1988 PONTIAC FIERO low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 364 of 1825

2.8 LITER V.6 6A2.13
Torque bolts as shown in Figure 6A2-15.
4. Install
push rods and loosely retain with rocker
arms. Make sure lower ends of
pushrods are in
lifter seats.
5. Install intake manifold.
6. Raise vehicle.
7. Install dipstick tube bracket.
8. Connect exhaust pipe
to exhaust manifold flange.
9. Lower vehicle.
10. Adjust
valve lash as previously outlined.
11. Continue
following intake manifold installation
for build up.
Removal (Right)
Remove intake manifold as previously outlined.
Raise vehicle.
Disconnect exhaust pipe.
Drain engine block.
Lower vehicle.
Loosen rocker arms until able to remove push
rod.
Remove serpentine belt.
Remove tensioner.
Remove A.I.R. bracket.
Remove generator bracket.
Remove head bolts.
Remove head.
Installation (Right)
The gasket surfaces on both the head and cylinder
case
deck must be clean of any foreign matter and free
of nicks of heavy scratches. Cylinder bolt threads in the
case and threads on the cylinder head bolts must be
clean. Dirt will affect bolt torque.
1. Place the gasket in position, over the dowel pins,
with the note "This Side Up" showing.
2. Install cylinder head.
3. Coat cylinder head bolt threads with sealer,
#lo52080 or equivalent, and install bolts.
Torque bolts as shown in (Figure
6A2-15).
Install push rods and loosely retain with rocker
arms. Make sure lower ends of push rods are in
lifter seats.
Install intake manifold.
Raise vehicle.
Install exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold flange.
Lower vehicle.
Adjust valve lash as previously outlined.
Install AIR bracket.
Install tensioner.
Install generator bracket.
Continue following intake manifold installation
for build up.
Disassembly
1. With cylinder head removed, remove rocker arm
nuts, balls and rocker arms (if not previously
done).
2. Using tool J-8062, compress the valve springs and
remove valve keys. Release the compressor tool and
remove spring caps, oil shedders, springs and
damper assemblies, then remove oil seals.
3. Remove valves from cylinder head and place
them in a rack so they can be installed in their
original positions.
Cleaning and Inspection
Clean all carbon from combustion chambers and
valve ports using 'tool
5-8089.
Thoroughly clean valve guides using 5-8 10 1.
Clean all carbon and sludge from push rods,
rocker arms and push rod guides.
Clean valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel.
Clean carbon deposits from head gasket mating
surface.
Inspect cylinder head for cracks in the exhaust
ports, combustion chambers, or external cracks
to the water jacket.
Inspect the valves for burned heads, cracked faces
or damaged stems.
NOTICE: Excessive valve stem to bore clearance
will cause high oil consumption and may cause
valve breakage. Insufficient clearance will result in
noise and sticky functioning of the valve and
disturb engine smoothness.
8. Measure valve stem clearance as follows:
a. Clamp
a dial indicator on one side of the
cylinder head. Locate the indicator so that
movement of the valve stem from side to
side (crosswise to the head) will cause direct
movement of the indicator stem. The
indicator stem must contact the side of the
valve stem just above the guide.
b. Drop
the valve head
1.5mm off the valve
seat.
c. Move
the stem of the valve from side to side,
using light pressure, to obtain a clearance
reading. If clearance exceeds specifications,
it will be necessary to ream valve guides for
oversize valves. Service valves are available
in std., 089,
.394 and .775mm O.S. sizes.
9. Check
valve spring tension with tool J-8056,
spring tester. Springs should be compressed to the
specified height and checked against the
specifications chart. Springs should be replaced if
not within 44
N (10 Ibs.) of the specified load
(without dampers).
10. Inspect
rocker arm studs for wear or damage.
ROCKER ARM STUDS
Cylinder heads use threaded rocker arm studs.
Rocker arm studs that have damaged threads should
be replaced with new studs. If, for some reason, the
threads in the head
are damaged or stripped, the head
can be retapped, and a helical type insert added. If such
an insert is not available, the head should be replaced.
VALVE GUIDES
Valves with oversize stems are available in .089,
,394 and ,775mm over sizes. To ream the valve guide
Page 369 of 1825

6A2-18 2.8 LITER V-6
Installation
Clean sealing surfaces on cylinder case and oil
pan.
Install gasket and attach retaining bolts.
Remove jack and lower engine.
Install motor mount through bolts.
Install starter.
Install exhaust pipes.
Install converter dust cover.
Lower vehicle.
Install fan shroud.
Install distributor cap.
Refill crankcase.
Install air cleaner.
Connect battery.
Start engine, check for leaks.
