1987 NISSAN PULSAR oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 11 of 238

General Information 11
Lifting Equipment
When using lifting equipment to lift heavy com-
ponents such as the engine and/or transmission, use
metal slings or chain in preference to rope. If rope
must be used, ensure that it is not placed against sharp
edges on the component.
Automotive Lubricants and Solvents
Avoid prolonged skin contact with oils, greases
and solvents as some can cause skin irritations and
dermatitis.
Exercise caution when us ing cleaning solvents as
many are inflammable. Do not smoke. Keep naked
flames and sparks clear of the work area.
Compressed Air
Never point an air hose at another person or allow
compressed air to blow onto your skin. High pressure
air forced against the skin can enter the bloodstream
and prove fatal.
Suspension and Steering Components
Damaged suspension and steering components
should not be welded. Many of these components are
fabricated from toughened metals. If welded they may
lose their strength or become brittle. Damaged com-
ponents should be renewed.
Air Conditioning
Avoid disconnecting air conditioning hoses as
escaping refrigerant can cause frostbite. The refriger-
ant is highly flammable and when burnt, a poisonous
gas is produced.
VEHICLE SAFETY
To prevent damage to the vehicle during servicing
or repair work, note the following precautions.
Brake Fluid
If spilt on the vehicle paintwork, brake fluid
should be immediately washed away with clean water
and allowed to dry naturally, not wiped with a cloth.
Catalytic Converter
The following should be observed to prevent
damage to the catalytic converter:
Do not operate the vehicle on leaded fuel.
Do not push or tow start the vehicle.
Do not allow the engine to idle for prolonged
periods.
Do not switch the ignition off while the vehicle is
in motion and the transmission is in gear.
Do not 'prime' the engine by pouring fuel into the
inlet manifold.
Do not operate the vehicle if the engine is
misfiring.
Avoid running the vehicle out of fuel.
Ensure that the engine oil is formulated to contain
low phosphorus levels.
Electronic Components
The electronic components of the ignition and
fuel injection systems can be damaged by the use of
incorrect testing equipment.
It is essential in all tests where voltage or resis-
tance is to be measured that a digital display multi-
meter with a minimum 10 megohm input impedance
be used.
Some types of tachometers, timing lights and
ignition system analyzers are not compatible with
certain engine electronic systems. It is therefore
recommended that the manufacturer of the test equip-
ment be consulted before using the equipment.
Jump starting, or being jump started by another
vehicle can cause damage to the electronic compon-
ents of the vehicle. Refer to the Roadside Trouble
shooting section for the correct jump starting proce-
dure.
3. GENERAL REPAIR PROCEDURES
SEIZED FASTENERS
Seized bolts, nuts or screws should first have a
liberal amount of penetrating oil applied. The fastener
should be left for a period of time to allow the oil to
penetrate and soften the corrosion which is causing
the binding.
Often, a sharp hammer blow to the head of the
fastener can dislodge the corrosion and permit it to be
loosened.
An impact driver, which can be fitted with a
socket or screwdriver bit, can be used to loosen a
seized fastener.
Another method is to heat the component in
which the fastener is seized. However, extreme cau-
tion should be exercised when heating aluminum
alloy components as the melting point is much lower
than that of steel.
If the above methods fail to free a seized nut,
carefully hacksaw through one side of the nut until it
can be split. Care should be taken that the threads of
the bolt or stud are not damaged.
Should a bolt or stud break below the surface of
the component, it will be necessary to use a screw
extractor to remove the remaining part. Follow the
screw extractor manuf acturers instructions.
Tap and die set and assorted screw extractors.
Page 12 of 238

12 General Information
Damaged threads can be repaired using a die nut
on studs and bolts, and a tap on nuts and threaded
holes in castings. If the threads of a threaded hole are
damaged beyond repair, it will be necessary to drill
and tap the hole to a larger size. Alternatively, a
Helicoil insert can be used to Testore the hole to the
original thread size.
STUDS
The simplest method for removing studs is to lock
two nuts together on the threaded section. The stud
should then be able to be removed by applying an
unscrewing action to the lower nut.
Alternatively, there are various makes of stud
extracting tools available.
Using two nuts locked together to remove a stud.
OIL SEALS
Oil seals can usually be removed by levering out
with a flat screwdriver or other suitable lever. Care
should be taken not to damage the surface of the
component which the seal lip runs on.
Seals can also be removed by inserting a number
of self tapping screws into the seal body. The seal can
then be withdrawn using pliers gripping the self
tapping screws.
