1988 OPEL VECTRA engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 12 of 525

Refitting
6On refitting the filter, press it into the union
until it catches (see illustration). The
remainder of the reassembly procedure is the
reverse of removal.
22Throttle valve dashpot
(automatic models) -
adjustment
2
1Remove the air cleaner or air box, refer to
Section 3.
2Ensure that the lever (see illustration)is in
the idling position.
3Slacken the locknut and unscrew the
dashpot until a gap of 0.05 mm (0.002 in)
exists between the lever and the dashpot tip.
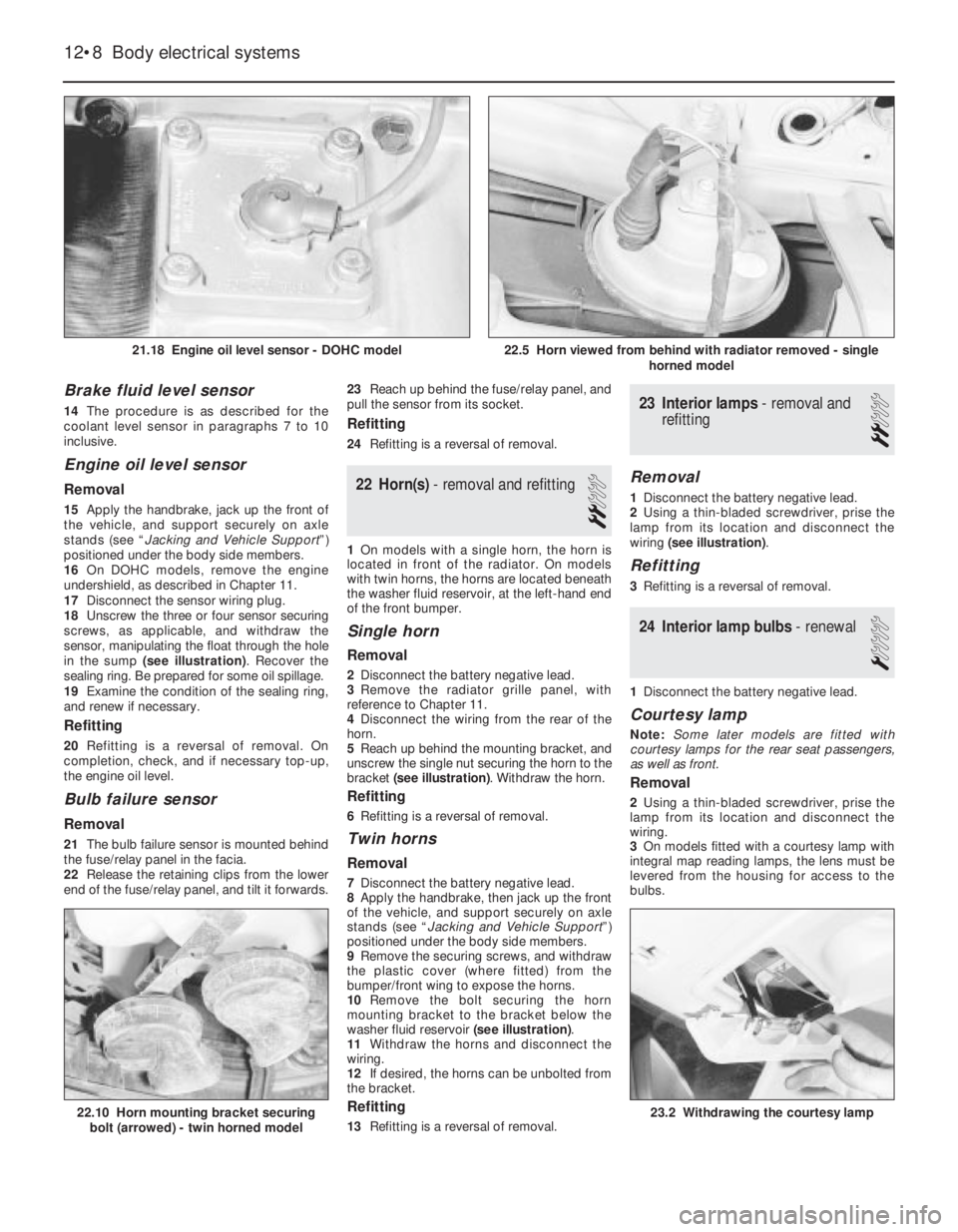
Then screw the dashpot downwards 2.5 full
turns and tighten the locknut.
