1987 NISSAN PULSAR torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 177 of 238

Brakes 177
installed. Install the second back up ring, large
diam-
eter first.
(6) Install the second garter spring. Insert
a
machined drift into the bore and lightly push the
garter spring into its locating groove.
(7) Smear the secondary piston with clean brake
fluid. Ease the seal over the piston body into the
groove adjacent to the spring, ensuring that the seal lip
faces the spring and that the nylon spacer is against
the back of the seal. (8) Install the guide onto the secondary
piston,
large internal diameter first, followed by the main seal
with the lip facing away from the spring. (9) Lubricate the secondary piston assembly
with clean brake fluid and install the secondary spring
and retainer to the piston. Install the complete assem-
bly into the master cylinder bore. (10) Smear the primary piston with clean brake
fluid. Install the guide, large internal diameter first,
followed by the main seal with the lip facing towards
the small end of the piston.
(11) Install the retainer to the spigot on the front
end of the primary piston ensuring that the legs of the
retainer engage with the groove on the piston. (12) Lubricate the primary piston assembly with
clean brake fluid and install the assembly into the
master cylinder bore. With a blunt rod, push the
assembly down the bore sufficiently to preload the
pistons. While holding the preload, install the stop pin
and valve assemblies into
the master cylinder body and tighten securely. (13) Install a new O ring to the groove on the boss
of the mounting flange of the master cylinder.
(14) Install new O rings to th e pressure differential
pistons, smear them with cl ean brake fluid and install
them into the master cylinder body. (15) Install a new O ring to the pressure differen-
tial end plug, install the plug to the master
cylinder
body and tighten to the specified torque. (16) Using a blunt probe entered through the
sensing switch location hole, separate the pressure
differential pistons and install the switch actuating
lever between them. (17) Screw the sensing switch into its locating
hole until the detents on the switch body just contact
the locating hole facing (w ith the radial grooves).
Screw the switch assembly in a further half to one full
turn ensuring that the dete nts locate in the grooves.
(18) Install new valve seal s to the proportioning
valve plungers, with the serrations of the seals facing
away from the hexagons of the plungers.
(19) Install the new O rings to the
proportioning
valve plugs. (20) Install the valve springs over the stems of the
proportioning valves, insert the install the valve
plugs.
Tighten the plugs to the specified torque.
(21) Install a new O ring to the base of the fast fill
valve assembly. Install a new valve washer to the base
of the valve.
(22) Install the fast fill valve assembly in
the
primary reservoir port (nearest to the mounting flange
of the master cylinder) and install the snap ring
to
retain the assembly. Ensure that the snap ring is
correctly seated in the groove. (23) Smear the new reservoir retainers with clean
brake fluid and install them into the reservoir ports.
Carefully press the brake fluid reservoir into position,
ensuring that the outlet extensions are fully inserted in
the reservoir retainers. (24) Install the reservoir cap insert to the dia-
phragm and press the cap assembly onto the reservoir.
TO INSTAL
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Pour a small amount of clean brake fluid into
the reservoir and pump the master cylinder pistons
with a blunt rod until fluid begins to emerge from the
outlets. (2) Install the master cylinder to the brake servo
unit and loosely install the master cylinder retaining
nuts. (3) Connect the brake pipes to the master cylin-
der outlets, but do not tighten at this stage. (4) Securely tighten the nuts retaining the master
cylinder to the brake servo unit.
(5) Securely tighten the brake pipes and connect
the wiring to the pressure sensing switch.
(6) Fill the master cylinder reservoir with clean
brake fluid and bleed the brakes as described under
the Hydraulic System heading. (7) Check and if necessary adjust the brake
pedal height and free play as described under the
Brake Pedal heading.
4. BRAKE SERVO UNIT
TO CHECK OPERATION
(1) With the engine switched off, apply the
footbrake several times to exhaust all vacuum from
the system.
(2) Apply the footbrake and hold the brake pedal
fully depressed.
