1987 NISSAN PULSAR warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 33 of 238
Roadside Trouble Shooting
(5) Place the vent caps loosely over the cell
apertures.
(6) Connect one end of the red jumper lead to
the positive ( + ) battery terminal of the booster
battery and the other end of the red lead to the
positive (+) battery terminal of the discharged bat-
tery.
NOTE: The battery emits hydrogen gas
which is explosive. Do not expose the battery
to naked /lames or sparks.
Do not lean over the battery when con-
necting the jumper leads.
Do not allow the ends of the jumper leads
to touch one another or any part of the
engine.
(7) Connect one end of the black juniper lead to
the negative (-) battery terminal of the booster
battery and the other end of the black lead to a good
earthing point on the engine of the vehicle with the
discharged battery.
NOTE: Do not connect the jumper lead
directly to the negative (-) battery terminal
of the discharged battery.
(8) Start the engine on the vehicle with the
booster battery and run the engine at a moderate
speed. (9) Start the engine on the vehicle with the
discharged battery.
(10) If possible, leave the engines of both vehi-
cles running for 10 minutes.
(11) Disconnect the jumper leads in the reverse
order of the sequence in which they were connected.
2. TO CHECK IGNITION AND ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
(1) Switch on the ignition and check for warning
lamp illumination on the dashboard. (2) Operate the starter and check that the starter
rotates the engine at a steady speed.
(3) Switch on the headlamps and check for good
light intensity. Should the lamps not illum inate or the starter
motor not turn the engine, carry out the following
steps:
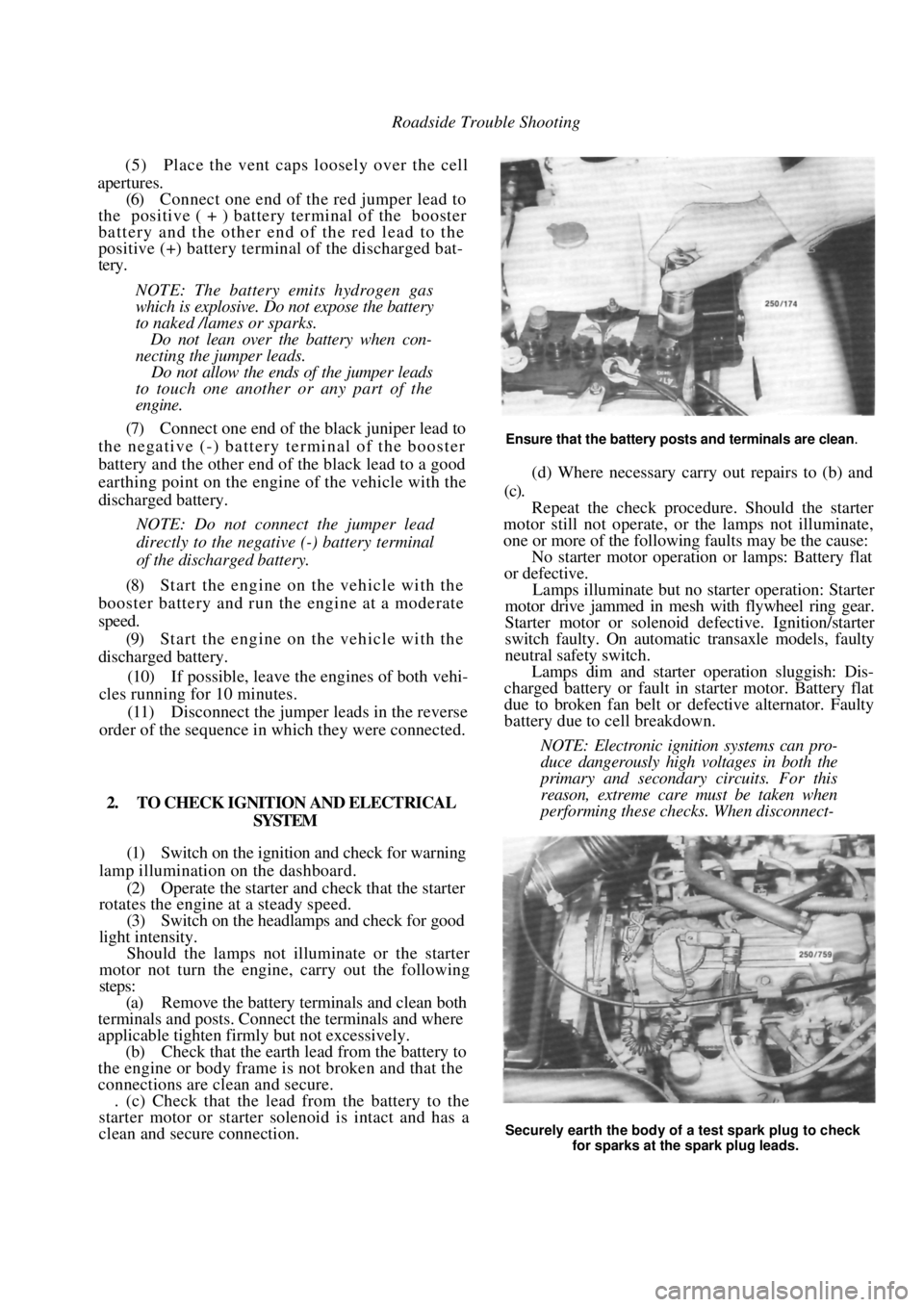
(a) Remove the battery terminals and clean both
terminals and posts. Connect the terminals and where
applicable tighten firmly but not excessively.
(b) Check that the earth lead from the battery to
the engine or body frame is not broken and that the
connections are clean and secure. . (c) Check that the lead from the battery to the
starter motor or starter solenoid is intact and has a
clean and secure connection.
Ensure that the battery posts and terminals are clean.
