1988 PONTIAC FIERO change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 1556 of 1825
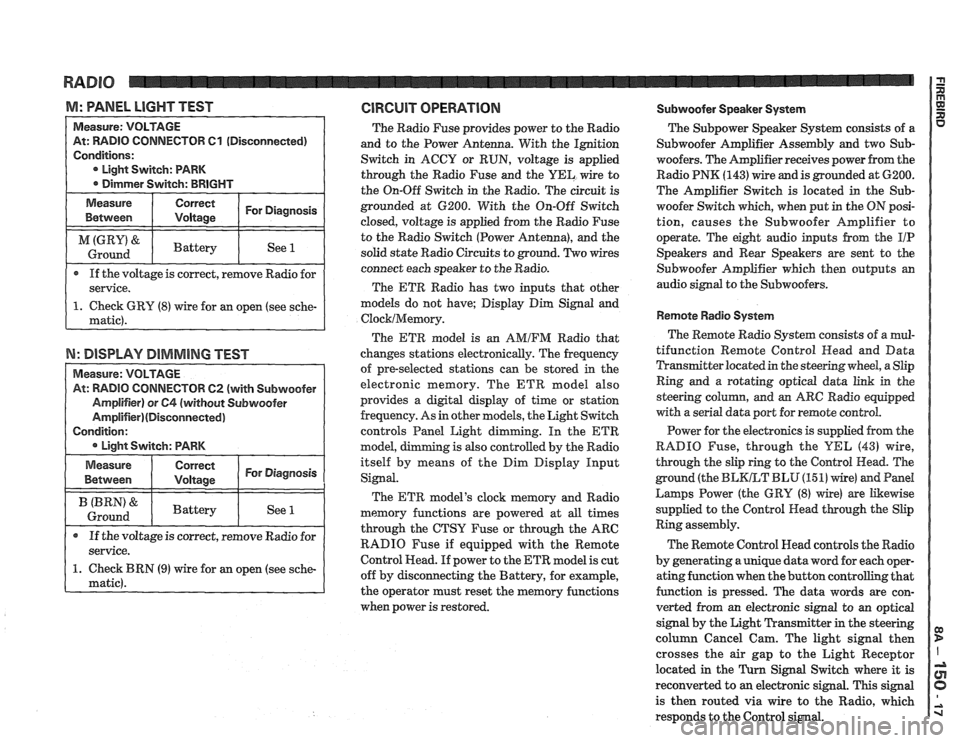
M: WNEL LIGHT TEST GlRGUlT OPERATION Subwoofer Speaker System
TOR 61 (Disconnected)
If the voltage is correct, remove Radio for
N: DISPLAY DIMMING TEST
TOW 62 (with Subwoofer
The Radio Fuse provides power to the Radio
and to the Power Antenna. With the Ignition
Switch in ACCY or RUN, voltage is applied
through the Radio Fuse and the
UEL wire to
the On-Off Switch in the Radio. The circuit is
grounded at 6200. With the On-Off Switch
closed, voltage is applied from the Radio Fuse
to the Radio Switch (Power Antenna), and the
solid state Radio Circuits to ground. Two wires
connect each speaker to the Radio.
The ETR Radio has two inputs that other
models do not have; Display Dim Signal and
ClocklMemory.
The ETR model is an AMIFM Radio that
changes stations electronically. The frequency
of pre-selected stations can be stored
in the
electronic memory. The ETR model also
provides a digital display of time or station
frequency. As in other models, the Light Switch
controls Panel Light dimming. In the
ETR
model, g is also controlled by the Radio
itself by means of the Dim Display Input
Signal.
The ETR model's clock memory and Radio
memory functions are powered at all times
through the CTSY Fuse or through the ARC
RADIO Fuse if equipped with the Remote
Control Head. If power to the ETR model is cut
off by disconnecting the Battery, for example,
the operator must reset the memory functions
when power is restored. The
Subpower Speaker
System consists of a
Subwoofer Amplifier Assembly and two Sub-
woofers. The Amplifier receives power from the
Radio PNK
(143) wire and is grounded at 6200.
The Amplifier Switch is located in the
Sub-
woofer Switch which, when put in the ON posi-
tion, causes the Subwoofer Amplifier to
operate. The eight audio inputs from the
I/P
Speakers and Rear Speakers are sent to the
Subwoofer Amplifier which then outputs an
audio signal to the Subwoofers.
Remote Radio System
The Remote Radio System consists of a mul-
tifunction Remote Control
Head and Data
Transmitter located in the steering wheel, a Slip
Ring and a rotating optical data link in the
steering
colurnn, and an ARC Radio equipped
with a serial data port for remote control.
Power for the electronics is supplied from the
RADIO Fuse, through the
YEL (43) wire,
through the slip ring to the Control Head. The
ground (the
BLKLT BLU (15 1) wire) and Pand
Larnps Power (the GRY (8) wire) are Likewise
supplied to the Control Head through the Slip
Ring assembly.
