1988 FIAT TEMPRA fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 60 of 171

Please read the whole of CHAPTER
1,
SAFETY FIRST before carrying out any work on your car.
CHAPTER 6
REPAIRS AND REPLACEMENTS
This chapter shows you how
to remove and overhaul all
the major 'wearing' parts of
the car. We deliberately don't
show how to rebuild major
components, such as the
gearbox, or differential. You
are much better off, in terms
of time, cost and the
provision of a guarantee, to
buy a replacement unit.
The same applies to major
electrical components, such
as alternator and starter
motor. If, as we recommend,
you stick to 'original' FIAT
replacement parts, you will
maintain the original quality
of your car.
PART A: ENGINE
PART B: TRANSMISSION AND CLUTCH
PART C: COOLING SYSTEM
PART D: IGNITION
PART E: ELECTRICAL AND INSTRUMENTS
:er Contents
PARTf: FUEL AND EXHAUST
PART G: STEERING AND SUSPENSION
PART H: BRAKES
PART I: BODY AND INTERIOR
110
Page No.
116
127
134
143
Illustration and Section Numbers
• In this chapter, each area of the car is dealt with in a
different PART of the chapter, such as, PART A: ENGINE.
• Each job in each PART has a separate identifying number.
For example Job 2. Cylinder head removal.
• Every Job is broken down into easy-to-follow Steps,
numbered from 1-on.
• Illustrations are numbered so that you can see at a glance
where they belong!
• The illustration Job
1-3
(in PART A) for example, relates to
the text in Job 1, Step 3.
SAFETY FIRST!
• Before carrying out any of the work in this chapter,
be sure to read and understand Chapter 1, Safety
First!
• Be sure to read any safety notes supplied with any
of
the materials for equipment you purchase in
connection with the work described in this chapter.
• If you are not sure about your competence or
skills in
carrying out any of the work described in this chapter,
have the work carried out by your FIAT dealership.
FACT FILE: TIPO and TEMPRA ENGINE TYPES
PETROL ENGINES: The engines covered by
this manual are by far the most commonly
found in the UK. There may be the odd few with
different capacities or specifications which have been imported
from other countries but even they are usually similar. Here we
are concerned with one type of OHC (overhead camshaft)
PETROL engine, in 1372cc (1400) and 1581cc (1600) capacities.
They are best identified by the fact that the 1400 has its
distributor mounted on the side of the cylinder block and the
1600 has a distributor which is mounted on the end of the
camshaft, flywheel end.
DIESEL ENGINES: The Diesel engines covered here are the
1697cc (1700), the 1929cc (1900) and the 1929cc (1900) turbo.
It would take a trained eye to spot any differences between the
normally aspirated engines, but the turbo mounted on the
exhaust manifold together with its associated extra 'plumbing'
easily identifies the most powerful version.
Page 64 of 171

SAFETY FIRST! • Step 7:
Disconnect the
electrical leads from
the following: the
inlet manifold
• Step 2: Disconnect both battery leads, negative
terminal first.
Q Step 3: Drain the cooling system and depressurise the
fuel system, if yours is a fuel injection engine
-
see PART
F:
FUEL AND EXHAUST
• Step 6B:
INJECTION
ENGINES.
Disconnect the
engine end of the
accelerator cable (a),
the idle speed check
actuator (b) and the
injector supply (c).
• Step 8: Detach
the exhaust
downpipe from the
manifold.
• Step 9: Remove
the dipstick
(arrowed) and the
cylinder head
coolant temperature
sensor (arrowed).
• Step 10: Also remove all the HT leads (along with the
distributor cap). Place them to one side.
• Step 11: Undo the brake servo hose from the manifold.
Q Step 4: Remove the air cleaner by releasing the spring
clips (a) at the front of the unit and the screw on the top face
(b) and disconnect the hoses
recovery pipe clips from beneath the rear of the housing, once
it is free to lift up.
Q Step 5: Disconnect the crankcase vent hose from the
cylinder head and the inlet tract or the SPI injector unit, as
appropriate and blank off with a bolt of suitable size.
• Step 6A:
CARBURETTOR
ENGINES.
Disconnect the
engine end of the
accelerator cable
from its idler and
the choke cable
from its mounting.
Q Step 12: Remove the
water hoses connected to
the inlet manifold and
thermostat.
• Step 13 A:
CARBURETTOR
ENGINES. Disconnect the
fuel pipe from the carbu-
rettor and both pipes
from the fuel pump.
(Label both the pipes and
stubs so that they will be
reconnected the
right way round.)
• Step 13B:
INJECTION
ENGINES.
