If,
however, the vibration is felt through the
whole car, the rear wheels could be out of
balance. Wheel balancing should be carried
out by a tyre dealer or garage.
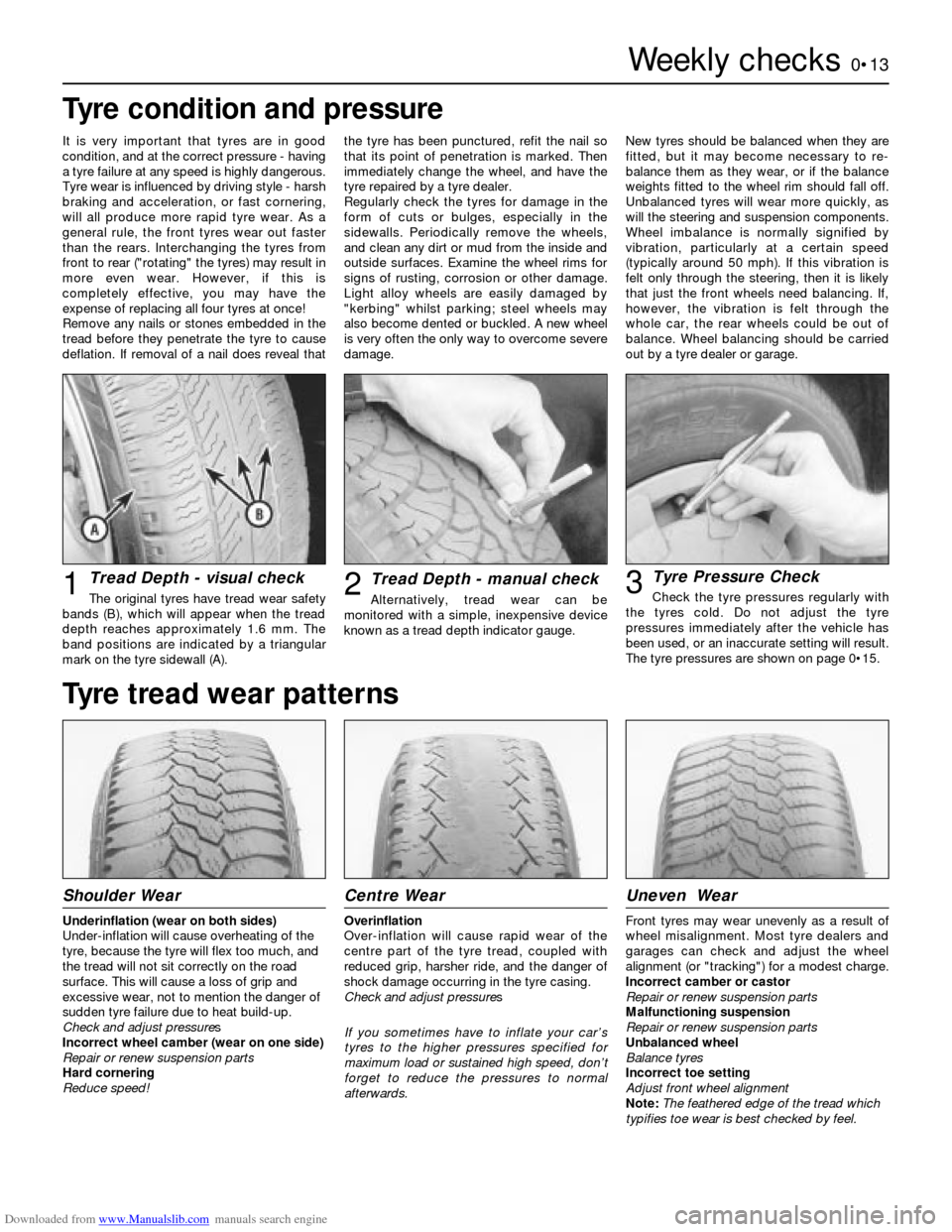
Tread Depth - visual check
The original tyres have tread wear safety
bands (B), which will appear when the tread
depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm. The
band positions are indicated by a triangular
mark on the tyre sidewall (A).1Tread Depth - manual check
Alternatively, tread wear can be
monitored with a simple, inexpensive device
known as a tread depth indicator gauge.2Tyre Pressure Check
Check the tyre pressures regularly with
the tyres cold. Do not adjust the tyre
pressures immediately after the vehicle has
been used, or an inaccurate setting will result.