OIL PUMP (FIGURE 6A2-22)
Removal
1. Remove oil pan as previously outlined.
2. Remove pump to rear main bearing cap bolt and
remove pump and extension shaft.
Disassembly
1. Remove
the pump cover attaching bolts and the
pump cover. Mark gear teeth so they may be
reassembled with the same teeth indexing.
2. Remove the idler gear and the drive gear and
shaft from the pump body.
3. Remove the pressure regulator valve retaining
pin pressure regulator spring and valve.
4. If the pickup screen and pipe assembly need
replacing, mount the pump in a soft-jawed vise
and extract pipe from pump cover. Do not disturb
the pickup screen on the pipe. This is serviced as
an assembly.
Cleaning and lnspection
1. Wash all parts in cleaning solvent and dry with
compressed air.
2. Inspect the pump body and cover for cracks or
excessive wear.
3. Inspect pump gears for damage or excessive wear.
The pump gears and body are not serviced
separately. If the pump gears or body are
damaged or worn, replacement of the entire oil
pump assembly is necessary.
4. Check the drive gear shaft for looseness in the
pump body.
5. Inspect inside of pump cover for wear that would
permit oil to leak past the ends of the gears.
6. Inspect the pickup screen and pipe assembly for
damage to screen or pipe.
7. Check the pressure regulator valve for fit.
Assembly
1. If the pickup screen and pipe assembly was
removed, it should be replaced with a new part.
Loss of press fit condition could result in an air
leak and loss of oil pressure. Mount the pump in
a soft-jawed vise, apply sealer to outside diameter of
swaged end of pipe, and using Tool
J-8369 tap
the pipe in place with a plastic hammer.
NOTICE: Be careful of twisting, shearing or
collapsing pipe while installing in pump.
2. Install the pressure regulator valve and related
parts.
3. Install the drive gear and shaft in the pump body.
4. Install the idler gear in the pump body in the
original orientation.
5. Install cover gasket.
6. Install the pump cover and torque attaching
screws to specifications.
7. Turn drive shaft by hand to check for smooth
operation.
Installation
1. Assemble pump and extension shaft with retainer
to rear main bearing cap, aligning top end of
hexagon extension shaft with hexagon socket
lower end of distributor drive gear.
2. Install pump to rear bearing cap bolt and torque
to specifications.
3. Install oil pan as previously outlined.
ROD CAP AND
Figure 6A2-23 Measuring Connecting Rod Side
Clearance
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
Connecting rod bearings are of the precision
insert type and do not utilize shims for adjustment. DO
NOT FILE RODS OR ROD CAPS. If clearances are
found to be excessive, a new bearing will be required.
Service bearings are available in standard size and
.013mm and .026mm undersize for use with new and
used standard size crankshafts.
lnspection and Replacement
1. With oil pan and oil pump removed, remove the
connecting rod cap and bearing.
2. Inspect the bearing for evidence of wear or
damage. (Bearings showing the above should not
be reinstalled.)
3. Wipe both upper and lower bearing shells and
crankpin clean of oil.
Page 373 of 1825
rebore the cylinder to fit an oversize piston in
order to insure satisfactory results.
3. If cylinder bore is tapered 0. lmm or more or is
out-of-round
O.lmm or more, it is advisable to
rebore for the smallest possible oversize piston
and rings. Below these limits, the cylinder bore
can be trued up with honing.
4. Clean carbon from piston surfaces and under side
of piston heads. Clean carbon from ring grooves
with suitable tool and remove any gum or varnish
from piston skirts with suitable solvent.
5. Carefully examine pistons for
rough or scored
surfaces; cracks in skirt or head; cracked or
broken ring lands; chipped or uneven wearing
pistons would cause rings to seat improperly or
have excessive clearance in ring grooves.
Damaged or faulty pistons should be replaced.
The pistons are cam ground, which means that
the diameter at a right angle to the wrist pin is
greater than the diameter parallel to the wrist pin.
When a piston is checked for size, it must be done
at points 90" to the piston pin. The piston should
be checked (for fitting purposes) in a plane
through the piston pin centerline.
6. Inspect surfaces of wrist pins and check for wear
by measuring worn or unworn surfaces with
micrometers. Occasionally pins will be found
tight due to gum or varnish deposits. This may be
corrected by removing the deposit with a suitable
solvent. If piston bosses are worn out-of-round or
oversize, the piston and pin assembly must be
replaced. Oversize pins are not practical due to
the pin being a press fit in the connecting rod.
Piston pins must fit the piston with an easy finger
push at 70°F (21°C)
(.0065 to .0091mm
clearance).
7. Examine all piston rings for scores, chips or
cracks. Check compression rings for tension by
comparing with new rings. Check gap of
compression rings by placing rings in bore at
bottom of ring travel. Measure gap with feeler
gage. Gap should be between
0.25mm and 0.