Disconnect the fuel
supply and return
hoses from the
injector unit housing
(a). Plug the ends.
• Step 14A: CARBURETTOR ENGINES. Disconnect the
distributor vacuum pipe and oil vapour pipes from the carbu-
rettor.
vacuum sensor
(arrowed), the
manifold coolant
temperature sensors
(arrowed) and the
throttle position
switch and any
other leads which your engine may have.
Page 69 of 171

G Step 17: Now repeat this operation on the remaining
valves.
G Step 18: Wash the whole cylinder head again using
paraffin and an old brush, making sure that all traces of
grinding paste are removed, then dry off. Use compressed air
if
available.
SAFETY FIRST!
•
Treat
compressed air with respect. Always wear
goggles
to protect your eyes.
•
Never
allow the airline nozzle near any of the body Sep apertures.
H INSIDE INFORMATION! Check the height of the valve
springs against new ones if possible, but if not, compare
them with each other. If any are shorter than the others,
play safe and replace the complete set. They are bound
to have suffered fatigue which could cause premature
valve failure. H
G Step 19: To install the valves, start from one end.
Lubricate a valve stem with fresh engine oil and slide it in to its
guide.
G Step 20: Locate a new valve stem seal over the stem of
the valve
(if applicable) and push down into contact with the
guide. Position the seal on its seat using a suitable metal tube.
G Step 21: Refit the flat washer and spring seat.
G Step 22: Position the inner and outer springs and the
spring
cap.
G Step 23: Re-apply the valve spring compressor and
compress
the springs enough to allow you to engage the split
collets
in
the stem grooves.
D INSIDE INFORMATION! Grease the grooves so that the
collets will 'stick' in place. The collets are easily fitted by
'sticking' the backs of them onto the end of a screw-
driver with some grease and feeding them into
position. B
G Step 24: Carefully release the spring compressor and
check
that the collets are correctly located. Tap the end of the
stem with
a hammer, to bed them in.
G Step 25: Fit the remaining valves.
Job 5. Petrol engine -
dismantling.
G Step 1: Familiarise yourself with the layout of the engine.
Refer to
illustration Job
2-1
for an exploded view of the
engine
components.
G Step 2: Drain the engine oil. Remove the cylinder head.
See
Job 2.
G Step 3: Remove the distributor. See PART D: IGNITION
• Step 4:
Remove the petrol
pump and spacer
block, if the
mechanical type
(a). (Electric fuel
pumps are in the
fuel tank.)
• Step 5:
Remove and
discard the oil filter
illustration Job
5-4,
• Step 6: Remove the water pump complete with its distri-
bution pipe, and the power steering pump (if fitted).
Q Step 7: Remove the alternator, the crankshaft pulley, the
crankshaft and camshaft sprockets, the cam belt tensioner
and the cam belt cover backplate.
• Step 8:
Remove the
auxiliary shaft
sprocket...
• Step 9: ...the
end plate and
seal, and remove
the auxiliary shaft.
• Step 10:
Undo and remove
the clutch, and
then the flywheel.
• Step 11: Turr
engine assembly c
remove the sump
and remove the crankcase breather (see
part b) with its pipe.
Page 74 of 171

• Step 30: Fit
the crankshaft
pulley and
tighten. See
Chapter 3,
Facts and
Figures.
• Step 31: Fit the
water pump and
distribution pipe.
• Step 32A: Refit the
flywheel. Do not unbolt the
TDC sensor (1) from the oil seal
housing at its mounting plate
bolts
(2)
unless it is essential to
do so.
• Step 32B: If
the sensor
mounting plate has
to be disturbed, you
will need the FIAT
special tool illus-
trated here (inset) in
order to reposition it
correctly. Position
the timing mark on
the crankshaft
pulley with the zero
degrees mark on the outer timing belt cover (and double
check that the timing mark on the flywheel
-
rubber bung
removed
-
is aligned at zero degrees).
With the bracket fitted to the oil seal housing, fit the FIAT
special tool onto the bracket in place of the sensor with a slot
in the tool fitting exactly over the TDC pin on the flywheel.
When everything is lined up, position the bracket accurately
and tighten the bolts. Remove the tool and refit the sensor.
IMPORTANT NOTE: During assembly, a shear-bolt will
have been fitted to prevent accidental movement of the
bracket. If you need to undo it, you will need to drill it
out and you should replace it with a new one obtained
from your FIAT dealership.
• Step 33: Refit the clutch. See PARTB: TRANSMISSION,
Job 4.