(d) Where necessary carry out repairs to (b) and
(c).
Repeat the check procedur e. Should the starter
motor still not operate, or the lamps not illuminate,
one or more of the following faults may be the cause:
No starter motor operation or lamps: Battery flat
or defective.
Lamps illuminate but no starter operation: Starter
motor drive jammed in mesh with flywheel ring gear.
Starter motor or solenoid defective. Ignition/starter
switch faulty. On automatic transaxle models, faulty
neutral safety switch.
Lamps dim and starter operation sluggish: Dis-
charged battery or fault in starter motor. Battery flat
due to broken fan belt or de fective alternator. Faulty
battery due to cell breakdown.
NOTE: Electronic ignition systems can pro-
duce dangerously high voltages in both the
primary and secondary circuits. For this
reason, extreme care must be taken when
performing these checks. When disconnect-
Securely earth the body of a test spark plug to check
for sparks at the spark plug leads.
Page 35 of 238

Roadside Trouble Shooting 35
View showing the location of the fuel pump fuse and the EGI and fuel pump relays.
switch. When starting the engine, the fuel
pump will not operate until the oil pressure
is sufficient to extinguish the oil pressure
warning lamp. Therefore it will be necessary
to operate the starter motor for a longer
period than usual to start the engine.
(3) If the fuel pump cannot be felt operating,
check the fuel pump fuse located in the fuse panel
adjacent to the steering column.
If the fuel pump fuse is serviceable, refer to the
Fuel and Engine Management section for detailed
tests on the fuel pump.
(4) Check that all fuel hose connections are
secure.
(5) Remove the spark plugs and check for petrol
saturation of the electrodes which indicates flooding.
Thoroughly clean and dry the spark plugs before
replacement. Fully depress the throttle pedal and turn the
ignition switch to the start position. If the engine does
not start, proceed as follows.
Check that the MAP sensor hose is not blocked or split
and ensure that all electrical connections are clean and
secure.
If flooding persists, refer to the Fuel and Engine
Management section.
(6) Check that all EFI electrical wiring connec-
tors are clean and secure.