(3) Start the engine. If the servo unit is function-
ing satisfactorily a distinct downward movement of
the
brake pedal should be noticed. Should the pedal fail to move downward when the
engine has been started, the vacuum system can be
considered inoperative.
NOTE: If the pedal continues to fall away
there is a fault in the hydraulic system.
(4) Ensure that the brake pedal is fully released,
start the engine and run it at medium speed. Stop the
engine.
Page 179 of 238
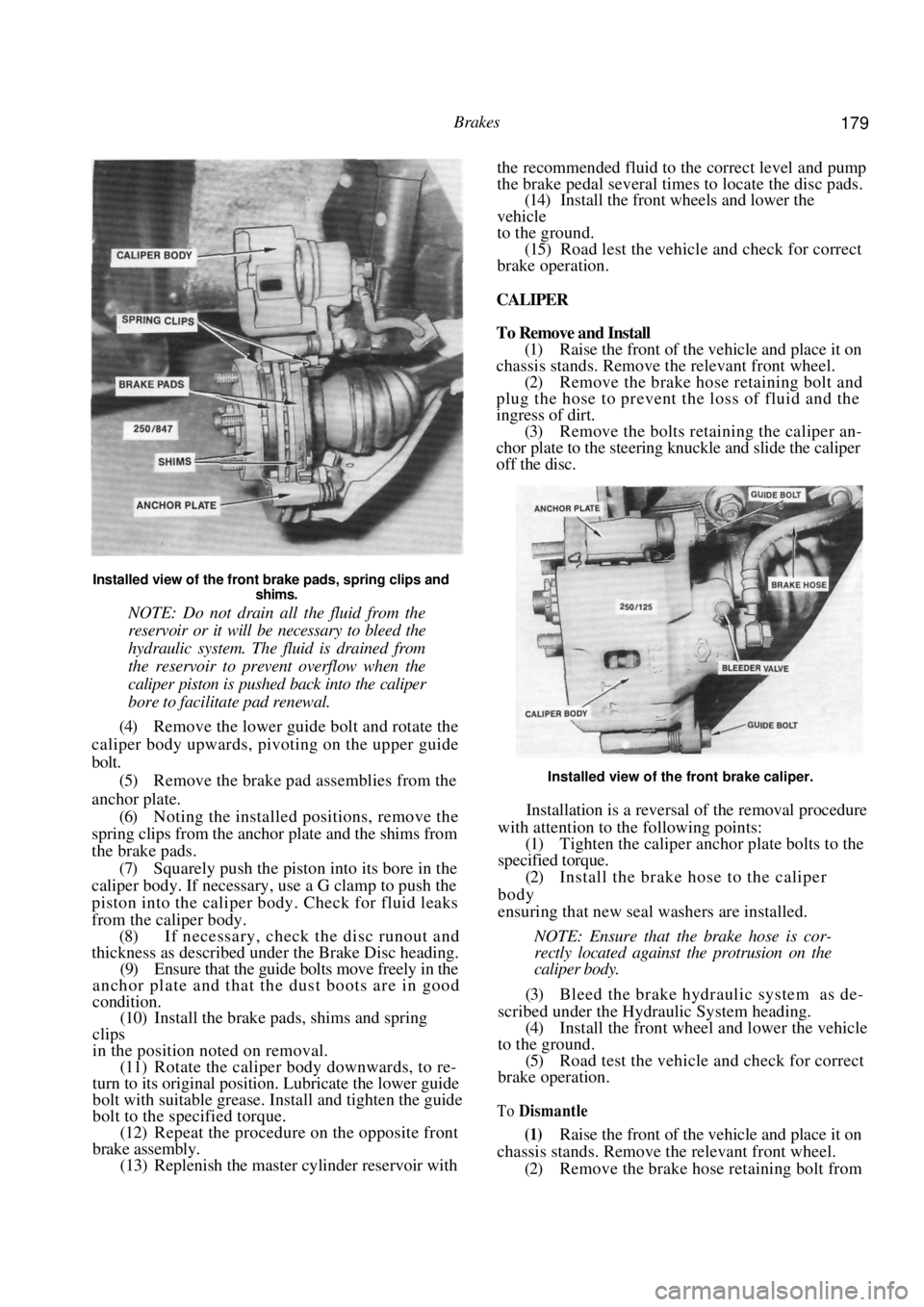
Brakes 179
Installed view of the front brake pads, spring clips and shims.
