1984 BMW 3 SERIES steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 155 of 228

Where power-assistance is fitted, hydraulic
pressure (provided by an engine-driven pump)
delivers power steering fluid to the rack-and-
pinion steering gear or the recirculating-ball
steering box - this enhances steering
response and reduces steering effort.
Aside from maintaining the proper level of
power steering fluid in the system and
checking the tension of the drivebelt (see
Chapter 1, where applicable), the steering
system requires no maintenance. However,
on high-mileage vehicles, the track rod end
balljoints, the universal joints on either end of
the universal joint shaft, and the rubber
coupling between the steering column and the
universal joint shaft will wear, develop
excessive play, and cause the steering to feel
somewhat loose. At this point, you’ll have to
renew these items; they can’t be serviced.
Before you conclude that the steering
system needs work, however, always check
the tyres (see Section 25) and tyre pressures
(see Chapter 1). Also inspect the bearings in
the strut upper mounts (see Section 5), the
front hub bearings (see Section 8) and other
suspension parts, which may also be
contributing to an imprecise steering feel.
17 Track rod ends-
removal and refitting
4
1Loosen but do not remove the wheel bolts,
then raise the front of the vehicle and secure it
on axle stands. Remove the front wheel.
3-Series models
2Loosen the nut on the track rod balljoint
stud, and free the balljoint stud from the
steering arm using a balljoint separator. In the
absence of a separator tool, try giving the
steering arm a few light blows with a hammer
(see illustration). Remove the nut, and
separate the balljoint stud from the steering
arm.3Loosen the clamp bolt that locks the track
rod end to the inner track rod. Measure the
length of the track rod end, or paint an
alignment mark on the threads to ensure the
track rod end is refitted in the same position
(see illustration). Unscrew the track rod end
from the inner track rod.
4Refitting is the reverse of removal. Make
sure the mark you made on the threads of the
track rod end is aligned correctly, if
applicable. If you measured the track rod end,
make sure it is refitted to the same distance.
5Have the toe-in checked and, if necessary,
adjusted at a dealer service department or
qualified garage.
5-Series models
6Measure the length of the track rod and
record your measurement, or paint an
alignment mark on the threads to ensure the
track rod end is refitted in the same position
(see illustration). Loosen the clamp bolt.
7Use a balljoint separator or a puller to
separate the track rod end from the steering
arm (see illustration).
8Unscrew the track rod end.
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Make
sure you align the paint mark made on the
threads of the track rod end, if applicable. If
you measured the track rod end, make sure it
is refitted to the same distance.
10Have the toe-in checked and, if
necessary, adjusted at a dealer service
department or qualified garage.
18 Steering gear boots
(3-Series)- renewal
4
1Remove the track rod ends (see Sec-
tion 17).
2Cut the boot clamps at both ends of the old
boots, and slide off the boots.
3While the boots are removed, inspect the
seals in the end of the steering gear. If they’releaking, renew the steering gear (see Sec-
tion 19).
4Slide the new boots into place and fit new
boot clamps.
5Refit the track rod ends (see Section 17).
19 Rack-and-pinion steering
gear (3-Series)-
removal and refitting
4
Removal
1Loosen but do not remove the wheel bolts,
raise the vehicle and support it securely on
axle stands. Remove the front wheels.
2Mark the lower universal joint on the
steering shaft and the pinion shaft, to ensure
proper alignment when they’re reassembled.
Remove the nut and bolt that attach the lower
end of the universal joint shaft to the steering
gear pinion shaft. Loosen the bolt and nut at
the upper end of the universal joint shaft. Slide
the universal joint shaft up a little, disengage it
from the pinion shaft, and remove it. Inspect
the universal joints and the rubber coupling
for wear. If any of them are worn or defective,
renew the universal joint shaft.
3On power steering models, using a large
Suspension and steering systems 10•13
17.6 Measure the length of the track rod
and record your measurement, or paint an
alignment mark on the threads to ensure
the track rod end is refitted in the same
position, then loosen the clamp bolt
(arrowed)17.3 Loosen the clamp bolt (arrowed) that
locks the track rod end to the inner track
rod. Paint an alignment mark on the
threads, to ensure the track rod end is
refitted in the same position, and
unscrew the track rod end from the inner
track rod17.2 Loosen the nut on the track rod
balljoint stud. For preference use a
balljoint separator; otherwise, give the
steering arm a few light blows with a
hammer to release the balljoint stud.
