1985 FORD GRANADA drain bolt
[x] Cancel search: drain boltPage 112 of 255

24Unbolt and remove the regulator from the
fuel rail. Remove the sealing O-ring and
discard it; a new one must be used on
refitting.
25Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure applying a smear of clean engine oil
to the new regulator O-ring. On models
equipped with a late level regulator, ensure
that the return pipe is securely held in position
by the retaining collar.
26On completion, switch the ignition on and
off five times without cranking the engine to
pressurise the fuel system.
27With the system pressurised check all
disturbed fuel unions for signs of leakage.
1The potentiometer is located on the right-
hand side of the engine compartment, behind
the MAP sensor.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the securing screw, then withdraw
the potentiometer and disconnect the wiring
plug.
4Refitting is a reversal of removal. On
completion adjust the idle mixture.1On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines, disconnect the
battery.
2Disconnect the switch wiring connector.
3Slacken and remove the switch from the
fuel rail (see illustration).
4Refitting is a reverse of removal, tightening
the switch to the specified torque setting.
Carburettor models
All engines except DOHC
1Remove the carburettor or, if preferred, the
final removal of the carburettor from the
manifold can be left until the manifold has
been removed).
2Drain the cooling system.
3Disconnect the coolant and vacuum pipes
from the manifold, noting their positions if
there is any possibility of confusion.
4Disconnect the wires from the manifold
heater and the coolant temperature sender
unit.
5Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose
from the manifold.
6Unscrew the six nuts and bolts which
secure the manifold and withdraw it. Recover
the gasket.
7Before refitting the manifold, make sure that
the mating surfaces are perfectly clean.
8Apply a bead of sealant at least 5 mm (0.2 in)
wide around the central coolant aperture on
both sides of a new gasket.
9Place the gasket over the studs, then fit the
manifold and secure it with the six nuts and
bolts. Tighten the nuts and bolts evenly to the
specified torque.
10The remainder of refitting is a reversal of
the removal procedure. Refill the cooling
system on completion.
DOHC engine
11Disconnect the battery negative lead.
12Drain the cooling system.13Remove the air cleaner.
14Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing and the inlet manifold,
noting the locations to assist with refitting.
15Disconnect the fuel supply and return
hoses from the carburettor. Plug their ends to
minimise petrol spillage.
16Release the coolant hose from the bracket
under the automatic choke housing.
17Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs, and move them to one side.
18Disconnect all relevant wiring and vacuum
pipes from the carburettor, thermostat
housing and inlet manifold, noting the
locations as an aid to refitting.
19Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the inlet manifold.
20Disconnect the throttle cable from the
throttle linkage.
21Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected to facilitate removal of the
manifold.
22Unscrew the ten bolts and two nuts
securing the manifold to the cylinder head.
23Lift the manifold clear of the cylinder head
and recover the gasket.
24Recover the two plastic spark plug spacers
from the recesses in the cylinder head.
25If desired, the carburettor can be removed
from the manifold by unscrewing the securing
screws.
26Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that all mating faces are clean and
renew all gaskets.
b)Ensure that the spark plug spacers are in
position in the cylinder head recesses
before refitting the manifold.
c)Tighten all manifold securing nuts and
bolts progressively to the specified torque.
d)Make sure that all hoses, pipes and wires
are securely reconnected in their original
positions. Replace all crimp-type hose
clips (where fitted) with standard worm
drive hose clips.
e)On completion, refill the cooling system,
check the adjustment of the throttle cable,
then check, and if necessary adjust the
idle speed and mixture.
Fuel-injection models
SOHC engine
27Disconnect the battery negative lead.
28Drain the cooling system.
29Disconnect the vacuum pipe(s) from the
manifold. The number of pipes varies
according to equipment. Label the pipes if
necessary (see illustration).
30Disconnect the fuel-injection harness
multi-plugs at the bulkhead end of the
manifold (see illustration).
31Disconnect the oil pressure warning light
sender wire from below the manifold.
32Release the hose clips and move the
airflow meter-to-manifold trunking clear of the
manifold.