4Refit all removed components.
23Throttle position sensor
(automatic transmission
models) - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery earth lead.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor.
3Either unscrew the two securing screws
and withdraw the sensor from its bracket, or
unbolt the bracket.
Refitting
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points.
a)Install the sensor when the throttle valve
is fully closed and ensure that the
adapter, “1” (see illustration),seats
correctly on the throttle valve spindle.
b)Tighten the screws carefully.
24Idle speed increase valve -
testing
2
1Certain models are fitted with an idle speed
increase valve that is attached to the side of
the carburettor.
2To test the operation of this valve first
remove the air filter and vacuum hose.
3With the valve’s plug connected, have
someone turn the ignition on (but do not start
the engine). A mechanical shifting noise
should be heard. If not replace the unit.
4After refitting replace the vacuum hose and
air filter.
25Idle cut-off solenoid (1.8 litre
models) - description and
testing
2
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Description
1On 1.8 litre models, the carburettor is fitted
with an idle cut-off solenoid. This is an
electrically operated valve, which interrupts
the idle mixture circuit when the ignition isswitched off, thus preventing the engine from
running-on (see illustration).
2The idle cut-off solenoid is energised all the
time that the ignition is switched on. A
defective solenoid, or a break in its power
supply, will cause the engine to stall or idle
roughly, although it will run normally at speed.
Testing
3If the operation of the solenoid is suspect,
first check that battery voltage is present at
the solenoid terminal when the ignition is
switched on. Use a 12 volt test lamp or similar
test device.
4If no voltage is present, then the fault lies in
the wiring to the solenoid. If voltage is
present, the solenoid can be tested as
follows.
5With the solenoid unscrewed from the
carburettor, connect the body of the solenoid
to the negative terminal of a 12 volt battery.
When the battery positive terminal is
connected to the solenoid centre terminal,
there should be an audible click, and the
needle at the tip of the solenoid should
retract.
6A defective idle cut-off solenoid must be
renewed.
26Inlet manifold - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding. A
new manifold gasket must be used on refitting
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
3Proceed as described in Section 13,
paragraphs 2 to 7 inclusive, ignoring the
reference to coolant spillage in paragraph 5.
4A•12Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
21.6 Refitting the carburettor fuel filter
23.4 Throttle position sensor - models with automatic
transmission
1 Adapter 2 Sensor22.2 Adjusting the throttle valve dashpot - models with
automatic transmission
1 Lever2 Locknut3 Dashpot
Page 13 of 525

4Disconnect the coolant hose from the rear
of the manifold (see illustration).
5Where applicable, disconnect the camshaft
cover breather hose from the rear of the
manifold (see illustration).
6Unscrew the union and disconnect the
brake servo vacuum hose from the manifold.
7On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect the
wiring from the temperature gauge sender.
8Unscrew and remove the top alternator
mounting nut and bolt.
9On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect and
remove the stub hose that connects the
crankcase breather tube to the rear of the
camshaft housing.
10Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
11Unscrew the securing nuts, and withdraw
the manifold from the cylinder head (see
illustration). Note the position of the rear
engine lifting bracket, which is secured by one
of the manifold nuts, and recover the manifoldgasket.
12It is possible that some of the manifold
studs may be unscrewed from the cylinder
head when the manifold securing nuts are
unscrewed. In this event, the studs should be
screwed back into the cylinder head once the
manifold has been removed, using two
manifold nuts locked together.