Remove the nut, and separate the balljoint
stud from the steering arm
17.7 Using a puller to separate the track
rod end from the steering arm
10
Page 156 of 228

syringe or hand pump, empty the power
steering fluid reservoir.
4On power steering models, remove the
banjo bolts and disconnect the power
steering pressure and return lines from the
steering gear. Place a container under the
lines to catch spilled fluid. Plug the lines to
prevent excessive fluid loss and
contamination. Discard the sealing washers
(new ones should be used when
reassembling).
5Disconnect the track rod ends from the
steering arms (see Section 17).
6Remove the nuts and bolts from the
steering gear mounting brackets (see
illustration). Discard the old nuts.
7Withdraw the assembly from beneath the
vehicle. Take care not to damage the steering
gear boots.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Make
sure the marks you made on the lower
universal joint and the pinion shaft are aligned
before you tighten the clamping bolts for the
upper and lower universal joints. Use new
self-locking nuts on the steering rackmounting bolts, and new sealing washers on
the hydraulic line fittings. Tighten the
mounting bolts, the track rod end nuts and the
universal joint shaft clamping bolts to the
torque values listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.
9Lower the vehicle to the ground.
10On power steering models, fill the
reservoir with the recommended fluid (see
Chapter 1) and bleed the power steering
system (see Section 23).
11It’s a good idea to have the front wheel
alignment checked by a dealer service
department or qualified garage.
20 Steering linkage (5-Series)-
inspection, removal and
refitting
4
Inspection
1Raise the vehicle and place it securely on
axle stands.
2Firmly grasp each front tyre at the top and
bottom, then at the front and rear, and check
for play in the steering linkage by rocking the
tyre back and forth. There should be little or
no play in any of the linkage balljoints. Inspect
the Pitman arm, the idler arm, the centre track
rod, the inner track rods, the track rod ends
and the steering arms for any obvious
damage. Try forcing the linkage parts in
opposite directions from one another. There
should be no play between any of them. If any
of the parts are bent or damaged in any way,
or if any of the balljoints are worn, renew the
parts concerned.
Removal
3Before dismantling the steering linkage,
obtain a suitable balljoint separator. A two-jaw
puller or a wedge-type tool will work (although
the wedge-type tends to tear the balljoint
boots). Sometimes, you can also jar a balljoint
taper pin free from its eye by striking opposite
sides of the eye simultaneously with two large
hammers, but the space available to do this is
limited, and the balljoint stud sometimessticks to the eye because of rust and dirt.
There is also a risk of damaging the
component being struck.
4To remove the outer track rods, disconnect
the track rod ends from the steering arms (see
Section 17). Remove the nut that attaches the
balljoint on the inner end of each outer track
rod to the centre track rod (see illustration).
Using a balljoint separator, disconnect the
outer track rods from the centre track rod. If
you’re renewing the balljoint at either end of
the outer track rods, paint or scribe alignment
marks on the threads to mark their respective
positions as a guide to adjustment during
reassembly (see illustration 17.3).
5To remove the centre track rod, remove the
nuts that attach the centre track rod balljoints
to the Pitman arm and the idler arm, and use a
balljoint separator to disconnect the balljoints
from the two arms.
6To remove the Pitman arm, you’ll have to
remove the steering box first (see Section 21).
Look for match marks between the sector
shaft and arm. If there aren’t any, scribe a
mark across the bottom face of both parts.
Remove the Pitman arm pinch-bolt and nut,
then remove the arm with a puller.
7To unbolt the idler arm, first remove the
small cover bolted to the top of the subframe
crossmember. Put a spanner on the bolt, and
remove the nut recessed into the underside of
the subframe crossmember (see illustration).
Check the idler arm rubber bush for wear. If
it’s damaged or worn, renew it.
8Check each balljoint for excessive play or
stiffness, and for split or deteriorated rubber
dust boots. Renew all worn or damaged
balljoints. The inner and outer track rod ends
on the outer track rods can be renewed
individually; if either balljoint on the centre
track rod is damaged or worn, you must
renew the centre track rod.
Refitting
9Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, but observe the following points:
a) Realign the match marks on the Pitman
arm and the steering box sector shaft
when reassembling them.
b) If you’re fitting new inner or outer track
rod ends on the outer track rods, position
them so that the match marks made
during dismantling are aligned, and make
sure they are equally spaced on each
side.
c) Position the track rod end balljoint studs
on the outer track rods at an angle of 90°
to each other.
d) Make sure the left and right outer track
rods are equal in length when they are
fitted.
e) Tighten all retaining bolts to the torque
values listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations.
f) When reassembly of the linkage is
complete, have the front wheel alignment
checked, and if necessary, adjusted.