40Inlet manifold - removal and
refitting
39Fuel rail temperature switch -
removal and refitting
38Mixture adjustment
potentiometer - removal and
refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•19
4
39.3 Fuel rail components
A Fuel pressure regulator
B Fuel temperature switch
C Fuel rail
D Fuel injectors
40.29 Manifold vacuum pipe T-piece
(arrowed)40.30 Fuel-injection wiring harness plugs
procarmanuals.com
Page 113 of 255
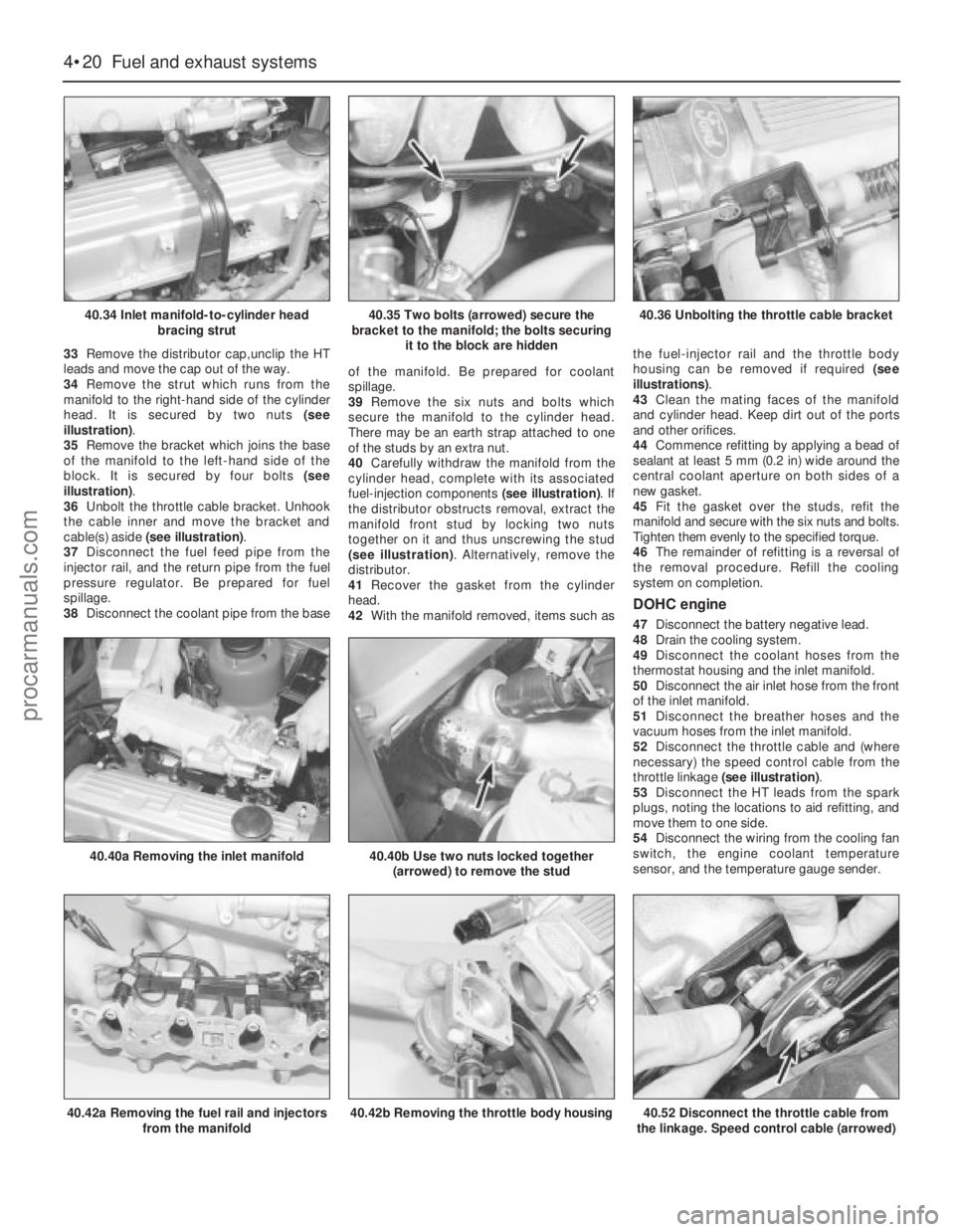
33Remove the distributor cap,unclip the HT
leads and move the cap out of the way.
34Remove the strut which runs from the
manifold to the right-hand side of the cylinder
head. It is secured by two nuts (see
illustration).
35Remove the bracket which joins the base
of the manifold to the left-hand side of the
block. It is secured by four bolts (see
illustration).
36Unbolt the throttle cable bracket. Unhook
the cable inner and move the bracket and
cable(s) aside (see illustration).
37Disconnect the fuel feed pipe from the
injector rail, and the return pipe from the fuel
pressure regulator. Be prepared for fuel
spillage.
38Disconnect the coolant pipe from the baseof the manifold. Be prepared for coolant
spillage.