NOTE: Do not drain all the fluid from the
reservoir or it will be necessary to bleed the
hydraulic system. The fluid is drained from
the reservoir to prevent overflow when the
caliper piston is pushed back into the caliper
bore to facilitate pad renewal.
(4) Remove the lower guide bolt and rotate the
caliper body upwards, pivoting on the upper guide
bolt.
(5) Remove the brake pad assemblies from the
anchor plate. (6) Noting the installed positions, remove the
spring clips from the anchor plate and the shims from
the brake pads.
(7) Squarely push the piston into its bore in the
caliper body. If necessary, us e a G clamp to push the
piston into the caliper b ody. Check for fluid leaks
from the calip er body.
(8) If necessary, check the disc runout and
thickness as described under the Brake Disc heading.
(9) Ensure that the guide bolts move freely in the
anchor plate and that the dust boots are in good
condition. (10) Install the brake pads, shims and spring
clips
in the position noted on removal. (11) Rotate the caliper body downwards, to re-
turn to its original position. Lubricate the lower guide
bolt with suitable grease. In stall and tighten the guide
bolt to the specified torque. (12) Repeat the procedure on the opposite front
brake assembly. (13) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with the recommended fluid to the correct level and pump
the brake pedal several times to locate the disc pads.
(14)
Install the front wheels and lower the
vehicle
to the ground. (15) Road lest the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
CALIPER
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel. (2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt and
plug the hose to prevent the loss of fluid and the
ingress of dirt. (3) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-
chor plate to the steering knuckle and slide the caliper
off the disc.
Installed view of the front brake caliper.
Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Tighten the caliper anch or plate bolts to the
specified torque.
(2) Install the brake hose to the caliper
body
ensuring that new seal washers are installed.
NOTE: Ensure that the brake hose is cor-
rectly located against the protrusion on the
caliper body.
(3) Bleed the brake hydraulic system as de-
scribed under the Hydraulic System heading. (4) Install the fron t wheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. (5) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
To Dismantle
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel.
(2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt from
Page 180 of 238

180 Brakes
the caliper body. Plug the brake hose to prevent the
loss of fluid and the ingress of dirt. Remove and
discard the sealing washers.
(3) Remove the guide bolts and slide the caliper
body from the anchor plate and pad assembly. (4) Remove the piston dust cover retaining clip.
Remove and discard the dust cover.
BRAKEPAD BRAKE PAD
Dismantled view of the front brake caliper.
(5) Place a piece of wood in front of the piston
and using low air pressure applied to the brake hose
aperture, gently force the piston from the caliper bore.
(6) Using a thin blunt probe, preferably made
from wood or plastic, remove and discard the piston
seal from the groove in the caliper bore. (7) Clean all the caliper components in methyl-
ated spirits and arrange the components in order, on
a clean, dry surface to aid in assembly.
To Inspect
(1) Inspect the caliper bore and piston for pit-
ting, wear or damage. Renew the caliper assembly or
piston if damage is evident.
NOTE: Slight rust spots in the caliper bore
may he removed with fine emery paper. The
piston must not be polished as the plated
surface wilt be damaged.
(2) Inspect the guide bolts for wear or damage.
Renew as necessary.
To Assemble
(1) Dip a new piston seal in clean hydraulic
brake fluid. Insert the seal into the groove in the
caliper bore ensuring that the seal is correctly seated
and not twisted.