10•14 Suspension and steering systems
20.7 To unbolt the idler arm from the
subframe crossmember, remove this nut
(arrowed)
20.4 To remove an outer track rod,
remove this nut (arrowed) from the end of
the centre track rod, and use a balljoint
separator to separate the balljoint stud
from the centre track rod (if you’re
renewing the inner track rod end, mark the
threads with paint before loosening the
clamp bolt and nut)
19.6 Rack-and-pinion steering gear
mounting bolts (arrowed) - 3-Series
models - (self-locking nuts not visible in
this photo)
Page 158 of 228

Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the nuts and bolts securely. Adjust the
drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1).
8Top-up the fluid level in the reservoir (see
Chapter 1) and bleed the system (see Sec-
tion 23).
23 Power steering system-
bleeding
1
1To bleed the power steering system, begin
by checking the power steering fluid level and
adding fluid if necessary (see Chapter 1).
2Raise and support the front of the vehicle
on axle stands.
3Turn the steering wheel from lock-to-lock
several times. Recheck the fluid level and top
up if necessary.
4Start the engine and run it at 1000 rpm or
less. Turn the steering wheel from lock-to-
lock again (three or four times) and recheck
the fluid level one more time. Note:On 5-Series E28 (“old-shape”) models, pump the
brake pedal five or six times before turning the
steering wheel. Once the fluid level remains
constant, continue turning the wheel back and
forth until no more bubbles appear in the fluid
in the reservoir.
5Lower the vehicle to the ground. Run the
engine and again turn the wheels from lock-
to-lock several more times. Recheck the fluid
level. Position the wheels straight-ahead.24 Steering wheel-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: If the vehicle is
equipped with an airbag, do not
attempt this procedure. Have it
performed by a dealer service
department or other qualified specialist, as
there is a risk of injury if the airbag is
accidentally triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Using a small screwdriver, prise off the
BMW emblem in the centre of the steering
wheel.
3Remove the steering wheel nut, and mark
the relationship of the steering wheel hub to
the shaft (see illustration).
4On all 3-Series models, and on 1986 and
later 5-Series models, turn the ignition key to
the first position to unlock the ignition lock.
5Remove the steering wheel from thesteering shaft. If the wheel is difficult to
remove from the shaft, use a steering wheel
puller to remove it - don’t hammer on the
shaft.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to align the match marks you made on the
steering wheel and the shaft. Tighten the
steering wheel nut to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
25 Wheels and tyres-
general information
1
Note:For more information on care and
maintenance of tyres, refer to Chapter 1.
1All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with steel-belted radial tyres as
original equipment. Use of other types or
sizes of tyres may affect the ride and handling
of the vehicle. Don’t mix different types or
sizes of tyres, as the handling and braking
may be seriously affected. It’s recommended
that tyres be renewed in pairs on the same
axle; if only one new tyre is being fitted, be
sure it’s the same size, structure and tread
design as the other.
2Because tyre pressure has a substantial
effect on handling and wear, the pressure on
all tyres should be checked at least once a
month or before any extended trips (see
Chapter 1).
3Wheels must be renewed if they are bent,
heavily dented, leak air, or are otherwise
damaged.
4Tyre and wheel balance is important in the
overall handling, braking and performance of
the vehicle. Unbalanced wheels can adversely
affect handling and ride characteristics, as
well as tyre life. Whenever a new tyre is fitted,
the tyre and wheel should be balanced.