(7) Check that the MAP sensor vacuum hose is
securely connected at each end and is not split or
blocked.
4. TO CHECK MECHANICAL SYSTEM
The following check procedure assumes that the
starter motor will rotate the engine. If not, on manual
transaxle models, depress the clutch pedal to disen-
gage the engine from the tr ansaxle in case the fault lies
within the transaxle.
If the starter motor will not rotate the engine, it
will be necessary to remove the starter motor and
attempt to turn the engine over manually. This will
establish whether the fault lies with the starter motor,
which could be jammed or defective, or with the
engine, which could be seized or have broken internal
components such as connecting rods, pistons and
crankshafts etc.
If the starter motor is not at fault and the engine
will not rotate manually, refer to the Engine Mechan-
ical Trouble Shooting heading in the Engine section.
It should be noted that the only way that cylinder
compression can be accurately tested is with a com-
pression gauge. The method described in the following
procedure is only intended to give a rough indication
when checking for causes of engine breakdown,
(I) When the engine is cool, check for loss of
coolant from the cooling system.
If coolant loss is evident, check carefully for any
indication of external leakage. Remove the engine oil
dipstick and check for wate r contamination (emulsi-
fication) of the oil. When oil mixes with water it will
Ensure that all fuel connections are securely tightened.
Page 83 of 238

Fuel and Engine Management 83
the fuel pump will not operate until the oil
pressure is sufficient to extinguish the oil
pressure warning lamp. Therefore it will be
necessary to operate the starter motor for a
longer period than usual to start the engine.
(3) Faulty EFI component wiring connections:
Check that all component wiring connections are
clean and secure.
(4) Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
vacuum hose blocked or disconnected: Clear or recon-
nect the vacuum hose. (5) Fault in the ignition system: Check the
primary and secondary ignition circuits.
(6) Engine flooded: Fully depress the throttle
pedal until the engine starts. Check the coolant
temperature sensor. Check th e injector(s) for leakage.
ENGINE STARTS THEN STALLS
(1) Water in the fuel: Dr ain the fuel from the
system and renew the fuel filter.
(2) Air leakage at the inlet manifold: Check all
joints and hoses for air leaks. (3) Faulty EFI wiring connections: Check that
all component wiring connections are clean and
secure.
(4) Ignition timing incorrectly set: Check and
adjust the timing. (5) MAP sensor faulty or supply hose discon-
nected or blocked: Check the vacuum supply hose.
Check the operation of the MAP sensor.
ENGINE MISFIRES
(1) Faulty, dirty or incorrectly adjusted spark
plugs: Renew or clean and adjust the spark plugs.
(2) Condensation in the distributor cap: Dry and
examine the cap for cracks. (3) Faulty high tension leads: Check and renew
the high tension leads.
Testing the fuel system pressure using a pressure
gauge.
(4) Faulty ignition coil: Check and renew the
ignition coil.
(5) Fuel blockage: Check for blockage in the fuel
filter, lines and injector(s). (6) Low fuel pressure: Check the fuel pump and
fuel pressure regulator. (7) Water in the fuel: Dr ain the fuel from the
system and renew the fuel filter. (8) Loose fuel supply wiring connectors: Check
all connectors for tightness. (9) Faulty fuel injector: Check the connections
and test the condition of the fuel injectors.
ENGINE LACKS POWER
(1) Ignition timing incorrectly set: Check and
adjust the timing.
(2) Water in the fuel: Dr ain the fuel from the
system and renew the fuel filter.
(3) Incorrectly adjusted throttle cable: Adjust the
throttle cable.
Check the distributor cap for cracks or tracking be- tween the terminals. The air filter element should be renewed at 40 000 km
intervals. 1.8 liter engine.
Page 85 of 238

Fuel and Engine Management 85
View of the 1.6 liter engine showing the engine management components. Air cleaner removed for clarity.
series of tests on various components in the system
and records the results, If a fault is discovered, the
ECM warning lamp on the instrument cluster will
illuminate while the engine is running. When the self
diagnosis mode is activated, the ECM warning lamp
will flash codes indicating the area in which the fault
has occurred.