Always apply a smear of grease or oil to the seal lip
prior to installation to provide initial lubrication.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals should always be
installed with the lip facing inwards or towards the
substance to be sealed. Duri ng installation, the seal l i p
should be protected from damage from sharp com-
ponents such as shaft splines by wrapping tape around
the sharp edges.
Install the new seal using a wooden block, or a
socket or length of tube of the appropriate diameter.
Ensure that the seal is installed squarely or distortion
and subsequent leakage may occur. If an installation
depth is not specified, th e seal should be installed
flush with the component surface.
GASKETS
When separating mating components (i.e.
cylinder
head and cylinder block), do not insert screwdrivers or
similar levers between the components in an attempt
to lever them apart. This can cause severe damage to
the sealing surfaces, particularly if the components are
made of alloy compounds.
The components can be separated by tapping
along the joint with a soft faced hammer or piece of
wood. Before installing a new gasket, the mating
surfaces should be cleaned of all traces of old gasket
material and sealant.
Check that the new gasket is correct by comparing
the bolt holes and passages on the component face
with the openings in the gasket.
Cork and paper gaskets which have been stored
for some time may suffer from shrinkage. This can be
rectified by soaking the gasket in water.
BEARINGS AND BUSHES
If the correct equipment is not available when
removing and installing bearings and bushes, it is
often possible to improvise.
Bearings can often be removed from shafts by
tapping alternately on opposite sides with a hammer
and drift.
A simple bush installing tool using a bolt, nut and two
washers.
If a press is unavailable, bushes can be installed by
placing the bush and component between the jaws of a
vice and screwing the jaws together until the bush is
fully inserted. A vice can also be used to remove
bushes by using suitably sized spacers against either
vice jaw, one bearing on the bush and the other on the
component. This method can also be used with a G
clamp.
A simple removing and installing tool can be
made using a long bolt, large and small washers, a nut
and a tubular spacer. Refer to the illustrations for the
method and applications.
Rubber bushes and bushes in blind holes can be
removed using an expanding type masonry bolt
(Rawlbolt Loxin). Install a neat fitting masonry bolt to
the bush. Install and tighten the bolt until it grips the
bush. The bolt and bush can then be removed using a
slide hammer or levers.
Page 14 of 238

14
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
SPECIFICATIONS
CAPACITY AND GRADE
Engine:
Lubricant........................................... 15W-50 SF
Sump capacity including filter ........... 3.3 liters
Cooling system capacity............................ 6.0 liters
Manual transaxle:
Lubricant....................................... 80W-90 GL-4
Capacity ............................................... 2.7 liters
Automatic transaxle:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 6.0 liters
Power steering:
Lubricant.............................................. Dexron II
Capacity ............................................... 1.0 liters
Manual steering lubricant ........ Castrol EPLl grease
Brake fluid type ................................................ Dot 4
1. HOW TO GREASE AND OIL CHANGE
(1) Run the front of the vehicle onto car ramps
and stop the engine. Chock the front wheels. (2) Raise the rear of the vehicle and place
chassis stands under the rear jacking points.
NOTE: It is best if the vehicle is kept as level
as possible to avoi d false readings when
checking the lubricant levels.
(3) Clean around the engine sump drain plug.
(4) Place a drain tin under the engine sump,
remove the engine sump drain plug and allow the
engine sump to completely drain.
NOTE: It is best to drain the engine sump
with the oil at operating temperature. How-
ever, if the oil is hot take care to avoid
scalding.
(5) Check that the sealing gasket on the sump
plug is in a serviceable condition. (6) When the engine sump has completely
drained, install and firmly tighten the sump drain plug.
Wipe around the plug after installation. (7) Place the drain tin under the oil filler,
remove the oil filter using a filter removal tool and
allow the residual engine oil to drain. Smear the
scaling ring of the new filter with engine oil and
lighten the filter by hand as per the instructions
supplied with the new filter.
NOTE: Before installing the new filter, en-
sure that the sealing gasket from the old
filter has not adhered to the filter sealing
surface on the engine.
(8) Remove the level checking plug from the
Location of the engine sump drain plug.
Removing the engine oil filter using a filter removal tool.
Page 25 of 238

25
ENGINE TUNE-UP
CAUTION: To prevent severe electrical shock, extreme care must be taken when
working on or near the electronic ignition system as dangerous high tension voltages
are produced in both the primary and secondary circuits. See the text fo\
r
precautionary notes.
1. TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS
Firing orde r................................................... 1 -3-4-2
Spark plugs:
Type .............................................NGK BPR 6ES
Gap ........................................................... 1.1 mm
Tightening torque...................................... 20 Nm
Ignition timing with diagnostic link
connector jumped........................... 10 deg BTDC
Idle speed (ECU controlled):
Manual transaxle 1.8 liter ............ 850 ± 50 rpm
Manual transaxle 1.6 liter............800 ± 50 rpm
Automatic transaxle
(Park or Neutral).......................... 825 ± 50 rpm
Drive belt deflection:
Alternator ........................................... 14-16 mm
Power steering pump ......................... 14-16 mm
Air conditioner compressor .................. 9-11 mm
NOTE: When performing an engine tune-
up, a/ways compare the above Specifications
with the emission control information label
inside the engine compartment.
2. TUNE-UP OPERATIONS
Special Equipment Required:
To Test Compression — Compression gauge
TO SERVICE AIR CLEANER
The air cleaner is equipped with a paper element.
The element should be regu larly inspected but should
not be cleaned in service.
The element should be renewed every 40 000 km.
This distance is only a guide for normal operating
conditions and should be reduced accordingly if the
vehicle is operating under ex tremely dusty conditions.
NOTE: Paper air cleaner elements should
not be washed in petrol or any other type of
cleaning solvent. If the element has been
washed in solvent or has become oil soaked,
it should be discarded and a new element
installed.
1.8 Liter Engine
(1) Release the clamp securing the air intake
hose to the throttle body and disconnect the throttle
cable from the support bracket. (2) Release the clips reta ining the upper air
cleaner housing to the lowe r air cleaner housing and
raise the upper housing while disconnecting the air
intake hose from the throttle body. Remove the air
cleaner element.
The air cleaner element should be renewed at 40 000
km intervals. 1.8 liter engine.
(3) Clean the inside of the air cleaner housing
using a damp rag to remove all traces of dust and
check the upper housing and air inlet hose for cracks
and air leaks. Renew if necessary. (4) Install a new air cleaner element to the lower
housing ensuring that the element is correctly seated
around the edges. (5) Install the upper housing and lock the clips,
securing it to the lower housing. Connect the air
intake hose to the throttle body and the throttle cable
to the support bracket. Tighten the hose clamp
securely. (6) Start the engine and check the air cleaner
assembly for air leaks.
Page 27 of 238

Engine Tune-up 27
move the alternator or power steering pump as
required until the drive belt concerned has the
specified deflection.
On models with air conditioning, loosen the nut
in the centre of the idler pulley and turn the adjusting
bolt until the drive belt has the specified deflection.
(3) Tighten the alternator or power steering
pump bolts securely and check the belt tension.
On models with air conditioning, tighten the idler
pulley nut securely.
TO SERVICE SPARK PLUGS
The spark plugs should be renewed at intervals of
40 000 km.
Before removing the spark plugs ensure that the
area around each plug is cl ean to prevent foreign
matter entering the cylinder when the plugs are
removed.
Spark plugs removed from an engine in good
mechanical condition should have a light powdery
deposit ranging from light brown to grayish tan in
color. After considerable service the electrodes will
show signs of wear or no rmal burning. Spark plugs
showing a thick black oily deposit indicate an engine
in poor mechanical condition or possibly, that a plug
with too low a heat range has been installed.
Spark plugs showing a white or yellowish deposit
indicate sustained high speed driving or possibly that
plugs with too high a heat range have been installed,
particularly when these deposits are accompanied by
blistering of the porcelain and burning of the elec-
trodes.
If the spark plugs are to be cleaned, use a
sandblasting machine and blow clean with com-
pressed air. Ensure that all traces of abrasive grit are
removed from the spark plug threads and from the
well in the plug body. Carefully open the electrode gap
a little, by bending the side electrode, and lightly file
the electrodes flat with a points file.
Black damp deposits can be caused by excessive oil
consumption or incorrect plug type. Spark plugs in this
condition are usually not firing.
Cutaway view of spark plug showing a crack in the
insulator nose which can be caused by exerting pres-
sure against the centre electrode when adjusting the
gap. The other crack shown on the insulator is caused
by tilting the plug spanner.
When plug electrodes are eroded to this degree the
spark can be considered worn out and should be
renewed using a plug of the recommended heat range
.