10•16 Suspension and steering systems
24.3 After removing the steering wheel
nut, mark the relationship of the steering
wheel to the steering shaft (arrowed) to
ensure proper alignment during
reassembly
22.6c Typical 5-Series power steering pump mounting bolts
(arrowed)22.6b . . . and mounting nut and bolt (arrowed)
Page 159 of 228
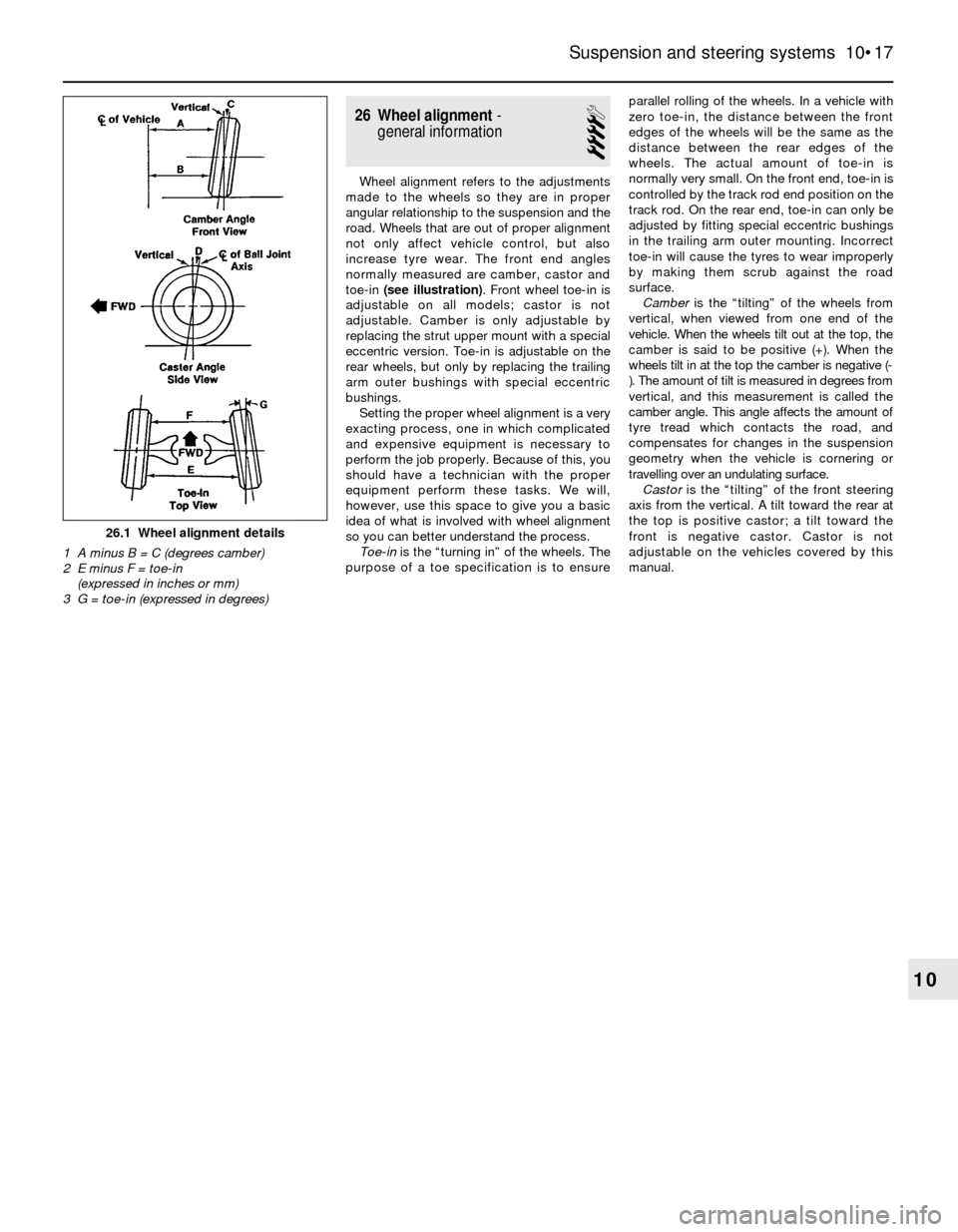
26 Wheel alignment-
general information
4
Wheel alignment refers to the adjustments
made to the wheels so they are in proper
angular relationship to the suspension and the
road. Wheels that are out of proper alignment
not only affect vehicle control, but also
increase tyre wear. The front end angles
normally measured are camber, castor and
toe-in (see illustration). Front wheel toe-in is
adjustable on all models; castor is not
adjustable. Camber is only adjustable by
replacing the strut upper mount with a special
eccentric version. Toe-in is adjustable on the
rear wheels, but only by replacing the trailing
arm outer bushings with special eccentric
bushings.
Setting the proper wheel alignment is a very
exacting process, one in which complicated
and expensive equipment is necessary to
perform the job properly. Because of this, you
should have a technician with the proper
equipment perform these tasks. We will,
however, use this space to give you a basic
idea of what is involved with wheel alignment
so you can better understand the process.