This function is very useful in locating system
faults, particularly intermittent problems. However,
the self diagnosis mode does not provide comprehen-
sive testing of the EFI system, and therefore should
always be used in conjunction with the other test
procedures described later in this section in order to
accurately locate system faults.
The high energy electronic ignition system con-
sists of a distributor and an ignition coil.
The distributor has two functions. The first is to
produce and distribute secondary high tension voltage
to the spark plugs.
The second function is to provide the control unit
with information on engine speed and crankshaft
position.
The ignition timing is constantly adjusted by the
control unit to suit varying engine and vehicle oper-
ating conditions.
In the fuel injection system, a metered amount of
fuel is sprayed into the air stream. The air/fuel
mixture then enters the combustion chamber via the
inlet valves.
On 1.6 liter engines, the fuel is injected by a single
injector, located above the throttle valve within the
throttle body assembly. The injector fires twice per
engine revolution under most operating conditions.
On 1.8 liter engines, four injectors are used. The
fuel is distributed to the injectors via the fuel rail. All
injectors fire simultaneous ly once per engine revolu-
tion under most operating conditions.
Under conditions of high load the control unit
may signal the injector(s) to fire more often. However,
if the engine speed exceeds 6 700 rpm the control unit
will cease firing the injectors until the engine speed is
below 6 200 rpm.
Fuel is supplied under pressu re by an electric fuel
pump mounted in the fuel tank and the pressure is
regulated by a pressure regulator.
On 1.6 liter engines, the regulator consists of a
spring tensioned diaphragm which is mounted to the
side of the throttle body assembly. The fuel pressure is
regulated by the tension of the spring against the
diaphragm, opening and closing the fuel return port.
On 1.8 liter engines, the pressure regulator is
mounted adjacent to the fuel rail and consists of a
diaphragm with fuel pressu re acting on one side and
spring tension and manifold vacuum acting on the
Page 89 of 238

Fuel and Engine Management 89
The procedure for fabricating an LED test lamp is
fully described in the El ectrical System section.
If a conventional test lamp with a filament type
bulb is to be used, ensure that the current draw of the
test lamp does not exceed 0.3 amp to avoid damage to
the electronic components.
To check the current draw connect an accurate
ammeter, such as the multimeter described previ-
ously, in series with the test lamp and a battery.
If the ammeter reads less than 0.3 amp the test
lamp is suitable.
Tachometer
(1) Disconnect the resistor from the tachometer
pick-up wiring connector which is located on the
ignition coil wiring harness, and connect the positive
lead of an accurate tachometer to the brown wire
terminal in the wiring connector. (2) Connect the negative lead to a good earthing
point.
View showing the location of the tachometer pickup
wiring connector with the resistor installed.
Timing Light
(1) Connect the timing light to the engine fol-
lowing the instrument manufacturers instructions.
NOTE: Do not connect or disconnect the
timing light with the engine running as
voltage surges could damage the alternator
or control unit. Do not allow the high
tension leads to open circuit with the engine
running as damage to the engine manage-
ment system could result.
(2) Do not connect the timing light positive lead
to the alternator output terminal. Where possible,
connect the power leads of the timing light to an
external power source to prevent possible transient
voltages damaging the alternator or control unit.
4. SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS AND ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: Due to the use of complex electronic
components in the engine management sys-
tem, the diagnosis and testing procedures
described in this section should not be
carried out by persons lacking an under-
standing of electronics and the precautions
associated with the servicing of electronic
components. It is rec ommended that should
a fault arise in the system, the vehicle be
referred to an authorized workshop.
The control unit can be damaged by
component faults not indicated by the self
diagnosis codes and the renewal of the
control unit without lo cating the cause of
the failure will result in the failure of the
replacement unit. It is for this reason that
the practice of substituting components to
isolate faults is not recommended.