Q Step 34: Refit the fuel pump and pushrod using new
gaskets on both sides of the spacer block, 0.3 mm thick
between the spacer and the engine and 0.7 mm between the
spacer and the pump. See PART F: FUEL AND EXHAUST for
information on setting the pump position.
• Step 35:
Lubricate the sealing
ring and screw on a
new oil filter.
• Step 36:
Before refitting the
distributor, (see
PART D: IGNITION)
refit, if necessary,
the oil pump drive
gear.
• Step 37: Refit
all remaining
auxiliary compo-
nents (including the
oil vapour recovery
device, shown here),
using new gaskets
as necessary and
referring to
Chapter
3,
Facts
and Figures for the
torque settings.
Q Step 38: Reconnect the engine to the transmission. See
Job 11.
Q Step 39: Refit the complete unit to the car. See Job
9.
• Step 40: fl INSIDE INFORMATION! Before fitting the
spark plugs and with a fully charged battery, turn the
engine on the starter until the oil warning light goes
out. This primes the lubrication system and gives more
immediate oil pressure on initial start up after overhaul-
a critical time in the life of an engine. B
• Step 41: Fit the spark plugs and start the engine
-
this
might take a few seconds more than normal on the initial start
up.
• Step 42: Allow the engine to warm up on fast idle
until
it
reaches working temperature and then slow it down to its
normal speed (if adjustable
-
see PART F: FUEL AND
EXHAUST)
Page 76 of 171

Job 8. Petrol engine/transmission
- removal.
IMPORTANT NOTE: See PARTB: TRANSMISSION for
gearbox removal by itself.
H INSIDE INFORMATION! The complete engine/trans-
mission unit is removed and replaced from under the car
- and this applies to all types. Make sure you can raise
the front of the car high enough (and support it safely
and securely!) to allow the power unit to be pulled clear
from underneath, before starting work! 13
• Step 1: Remove the bonnet
-
see PARTI: BODY AND
INTERIOR, Job 1.
• Step 5:
Disconnect the
carburettor or
injector fuel lines,
choke and throttle
cables and hoses and
electrical connections
(arrowed).
Q Step 6: Disconnect the starter motor cables, HT leads,
fuel pump lines, sensors and electrical connectors arrowed.
Job
8-7
• Step 2: Disconnect the battery earth lead.
• Step 3: Drain the cooling system and the engine oil.
Disconnect all hoses shown.
• Step 7: Disconnect the clutch cable (3) or clutch slave
cylinder, if hydraulic, the earth cable (2) and the reversing
lights switch cable
(1)
from the top of the gearbox.
• Step 8: Disconnect the alternator cables.
Q Step 9: Slacken the front wheel bolts, raise the car and
support securely on axle stands. Remove the wheels.
• Step 10: Drain
the gearbox oil.
• Step 4:
Remove the air
filter-to-engine
connections
-
earlier type illus-
trated. (There are
some hose
connections
underneath on
the later type,
mounted on top
of the engine.) Disconnect the electrical connection and all
other hoses from the filter housing.
• Step 11:
Remove the buttons
(gearbox side,
arrowed) fixing the
dust shield to the
wheel arch on each
side.
Page 82 of 171

PART A
-
ENGINES PRIOR TO ENGINE NO. 1723291 • Step A15: Ease the timing belt off the sprockets.
Gl Step A10: Use a spanner on the crankshaft bolt (a) to
turn the engine until the timing marks on the crankshaft,
camshaft and injection pump sprockets align with their
respective reference marks. Align the crankshaft sprocket with
the notch on the front cover (b). Align the camshaft sprocket
with the hole in the timing belt cover (c). Align the injection
pump sprocket with the reference on the timing belt rear
guard (d).
• Step A11: Use
the FIAT flywheel
lock, part no.
1860766000 (or
construct your own
tool) to stop the
crankshaft from
turning.
• Step A12:
Remove the
alternator belt
pulley/damper.
• Step A13:
Using FIAT tool no.
1842128000 (see illustration Job
13-A10,
parte), lock the
injection pump sprocket to prevent it turning.
• Step A14: Slacken the belt tensioner nut (see illustration
Job
13-A10,
part f), move the tensioner away from the belt
and temporarily lock it in position.
• Step A16: Fit the new belt, first making sure that all of
the timing marks still align.
• Step A17: If you do not have access to the correct FIAT
tensioning tool, release the locknut, push the tensioner firmly
into the belt and lock it up by tightening its bolt.
If you do have the FIAT special tool (a weighted bar), attach it
to the tensioner, which will move to the position of correct
tension. Lock the tensioner bolt. Remove the special tool
locking the injection pump sprocket.