50mm. If gaps are excessive (over 0.50mm) it
indicates the rings have worn considerably and
should be replaced. Bore wear should be checked
before rings are replaced,
. l25mm bore wear will
result in
.39mm increase in ring gap.
Assembly
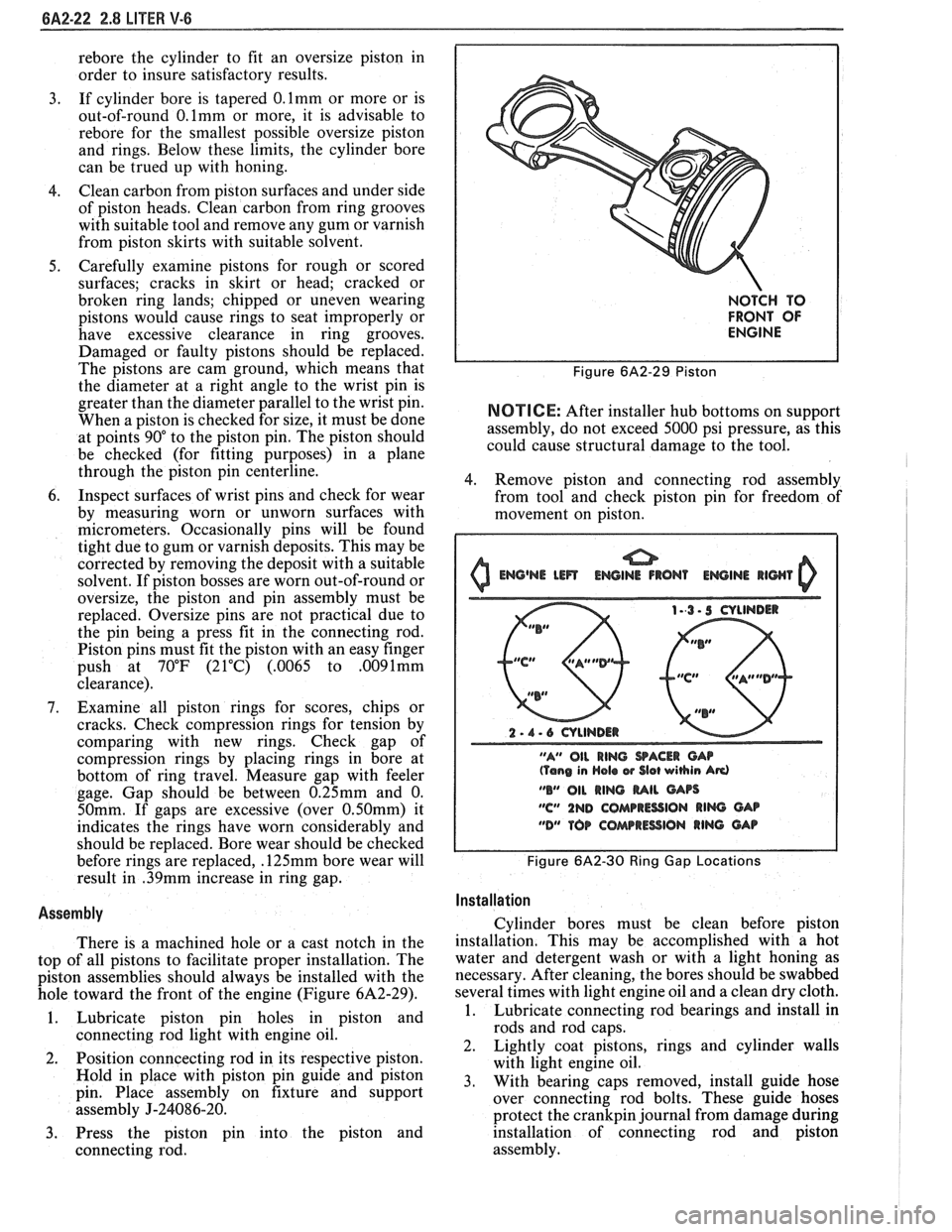
There is a machined hole or a cast notch in the
top of all pistons to facilitate proper installation. The
piston assemblies should always be installed with the
hole toward the front of the engine (Figure
6A2-29).
1. Lubricate piston pin holes in piston and
connecting rod light with engine oil.
2. Position
conncecting rod in its respective piston.
Hold in place with piston pin guide and piston
pin. Place assembly on fixture and support
assembly
J-24086-20.
3. Press the piston pin into the piston and
connecting rod.
NOTCH TO
FRONT OF
ENGINE
Figure 6A2-29 Piston
NOTICE: After installer hub bottoms on support
assembly, do not exceed 5000 psi pressure, as this
could cause structural damage to the tool.