The Remote Control Head controls the Radio
by generating a unique data word for each oper-
ating function when the button controlling that
function is pressed. The data words are con-
verted from an electronic signal to an optical
signal by the Light Transmitter in the steering
column Cancel Cam. The light signal then
crosses the air gap to the Light Receptor
located in the
Turn Signal Switch where it is
reconverted to
an electronic signal. This signal
is then routed via wire to the Radio, which
responds to the Control signal.
Page 1665 of 1825
98-2 CRUISE CONTROL
Fig. 1 Multi-Function Lever
e The Set Position - With the button switch
depressed and then released (car speed must
exceed the low speed limit point, and the
Off/On/Resume/Accel Switch must be in the
ON position) the cruise speed will be set at the
speed the car was at when the button was
released. Car cruise speed will be within
& 1 mph
of the actual speed at engaged speed. The system
will cruise until either the
Off/On/Resume/Accel Switch is moved to OFF,
the ignition switch is turned off, and/or the
Set/Coast Button is pushed in fully and held.
Pushing the brake pedal (or clutch pedal) releases
the cruise but not the resume capability.
The Coast Position - With the button switch
fully depressed, the driver can raise or lower his
speed. To increase speed, the driver can
accelerate to a new speed, fully depress the switch
and release the button. The controller "forgets"
the previously set speed. An increased control
speed can also be more easily set by the
Off/On/Resume/Accel Switch as previously
described. To decrease cruise speed, the button
switch is held in, disengaging the cruise system,
which allows the throttle to return to the idle
position. When the car has slowed to the aesired
cruise speed, releasing the switch will re-engage
the system.
e The "Tap-Down" Position - In order to do
this the cruise must be engaged and operating.
"Tapping-down" is done by quickly pressing and
releasing the
Set/Coast Button, or "tapping" the
button. Do not hold the button in the depressed
position or the system will go into the "coast"
mode. "Tap-down" is a function in which cruise
speed can be decreased by
1 mph increments (one
tap = 1 mph decrease).
The accelerator may be depressed at any
time
to override the cruise system.
Release of the accelerator will return the
car
te the previous set cruise speed.
NOTICE:
To keep the vehic:e under control, and
to prevent possible vehicle damage, it is not
advisable to use the cruise control on slippery
roads. It is not recommended to use the cruise
control in conditions such as on winding roads or
in traffic of heavy or varying volume. When
traveling down
a steeply graded hill, the cruise control
should be disengaged by depressing the
bralte pedal lightly. The transmission can then be
shifted into a lower gear range to help control
vehicle speed.
ELECTRONIC CONTROLLER (MODULE)
Figure 2
Fig. 2 Controller (Module)
The controller interprets the position of the servo,
the position of the control switches and the output of
the speed sensor. In response to these inputs, the
controller electrically signals the opening or closing of
the vent and vacuum solenoid valves in the servo.
The controller is usually mounted on the pedal
bracket, but is integral with the ECM on some models
with certain engines. For specific location, see the
On-Car Service portion of this section.
SERVO UNIT
Figure 3
The servo consists of a vacuum operated
diaphragm, a normally open solenoid valve to vent the
diaphragm chamber to atmosphere, a normally closed
solenoid valve to connect the diaphragm chamber to
the vacuum source, and a variable inductance position
sensor.
The servo incorporates a steel core which moves
within a coil. Its resulting variable inductance provides
a continuous (voltage) servo position signal to the
controller. This voltage signal is constantly compared
to the vehicle speed signal. This comparison
determines if the cruise system has corrected the speed
error or if additional changes are required.
The servo operates the throttle in response to
signals from the electronic controller as follows:
Steady Cruise State (system engaged and
operating)
- Both vacuum and vent valves are
closed or sealed. The servo has a constant vacuum
on the diaphragm and places no requirements on
the vacuum source, as vacuum is trapped in the
diaphragm chamber.