Prior to performing any of the follow-
ing operations, refer to the Service Pre-
cautions and Procedures heading.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Prior to performing the Self Diagnosis Test Pro-
cedures, perform the following preliminary checks and
rectify any problems as necessary.
(1) Check for an adequate supply of fuel in the
fuel tank. (2) Check the wiring connectors and earth points
of all engine management components for clean,
secure connections. To prevent damage to the control
unit, disconnect the negative battery terminal before
disconnecting any engine ma nagement wiring connec-
tors. (3) Check the condition of the battery. Refer to
the Electrical System sectio n for checking procedures.
Rectify any faults as necessary. (4) Check the air cleaner element for restriction.
(5) Check for air leaks at the throttle body, inlet
manifold and all related hoses. (6) Check the fuel pump pr essure as described
later in this section. (7) Ensure that the engine is in a satisfactory
mechanical condition and is in tune. Refer to the
Engine and Engine Tune-up sections as necessary.
SELF DIAGNOSIS
This function is very useful in locating system
faults particularly intermittent problems. However,
the self diagnosis mode does not provide comprehen-
sive testing of the engine management system, and
therefore should always be used in conjunction with
the other test procedures described later, in order to
accurately locate system faults.
To Interpret Self Diagnosis Codes
Once the self diagnosis mode is activated, various
fault codes will be displayed as a series of flashes by
the ECM warning lamp on the instrument cluster.
Page 90 of 238

90 Fuel and Engine Management
To identify the code number, count the number of
times the ECM warning lamp flashes. Each fault code
comprises two groups of flashes separated by a 1.2
second pause. The first group represents tens and the
second group represents single units. For example 1
flash followed by a 1.2 second pause followed by 4
flashes would be code number 14. Similarly 4 flashes
followed by a 1.2 second pause followed by 2 flashes
would be code number 42.
The code will be displayed three times. If more
than one fault code is present, the self diagnosis
system will indicate each one in numerical order, with
a 3.2 second pause between each code, and then
repeat the sequence.
The fault codes can be identified as follows:
CODE NUMBER FAULT AREA
12 Satisfactory operation
13 Oxygen sensor open circuit
14 Coolant temperature sensor circuit (voltage low)
15 Coolant temperature sensor circuit (voltage high)
21 Throttle position sensor circuit (voltage high)
22Throttle position sensor circuit (voltage low)
23MAT sensor circuit (voltage' high) 1.8 liter engine
only
24 Vehicle speed sensor circuit
25 MAT sensor circuit
(voltage low) 1.8 liter engine
only
33 MAP sensor circuit
(voltage high)
34MAP sensor circuit (voltage low)
42 Electronic spark timing circuit
44
Oxygen sensor circuit
(lean exhaust)
45Oxygen sensor circuit (rich exhaust)
51 Mem-Cal
55 Control unit input circuits
Test Procedure
(1) Perform the following checks:
(a) Ensure that the battery voltage is above 11
volts. (b) Ensure that the throttle valve is fully closed.
(c) Place the transaxle in neutral.
(d) Ensure that the air conditioner, fan, tights
and all other accessories are switched off.
(2) Turn the ignition On and confirm that the
ECM warning lamp on the instrument cluster is
illuminated but not flashing.
If code 55 is displayed, refer to the Control Unit
heading, perform the circuit test procedure and rectify
the cause of the code before proceeding.
If the ECM warning lamp flashes codes other than
code 55, check the wiring harness between the diag-
nostic link connector terminal B and the control unit
wiring connector terminal A9 for shorts. Repair or
renew the wiring harness as necessary.
If no fault can be found, renew the control unit.
If the ECM warning lamp does not illuminate,
proceed as follows:
(a) Check the METER fuse located in the fuse
panel adjacent to the steering column and the fusible
links located in the fusible link connecting block at the
rear of the battery. Renew the fuse or fusible links as
necessary. (b) Check the wiring harness to the instrument
cluster. Repair or renew the harness. (c) Check the Check Engine lamp bulb. Renew if
necessary. (d) Check the EGI relay. Renew as necessary.