4. Remove piston and connecting rod assembly
from tool and check piston pin for freedom of
movement on piston.
0 Emj@NE Lm ENGINE IRON1 EWINI llWl 0
2 - 1 - 6 CYLINDER
"A" OIL
RING SACER CAP (Tang in Hola w Slot wihin Ad
"B" 011 RING MIL GArs
"C" 1ND COMPRESSION RIM GAB
"DM TOP COAarRESSlON RING GAP
Figure 6A2-30 Ring Gap Locations I
I
Installation I
Cylinder bores must be clean before piston
installation. This may be accomplished with a hot
water and detergent wash or with a light honing as
necessary. After cleaning, the bores should be swabbed
several times with light engine oil and a clean dry cloth.
1. Lubricate connecting rod bearings and install in
rods and rod caps.
2. Lightly coat pistons, rings and cylinder walls
with light engine oil.
3. With bearing caps removed, install guide hose
over connecting rod bolts. These guide hoses
protect the
crankpin journal from damage during
installation of connecting rod and piston
assembly.
Page 381 of 1825

6A3-2 V-8 ENGINE
VALVE TRAIN
A very simple ball pivot-type train is used.
Motion is transmitted from the camshaft through the
hydraulic lifter and push rod to the rocker arm. The
rocker arm pivots on its ball and transmits the
camshaft motion to the valve. The rocker-arm ball is
retained by a nut.
HYDRAULIC VALVE LIFTERS
Hydraulic Valve Lifters are used to keep all parts
of the valve train in constant contact.
The hydraulic lifter assembly consists of: a roller,
the lifter body, which rides in the cylinder block boss,
a plunger, a push rod seat, a metering valve, a plunger
spring, a check ball and spring, a check ball retainer
and a push rod seat retainer.
When the lifter is riding on the low point of the
cam, the plunger spring keeps the plunger and push rod
seat in contact with the push rod.
When the lifter body begins to ride up the cam
lobe, the check ball cuts off the transfer of oil from the
reservoir below the plunger. The plunger and lifter
body then rise as a unit, pushing up the push rod and
opening the valve.
As the lifter body rides down the other side of the
cam, the plunger follows with it until the valve closes.
The lifter body continues to follow the cam to its low
point, but the plunger spring keeps the plunger in
contact with the push rod. The ball check valve will then
move off its seat and the lifter reservoir will
remain full.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold for those engines with
carburetors are made of cast iron or aluminum double
level design for efficient fuel distribution. An Exhaust
Gas Recirculation (EGR) port is also cast into the
manifold for the mixture of exhaust gases with the fuel
air mixture.
The intake manifold for those vehicles equipped
with
PFI is a cast aluminum unit. It centrally supports
a fuel rail with
8 fuel injectors.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS
Two cast iron exhaust manifolds are used to
direct exhaust gases from the combustion chambers to
the exhaust system. The left hand side manifold
receives a heat shield that is used to route heated air
to the air cleaner. for better fuel vaporization during
warm-up.
COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
Combustion Chambers are cast to insure uniform
shape for all cylinders. Spark plugs are located between
the intake and exhaust valves. The contoured wedge
shape of the combustion chamber minimizes the
possibility of detonation, facilitates breathing and
provides swirling turbulence for smooth, complete
combustion.
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Full pressure lubrication through a full flow oil through drilled passages, to the camshaft and
filter, is furnished by a gear-type oil pump. The crankshaft to lubricate the bearings. The valve lifter oil
distributor, driven by a helical gear on the camshaft,
gallery feeds the valve lifters which, through hollow
drives the oil pump. The main oil gallery feeds oil,
push rods, feed the individually mounted rocker arms.
Page 391 of 1825
6A3-12 V-8 ENGINE
Fig. 6A3-15 Cylinder Head
2. Remove generator lower mounting bolt and lay
unit aside.
3. Remove exhaust manifolds as previously
outlined.
4. Remove rocker arm covers as previously
outlined.
5. Remove valve mechanism as previously outlined.
6. Drain cylinder block of coolant.
7. Remove diverter valve.
8. Remove cylinder head bolts, cylinder head and
gasket. Place cylinder head on two blocks of
wood to prevent damage.
Disassembly
1. With cylinder head removed, remove valve
rocker arm nuts, balls and rocker arms (if not
previously done).
2. Using Tool
5-8062, compress the valve springs
(fig.
6A3-16) and remove valve keys. Release the
compressor tool and remove rotators or spring caps, oil shedders,
springs and spring damper,
then remove oil seals and valve spring shims.
3. Remove valves from cylinder head and place
them in a rack in their proper sequence so that
they can be assembled in their original positions.