E3 INSIDE INFORMATION: If you can't put enough
pressure on the tensioner with your fingers, carefully use
a long screwdriver as a lever. Alternatively, push a pair of
bolts into the two holes in the tensioner and lever
between them to turn the tensioner. E9
Q Step A18: Rotate the engine through two revolutions. If
the belt is correctly tensioned you should just be able to twist
it through a quarter-turn when gripping it between thumb
and finger in the centre of its longest run between sprockets.
Adjust as necessary.
Q Step A19: Refit the remaining parts in the reverse order,
then check the injection timing (see Chapter
5,
Servicing
Your Car, Job
39)
PART B
-
ENGINES FROM ENGINE NO. 1723291-ON
Job 13-B10
Q Step B10: Turn the crankshaft in its normal direction of
rotation until the marks on the crankshaft sprocket (a) and
fuel injection pump sprocket (b) line up with the fixed marks
on the engine. This will place cylinder No. 1 at Top Dead
Centre TDC and set the camshaft for the power stroke of the
same cylinder. Lock the flywheel (see Step A11) and remove
the alternator belt pulley (see Step A12).
IMPORTANT NOTE: The hole for fixing the camshaft
sprocket (c) has a fine-adjustment slot, so it is possible
that the mark on the sprocket may not line up exactly
with the mark on the cover.
Page 83 of 171

Q Step B11: Undo the belt tensioner nut (see illustration
Job 13-B10, part d), then remove the timing belt.
Q Step B12: Undo the nuts securing the brake vacuum
pump to the cylinder head (see illustration Job
16-1),
and
remove it.
• Step B13: Fit FIAT tool no. 1860932000 (for setting
camshaft timing) to the vacuum pump end of the camshaft,
matching the camshaft groove (1) with the lug (2) on the tool
Secure
the tool to the cylinder head, positioning the centring
dowel
(3) as shown. The dowel must be perfectly centred on
the tool,
and if it isn't, you should adjust the hexagonal bolt
(4) with
a spanner, and centre it with tiny movements.
• Step B14:
Remove
the bolt
(arrowed) which
secures
the front
cover
to the engine
block,
then fit the
timing belt on the
crankshaft sprocket.
• Step B16:
Lock the injection
pump sprocket (see
StepA13). Now,
using FIAT tool no.
1860831000,
slacken the bolt
securing the
camshaft sprocket.
• Step B17: Continue fitting the timing belt in the
following sequence: crankshaft sprocket, fixed tensioner,
injection pump sprocket, timing sprocket, belt tensioner... and
check that the mark on the injection pump lines up with the
fixed mark on the rear cover.
• Step B18: Use the timing belt tensioner to correctly
tension the belt.
B INSIDE INFORMATION: If you do not have the correct
tensioning tool, follow Steps A16 and A17. B
• Step B19: Tighten the camshaft sprocket bolt to the 1
specified torque (see Chapter
3,
Facts and Figures).
Q Step B20: Turn the crankshaft by two revolutions
(clockwise), tighten the belt tensioner to the specified torque
(see Chapter
3,
Facts and Figures) and remove the
tensioning tools. If the belt is correctly tensioned you should
just be able to twist it through a quarter-turn when gripping it
between thumb and finger in the centre of its longest run
between sprockets. Adjust as necessary.
O Step B21: Refit the remaining components in the reverse
order of removal, then check the injection timing. See
Chapter
5,
Servicing Your Car, Job 25.
Job 14. Diesel engine.
Cylinder head - removal.
• Disconnecting the high pressure pipes on a diesel
injection system can be dangerous!
• Read the Safety First! information at the start of
PART F: FUEL AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS before
starting work.
Q Step 1: Refer to Job
13
and remove the timing belt.
• Step 2: Drain the cooling system and disconnect the air
pipes from the inlet manifold.
Q Step 3: Disconnect
and remove the oil vapour
pipes from the cylinder
block device.
Job 13-B13
• Step B15: Fit
FIAT tool
No.
1860933000 for
precise
determination
of TDC
on cylinder
No. 1. The
tool must
be secured
firmly by
two bolts
to the
crankshaft sprocket,
and by
another bolt
to the
crankshaft front cover (where the bolt was previously
removed in Step B14).