(2) Install a new dust cover to the piston prior to
installing the piston to the caliper bore. (3) Coat the piston and caliper bore with clean
hydraulic brake fluid and insert the piston squarely
into the caliper bore.
(4) Locate the dust seal in the groove of the
caliper body and install the retaining clip.
(5) Lubricate the guide bolts using a suitable
grease. Install the caliper body to the anchor plate and
install and tighten the guide bolts to the
specified
torque. (6) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with
the recommended fluid and bleed the brakes as
described under the Hydr aulic System heading.
(7) Install the front wheels and lower the vehicle
to the ground. (8) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
BRAKE DISC
To Check Runout
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the relevant front wheel. (2) Install the wheel nuts with the flat side of
the
wheel nut towards the disc. Lightly tighten the nuts to
secure the disc against the hub.
Rotate the hub and check for disc runout.
(3) Mount a dial gauge stand to a suspension
component and position the dial gauge plunger
against the wheel hub. Check that the end float is less
than 0.05 mm. Excessive e nd float will necessitate
renewal of the hub bearing. (4) Position the dial gauge plunger against the
centre of the brake disc. Ro tate the hub and measure
the runout. Maximum allowable runout is 0.07 mm. (5) If the runout exceeds Specifications, machine
or renew the brake disc. (6) Install the fron t wheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground.
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the relevant wheel. (2) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-
Page 182 of 238

182 Brakes
Illustration of the rear disc caliper showing the correct
piston alignment.
(9) Install the brake pads, shims and spring
clips
in the position noted on removal. (10) Install the caliper body to its original posi-
tion. Lubricate the guide bolts with suitable grease.
Install and tighten the guide bolts to the specified
torque. (11) Repeat the procedure on the opposite rear
brake assembly.
(12) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with
the recommended fluid to the correct level and pump
the brake pedal several times to locate the disc pads. (13) Install the rear wheels and lower the vehicle
to the ground. (14) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
CALIPER
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant rear wheel. (2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt from
the caliper body and plug the hose to prevent the
loss of fluid and the ingress of dirt.
Installed view of the rear brake caliper.
(3) Remove the handbrake cable bracket retain-
ing bolts and disconnect the handbrake cable from the
cam lever. (4) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-
chor plate. Remove the caliper from the disc. Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Tighten the caliper anch or plate bolts to the
specified torque. (2) Install the brake hose to the caliper body
ensuring that new seal washers are installed.
NOTE: Ensure that the brake hose locating
pin is correctly installed in the caliper body.
de-
(3) Bleed the brake hydraulic system as
scribed under the Hydraulic System heading. (4) Install the rear wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground. (5) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
Dismantled view of the rear brake caliper
Page 183 of 238

Brakes 183
To Dismantle
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and place it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant rear wheel.
(2) Remove the brake hose retaining bolt from
the caliper body and plug the hose to prevent the loss
of fluid and the ingress of dirt. (3) Remove the handbrake cable bracket retain-
ing bolt and disconnect the handbrake cable from the
cam lever.
(4) Remove the guide bolts and slide the caliper
body off the pads. (5) Using a pair of long nose pliers with the nose
located in the recesses of the piston, rotate the piston
anticlockwise to remove it from the caliper body.
(6) Remove the dust cover retaining clip and dust
cover. Discard the dust cover. (7) Using a thin blunt probe, preferably made
from wood or plastic, remove and discard the piston
seal from the groove in the caliper bore. (8) Using internal snap ring pliers, remove the
snap ring from the caliper bore. (9) Withdraw the spring cover, spring, key plate,
pushrod and link from the caliper bore. Do not mix
these components from the left and right hand sides as
they differ. (10) Remove and discard the O ring from the
pushrod. (11) Remove the spring, nut and washer from the
cam lever. Remove the cam lever and cam from the
caliper body. (12) Remove the cam seal from the caliper using a
screwdriver.
(13) Clean all the caliper components in methy-
lated spirits and arrange the components in order on a
clean dry surface to aid assembly.