13If desired, the carburettor can be removed
from the manifold, referring to Section 13, if
necessary.
Refitting
14Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
15If the carburettor has been removed from
the manifold, refit it, using a new gasket.
16If the alternator mounting bracket has
been unbolted from the manifold, refit it
before refitting the manifold, as access to the
securing bolt is extremely limited once the
manifold is in place.
17Refit the manifold using a new gasket,and ensure that the engine lifting bracket is in
place under the relevant manifold nut. Tighten
the nuts to the specified torque.
18Ensure that all relevant hoses, pipes and
wires are correctly reconnected.
19Refill the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
20Check the throttle cable free play and
adjust if necessary, as described in Section
11.
21If the carburettor has been disturbed,
check and if necessary adjust the idle speed
and mixture, as described in Section 14.
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models 4A•13
26.5 . . .and the camshaft cover breather
hose (arrowed) from the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.11 Withdrawing the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.4 Disconnecting the coolant hose . . .
4A
25.1 Carburettor idle cut-off solenoid
(arrowed) - 1.8 litre models
Page 16 of 525

1General information and
precautions
The electrical system is of 12-volt negative
earth type. Power for the lights and all
electrical accessories is supplied by a
lead/acid type battery, which is charged by
the alternator.
This Chapter covers repair and service
procedures for the various electrical
components not associated with engine.
Information on the battery, alternator and
starter motor can be found in Chapter 5.
It should be noted that, before working on
any component in the electrical system, the
battery negative terminal should first be
disconnected, to prevent the possibility of
electrical short-circuits and/or fires.
Whenever the occasion arises, carefully
check the routing of the wiring harness,
ensuring that it is correctly secured by the
clips or ties provided so that it cannot chafe
against other components. Carefully check
points such as the clutch cable bracket,
clutch housing and harness support bracket,
the inlet manifold, the horn mounting bracket,
the starter motor terminals, and the rear
bumper and number plate lamp.
If evidence is found of the harness having
chafed against other components, repair the
damage and ensure that the harness is
secured or protected so that the problem
cannot occur again.
2Electrical fault-finding -
general information
Note:Refer to the precautions given in “Safety
first!” (at the beginning of this manual) and to
Section 1 of this Chapter before starting work.
The following tests relate to testing of the main
electrical circuits, and should not be used to
test delicate electronic circuits (such as anti-
lock braking systems), particularly where an
electronic control module is used.
A typical electrical circuit consists of an
electrical component, any switches, relays,
motors, fuses, fusible links or circuit breakers
related to that component, and the wiring and
connectors that link the component to boththe battery and the chassis. To help to
pinpoint a problem in an electrical circuit,
wiring diagrams are included at the end of this
Chapter.
Before attempting to diagnose an electrical
fault, first study the appropriate wiring
diagram, to obtain a complete understanding
of the components included in the particular
circuit concerned. The possible sources of a
fault can be narrowed down by noting
whether other components related to the
circuit are operating properly. If several
components or circuits fail at one time, the
problem is likely to be related to a shared fuse
or earth connection.
Electrical problems usually stem from
simple causes, such as loose or corroded
connections, a faulty earth connection, a
blown fuse, a melted fusible link, or a faulty
relay (refer to Section 3 for details of testing
relays). Visually inspect the condition of all
fuses, wires and connections in a problem
circuit before testing the components. Use
the wiring diagrams to determine which
terminal connections will need to be checked,
to pinpoint the trouble-spot.
The basic tools required for electrical fault-
finding include the following:
a)a circuit tester or voltmeter (a 12-volt bulb
with a set of test leads can also be used
for certain tests).
b)a self-powered test light (sometimes
known as a continuity tester).
c)an ohmmeter (to measure resistance).
d)a battery.
e)a set of test leads.
f)a jumper wire, preferably with a circuit
breaker or fuse incorporated, which can
be used to bypass suspect wires or
electrical components.