39Remove the six nuts and bolts which
secure the manifold to the cylinder head.
There may be an earth strap attached to one
of the studs by an extra nut.
40Carefully withdraw the manifold from the
cylinder head, complete with its associated
fuel-injection components (see illustration). If
the distributor obstructs removal, extract the
manifold front stud by locking two nuts
together on it and thus unscrewing the stud
(see illustration). Alternatively, remove the
distributor.
41Recover the gasket from the cylinder
head.
42With the manifold removed, items such asthe fuel-injector rail and the throttle body
housing can be removed if required (see
illustrations).
43Clean the mating faces of the manifold
and cylinder head. Keep dirt out of the ports
and other orifices.
44Commence refitting by applying a bead of
sealant at least 5 mm (0.2 in) wide around the
central coolant aperture on both sides of a
new gasket.
45Fit the gasket over the studs, refit the
manifold and secure with the six nuts and bolts.
Tighten them evenly to the specified torque.
46The remainder of refitting is a reversal of
the removal procedure. Refill the cooling
system on completion.
DOHC engine
47Disconnect the battery negative lead.
48Drain the cooling system.
49Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing and the inlet manifold.
50Disconnect the air inlet hose from the front
of the inlet manifold.
51Disconnect the breather hoses and the
vacuum hoses from the inlet manifold.
52Disconnect the throttle cable and (where
necessary) the speed control cable from the
throttle linkage (see illustration).
53Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs, noting the locations to aid refitting, and
move them to one side.
54Disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan
switch, the engine coolant temperature
sensor, and the temperature gauge sender.
4•20Fuel and exhaust systems
40.34 Inlet manifold-to-cylinder head
bracing strut
40.42a Removing the fuel rail and injectors
from the manifold
40.40a Removing the inlet manifold40.40b Use two nuts locked together
(arrowed) to remove the stud
40.42b Removing the throttle body housing40.52 Disconnect the throttle cable from
the linkage. Speed control cable (arrowed)
40.35 Two bolts (arrowed) secure the
bracket to the manifold; the bolts securing
it to the block are hidden40.36 Unbolting the throttle cable bracket
procarmanuals.com
Page 114 of 255

55Release the throttle position sensor wiring
connector from the clip under the throttle
body, and separate the two halves of the
connector.
56Remove the fuel-injectors.
57Check that all relevant wiring, hoses and
pipes have been disconnected to facilitate
removal of the manifold.
58Unscrew the ten bolts and two nuts
securing the inlet manifold to the cylinder
head, and carefully withdraw the manifold.
Recover the gasket.
59Recover the two plastic spark plug
spacers from the recesses in the cylinder head
(see illustration).
60If desired, the manifold can be dismantled
with reference to the relevant paragraphs of
this Chapter.
61Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that the spark plug spacers are in
position in the cylinder head recesses
before refitting the manifold.
b)Ensure manifold and cylinder head mating
surfaces are clean and dry and fit a new
gasket.
c)Tighten the manifold retaining nuts and
bolts evenly and progressively to the
specified torque.
d)Refit the fuel-injectors.
e)Make sure that all hoses, pipes and wires
are securely reconnected in their original
positions.
f)On completion, refill the cooling system.
g)Check the adjustment of the throttle cable
and where necessary, adjust the speed
control cable so that only a small amount
of slack is present in the cable.
h)Where applicable, check and if necessary
adjust the idle speed and mixture.
V6 engines
62Disconnect the battery negative lead.
63Drain the cooling system.
64Remove the throttle linkage cover.
65Release the hose clips and move the
airflow meter-to-manifold trunking aside.
Unclip or remove the crankcase ventilation
hose.
66Disconnect the radiator top hose and the
heater hose from the outlet at the front of the
manifold. Be prepared for some coolant spillage.67Disconnect the multi-plugs from the idle
speed control valve, the temperature gauge
sender unit; the coolant temperature sensor
and the throttle position sensor. Also
disconnect the injector wiring harness.
68Disconnect the throttle cable from the
linkage, unclip it and move it aside. On
automatic transmission models, also
disconnect the downshift cable or multi-plug,
as applicable.
69Disconnect the fuel feed and return pipes.
Be prepared for fuel spillage.
70Remove the HT leads and the distributor.
71Remove the plenum chamber, which is
secured by eight bolts.
72Remove the rocker covers, which are each
secured by seven bolts.
73Disconnect the water pump bypass hose
from the inlet manifold.
74Remove the eight bolts which secure the
inlet manifold to the cylinder heads.