To Inspect
(1) Inspect the caliper bore and piston for pit-
ting, wear or damage. Renew the caliper assembly or
piston if damage is evident.
NOTE: Slight rust spots in the caliper bore
may be removed with fine emery paper. The
piston must not be polished as the plated
surface will be damaged.
(2) Inspect the guide bolts for wear or damage
and renew as necessary.
(3) Inspect the threads of the pushrod for wear or
damage and renew as necessary. (4) Inspect the nut inside the piston for wear,
damage and security. Renew the piston if any damage
is evident. (5) Inspect the cam for wear, damage or pitting,
renew as necessary. (6) Inspect the cam bearing in the caliper body
for wear, damage or pitting and renew the seal and
bearing as necessary. (7) Inspect the guide bolt rubbers for deteriora-
tion, wear or damage. Renew as required. To Assemble
(1)
Lubricate the cam bearing with multipurpose
grease and install the seal. (2) Install the cam and cam lever to the
caliper
body. Install the cam lever spring, washer and nut, and
tighten the nut to the specified torque. (3) Install a new O ring to the pushrod and
install
the link, pushrod, key plate, spring and spring cover to
the caliper body. The key plate must engage the caliper
body. Secure the assembly with the snap ring. (4) Dip a new piston seal in clean hydraulic brake
fluid. Insert the seal into the groove in the caliper bore
ensuring that the seal is correctly seated and not
twisted. (5) Install a new dust cover to the piston prior
to
installing the piston to the caliper bore.
(6) Coat the piston and caliper bore with clean
hydraulic brake fluid and using long nose pliers rotate
the piston clockwise into the caliper bore. (7) Locate the dust seal in the groove of the
caliper body and install the retaining clip.
(8) Lubricate the guide bolts using a suitable
grease. Install the caliper body and tighten the guide
bolts to the specified torque. (9) Replenish the master cylinder reservoir with
the recommended fluid and bleed the brakes as
described under the Hydraulic System heading. (10) Install the rear wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground. (11) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
BRAKE DISC
To Check Runout
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and support it on
chassis stands. Remove the relevant rear wheel.
(2) Mount a dial gauge stand to a suspension
component and position the dial gauge plunger
against the wheel hub. Check that the end float is less
Using a dial gauge to measure the rear disc runout.
Page 184 of 238

184 Brakes
than 0.05 mm. If the wheel hub end float exceeds
Specifications, the bearing must be renewed as de-
scribed in the Rear Suspension section.
(3) Position the dial gauge plunger against the
centre of the brake disc contact area. Rotate the hub
and measure the runout. Ma ximum allowable runout
is 0.07 mm. (4) If the runout exceeds the specified amount,
machine or renew the brake disc. (5) Install the rear wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground. (6) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
To Remove and Install
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove the relevant rear wheel.
(2) Remove the clip securing the brake hose to
the suspension unit and disengage the hose. (3) Remove the bolts retaining the caliper an-
chor plate. (4) Slide the caliper from the brake disc and
suspend the caliper clear of the work area using wire
or cord.
NOTE: Do not allow the caliper to hang on
the brake hose.
(5) Remove the grease cap from the rear hub.
(6) Remove the split pin, nut retainer, hub nut
and washer from the stub axle. (7) Remove the hub assembly from the stud
axle. Installation is a reversal of the removal procedure
with attention to the following points:
(1) Tighten the rear hub to the specified torque.
(2) Install the brake caliper and tighten all the
bolts to the specified torque. (3) Rotate the hub and check for roughness. If
the hub does not rotate smoothly, renew the hub
bearing as described in the Rear Suspension section. (4) Install the rear wheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground.
(5) Road test the vehicle and check for correct
brake operation.
To Inspect
(1) Inspect the machined faces of the disc for
scores, cracks, wear and signs of overheating. (2) Using a micrometer, measure the thickness
of the disc at several posit ions around the face of the
disc. Renew the disc if the minimum thickness is
below Specifications.