Cleaning I
1. Clean all carbon from combustion chambers and
valve ports using Tool J-8089 (fig.
6A3-17).
2. Thoroughly clean the valve guides using Tool
5-8101.
3. Clean
all carbon and sludge from push rods,
rocker arms and push rod guides.
4. Clean valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel.
5. Clean carbon deposits from head gasket mating
surface.
Inspection I
1. Inspect
the cylinder head for cracks in the
exhaust ports, combustion chambers, or external
cracks to the water chamber.
2. Inspect the valves for burned heads, cracked faces
or damaged stems.
e Excessive valve stem to bore clearance will
cause excessive oil consumption and may
cause valve breakage. Insufficient clearance
will result in noisy and sticky functioning of
the valve and disturb engine smoothness.
3. Measure valve stem clearance (Fig. 6A3-19) as
follows:
a. Clamp a dial indicator
on one side of the
cylinder head rocker arm cover gasket rail.
b. Locate
the indicator so that movement of
the valve stem from side to side (crosswise
to the head) will cause a direct movement
of the indicator stem. The indicator stem
must contact the side of the valve stem just
above the valve guide.
c. Drop
the valve head about 1/16"
(1.6mm)
off the valve seat.
d. Move the stem of the valve from side to side
using light pressure to obtain a clearance
Page 397 of 1825
6A3-18 V-8 ENGINE
bore, remove remover and installer tool and
bearing from puller screw.
5. Remove remaining bearings (except front and
rear) in the same manner. It will be necessary to
index pilot in camshaft rear bearing to remove the
rear intermediate bearing.
6. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and remove camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
lnstallation
The camshaft front and rear bearings should be
installed first. These bearings will act as guides for the
pilot and center the remaining bearings being pulled
into place.
1. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and install camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
2. Using Tool Set J-6098, with nut then thrust
washer installed to end of threads, index pilot in
camshaft front bearing and install puller screw
through pilot.
3. Index camshaft bearing in bore (with oil hole
aligned as outlined below), then install remover
and installer tool on puller screw with shoulder
toward bearing.
e Number one cam bearing oil hole must be
positioned so that oil holes are equidistant
from 6 o'clock position.
e Number two through number four bearing
oil holes must be positioned at 5 o'clock
position (toward left side of engine and at a
position even with bottom of cylinder bore).
e Number five bearing oil hole must be in 12
o'clock position.
4. Using two wrenches, hold puller screw while
turning nut. After bearing has been pulled into
bore, remove the remover and installer tool from
puller screw and check alignment of oil hole in
camshaft bearing.
5. Install remaining bearings in the same manner. It
will be necessary to index pilot in the camshaft
rear bearing to install the rear intermediate
bearing.
6. Coat new camshaft rear plug O.D. with
# 1052080 sealant, or equivalent, and install
flush to 1/32"
(.80mm) deep.
OIL PAN
Removal
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Remove fan shroud.
3. Remove air cleaner and lay aside if equipped.
4. Remove distributor cap and lay aside.
5. Raise vehicle.
6. Drain crankcase.
7. Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
8. Disconnect AIR pipe clamp.
9. Disconnect converter hanger bolts and allow
exhaust to hang down.
GASKET
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE 10 LBS.
1 REINFORCEMENT
MINIMUM AT 500 RPM AND 30-55
1 OIL PAN
LBS. AT 2000 RPM.
161 RETAINER
OIL FILTER BY-PASS VALVE STUD
(LB9, L98)
OPERATES
AT 9- TO 11 LBS. STUD (L98)
PRESSURE.
OIL PUMP
Fig. 6A3-32 Oil Pan
10. Remove front starter brace.
11. Remove starter bolts and let starter hang.
12. On vehicles equipped with manual transmission,
it may be necessary to remove the oil filter in
order to remove the inspection cover.
13. Remove inspection cover.
14. Remove engine mount through bolts.
15. Remove oil pan bolts.
16. Raise engine.
17. Rotate crankshaft to position throws so as not to
block pan removal.
18. Remove oil pan.
lnstallation
1.
Clean sealing surfaces on cylinder case and oil
pan.
2. Check oil pan gasket for damage and replace if
necessary.
3. Apply a small amount of 1052751, or equivalent,
to front and rear corners of oil pan.
NOTICE: Only a small amount of sealant is
required. Excessive amounts of sealant may cause
a problem with proper sealing of oil pan.
4. Reverse removal procedures.
OIL PUMP
Removal
1. Remove oil pan as previously outlined.
2. Remove pump to rear main bearing cap bolt and
remove pump and extension shaft.
Disassembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. Remove the pump cover attaching screws and the
pump cover.