75Lift off the manifold complete with fuel
pressure regulator, fuel rail, throttle body
housing etc. If it is stuck, carefully lever it free.
Do not apply leverage at the mating faces.
Recover the gasket.
76Clean all mating faces, being careful to
keep dirt out of ports and other orifices.
Obtain new gaskets for both the cylinder head
and plenum chamber sides of the manifold,
and for the rocker covers.
77Commence refitting by applying sealant
(Ford part No A70X-19554-BA, or equivalent)
around the ports and coolant passages on the
cylinder head.
78Apply sealant around the apertures on
both sides of the gasket. then fit the gasket to
the cylinder heads.
79Refit the manifold and insert the securing
bolts. Tighten the bolts, in the order shown
(see illustration),through the first four stages
given in the Specifications.
80Refit the water pump bypass hose.
81Refit the rocker covers, using new
gaskets. The adhesive sides of the gaskets
must face the covers.
82Reverse the remaining removal
operations, but do not refit the throttle linkage
cover yet.
83When the cooling system has beenrefilled, reconnect the battery and start the
engine. Check for fuel and other leaks.
84Bring the engine to operating temperature,
then stop it and carry out the final tightening of
the inlet manifold bolts as follows.
85Release the air inlet trunking. Unplug the
idle speed control valve and the throttle
position sensor. Unbolt the plenum chamber
and move it aside, disconnecting vacuum and
breather hoses as necessary.
86Slacken, but do not remove, the two bolts
which secure the fuel rail to the manifold.
87Tighten the inlet manifold bolts to the
Stage 5 specified torque, again following the
sequence shown. A special cranked spanner
(Ford tool No 21-079, or equivalent)(see
illustration)will be needed to tighten No 4
bolt when the distributor is fitted. In the
absence of such a spanner, remove the
distributor again.
88Tighten the fuel rail securing bolts.
89Refit the disturbed components. Run the
engine again and check the ignition timing and
the exhaust CO level .
90Refit the throttle linkage cover.
SOHC and all V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Apply copious quantities of penetrating oil
to the manifold and exhaust pipe flange nuts
and bolts.
3On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner and the hot air pick-up pipe.
4Unbolt any heat shields or shrouds from the
manifold.
5Unbolt the exhaust pipe(s) from the manifold
flange. Support the exhaust system if
necessary.
6Unbolt the manifold from the cylinder head
and remove it. Recover the gasket.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Use a new gasket, and apply anti-seize
compound to the various nuts and bolts.
Tighten the manifold fastenings to the
specified torque.
41Exhaust manifold(s) - removal
and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•21
4
40.59 Removing a spark plug spacer from
the cylinder head recess40.79 Inlet manifold bolt tightening
sequence
Arrow points to front of engine40.87 Cranked spanner needed for
tightening V6 inlet manifold bolt with
distributor fitted
procarmanuals.com
Page 128 of 255

2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Drain the cooling system (Chapter 3). Save
the coolant if it is fit for re-use.
4Disconnect the multi-plug from the sensor.
Pull on the plug, not on the wiring (see
illustration).
5Unscrew the sensor and remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Refill the cooling system.
Note: The manifold heater must not be
removed while it is hot.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead. 2Remove the air cleaner to improve access.
3Remove the three bolts which secure the
heater to the underside of the manifold.
4Disconnect the electrical feed from the heater.
5Remove the heater. Recover the gasket and
O-ring (see illustration).
6Use a new gasket and O-ring when refitting.
Offer the heater to the manifold, insert the
three bolts and tighten them evenly, making
sure that the heater does not tip or jam.
7Reconnect the electrical feed.
8Refit the air cleaner and reconnect the
battery.
All relays are located behind the facia panel.
Access is gained by removing the facia top
(see illustration).
Testing of a suspect relay is by substitution
of a known good unit.
1All models have a facility for retarding the
ignition timing by up to six degrees without
physically disturbing the distributor. The
adjustment is intended for use when the
correct grade of fuel is not available.
2Adjustment is made by earthing one or two
leads (sometimes called “octane adjustment”
leads) which terminate in a multi-plug next to
the ignition coil (see illustrations). Ideally a
service adjustment lead, available from a Ford
dealer, should be used. Cut and insulate the
wires in the adjustment lead which are not to
be earthed.
3The amount of ignition retardation is as
follows:
Wire(s) Degrees retard
earthed Carb. injection V6
Blue 2 4 6
Red 4 2 3
Blue and red 6 6 Forbidden
4Performance and efficiency will suffer as a
result of this adjustment. Normal timing should
be restored (by isolating the adjustment leads)
when the correct grade of fuel is available.