Before attempting to locate a problem with
test instruments, use the wiring diagram to
determine where to make the connections.
To find the source of an intermittent wiring
fault (usually due to a poor or dirty
connection, or damaged wiring insulation), a
“wiggle” test can be performed on the wiring.
This involves wiggling the wiring by hand, to
see if the fault occurs as the wiring is moved.
It should be possible to narrow down the
source of the fault to a particular section of
wiring. This method of testing can be used in
conjunction with any of the tests described in
the following sub-Sections.
Apart from problems due to poor
connections, two basic types of fault can
occur in an electrical circuit - open-circuit, or
short-circuit.
Open-circuit faults are caused by a break
somewhere in the circuit, which prevents
current from flowing. An open-circuit fault will
prevent a component from working, but will
not cause the relevant circuit fuse to blow.
Short-circuit faults are caused by a “short”
somewhere in the circuit, which allows the
current flowing in the circuit to “escape” along
an alternative route, usually to earth. Short-
circuit faults are normally caused by abreakdown in wiring insulation, which allows a
feed wire to touch either another wire, or an
earthed component such as the bodyshell. A
short-circuit fault will normally cause the
relevant circuit fuse to blow.
Finding an open-circuit
To check for an open-circuit, connect one
lead of a circuit tester or voltmeter to either
the negative battery terminal or a known good
earth.
Connect the other lead to a connector in
the circuit being tested, preferably nearest to
the battery or fuse.
Switch on the circuit, remembering that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
If voltage is present (indicated either by the
tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading, as
applicable), this means that the section of the
circuit between the relevant connector and
the battery is problem-free.
Continue to check the remainder of the
circuit in the same fashion.
When a point is reached at which no
voltage is present, the problem must lie
between that point and the previous test point
with voltage. Most problems can be traced to
a broken, corroded or loose connection.
Finding a short-circuit
To check for a short-circuit, first disconnect
the load(s) from the circuit (loads are the
components that draw current from a circuit,
such as bulbs, motors, heating elements, etc.).
Remove the relevant fuse from the circuit,
and connect a circuit tester or voltmeter to the
fuse connections.
Switch on the circuit, remembering that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
If voltage is present (indicated either by the
tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading, as
applicable), this means that there is a short-
circuit.
If no voltage is present, but the fuse still
blows with the load(s) connected, this indicates
an internal fault in the load(s).
Finding an earth fault
The battery negative terminal is connected
to “earth” (the metal of the
engine/transmission and the car body), and
most systems are wired so that they only
receive a positive feed. The current returning
through the metal of the car body. This means
that the component mounting and the body
form part of that circuit. Loose or corroded
mountings can therefore cause a range of
electrical faults, ranging from total failure of a
circuit, to a puzzling partial fault. In particular,
lights may shine dimly (especially when
another circuit sharing the same earth point is
in operation). Motors (e.g. wiper motors or the
radiator cooling fan motor) may run slowly,
and the operation of one circuit may have an
affect on another. Note that on many vehicles,
earth straps are used between certain
components, such as the engine/transmission
and the body, usually where there is no metal-
12•2Body electrical systems
Warning: Before carrying out
any work on the electrical
system, read through the
precautions given in “Safety
first!” at the beginning of this manual, and
in Chapter 5.
Caution:If the radio/cassette player fitted
to the vehicle is one with an anti-theft
security code, as the standard unit is, refer
to “Radio/cassette player anti-theft system
- precaution”in the Reference Section of
this manual before disconnecting the
battery.
Page 17 of 525

to-metal contact between components, due
to flexible rubber mountings, etc.
To check whether a component is properly
earthed, disconnect the battery, and connect
one lead of an ohmmeter to a known good
earth point. Connect the other lead to the wire
or earth connection being tested. The
resistance reading should be zero; if not,
check the connection as follows.