Page 398 of 1825
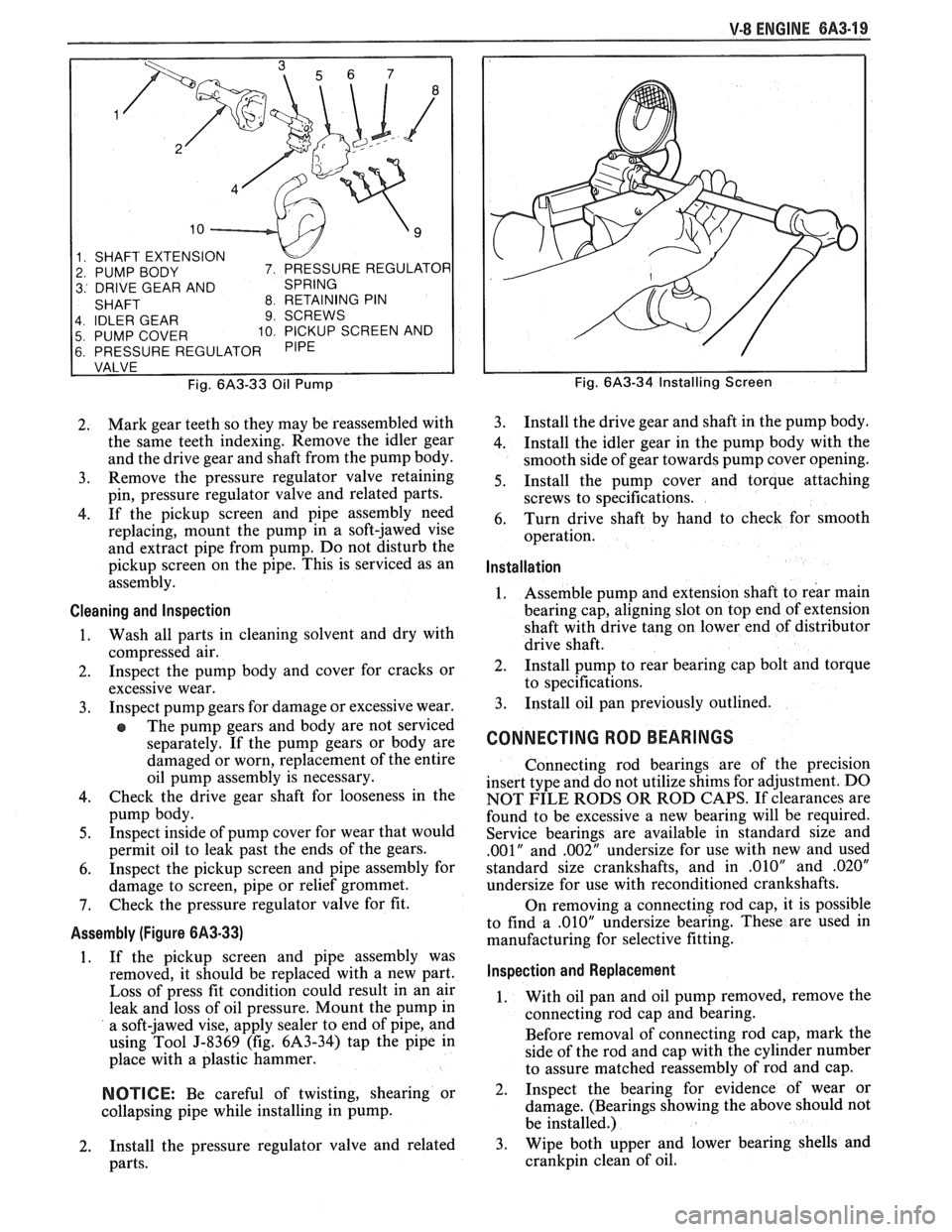
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-19
1 SHAFT EXTENSION
2 PUMP BODY
3 DRIVE GEAR AND
4 IDLER GEAR
9 SCREWS
5 PUMP COVER 10 PICKUP SCREEN AND
6 PRESSURE REGULATOR
Fig.
6A3-33 Oil Pump
2. Mark
gear teeth so they may be reassembled with
the same teeth indexing. Remove the idler gear
and the drive gear and shaft from the pump body.
3. Remove
the pressure regulator valve retaining
pin, pressure regulator valve and related parts.
4. If the pickup screen and pipe assembly need
replacing, mount the pump in a soft-jawed vise
and extract pipe from pump. Do not disturb the
pickup screen on the pipe. This is serviced as an
assembly.
Cleaning and lnspection
1. Wash all parts in cleaning solvent and dry with
compressed air.
2. Inspect the pump body and cover for cracks or
excessive wear.
3. Inspect
pump gears for damage or excessive wear.
The pump gears and body are not serviced
separately. If the pump gears or body are
damaged or worn, replacement of the entire
oil pump assembly is necessary.