5If the yellow adjustment lead is earthed, thiswill raise the idle speed by 75 rpm (OHC) or 50
rpm (V6). It may be found that the yellow lead
has already been earthed in production, in
which case disconnecting it will lower the idle
speed by the same amount. This adjustment
does not apply to 1.8 litre carburettor models.
1.8 models from January 1987
6The effect of the “octane adjustment” leads
on these models fitted with the ESC Hybrid
Module is as follows.
Red lead earthed2°retarded
Blue lead earthed4°retarded
Red and blue leads earthed6°retarded
1Fitted to DOHC engines,the sensor is
located at the right-hand rear of the cylinder
block, behind the oil filter (see illustration).
2To remove the sensor, first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Access is most easily obtained from
underneath the vehicle. To improve access,
apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
4Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor.
5Remove the securing screw and withdraw the
sensor from the location in the cylinder block.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, using a
new sensor O-ring and tightening the retaining
screw to the specified torque setting.
24Crankshaft speed/position
sensor - removal and refitting
23Ignition timing and idle speed
adjustments
22Engine management system
relays - testing
21Manifold heater (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•11
5
20.4 Coolant temperature sensor multi-plug21.5 Removing the manifold heater22.1 Engine management system relays
A Power holdB Manifold heater
23.2a Octane adjustment lead multi-plug
23.2b Service adjustment lead for timing
and idle adjustment
A Earthing point (coil
screw)
B Multi-plugC Cut wires not to be
earthed
24.1 Crankshaft speed/position sensor
(viewed from underneath)
procarmanuals.com
Page 139 of 255
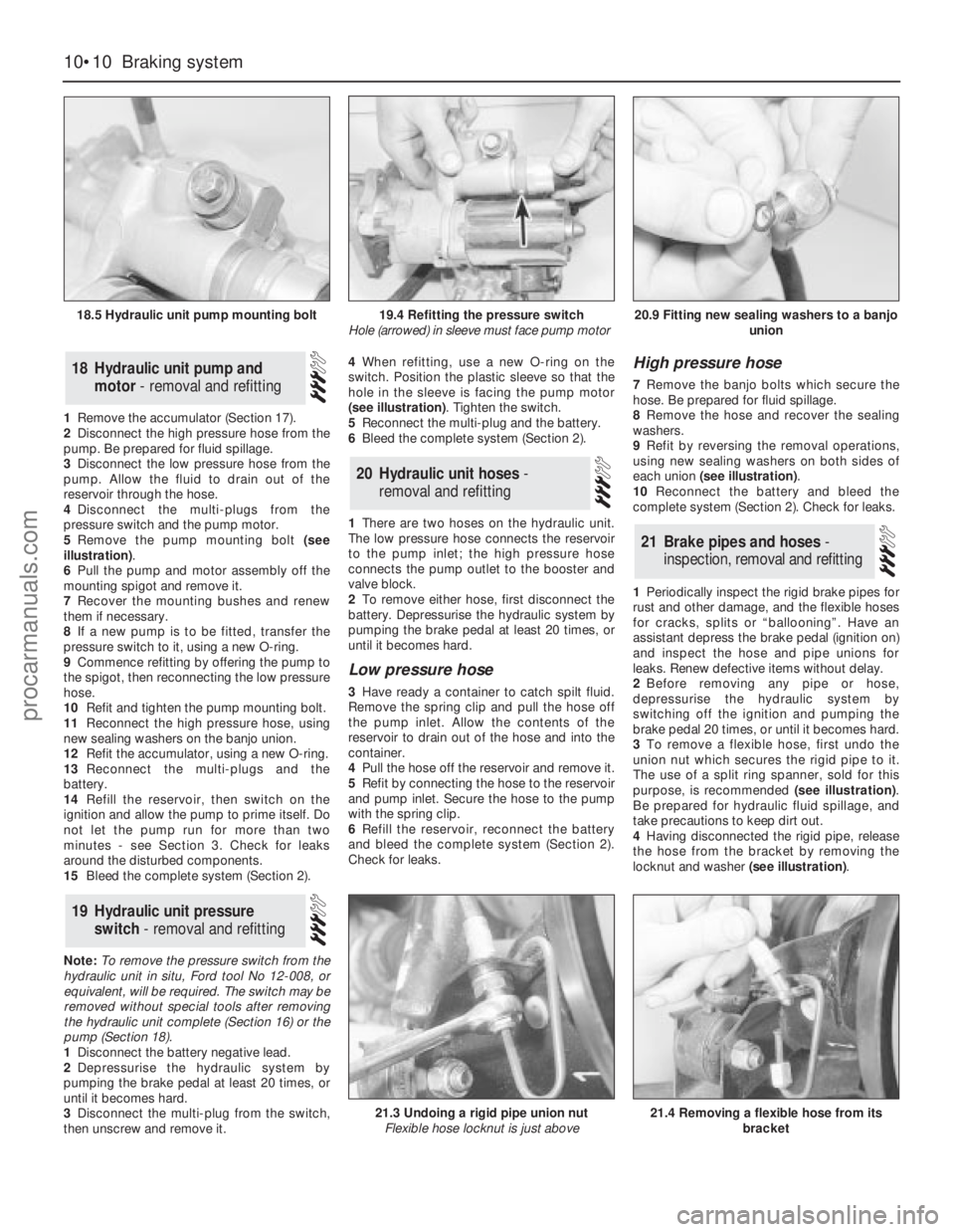
1Remove the accumulator (Section 17).