If an earth connection is thought to be
faulty, dismantle the connection, and clean
back to bare metal both the bodyshell and the
wire terminal or the component earth
connection mating surface. Be careful to
remove all traces of dirt and corrosion, then
use a knife to trim away any paint, so that a
clean metal-to-metal joint is made. On
reassembly, tighten the joint fasteners
securely; if a wire terminal is being refitted,
use serrated washers between the terminal
and the bodyshell, to ensure a clean and
secure connection. When the connection is
remade, prevent the onset of corrosion in the
future by applying a coat of petroleum jelly or
silicone-based grease.
3Fuses and relays - general
Fuses
1Fuses are designed to break a circuit when
a predetermined current is reached, to protect
the components and wiring which could be
damaged by excessive current flow. Any
excessive current flow will be due to a fault in
the circuit, usually a short-circuit (Section 2).
2The main fuses and relays are located in a
panel at the lower right-hand side of the facia,
under a hinged cover (see illustration).
3The circuits protected by the various fuses
and relays are marked on the inside of the
panel cover.
4A blown fuse can be recognised from its
melted or broken wire.
5To remove a fuse, first ensure that the
relevant circuit is switched off. Then open the
cover and pull the relevant fuse or relay from the
panel (see illustration). If desired, the lower
end of the panel can be tilted forwards, after
releasing the retaining clips to improve access. 6Before renewing a blown fuse, trace and
rectify the cause, and always use a fuse of the
correct rating. Never substitute a fuse of a
higher rating, or make temporary repairs using
wire or metal foil, as more serious damage or
even fire could result.
7Spare fuses are provided in the blank
terminal positions in the fusebox.
8Note that the fuses are colour-coded, see
Specifications. Refer to the wiring diagrams
for details of the fuse ratings and the circuits
protected.
Relays
9A relay is an electrically operated switch,
which is used for the following reasons:
a)A relay can switch a heavy current
remotely from the circuit in which the
current is flowing, allowing the use of
lighter-gauge wiring and switch contacts.
b)A relay can receive more than one control
input, unlike a mechanical switch.
c)A relay can have a timer function - for
example, the intermittent wiper relay.
10Most of the relays are located at the rear
of the main fusebox (remove the securing
screws and pull the fusebox forwards to
improve access). The rear wiper motor relay is
located in the tailgate, behind the tailgate trim
panel. On some models, additional engine-
related relays are located in the relay box
mounted on the left-hand side of the engine
compartment.
11On certain models, additional relays are
located in a box at the left-hand rear of the
engine compartment (see illustration).
12If a circuit or system controlled by a relay
develops a fault, and the relay is suspect,
operate the system. If the relay is functioning, it
should be possible to hear it “click” as it is
energised. If this is the case, the fault lies with
the components or wiring of the system. If the
relay is not being energised, then either the
relay is not receiving a main supply or a
switching voltage, or the relay itself is faulty.
Testing is by the substitution of a known good
unit, but be careful - while some relays are
identical in appearance and in operation, others
look similar but perform different functions.
13To remove a relay, first ensure that the
relevant circuit is switched off. The relay can
then simply be pulled out from the socket,
and pushed back into position.
4Ignition switch and lock
cylinder - removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Turn the steering wheel as necessary to
expose the two front steering column shroud
securing screws, which are covered by plastic
caps. Prise out the caps and remove the
screws.
3Remove the three securing screws from the
underside of the lower column shroud, then
remove both the upper and lower shrouds.
4To remove the lock cylinder, insert the
ignition key and turn it to position “II”.
5Insert a thin rod into the hole in the lock
housing, then press the rod to release the
detent spring, and pull out the lock cylinder
using the key.
6The ignition switch is secured to the
steering lock housing by two grub screws.
Disconnect the wiring plug, and remove the
screws to extract the switch (see illustration).