Toe-inis the “turning in” of the wheels. The
purpose of a toe specification is to ensureparallel rolling of the wheels. In a vehicle with
zero toe-in, the distance between the front
edges of the wheels will be the same as the
distance between the rear edges of the
wheels. The actual amount of toe-in is
normally very small. On the front end, toe-in is
controlled by the track rod end position on the
track rod. On the rear end, toe-in can only be
adjusted by fitting special eccentric bushings
in the trailing arm outer mounting. Incorrect
toe-in will cause the tyres to wear improperly
by making them scrub against the road
surface.
Camberis the “tilting” of the wheels from
vertical, when viewed from one end of the
vehicle. When the wheels tilt out at the top, the
camber is said to be positive (+). When the
wheels tilt in at the top the camber is negative (-
). The amount of tilt is measured in degrees from
vertical, and this measurement is called the
camber angle. This angle affects the amount of
tyre tread which contacts the road, and
compensates for changes in the suspension
geometry when the vehicle is cornering or
travelling over an undulating surface.
Castoris the “tilting” of the front steering
axis from the vertical. A tilt toward the rear at
the top is positive castor; a tilt toward the
front is negative castor. Castor is not
adjustable on the vehicles covered by this
manual.
Suspension and steering systems 10•17
10
26.1 Wheel alignment details
1 A minus B = C (degrees camber)
2 E minus F = toe-in
(expressed in inches or mm)
3 G = toe-in (expressed in degrees)
Page 160 of 228

11
1 General information
These models feature an all-steel welded
construction, where the floorpan and body
components are welded together and
attached to separate front and rear subframe
assemblies. Certain components are
particularly vulnerable to accident damage,
and can be unbolted and repaired or renewed.
Among these parts are the body mouldings,
bumpers, bonnet, doors, tailgate, and all
glass.
Only general body maintenance procedures
and body panel repair procedures within the
scope of the do-it-yourselfer are included in
this Chapter.
2 Bodywork and underframe-
maintenance
1
The general condition of a vehicle’s
bodywork is the one thing that significantly
affects its value. Maintenance is easy, but
needs to be regular. Neglect, particularly after
minor damage, can lead quickly to further
deterioration and costly repair bills. It is
important also to keep watch on those parts
of the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheelarches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam-cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam-cleaning is available at
many garages, and is necessary for the
removal of the accumulation of oily grime,
which sometimes is allowed to become thick
in certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-
applied; the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
Note that these methods should not be usedon vehicles with wax-based underbody
protective coating, or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just prior to Winter, when
the underbody should be washed down, and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc, as an additional safeguard against rust
damage, where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish will
give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen has
dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to be
taken with metallic paintwork, as special non-
abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to avoid
damage to the finish. Always check that the
door and ventilator opening drain holes and
pipes are completely clear, so that water can
be drained out. Brightwork should be treated in
the same way as paintwork. Windscreens and
windows can be kept clear of the smeary film
which often appears, by the use of proprietary
glass cleaner. Never use any form of wax or
other body or chromium polish on glass.
Chapter 11 Bodywork and fittings
Bodywork and underframe - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Bodywork repair - major damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Bodywork repair - minor damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Bonnet - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Boot lid/tailgate - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Door - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Door trim panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Door window glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Door window regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Exterior mirror - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18Fixed glass - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Hinges and locks - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Interior trim - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Latch, lock cylinder and handles - removal, refitting and
adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Radiator grille - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Seats - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Steering column shrouds - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Upholstery and carpets - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
11•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
Page 168 of 228

19 Steering column shrouds -
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (Chapter 10).
3Remove the upper shroud screws (see
illustration).
4Remove the two screws from the underside
of the column (see illustration).
5Detach the lower shroud, then lift the upper
half off the column (see illustrations).
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
20 Seats- removal and refitting
1
Front seat
1Remove the four bolts securing the seat
track to the floorpan, and lift the seat from the
vehicle (see illustration). On some models, it
will be necessary to disconnect the seat
heating wiring; it may also be necessary to
detach the seat belt from the seat.2Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the retaining bolts securely.
Rear seat cushion
3If applicable, first remove the two retaining
bolts. Grasp the front of the cushion
(Saloon/Convertible models) or the rear of the
cushion (Touring/Estate models) securely, and
pull up sharply (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal.
21 Seat belt check
1
1Check the seat belts, buckles, lock plates
and guide loops for obvious damage and
signs of wear.
2Where applicable, check that the seat belt
reminder light comes on when the ignition key
is turned to the Run or Start position.