2Disconnect the high pressure hose from the
pump. Be prepared for fluid spillage.
3Disconnect the low pressure hose from the
pump. Allow the fluid to drain out of the
reservoir through the hose.
4Disconnect the multi-plugs from the
pressure switch and the pump motor.
5Remove the pump mounting bolt (see
illustration).
6Pull the pump and motor assembly off the
mounting spigot and remove it.
7Recover the mounting bushes and renew
them if necessary.
8If a new pump is to be fitted, transfer the
pressure switch to it, using a new O-ring.
9Commence refitting by offering the pump to
the spigot, then reconnecting the low pressure
hose.
10Refit and tighten the pump mounting bolt.
11Reconnect the high pressure hose, using
new sealing washers on the banjo union.
12Refit the accumulator, using a new O-ring.
13Reconnect the multi-plugs and the
battery.
14Refill the reservoir, then switch on the
ignition and allow the pump to prime itself. Do
not let the pump run for more than two
minutes - see Section 3. Check for leaks
around the disturbed components.
15Bleed the complete system (Section 2).
Note: To remove the pressure switch from the
hydraulic unit in situ, Ford tool No 12-008, or
equivalent, will be required. The switch may be
removed without special tools after removing
the hydraulic unit complete (Section 16) or the
pump (Section 18).
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Depressurise the hydraulic system by
pumping the brake pedal at least 20 times, or
until it becomes hard.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the switch,
then unscrew and remove it.4When refitting, use a new O-ring on the
switch. Position the plastic sleeve so that the
hole in the sleeve is facing the pump motor
(see illustration). Tighten the switch.
5Reconnect the multi-plug and the battery.
6Bleed the complete system (Section 2).
1There are two hoses on the hydraulic unit.
The low pressure hose connects the reservoir
to the pump inlet; the high pressure hose
connects the pump outlet to the booster and
valve block.
2To remove either hose, first disconnect the
battery. Depressurise the hydraulic system by
pumping the brake pedal at least 20 times, or
until it becomes hard.
Low pressure hose
3Have ready a container to catch spilt fluid.
Remove the spring clip and pull the hose off
the pump inlet. Allow the contents of the
reservoir to drain out of the hose and into the
container.
4Pull the hose off the reservoir and remove it.
5Refit by connecting the hose to the reservoir
and pump inlet. Secure the hose to the pump
with the spring clip.
6Refill the reservoir, reconnect the battery
and bleed the complete system (Section 2).
Check for leaks.
High pressure hose
7Remove the banjo bolts which secure the
hose. Be prepared for fluid spillage.
8Remove the hose and recover the sealing
washers.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations,
using new sealing washers on both sides of
each union (see illustration).
10Reconnect the battery and bleed the
complete system (Section 2). Check for leaks.
1Periodically inspect the rigid brake pipes for
rust and other damage, and the flexible hoses
for cracks, splits or “ballooning”. Have an
assistant depress the brake pedal (ignition on)
and inspect the hose and pipe unions for
leaks. Renew defective items without delay.
2Before removing any pipe or hose,
depressurise the hydraulic system by
switching off the ignition and pumping the
brake pedal 20 times, or until it becomes hard.
3To remove a flexible hose, first undo the
union nut which secures the rigid pipe to it.
The use of a split ring spanner, sold for this
purpose, is recommended (see illustration).
Be prepared for hydraulic fluid spillage, and
take precautions to keep dirt out.
4Having disconnected the rigid pipe, release
the hose from the bracket by removing the
locknut and washer (see illustration).