e Vehicle Losing Speed (due to steep grades or
driver wishes to increase speed by using the Accel
or 'tap-up' feature)
- The controller energizes the
vacuum solenoid to open the vacuum valve to the
vacuum source. This increases the vacuum level
Page 1788 of 1825
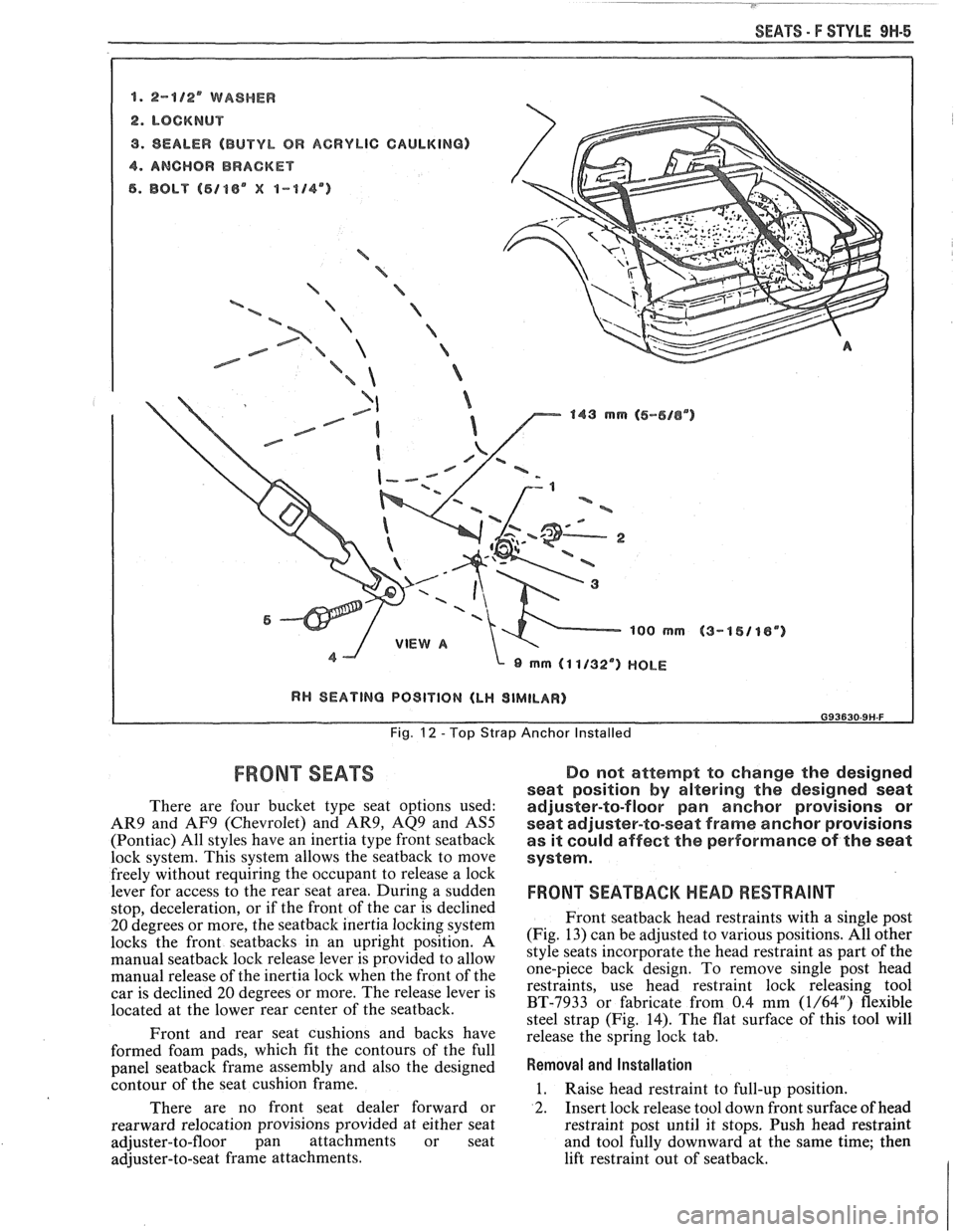
SEATS - F STYLE 9H-5
8. 2-8/2' WASHER
2. LOCKNUT
9. SEALER (BUTYL OR ACRYLIC CAULKING)
4. ANCHOR BRACKET
6. BOLT (5188" X 1-114")
a B -% ='-a
/ '%
/ e-5- B
a 143 mrn (6-616") 143 mrn (6-616")
~QO rnm 1QO rnm
I RH SEATING PO9lVlON (LH SIMILAR) I
Fig. 12 - Top Strap Anchor Installed
FRONT SEATS Do not attempt to change the designed
seat position
by altering the designed seat
There are four bucket type seat options used: adjuster-to-floor pan anchor provisions or
AR9 and AF9 (Chevrolet) and AR9, AQ9 and AS5 seat adjuster-to-seat frame anchor provisions
(Pontiac) All styles have an inertia type front seatback as it could affect the performance of the seat
lock system. This system allows the seatback to move system.
freelv without reauiring the occupant to release a lock
leve; for access to the rear seat a;ea. During a sudden
stop, deceleration, or if the front of the car is declined
20 degrees or more, the seatback inertia locking system
locks the front seatbacks in an upright position. A
manual
seatback lock release lever is provided to allow
manual release of the inertia lock when the front of the
car is declined
20 degrees or more. The release lever is
located at the lower rear center of the seatback.
Front and rear seat cushions and backs have
formed foam pads, which
fit the contours of the full
panel
seatback frame assembly and also the designed
contour of the seat cushion frame.
There are no front seat dealer forward or
rearward relocation provisions provided at either seat
adjuster-to-floor pan attachments or seat
adjuster-to-seat frame attachments.
FRONT SEATBACM HEAD RESTRAINT
Front seatback head restraints with a single post
(Fig. 13) can be adjusted to various positions. All other
style seats incorporate the head restraint as part of the
one-piece back design. To remove single post head
restraints, use head restraint lock releasing tool
BT-7933 or fabricate from 0.4 mm
(1/64") flexible
steel strap (Fig. 14). The flat surface of this tool will
release the spring lock tab.
Removal and Installation
1. Raise head restraint to full-up position.
2. Insert lock release tool down front surface of head
restraint post until it stops. Push head restraint
and tool fully downward at the same time; then
lift restraint out of seatback.