CRACK
Page 28 of 238
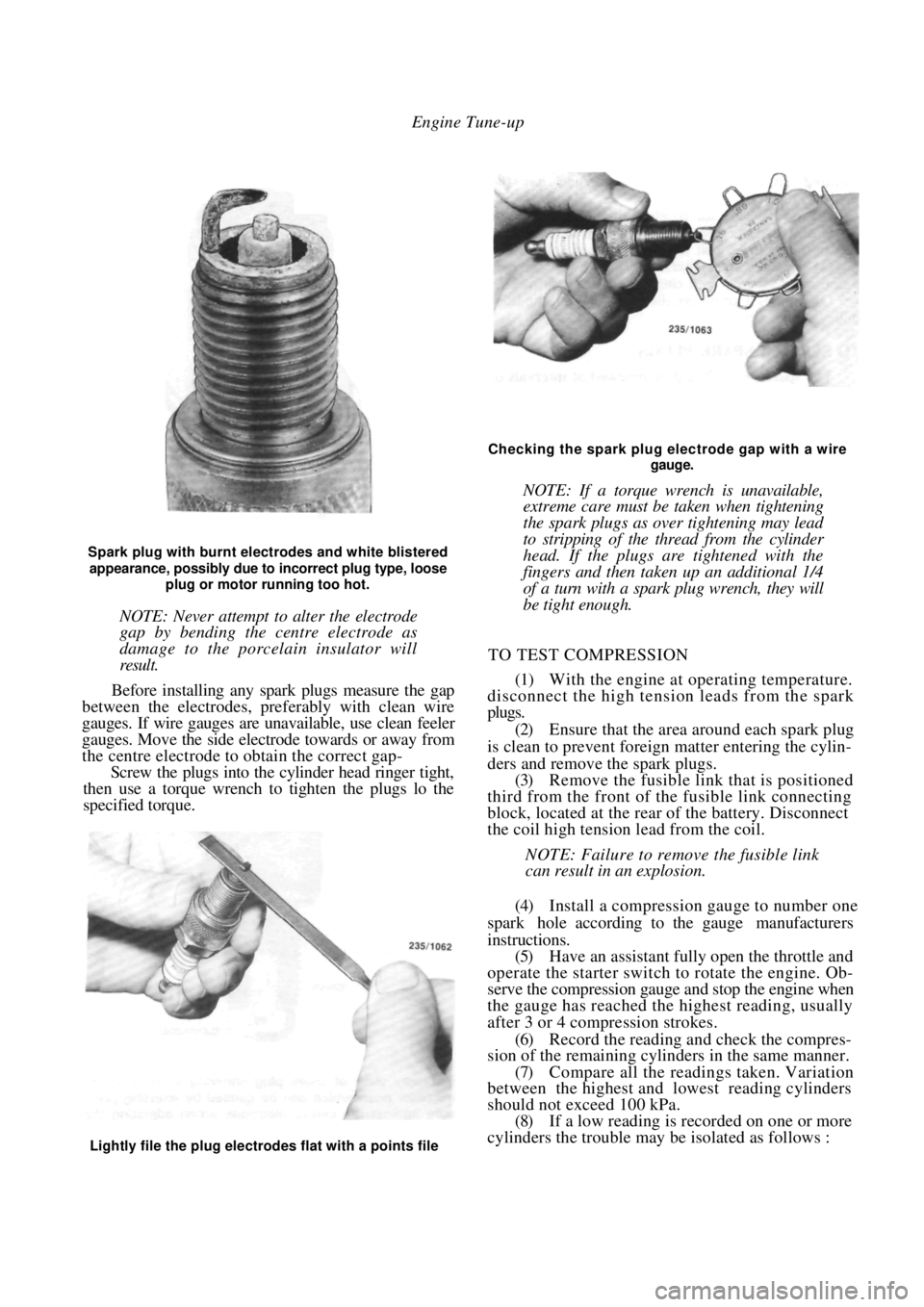
Engine Tune-up
Spark plug with burnt electrodes and white blistered
appearance, possibly due to incorrect plug type, loose
plug or motor running too hot.
NOTE: Never attempt to alter the electrode
gap by bending the centre electrode as
damage to the porcelain insulator will
result.
Before installing any spark plugs measure the gap
between the electrodes, pref erably with clean wire
gauges. If wire gauges are una vailable, use clean feeler
gauges. Move the side electrode towards or away from
the centre electrode to obtain the correct gap-
Screw the plugs into the cylinder head ringer tight,
then use a torque wrench to tighten the plugs lo the
specified torque.
Checking the spark plug electrode gap with a wire
gauge.