Page 84 of 171
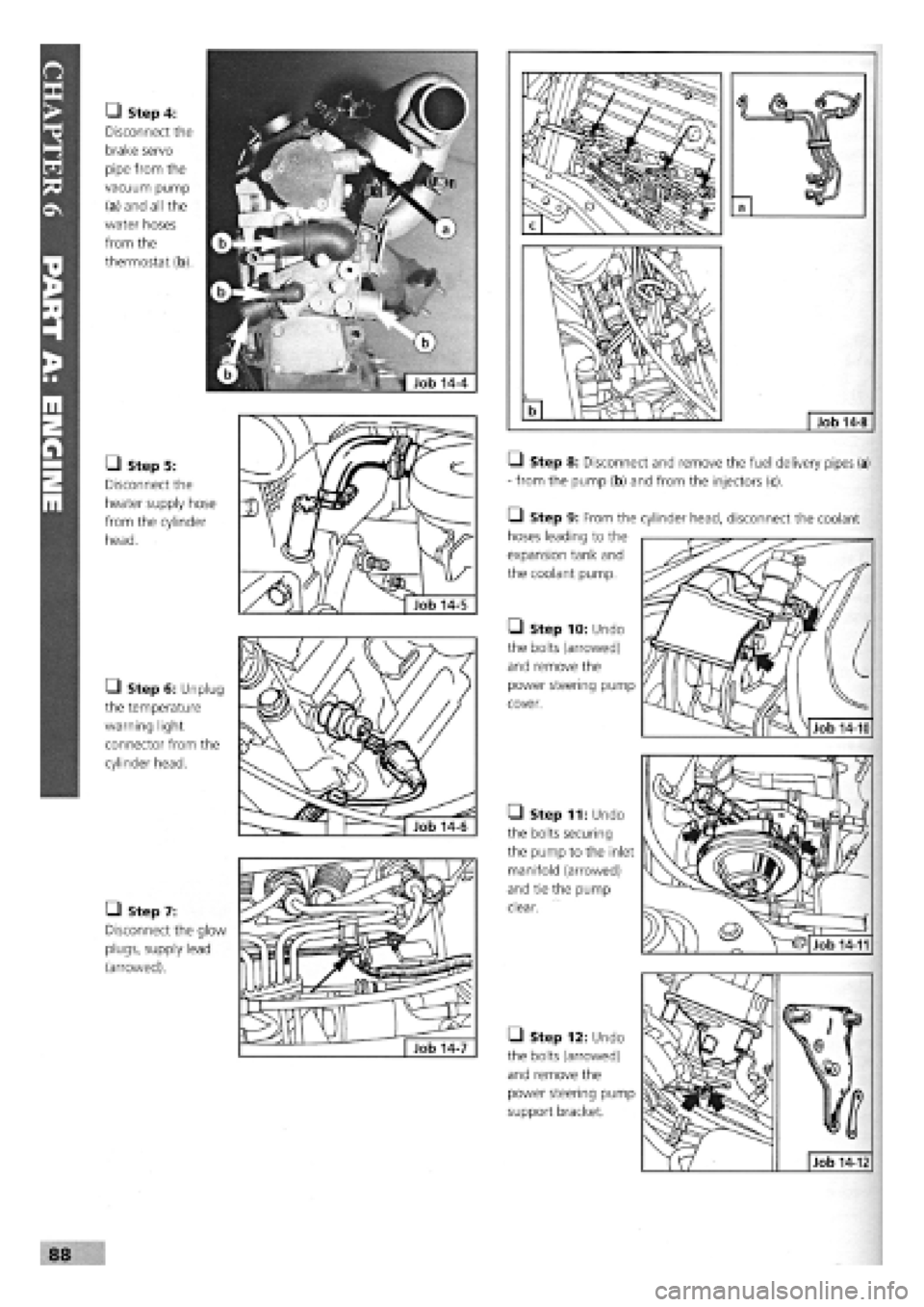
• Step 4:
Disconnect the
brake servo
pipe from the
vacuum pump
(a) and all the
water hoses
from the
thermostat (b).
• Step 5:
Disconnect the
heater supply hose
from the cylinder
head.
• Step 6: Unplug
the temperature
warning light
connector from the
cylinder head.
• Step 7:
Disconnect the glow
plugs, supply lead
(arrowed).
Q Step 8: Disconnect and remove the fuel delivery pipes (a)
- from the pump (b) and from the injectors (c).
• Step 9: From the
hoses leading to the
expansion tank and
the coolant pump.
• Step 10: Undo
the bolts (arrowed)
and remove the
power steering pump
cover.
• Step 11: Undo
the bolts securing
the pump to the inlet
manifold (arrowed)
and tie the pump
clear.
• Step 12: Undo
the bolts (arrowed)
and remove the
power steering pump
support bracket.
88
cylinder head, disconnect the coolant
Job 14-10
Job 14-12
Job 14-11