(3) If the disc thickness is satisfactory but the
disc is scored, machine equal amounts from the
machined face on each side of the disc, to restore the
serviceability of the disc.
Inspect the machined faces of the disc for scores,
cracks, wear and signs of overheating.
NOTE: Disc machining is best entrusted to
a reliable brake specialist who can advise on
disc serviceability.
7. REAR DRUM BRAKES
TO REMOVE AND DISMANTLE
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and support it
on chassis stands. Remove th e rear wheels and release
the handbrake.
(2) Remove the grease cap from the rear hub.
(3) Remove the split pin, nut retainer, hub nut
and washer from the stub axle. Remove the brake
drum and hub assembly.
(4) Mark each brake shoe and spring to ensure
correct assembly. (5) Rotate the star wheel until the adjuster
assembly is at its shortest length.
Installed view of the left hand side rear drum brake
components.
Page 190 of 238

190
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
CAUTION: To prevent severe electrical shock extreme care must be taken when
working on or near the electronic ignition system as dangerous high tension voltages
are produced in both the primary and secondary circuits. See the text fo\
r
precautionary notes.
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY
Type ..................................................12 volt lead acid
Polarity to earth .................................... Negative ( - )
Specific gravity:
Fully charged ................................... A bove 1.250
Fully discharged ................................Below 1.130
ALTERNATOR
Make .................................................Bosch or Hitachi
Maximum output .......................................... 70 amps
Polarity to earth .................................... Negative ( - )
Stator windings ......................................... Star wound
Regulator type ................................................ Integral
Brush length minimum:
Bosch ........................................................ 5.0 mm
Hitachi ............................. 6.0 mm or limit mark
STARTER MOTOR
Make .................................................Hitach i or Bosch
Type ............................ 4 pole 4 brush reduction gear
Operation control.................................. Solenoid and
overrunning clutch
Undercut of commutator (maximum):
Hitachi ...................................................... 0.8 mm
Brush length (minimum):
Bosch ........................................................ 8.0 mm
Hitachi ........................................................11 mm
Brush spring tension;
Hitachi ............................................... 15.7-19.6 N
Hitachi:
Drive pinion stopper clearance ........ 0.3-1.5 mm
Selective fit adjuster plates ........ 0.5 and 0.8 mm
IGNITION SYSTEM
The ignition system is an integral part of the
engine management system. The Specifications, testing
and overhaul procedures are fully covered in the Fuel
and Engine Management section.
TORQUE WRENCH SETTINGS
Alternator pulley retaining nut:
Bosch ......................................................... 50 Nm
Hitachi ....................................................... 59 Nm
1. BATTERY AND CHARGING SYSTEM
TROUBLE SHOOTING
BATTERY UNDERCHARGED
3. Loose or broken drive belt: Adjust or renew
the drive belt. 4. Faulty alternator regulator; Renew the regu-
lator unit.
5. Faulty battery: Install a new battery of
the
recommended type and capacity. 6. Faulty alternator: Overhaul or renew the
alternator. 7. Fault in the charging circuit wiring: Check
and repair or renew the wiring harness. 8. Faulty connections in the charging circuit:
Check and repair the connections. 9. Fusible link blown; Rectify the fault and
renew as necessary.
NOTE: Check the state of charge (specific
gravity) of the battery- as described under
the
Battery heading in this section. If the battery
is undercharged, check the possible causes in
the order given.
BATTERY OVERCHARGED
• Faulty alternator regulator unit:
Renew the
regulator unit.
• Faulty alternator: Overhaul or
renew the
alternator. • Faulty charging circuit wiring or
connec-
tions: Check and renew or repair the faulty
compo-
nents.
NOTE: An overcharged battery is indicated
by continual loss of water through boiling.
Page 201 of 238

Electrical System 201
nosed pliers. This will safeguard the diodes
by transferring any excess heat to the jaws of
the pliers.