NOTE: If a torque wrench is unavailable,
extreme care must be taken when tightening
the spark plugs as over tightening may lead
to stripping of the thread from the cylinder
head. If the plugs are tightened with the
fingers and then taken up an additional 1/4
of a turn with a spark plug wrench, they will
be tight enough.
TO TEST COMPRESSION
(1) With the engine at operating temperature.
disconnect the high tension leads from the spark
plugs.
(2) Ensure that the area around each spark plug
is clean to prevent foreign matter entering the cylin-
ders and remove the spark plugs. (3) Remove the fusible link that is positioned
third from the front of th e fusible link connecting
block, located at the rear of the battery. Disconnect
the coil high tension lead from the coil.
NOTE: Failure to remove the fusible link
can result in an explosion.
(4) Install a compression gauge to number one
spark hole according to the gauge manufacturers
instructions. (5) Have an assistant fully open the throttle and
operate the starter switch to rotate the engine. Ob-
serve the compression gauge and stop the engine when
the gauge has reached the highest reading, usually
after 3 or 4 compression strokes.
(6) Record the reading a nd check the compres-
sion of the remaining cylinders in the same manner.
(7) Compare all the readings taken. Variation
between the highest and lowest reading cylinders
should not exceed 100 kPa. (8) If a low reading is recorded on one or more
cylinders the trouble may be isolated as follows :
Lightly file the plug electrodes flat with a points file
Page 30 of 238

30 Engine Tune-up
(1) With the distributor cap and leads removed
as an assembly, test one lead at a time, connecting the
meter probes at the spark plug end of the lead and at
the corresponding terminal in side the cap. Resistance
should be less than 15 000 ohms.
(2) If the resistance is more than 15 000 ohms
remove the lead from the distributor cap and check
(he resistance in the lead only. The lead should be
renewed if the resistance is still more than 15 000
ohms. (3) High distributor cap resistance may be due
to corrosion deposits on the cap terminals. These
deposits should be removed with a small scraper or
emery cloth. Check the distributor cap for cracks or tracking
between the high tension terminals on both the inside
and outside of the cap. Renew the cap if cracks or
tracking are evident.
Check the carbon brush in the centre of the
distributor cap for evidence of arcing and renew as
necessary.
Check the condition of the rotor and renew if
arced excessively or cracked.
HOW TO CONNECT ELECTRICAL TEST
EQUIPMENT
NOTE: Some types of tachometers, timing
lights and ignition system analysers are not
compatible with this type of electronic igni-
tion system and may result in incorrect
readings. It is therefore recommended that
the manufacturer of the test equipment be
consulted before using the equipment.
Do not allow the tachometer lead connec-
tor to short to earth as damage to the test
equipment or ignition system may result.
Timing Light
(1) Connect the timing light to the engine fol-
lowing the instrument manufacturers instructions.
NOTE: Do not connect or disconnect the
timing light with the engine running as
voltage surges could damage the alternator.
Do not allow the high tension leads to open
circuit as damage to the ignition system
could result.
(2) Where necessary, connect the power leads of
the timing light to an external power source to prevent
possible transient voltages in the timing light damag-
ing the vehicle alternator.
Tachometer
(1) Ensure that the tachometer is compatible
with the vehicle ignition system. (2) Disconnect the resistor from the tachometer
View showing the location of the tachometer pickup
wiring connector with the resistor installed
.
pick up wiring connector which is located on the
ignition coil wiring harness, and connect the positive
lead of an accurate tachometer to the brown wire
terminal in the wiring connector.
(3) Connect the negative lead to a good earthing
point.
TO CHECK AND ADJUST IGNITION TIMING
( 1 ) Connect an accurate tachometer and timing
light to the engine as previously described.
View showing the location of the diagnostic link
connector. Passengers seat removed for clarity.
Inset shows the diagnostic link connector terminal
identification.
(2) Start the engine and allow it to reach normal
operating temperature. (3) Connect a jumper lead between terminals A
and B on the diagnostic link connector. (4) With the engine idling at the specified speed,
check the ignition timing with the timing light.
Correct timing exists when the marks on the
crankshaft pulley are aligned with the pointer on the
inner timing cover.