The tyre pressures are shown on page 0•15.3
Tyre tread wear patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation (wear on both sides)
Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, because the tyre will flex too much, and
the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause a loss of grip and
excessive wear, not to mention the danger of
sudden tyre failure due to heat build-up.
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber (wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of the
centre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced grip, harsher ride, and the danger of
shock damage occurring in the tyre casing.
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate your car’s
tyres to the higher pressures specified for
maximum load or sustained high speed, don’t
forget to reduce the pressures to normal
afterwards.
Uneven Wear
Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. Most tyre dealers and
garages can check and adjust the wheel
alignment (or "tracking") for a modest charge.
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of the tread which
typifies toe wear is best checked by feel.
Page 16 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0•16Lubricants, fluids and capacities
Component or system Lubricant or fluid Capacity
Engine:
BX and BX14 (with gearbox) Multigrade engine oil, viscosity 150A engine - 4.5 litres (oil change)
pre-August 1988 SAE 15W/40 or 20W/50, 150C engine - 5.0 litres (oil change)
(Duckhams QXR, QS,Hypergrade
Plus or Hypergrade)
BX (from August 88) As above K1G engine - 3.5 litres (with filter)
BX16 and BX19 As above171/159 engine 5.0 litres (oil change)
BX19 GTi 16v As above D6C engine - 5.3 litres (with filter)
Cooling systemEthylene - glycol based antifreeze D6A/C/D engine - 7.1 litres
(Duckhams Antifreeze and Summer Others - 6.5 litres
Coolant). Mixture in temperate climate
- 25% antifreeze to 75% water
Manual gearbox:
BX and BX14 pre-Aug. 88 N/A With engine
Later BX 14 (MA type) Gear oil, viscosity 75W/80W 2 litres
(Duckhams PT75W/80 Gear Oil)
BX16 and BX19 (Type BE1) As above 2 litres
BX16 and BX19 (Type BE3/5) As above Up to serial No. 2445106 - 2.2 litres
From serial No. 2445106 - 1.8 litres
Automatic transmissionDexron IID type ATF From dry - 6.5 litres
(Duckhams Uni-Matic) Drain and refill - 2.5 litres
Hydraulic systemGreen LHM fluid -
(Duckhams LHM fluid)
Fuel system97 to 99 RON leaded or 95 RON BX/BX14 - 44 or 52 litres
unleaded * BX16/BX19 - 52 or 66 litres
* Note: Models fitted with catalytic converters MUSTuse unleaded fuel at all times
Oils perform vital tasks in all engines. The
higher the engine’s performance, the greater
the demand on lubricants to minimise wear as
well as optimise power and economy.
Duckhams tailors lubricants to the highest
technical standards, meeting and exceeding
the demands of all modern engines.
HOW ENGINE OIL WORKS
• Beating friction
Without oil, the surfaces inside your engine
which rub together will heat, fuse and quickly
cause engine seizure. Oil, and its special
additives, forms a molecular barrier between
moving parts, to stop wear and minimise heat
build-up.
• Cooling hot spots
Oil cools parts that the engine’s water-based
coolant cannot reach, bathing the combustion
chamber and pistons, where temperatures
may exceed 1000°C. The oil assists intransferring the heat to the engine cooling
system. Heat in the oil is also lost by air flow
over the sump, and via any auxiliary oil cooler.
• Cleaning the inner engine
Oil washes away combustion by-products
(mainly carbon) on pistons and cylinders,
transporting them to the oil filter, and holding
the smallest particles in suspension until they
are flushed out by an oil change. Duckhams
oils undergo extensive tests in the laboratory,
and on the road.
Engine oil types
Mineral oilsare the “traditional” oils,
generally suited to older engines and cars not
used in harsh conditions. Duckhams
Hypergrade Plus and Hypergradeare well
suited for use in most popular family cars.
Diesel oilssuch as Duckhams Dieselare
specially formulated for Diesel engines,
including turbocharged models and 4x4s.
Synthetic oilsare the state-of-the-art in
lubricants, offering ultimate protection, but at
a fairly high price. One such is Duckhams QS,
for use in ultra-high performance engines.
Semi-synthetic oilsoffer high performance
engine protection, but at less cost than full
synthetic oils. Duckhams QXRis an ideal choice
for hot hatches and hard-driven cars.
For help with technical
queries on lubricants,
call Duckhams Oils
on 0181 290 8207
Choosing your engine oil
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump oil
down the drain.
To find the
location of your
local oil recycling
bank, call this
number free.