4. Check the drive gear shaft for looseness in the
pump body.
5. Inspect inside of pump cover for wear that would
permit oil to leak past the ends of the gears.
6. Inspect the pickup screen and pipe assembly for
damage to screen, pipe or relief grommet.
7. Check the pressure regulator valve for fit.
Assembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. If
the pickup screen and pipe assembly was
removed, it should be replaced with a new part.
Loss of press fit condition could result in an air
leak and loss of oil pressure. Mount the pump in
a soft-jawed vise, apply sealer to end of pipe, and
using Tool J-8369 (fig. 6A3-34) tap the pipe in
place with a plastic hammer.
NOTICE: Be careful of twisting, shearing or
collapsing pipe while installing in pump.
2. Install the
pressure regulator valve and related
parts.
Fig. 6A3-34 Installing Screen
3. Install the drive gear and shaft in the pump body.
4. Install
the idler gear in the pump body with the
smooth side of gear towards pump cover opening.
5. Install the pump cover and torque attaching
screws to specifications.
6. Turn
drive shaft by hand to check for smooth
operation.
Installation
1. Assemble
pump and extension shaft to rear main
bearing cap, aligning slot on top end of extension
shaft with drive tang on lower end of distributor
drive shaft.
2. Install
pump to rear bearing cap bolt and torque
to specifications.
3. Install
oil pan previously outlined.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
Connecting rod bearings are of the precision
insert type and do not utilize shims for adjustment. DO
NOT FILE RODS OR ROD CAPS. If clearances are
found to be excessive a new bearing will be required.
Service bearings are available in standard size and
.001" and ,002" undersize for use with new and used
standard size crankshafts, and in
.010" and .020"
undersize for use with reconditioned crankshafts.
On removing a connecting rod cap, it is possible
to find a
.010" undersize bearing. These are used in
manufacturing for selective fitting.
lnspection and Replacement
1. With
oil pan and oil pump removed, remove the
connecting rod cap and bearing.
Before removal of connecting rod cap, mark the
side of the rod and cap with the cylinder number
to assure matched reassembly of rod and cap.
2. Inspect
the bearing for evidence of wear or
damage. (Bearings showing the above should not
be installed.)
3. Wipe both upper and lower bearing shells and
crankpin clean of oil.
Page 404 of 1825
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-25
Assembly
1. Lubricate piston pin holes in piston and
connecting rod to facilitate installation of pin.
2. Place connecting rod in piston and hold in place
with piston pin guide and piston pin. Place
assembly on fixture and support assembly.
3. Using piston pin installer, 5-24086-9, press the
piston pin into the piston and connecting rod (Fig.
6A3-46).
NOTICE: After installer hub bottoms on support
assembly, do not exceed
5000 psi pressure, as this
could cause structural damage to the tool.
4. Remove piston
and connecting rod assembly
from tool and check piston for freedom of
movement on piston pin.
Piston Rings
All compression rings are marked on the upper
side of the ring. When installing compression rings,
make sure the MARKED SIDE IS TOWARD THE
TOP
OF THE PISTON. The top ring is chrome faced,
or treated with molybdenum for maximum life. The
second compression ring is a tapered face acting as
both a compression and oil control ring.
The oil control rings are of three piece type,
consisting of two segments (rails) and a spacer.
Fig. 6A3-47 Measuring Ring Gap
1. Select rings comparable in size to the piston being
used.
2. Slip the compression ring in the cylinder bore;
then press the ring down into the cylinder bore
about
1/4" (6.5mm) (above ring travel). Be sure
ring is square with cylinder wall.
3. Measure the space or gap between the ends of the
ring with a feeler gage (Fig.
6A3-47).
4. If the gap between the ends of the ring is below
specifications, remove the ring and try another
for fit.
5. Fit each compression ring to the cylinder in
which it is going to be used.
6. If the pistons have not been cleaned and inspected
as previously outlined, do so.