21Brake pipes and hoses -
inspection, removal and refitting
20Hydraulic unit hoses -
removal and refitting
19Hydraulic unit pressure
switch - removal and refitting
18Hydraulic unit pump and
motor - removal and refitting
10•10Braking system
18.5 Hydraulic unit pump mounting bolt
21.3 Undoing a rigid pipe union nut
Flexible hose locknut is just above21.4 Removing a flexible hose from its
bracket
19.4 Refitting the pressure switch
Hole (arrowed) in sleeve must face pump motor20.9 Fitting new sealing washers to a banjo
union
procarmanuals.com
Page 149 of 255

3Depress the locking button with a small
screwdriver. Draw the lock barrel out of its
housing using the key (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1The intermediate shaft and flexible coupling
are not available separately, and so must be
renewed as a unit.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Position the steering straight-ahead.
4Remove the pinch-bolts which secure the
upper and lower ends of the intermediate
shaft. Free the universal joint from the column
shaft, then pull the flexible coupling off the
pinion shaft.
5When refitting, engage the master spline on
the pinion shaft with the groove in the flexible
coupling.
6Tighten the pinch-bolts to the specified
torque.
7Reconnect the battery.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 21.
All engines except DOHC
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Wipe clean around the unions, then
disconnect the high pressure and return pipes
from the pump and the reservoir. Be prepared
for fluid spillage; take steps to keep fluid out of
the alternator.
3Remove the pump drivebelt(s).
4Remove the pump mounting, pivot and
adjustment bolts (as applicable) and lift the
pump from the engine (see illustration).
5If a new pump is to be fitted, recover the
pulley and mounting plate from the old pump.6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the drivebelt tension on completion and
bleed the steering hydraulic system.
DOHC engines
7The pump is mounted on a bracket on the
front right-hand side of the cylinder block. To
improve access to the pump, firmly apply the
handbrake then jack up the front of the car
and support it securely on axle stands (see
“Jacking”).
8Place a suitable container under the pump,
unscrew the fluid pipe unions, and drain the
fluid.
9Remove the drivebelt with reference to
Chapter 1.
10Prevent the pulley from rotating using a
strap wrench (which can be improvised using
an old drivebelt and a large socket and
wrench), and unscrew the three pulley
securing bolts (see illustration). Withdraw the
pulley.
11Unscrew the three pump securing bolts
from the front of the pump bracket, and the
single bolt from the rear of the bracket, and
withdraw the pump (see illustration).
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Reconnect the fluid unions using new O-
rings.
b)On completion, top-up and bleed the
power steering fluid circuit.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Clean around the hose unions on the
steering gear. Remove the single securing
bolt, withdraw the hoses and catch the fluid
which will drain from the reservoir.
3Clean around the hose unions on the pump.
Disconnect the unions and remove the hoses.
4Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings.
5Top-up the steering fluid and bleed the
system.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the front
wheel on the side concerned.
2Slacken the track rod end locknut by half a
turn.
3Remove the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut a few turns (see
illustration).
4Break the balljoint taper with a proprietary
balljoint separator (see illustration). Remove
the separator and the nut and disengage the
track rod end from the steering arm.
5Unscrew the track rod end from the track
rod, being careful not to disturb the locknut.
13Track rod end - removal and
refitting
12Power steering hoses -
removal and refitting
11Power steering pump -
removal and refitting
10Power steering pump
drivebelt - removal, refitting
and tensioning
9Steering intermediate shaft
and flexible coupling - removal
and refitting
11•6Steering and suspension
8.3 Depress the column lock locking button
11.11 . . . for access to the front pump
securing bolts (arrowed)13.3 Track rod end balljoint nut unscrewed
11.4 Steering pump pivot bolt (arrowed) -
V6 model shown11.10 Unbolt the power steering pump
pulley . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 193 of 255

1Remove the overhead console.
2Remove the three bolts which secure the
motor (see illustration).Lower the motor,
disconnect the multi-plug and remove it.
Recover the relay.
3When refitting, make sure that the motor
drivegear meshes with the roof operating
mechanism. Refit the relay, reconnect the
multi-plug and secure the motor with the three
bolts.
4Check the operation of the motor, then refit
the overhead console.1All vehicles are fitted with an electrical
speedometer sender unit instead of a
mechanical cable. The sender unit is located on
the left-hand side of the transmission extension.
2Raise and securely support the front of the
vehicle. Place a drain pan underneath the
speedometer sender unit.