(3) Connect a jumper lead across terminals A
and B on the diagnostic link connector located under
the front passengers seat above the control unit.
(4) Note the codes indicated by the flashing
ECM warning lamp.
If code 12 is displayed, the system is operating
correctly.
If codes other than code 12 are displayed, refer to
the component or circuit test procedure under the
appropriate heading as indicated by the code number.
If more than one code is being displayed, test each
indicated fault working in the order of display of the
code numbers.
(5) After completing the self diagnosis test pro-
cedure, remove the jumper lead from the diagnostic
link connector. (6) After repairing or renewing the necessary
View showing the location of the diagnostic link
connector. Passengers seat removed for clarity.
Inset shows the diagnostic link connector terminal identification.
Page 102 of 238

\(V2 Fuel and Engine Management
View of the IAC valve removed from the engine. Dimension A must not exceed 28 mm.
(3) Lubricate the IAC valve O ring with engine
oil and install the IAC valve. Tighten the retaining
screws securely.
(4). Install the IAC valve wiring connector and
the negative battery terminal.
(5) On 1.6 liter engines, install the air cleaner
assembly as previously described. (6) Run the engine until normal operating tem-
perature and idle speed are attained.
NOTE: Several minutes may elapse before
the normal idle speed is attained.
(7) Hold the throttle open at approximately
3 000 rpm for 10 seconds to reset the IAC valve.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR
To Test - Codes 33 and 34
NOTE: The following test procedure
assumes that fault codes 33 or 34 have
been
displayed during the self diagnosis test
pro-
cedure. If no codes have been displayed
but
the operation of the MAP sensor is suspect,
begin the test procedure at operation (15).
(1) Erase the self diagnosis code memory as
previously described.
(2) Start and run the engine at idle speed for 60
seconds or until the ECM warning lamp lights.
(3) Stop the engine, switch the ignition On and
connect a jumper lead between terminals A and B on
the diagnostic link connector. Note any fault codes
displayed. If code 34 is displayed, remove the jumper lead
from the diagnostic link connector, erase the self
diagnosis codes and proceed to operation (7).
If code 33 is displayed, remove the jumper lead
from the diagnostic link connector, erase the self
diagnosis code memory and proceed to operation (4).
If no codes are displayed, but codes 33 or 34
were
displayed when the self diagnosis test procedure was
originally performed, an intermittent fault is indi-
cated. Proceed as follows:
(a) Check for faulty wiring connections. Check
that all wiring connectors are clean and secure. (b) Check that all earth wires are secure.
(c) Check the vacuum hose to the MAP sensor
for deterioration or restriction.
(4) Disconnect the wiring connector from the
MAP sensor. (5) Start and run the engine at idle speed for 60
seconds or until the ECM warning lamp lights. (6) Stop the engine, switch the ignition On and
connect a jumper lead between terminals A and B on
the diagnostic link connector. Note any fault codes
displayed.
If code 33 is displayed, measure the voltage at
the
MAP sensor wiring connector terminal B with a
voltmeter to earth. Renew the control unit if the
voltage is less than 1 volt.
If the voltage is more than 1 volt, check the
wiring
harness for a short to voltage between terminal B and
the control unit wiring connector terminal Cll.
Repair or renew the wiring harness as necessary.
If code 34 is displayed, proceed as follows:
(a) Check for a restricted or leaking MAP sensor
vacuum hose.
(b) Check the wiring harness for continuity and
shorts between terminals A on the MAP sensor
connector and terminal A11 on the control unit wiring
connector. Repair or renew the wiring harness as
necessary.
If no faults are indicated in the above two checks,
proceed to operation (15).
(7) Disconnect the wiring connector from the
MAP sensor and connect a jumper lead between
terminals B and C on the wiring connector. (8) Start and run the engine at idle speed for 60
seconds or until the ECM warning lamp lights. (9) Stop the engine, switch the ignition On and
connect a jumper lead between terminals A and B on
the diagnostic link connector. Note any fault codes
displayed.