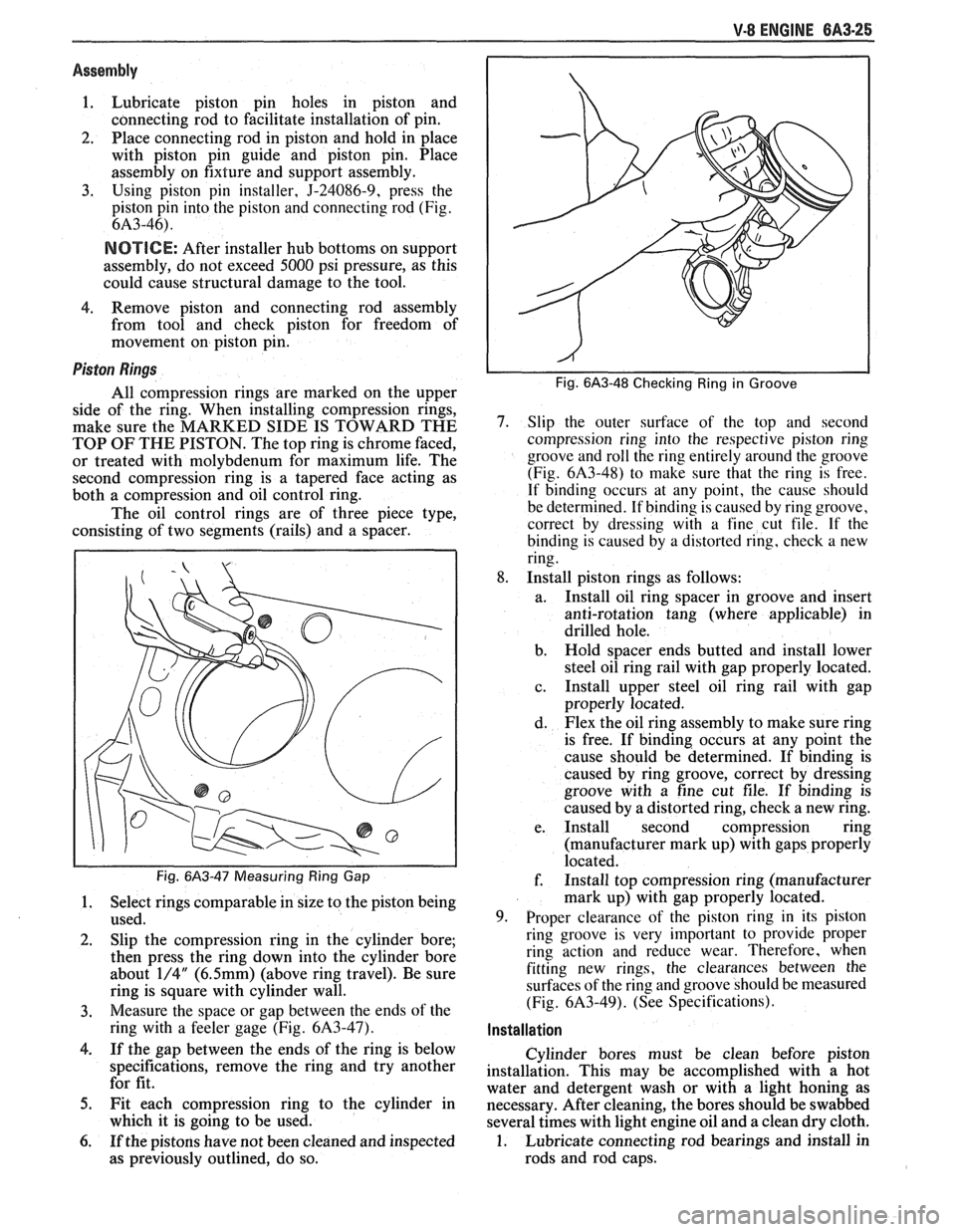
Fig. 6A3-48 Checking Ring in Groove
7. Slip the outer surface of the top and second
compression ring into the respective piston ring
groove and roll the ring entirely around the groove
(Fig.
6A3-48) to make sure that the ring is free.
If binding occurs at any point, the cause should
be determined. If binding is caused by ring groove,
correct by dressing with a fine cut file. If
the
binding is caused by a distorted ring, check a new
ring.
8. Install piston rings as follows:
a. Install oil ring spacer in groove and insert
anti-rotation tang (where applicable) in
drilled hole.
b. Hold spacer ends butted and install lower
steel oil ring rail with gap properly located.
c. Install
upper steel oil ring rail with gap
properly located.
d. Flex the oil ring assembly to make sure ring
is free. If binding occurs at any point the
cause should be determined. If binding is
caused by ring groove, correct by dressing
groove with a fine cut file. If binding is
caused by a distorted ring, check a new ring.
e. Install second compression ring
(manufacturer mark up) with gaps properly
located.
f. Install top compression ring (manufacturer
mark up) with gap properly located.
9. Proper clearance of the piston ring in its piston
ring groove is very important to provide proper
ring action and reduce wear. Therefore, when
fitting new rings, the clearances between the
surfaces of the ring and groove should be measured
(Fig.
6A3-49). (See Specifications).
Installation
Cylinder bores must be clean before piston
installation. This may be accomplished with a hot
water and detergent wash or with a light honing as
necessary. After cleaning, the bores should be swabbed
several times with light engine oil and a clean dry cloth.
1. Lubricate connecting rod bearings and install in
rods and rod caps.