Removal of the steering wheel, may aid
removal. Refer to Chapter 10 or Section 57, as
applicable. It is recommended that the switch
and the lock cylinder are not both removed at
the same time, so that their mutual alignment
is not lost.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Body electrical systems 12•3
3.11 Relays in engine compartment box -
2.0 litre SRi model shown
4.6 Removing an ignition switch securing
screw
3.5 Removing a fuse -
2.0 litre model shown3.2 Main fuses and relays in facia panel -
2.0 litre SRi model shown
12
Page 19 of 525

8Electric door mirror switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise the plastic surround from the door
interior handle.
3Free the trim panel from the top edge of the
door by releasing the securing clips. This can
be done using a screwdriver, but it is
preferable to use a forked tool, to minimise
the possibility of damage to the trim panel and
the clips.
4Note the position of the mirror switch wiring
connector in the bracket at the top of the
door, then separate the two halves of the
connector.
5Prise the switch from the door trim panel,
and feed the wiring through the panel.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the wiring is correctly routed, so as not to
foul the door interior handle mechanism.
9Sunroof operating switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise the courtesy lamp from the roof trim
panel, and disconnect the wiring.
3Remove the two trim panel securing
screws, and withdraw the trim panel from the
roof, disconnecting the wiring from the
sunroof operating switch.
4Release the securing clips, then pull the
switch from the rear face of the trim panel.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
10Courtesy lamp switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Open the door and remove the switch
securing screw.
3Withdraw the switch from the door pillar,
and pull the wiring out sufficiently to prevent it
from springing back into the pillar.4Disconnect the wiring and remove the
switch.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
11Luggage compartment lamp
switch - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Open the boot lid or tailgate, as applicable,
and remove the switch securing screw.
3Withdraw the switch from the body panel,
and pull the wiring out sufficiently to prevent it
from springing back into the body.
4Disconnect the wiring and remove the
switch.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
12Brake lamp switch - removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the lower trim panel from the
driver’s footwell.
3Disconnect the wiring plug from the brake
lamp switch, then twist the switch
anti-clockwise and remove it from its bracket.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
13Handbrake “on” warning
lamp switch - removal and
refitting
3
For access to the switch, the handbrake
lever must be removed. Removal and refitting
of the switch is described as part of the
handbrake lever removal and refitting
procedure, in Chapter 9.
14Oil pressure warning lamp
switch - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2The switch is screwed into the oil pump, on
the inlet manifold side of the engine. On 1.4
and 1.6 litre (except C16 NZ2), models the
switch projects at right-angles to the
crankshaft axis, while on C16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models it is parallel to the crankshaft
(see illustration).
3In most cases the switch can be reached
quite easily from above. However, on some
models access will be easier if the front of the
vehicle is jacked up and supported on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
(ensure that the handbrake is securely
applied) and the front right-hand roadwheel is
removed.
4Disconnect the switch wire and use a
spanner to unscrew the switch (see
illustration). As you withdraw the switch,
swiftly plug the hole in the oil pump to
minimise the loss of oil and to prevent the
entry of dirt.
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; tighten the switch securely but do
not overtighten it, reconnect its wire, then
check and if necessary top-up the oil level, as
described in Chapter 1. Wash off any spilt oil
and check for leaks when the engine is
restarted.
15Cigarette lighter - removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Slide the ashtray/cigarette lighter assembly
from the facia, then disconnect the wiring and
slide the illumination bulb from the cigarette
lighter.
Body electrical systems 12•5
14.4 Unscrewing the oil pressure warning
lamp switch -
SOHC model (engine removed)14.2 Oil pressure warning lamp switch
(arrowed) viewed from underneath vehicle
- SOHC model
12
Tape the wiring to the door
pillar, to prevent if falling
back into the door pillar.
Alternatively, tie a piece of
string to the wiring to retrieve it.
Page 22 of 525
Brake fluid level sensor
14The procedure is as described for the
coolant level sensor in paragraphs 7 to 10
inclusive.
Engine oil level sensor
Removal
15Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
16On DOHC models, remove the engine
undershield, as described in Chapter 11.
17Disconnect the sensor wiring plug.