If code 33 is displayed, proceed to operation (15).
If code 34 is displayed, proceed as follows.
Location of the MAP sensor. Inset shows the terminal
identification.
Page 106 of 238

106 Fuel and Engine Management
on the pickup coil wiring connector. The resistance
should be 500-1 500 ohms.
If the resistance is not as specified in either of the
above tests, renew the pickup coil.
(4) Remove the retaining spring from the dis-
tributor drive coupling.
(5) Using a pin punch, remove the drive pin
from the shaft. (6) Remove the drive coupling, washer, tang
washer and thrust spring from the shaft. (7) Remove the rotor and sh aft from the distrib-
utor housing. (8) Remove the retainer from the distributor
housing and withdraw the pickup coil. (9) Remove the retaining sc rews and remove the
control module from the distributor body. (10) Carefully lever the stationary pole from the
housing using a suitable screwdriver. Assembly is a reversal of the dismantling proce-
dure with attention to the following points:
(1) Ensure that the mating surfaces of the dis-
tributor housing and the control module are clean.
(2) Apply a silicone heat sink compound to the
surfaces between the control module and the distrib-
utor housing.
IGNITION COIL
To Test
(1) Disconnect the grey wiring connector and the
black wiring connector from the ignition coil in that
order. (2) Measure the resistance between coil terminal
I and the coil body. There should be a high resistance. (3) Measure the resistance between coil termi-
nals 2 and 4. There should be a low resistance. (4) Measure the resistance between coil terminal
3 and the high tension termin al. The resistance should
be other than infinity.
If any of the tests indicate a fault, renew the
ignition coil.
To Remove and Install
(1) Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
(2) Disconnect the grey wiring connector and the
black wiring connector from the ignition coil in that
order. Disconnect the high tension lead. (3) Remove the coil mounting bracket retaining
bolts and remove the coil and bracket from the
engine. Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure.
ELECTRONIC SPARK TIMING
To Test - Code 42
(1) Erase the self diagnosis code memory as
previously described. (2) Start and run the engine at idle speed for 60
seconds or until the ECM warning lamp lights.
(3) Stop the engine, switch the ignition On and
connect a jumper lead between terminals A and B on
the diagnostic link connector . Note any fault codes
displayed. If code 42 is displayed, proceed to operation (4).
If code 42 is not displayed, but was displayed
when the self diagnosis test procedure was originally
performed, an intermittent fault is indicated. Proceed
as follows:
(a) Check for faulty wiri ng connections. Check
that all wiring connectors are clean and secure.
(b) Check that all earth wires are secure.
(4) With the ignition switched Off, disconnect
the control unit wiring connectors. (5) With the ignition switched On, measure the
resistance between the contro l unit wiring connector
terminal D4 and a good earthing point. The resistance
should be less than 500 ohms.
If the ohmmeter reading is as specified, check the
wiring harness between the distributor 4 pin wiring
connector terminal D and the control unit wiring
connector terminal D4 for continuity. Repair or
renew the wiring harness as necessary. Also ensure
that the distributor 4 pin wiring connector is making
good contact when connected to the distributor.
If no fault can be found, renew the ignition
control module.
If the resistance is as specified proceed as follows.
(6) With the lead of a test lamp connected to the
positive battery terminal, backprobe the control unit
wiring connector terminal D5.
If the test lamp does not light, proceed to
operation (7).
If the test lamp lights, disconnect the 4 pin wiring
connector from the distributor. If the test lamp
remains illuminated check the wiring harness between
the distributor 4 pin wiring connector terminal B and
the control unit wiring connector terminal D5 for
shorts to earth. Repair or renew the wiring harness as
necessary. If the test lamp extinguishes, renew the
ignition system control module.
(7) Connect an ohmmeter between the control
Installed view of the ignition coil showing the coil
terminal identification.