Page 38 of 238

38 Engine
*Piston skirt to cylinder bore clearance:
1.6 liter .....................................0. 020-0.040 mm
1.8 liter .....................................0. 010-0.030 mm
Gudgeon pin length:
1.6 liter ...................................................... 53 mm
1.8 liter .................................................. 61.5 mm
Gudgeon pin diameter.................20.990-20.995 mm
Gudgeon pin clearance in piston:
1.6 liter .....................................0. 010-0.020 mm
1.8 liter ..................................0. 0055-0.0115 mm
Gudgeon pin offset in piston:
1.6 liter......... 0.35-0.65 mm towards thrust side
1.8 liter................... 0.8 mm towards thrust side
*Measured 9 mm from the bottom of the piston skirt
for 1.6 liter models and 6 mm from the bottom of the
piston skirt for 1.8 liter models.
PISTON RINGS
Rings per piston:
Compression .......................................................2
Oil contro l .......................................................... 1
End gap:
Compression ................................ 0.30-0.50 mm
Oil control —
1.6 liter ......................................... 0.33-1.10 mm
1.8 liter ......................................... 0.40-1.40 mm
CONNECTING RODS AND BEARINGS
Connecting rod side clearance............ 0.07-0.24 mm
Maximum connecting rod weight variation..8 grams
Crankpin bearing oil clearance ....... 0. 019-0.063 mm
CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN BEARINGS
Number of bearings .................................................. 5
End float taken at ...................... No. 3 main bearing
End float .......................................... 0.070-0.302 mm
Bend limit ...................................................0.03 mm
Main bearing oil clearance .............0. 015-0.040 mm
Main bearing journal diameter.. .57.982-57.995 mm
Crankpin diameter .......................48.971-48.987 mm
FLYWHEEL
Ring gear run out limit.................................. 0.3 mm
Clutch face regrind limit .............................. 0.3 mm
CAMSHAFT
Drive ...................................................... Toothed belt
End float .............................................. 0.04-0.14 mm
Bend limit ................................................... 0.03 mm
Bearings ...........................................Direct in housing
Journal diameter:
Standard —
No. 1 ..................................... 42. 455-42.470 mm
No. 2 ..................................... 42. 705-42.720 mm
No. 3 ..................................... 42.955-42.970 mm
No. 4 ..................................... 43.205-43.220 mm
No. 5 ..................................... 43.455-43.470 mm
Undersize —
No. 1 .....................................42.355-42.370 mm
No. 2 ......................................42.605-42.620 mm
No. 3 .....................................42.855-42.880 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.105-43.120 mm
No. 5 .....................................43. 355-43.370 mm
*An undersize camshaft can be identified by a violet
flash between the inlet and exhaust lobes of No. 2
cylinder.
Housing diameter;
Standard —
No. 1 .....................................42. 500-42.525 mm
No. 2 .....................................42.750-42.775 mm
No. 3 .....................................43.000-43.025 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.250-43.275 mm
No. 5 .....................................43.500-43.525 mm
*Undersize —
No. 1 .....................................42.400-42.425 mm
No. 2 .....................................42.650-42.675 mm
No. 3 .....................................42.900-42.925 mm
No. 4 ......................................43.150-43.175 mm
No. 5 .....................................43.400-43.425 mm
*An undersize camshaft housing can be identified by
a violet flash on the centre camshaft bearing support.
LUBRICATION
Oil pump type .......................................Involute gear
Filter type................................... Full flow disposable
Oil pressure at 4 000 rpm .....................480-620 kPa
Rotor assembly end float .................. 0.03-0. 010 mm
Rotor teeth backlash ......................... 0.010-0.20 mm
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
*Cylinder head bolts:
Initial torque ............................................. 25 Nm
1st stage ......................................... + 60 degrees
2nd stage ........................................ + 60 degrees
3rd stage......................................... + 60 degrees
4th stage, engine at operating
temperature .............................. + 30-50 degrees
Exhaust manifold nuts .................................... 22 Nm
Exhaust manifold flange nuts ......................... 22 Nm
Inlet manifold nuts.......................................... 22 Nm
Throttle body to inlet manifold nuts ..............12 Nm
Camshaft liming gear bolt ...............................45 Nm
Camshaft retainin g plate bolts ......................... 7 Nm
Camshaft cover bolts......................................... 8 Nm
Thermostat cover bolts ....................................15 Nm
*Main bearing bolts..................60 Nm + 45 degrees
Connecting rod bearing
cap nuts ................................... 35 Nm + 45 degrees
* Crankshaft timing
gear bolt.................................. 145 Nm + 35 degrees
*Flywheel bolts
(microencapsulated) ................ 60 Nm + 30 degrees
*Drive plate bolts (microencapsulated)........... 60 Nm
Water pump bolts............................................ 25 Nm