3Remove the securing bolt, pull the sender
unit out of the transmission and disconnect
the multi-plug (see illustration). Be prepared
for some spillage of gearbox oil or ATF
(automatic transmission fluid).
4If a new sender unit is being fitted, transfer
the driven gear and circlip from the old unit.
On automatic transmission models, also
transfer the O-ring.
5If the old sender unit had two connecting
wires and the new unit has three, the brown
wire must be cut at the multi-plug and an earth
tag fitted (see illustration).Consult a Ford
dealer if in doubt.
6Fit the new sender unit, using a new bolt
(M6 x 25 mm for manual gearbox, M6 x 35 mm
for automatic transmission). Besides the
sender unit, the bolt also secures the new
earth tag (when applicable), the radio earth
strap and the multi-plug retaining bracket.
7Connect the multi-plug and fit it to the
bracket.8If any spillage of gearbox oil or transmission
fluid occurred, top-up the level before the
vehicle is next run.
All models
1To remove a windscreen wiper arm, first
open the bonnet.
2Lift up the plastic cap and undo the wiper
arm retaining nut.
3Pull the arm off the drive spindle (see
illustrations).
4Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
the masking tape to indicate the correct fitted
position of the arm and blade.
5To remove a blade alone, hinge the arm and
blade away from the screen. Press the tab on
the spring clip in the middle of the blade and
unhook the blade from the arm (see
illustration).
6Refit the blade by sliding it onto the hook on
the arm.
22Wiper arms and blades -
removal and refitting
21Speedometer sender unit -
removal and refitting20Sliding roof motor - removal
and refitting
13•16Body electrical system
20.2 Sliding roof motor retaining bolts
(arrowed)
22.3b Pull the arm off the spindle
22.3a Lift the cap to expose the nut
22.5 Removing a wiper blade22.7 Disconnecting the rear wiper arm
washer hose
21.3 Speedometer sender unit securing
bolt (arrowed)
A Automatic transmission
B Manual gearbox21.5 Latest type speedometer sender unit
A Brown wire
B Brown/yellow wire
C Brown/black wire
D Earth tag (see text)E Sleeve
F Cut brown wire
here (see text)
Mark the position of the blade
on the windscreen or rear
window (as applicable) with a
piece of masking tape.
procarmanuals.com
Page 239 of 255

REF•4
Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components, it is
necessary to observe the following procedures
and instructions. This will assist in carrying out
the operation efficiently and to a professional
standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that this
method may not be suitable where dowels are
used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, ensure that it is
renewed on reassembly, and fit it dry unless
otherwise stated in the repair procedure. Make
sure that the mating faces are clean and dry,
with all traces of old gasket removed. When
cleaning a joint face, use a tool which is not
likely to score or damage the face, and remove
any burrs or nicks with an oilstone or fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used, unless
specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers
or some similar device in order to pull the seal
free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing is
unshouldered, the seal should be fitted with its
face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew
the stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a proprietary stud extractor. Always
ensure that a blind tapped hole is completely
free from oil, grease, water or other fluid
before installing the bolt or stud. Failure to do
this could cause the housing to crack due to
the hydraulic action of the bolt or stud as it is
screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never slacken
the nut to align the split pin hole, unless stated
in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably cylinder
head bolts or nuts, torque wrench settings are
no longer specified for the latter stages of
tightening, “angle-tightening” being called up
instead. Typically, a fairly low torque wrench
setting will be applied to the bolts/nuts in
the correct sequence, followed by one or
more stages of tightening through specified
angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing in the course of
tightening should always have a washer
between it and the relevant component or
housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt
or stud thread. However, it should be noted
that self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose theireffectiveness after long periods of use, and in
such cases should be renewed as a matter of
course.
Split pins must always be replaced with new
ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found on
the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring
compressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the
manufacturer’s special tools are described,
and are shown in use. Unless you are highly-
skilled and have a thorough understanding of
the procedures described, never attempt to
bypass the use of any special tool when the
procedure described specifies its use. Not
only is there a very great risk of personal injury,
but expensive damage could be caused to the
components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department for further
advice.
With the universal tightening-up of
legislation regarding the emission of
environmentally-harmful substances from
motor vehicles, most current vehicles have
tamperproof devices fitted to the main
adjustment points of the fuel system. These
devices are primarily designed to prevent
unqualified persons from adjusting the fuel/air
mixture, with the chance of a consequent
increase in toxic emissions. If such devices are
encountered during servicing or overhaul, they
should, wherever possible, be renewed or
refitted in accordance with the vehicle
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
General Repair Procedures
procarmanuals.com