18Unscrew the three or four sensor securing
screws, as applicable, and withdraw the
sensor, manipulating the float through the hole
in the sump (see illustration). Recover the
sealing ring. Be prepared for some oil spillage.
19Examine the condition of the sealing ring,
and renew if necessary.
Refitting
20Refitting is a reversal of removal. On
completion, check, and if necessary top-up,
the engine oil level.
Bulb failure sensor
Removal
21The bulb failure sensor is mounted behind
the fuse/relay panel in the facia.
22Release the retaining clips from the lower
end of the fuse/relay panel, and tilt it forwards.23Reach up behind the fuse/relay panel, and
pull the sensor from its socket.
Refitting
24Refitting is a reversal of removal.
22Horn(s) - removal and refitting
2
1On models with a single horn, the horn is
located in front of the radiator. On models
with twin horns, the horns are located beneath
the washer fluid reservoir, at the left-hand end
of the front bumper.
Single horn
Removal
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the radiator grille panel, with
reference to Chapter 11.
4Disconnect the wiring from the rear of the
horn.
5Reach up behind the mounting bracket, and
unscrew the single nut securing the horn to the
bracket (see illustration). Withdraw the horn.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Twin horns
Removal
7Disconnect the battery negative lead.
8Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
9Remove the securing screws, and withdraw
the plastic cover (where fitted) from the
bumper/front wing to expose the horns.
10Remove the bolt securing the horn
mounting bracket to the bracket below the
washer fluid reservoir (see illustration).
11Withdraw the horns and disconnect the
wiring.
12If desired, the horns can be unbolted from
the bracket.
Refitting
13Refitting is a reversal of removal.
23Interior lamps - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, prise the
lamp from its location and disconnect the
wiring (see illustration).
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
24Interior lamp bulbs - renewal
1
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Courtesy lamp
Note: Some later models are fitted with
courtesy lamps for the rear seat passengers,
as well as front.
Removal
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, prise the
lamp from its location and disconnect the
wiring.
3On models fitted with a courtesy lamp with
integral map reading lamps, the lens must be
levered from the housing for access to the
bulbs.
12•8Body electrical systems
21.18 Engine oil level sensor - DOHC model
22.10 Horn mounting bracket securing
bolt (arrowed) - twin horned model23.2 Withdrawing the courtesy lamp
22.5 Horn viewed from behind with radiator removed - single
horned model
Page 24 of 525

27Headlamps -alignment
2
1Correct alignment of the headlamp beams
is most important, not only to ensure good
vision for the driver, but also to protect other
drivers from being dazzled.
2Accurate alignment should be carried out
using optical beam setting equipment.
3In an emergency, adjustments may be
made by turning the adjustment screws
shown (see illustrations). If an adjustment is
made, the alignment should be checked using
beam setting equipment at the earliest
opportunity.
4All 1992-on models are fitted with the
headlamp aim adjustment system, operated
through the facia-mounted switch (see
illustration).
a)Position ‘0’, is for correct alignment if just
the driving seat is occupied.
b)Position ‘1’, if all seats are occupied.
c)Position ‘2’, if all seats occupied and
luggage.
d)Position ‘3’, for just driver and luggage.
28Headlamp dim-dip system -
general, removal and refitting
3
General
1The system (where fitted) is governed by the
dim-dip control unit mounted either behind
and above the glovebox (early models), or
behind the main fuse panel (later models).
2The control unit uses the oil pressure
warning lamp circuit to ensure that, when theengine is running and the sidelamps are
switched on, reduced current is fed to the
headlamp dipped-beam circuits. This lights
the headlamps with approximately one-sixth
of their normal power so that the vehicle
cannot be driven using sidelamps alone.
3To locate the dim-dip control unit, open the
main fuse panel covering flap and unclip it
from its bottom and top mountings (Section 3).
Then use a torch to see whether the unit is
fastened to the plastic bracket behind the facia
and fuse panel. The unit is usually rectangular,
of black plastic, and can be identified by the
colours of the five wires leading to it (see
applicable wiring diagram).