Using a suitable drift, install the bearing into
the drive end bracket, install the retainer plate and
screws. Tighten the screws securely. Using a suitable press and press plates, install
the bearing to the slip ring end of the rotor shaft.
Ensure that pressure is ex erted only on the inner race
and that the stop ring groove is nearest to the sl i p
rings. Ensure that the rotor sh aft rear bearing stop
ring is positioned so that the protruding part of the
ring is located in the deepest part of the groove. Install the stator, diode pack and
regulator
assembly to the slip ring e nd bracket. Install the
retaining nuts and washers and tighten securely. Install the nut and insulator to the terminal
and tighten securely. Using a piece of wire, hold the brushes in a
retracted position. Hold the drive end bracket in a soft jawed
vice and install the rotor shaft assembly to the drive
end bracket. Install the pulley, retaining nut and washer to
the rotor shaft and tighten the retaining nut to the
specified torque. Apply a heated 200 watt soldering iron to the
slip ring end bracket at the bearing mounting boss for
3-4 minutes to heat the bracket and allow the
installation of the rotor shaft rear bearing. Aligning the marks made on dismantling and
ensuring that the rotor sh aft rear bearing retaining
ring protrusion is located in the deepest part of its
groove, install the rotor/stator assembly to the slip ring
end bracket.
Remove the brush retr acting wire from the
alternator, ensure that the alternator component
marks are aligned, install the retaining through bolts
and tighten them securely. Check the alternator rotor for smooth oper-
ation and install the al ternator to the vehicle
as
previously described.
Check the alternator operation on the vehicle
as previously described.
8. STARTER MOTOR
Special Equipment Required:
To Renew Brushes — Soldering iron
To Renew Armature Bearings — Bearing puller
DESCRIPTION
Two types of starter motors are installed to the
range of vehicles covere d by this manual, either
Hitachi or Bosch.
The starter motor is the induced pole type with
four brushes and four pole shoes with field coils.
A solenoid switch is attached to the starter drive
end bracket. The solenoid plunger is connected to
the overrunning clutch and drive pinion assembly
through a lever and pivot arrangement.
When the solenoid windings are energized, the
plunger acting on the lever and pivot engages the drive
pinion with the flywheel ri ng gear and at the same
time closes the switch supplying power from the
positive lead of the battery to the starter motor field
coils and armature to operate the motor.
As the engine fires, the over-running clutch of the
drive pinion assembly prevents high speed rotation of.
and possible damage to, the starter armature if the
solenoid windings are not immediately de-energized
by releasing the ignition key.
The starter solenoid switch windings are energized
by the ignition switch.
TO TEST ON VEHICLE
Should the starter motor fail to operate when the
ignition switch is turned to the Start position, check
the following points:
Check the battery condition and state of
charge. Refer to the Battery heading for the correct
procedure.
Clean the battery terminals, taking particular
care to remove the scale from the positive ( + )
terminal post and terminal. Check the earth connection for tightness and
cleanliness.
Switch on the headlamps and turn the igni-
tion switch to Start. If the lamps dim but the starter
motor does not operate, it could indicate that a short
circuit has developed in the starting system. Check that the engine is not seized or that the
starter motor drive pinion and ring gear are not
locked as these conditions would -give the same
indications as above.
(5) If the lamps do not dim and the starter
motor does not operate, this would indicate an open
circuit such as a broken or disconnected wire or a
switch not operating.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transaxle, turn the ignition switch to Start and move
the selector lever through all the gear selection range.
If the starter motor operates in any position other
than N or P, the neutral safety switch is faulty.
(6) Check all the external wiring to ensure that
the fault is not external. If the external circuit proves
satisfactory, indicating that the problem is in the
starter motor, the unit will have to be removed and
tested.
TO REMOVE AND INSTAL
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
Disconnect the wiring from the starter motor
solenoid. Remove the starter motor mounting bolts,