Removal
4If the unit can be seen, remove the driver’s
side lower facia and footwell trim panels
(Chapter 11), then unscrew the four retaining
screws and lower the plastic bracket until the
control unit can be detached.
5If the unit cannot be seen, remove the
glovebox assembly (Chapter 11). The unit will
be fastened to the underside of the facia top
surface.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
26Headlamp aim adjustment
motor - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Remove the headlamp, (Section 25).
2Twist the motor clockwise to release it from
the headlamp, then carefully disconnect the
motor from the balljoint (see illustrations).
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the motor is correctly engaged with the
balljoint.
12•10Body electrical systems
26.2A Headlamp aim adjustment motor
(headlamp removed)
27.4 The headlamp aim adjustment switch
- 1992-on models
27.3B Headlamp alignment adjustment screws - models with
electric aim adjustment
A Vertical adjustment screw B Horizontal adjustment screw27.3A Headlamp alignment adjustment screws - models without
electric aim adjustment
A Vertical adjustment screw B Horizontal adjustment screw
26.2B Headlamp aim adjuster balljoint
(arrowed)
Page 25 of 525

29Front indicator lamp unit -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the single indicator lamp unit
securing screw, which is accessible through
the hole in the upper body panel (see
illustration).
3Pull the lamp unit forwards to release it
from the body, then disconnect the wiring
plug (see illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
30Side repeater lamp -removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the wheel arch liner, as described
in Chapter 11.
3Working in the engine compartment,
disconnect the wiring plug, and detach the
earth lead from the body panel.
4Working under the wheel arch, depress the
retaining tabs and manipulate the lamp
through the outside of the wing, pulling the
wiring and the grommet from the inner wing
panel.
5The lens can be removed from the lamp by
twisting it to release the retaining clips.
6Check the condition of the rubber sealing
ring, and renew if necessary.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal.
31Front foglamp - removal,
refitting and adjustment
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Removing (if necessary) the radiator grille
panel, as described in Chapter 11, disconnect
the appropriate foglamp wiring plug.
3Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
4If removing the driver’s side foglamp,
remove the securing screws and withdraw the
plastic cover from the bumper/front wing to
expose the lamp mountings.
5Unscrew the three securing bolts and
withdraw the lamp and wiring, the two bottom
bolts are obvious, but the third is well hidden
at the top of the lamp.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion check the foglamp adjustment.
Adjustment
7The vertical aim of the foglamps can be
adjusted by turning the adjuster screw at the
rear of the lamp in the required direction. It will
be necessary to remove the plastic cover
(driver’s side only) from the bumper/front wing
to expose the adjuster screw (see
illustration).
32Rear lamp unit - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Working in the luggage compartment,
remove the cover from the rear of the lamp.
3Release the top and bottom retaining clips,
and pull the bulbholder from the lamp.
Disconnect the wiring plug.
4Remove the securing screws, and withdraw
the lamp unit from outside the vehicle.
5Note that the lens cannot be renewed
separately, and if damaged, the complete
lamp unit must be renewed.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
33Number plate lamp -removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, carefully
prise the lamp surround from the bumper.
3Pull the lamp from the bumper, and
disconnect the wiring.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
34Exterior lamp bulbs - renewal
1
Note: The glass envelopes of the headlamp
and foglamp bulbs must not be touched with
the fingers. If the glass is accidentally
touched, it should be washed with methylated
spirits and dried with a soft cloth. Failure to
observe this procedure may result in
premature bulb failure
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Headlamps
Removal
2Working in the engine compartment,
release the retaining clip, and remove the
cover from the rear of the headlamp (see
illustration).
Body electrical systems 12•11
31.7 Foglamp aim adjustment screw
(arrowed)34.2 Removing the cover from the rear of
the headlamp
29.3 Disconnecting the front indicator
lamp unit wiring plug29.2 Unscrewing the front indicator lamp
unit securing screw
12