3The seat belts are designed to lock up
during a sudden stop or impact, yet allow free
movement during normal driving. Check thatthe retractors return the belt against your
chest while driving and rewind the belt fully
when the buckle is unlocked.
4If any of the above checks reveal problems
with the seat belt system, renew parts as
necessary.
5Belts which have been subject to impact
loads must be renewed.
Bodywork and fittings 11•9
19.5a Pull the tilt lever down (where fitted),
and lower the shroud from the steering
column19.4 The lower screws are located under
the tilt lever (where fitted)19.3 Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove
the upper column shroud screws
20.3 Grasp the seat at the front edge and
pull up sharply (Saloon/Convertible
models)20.1 The front seats are held in place by
bolts (arrowed)
19.5b Rotate the upper shroud up and off
the steering column
11
Page 171 of 228

indicates that the direction indicator and/or
hazard fuse has blown, check the wiring for a
short-circuit before fitting a new fuse.
4Make sure that the new unit is identical to
the original. Compare the old one to the new
one before fitting it.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Steering column switches-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the special
tools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable,
remove the steering wheel (see Chapter 10)
and steering column shrouds (see Chapter 11).
Direction indicator/headlight
switch
2Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws. Depress the tabs and pull
the switch out of the steering column
mounting (see illustration).
3Trace the switch wires down the steering
column to the electrical connector, and
unplug them (see illustration).
4Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Wiper/washer switch
5Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screws.
6Depress the release clip, and detach the
switch from the steering column mounting
(see illustration). Trace the switch wiring
down the steering column to the electrical
connector, and unplug it.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Cruise control switch
8Remove the wiper/washer switch.
9Where necessary, remove the switch
mounting screw. Squeeze the release tabs,
and withdraw the switch from the mounting
(see illustration).
10Disconnect the switch electrical
connector from the harness at the base of the
steering column.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7 Ignition switch-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Some later models are
equipped with an airbag or
Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS). To avoid possible damage
to this system, the manufacturer
recommends that, on airbag-equipped
models, the following procedure should be
left to a dealer service department, or
other specialist, because of the specialtools and techniques required. There is a
risk of injury if the airbag is accidentally
triggered.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the steering wheel (see Chap-
ter 10).
3Remove the steering column shrouds (see
Chapter 11).
4Where necessary, remove the direction
indicator/headlight control switch (see Sec-
tion 6).
5Detach the clips by inserting a small
screwdriver into the openings on the sides
while pulling out on the switch (see
illustration).
6Unplug the electrical connector from the
harness at the base of the steering column,
and remove the switch.
Refitting
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Body electrical systems 12•3
6.3 Follow the wiring down the steering
column to the connector6.2 Squeeze the tabs to release the switch
from the mounting
6.9 Cruise control switch removal6.6 Squeeze the wiper/washer switch tabs
and pull it directly out of the mounting
12
5.1 The direction indicator/hazard warning
flasher unit is located on the steering
column on most models - squeeze the
tabs to detach it
Page 176 of 228

12Refitting is a reversal of removal. When
fitting the motor, if necessary plug in the
connector and run the motor briefly until it is
in the “neutral” (wiper parked) position.
17 Heated rear window-
check and repair
2
1The heated rear window consists of a
number of horizontal elements on the glass
surface.
2Small breaks in the element can be repaired
without removing the rear window.
Check
3Switch on the ignition and the heated rear
window.
4Place the positive lead of a voltmeter to the
heater element nearest to the incoming power
source.
5Wrap a piece of aluminium foil around the
negative lead of the voltmeter on the positive
side of the suspected broken element, and
slide it slowly towards the negative side.
Watch the voltmeter needle - when it moves
from zero, you have located the break.
Repair
6Repair the break in the line using a repair kit
recommended specifically for this purpose,
such as BMW repair kit No. 81 22 9 (or
equivalent). Included in this kit is plastic
conductive epoxy. The following paragraphs
give general instructions for this type of repair;
follow the instructions supplied with the repair
kit if they are different.
7Prior to repairing a break, switch off the
circuit and allow it to cool down for a few
minutes.
8Lightly buff the element area with fine steel
wool, then clean it thoroughly.
9Use masking tape to mask off the area of
repair, leaving a slit to which the epoxy can be
applied.
10Mix the epoxy thoroughly, according to
the instructions on the package.
11Apply the epoxy material to the slit in the
masking tape, overlapping the undamaged
area about 20 mm on each end.12Allow the repair to cure for 24 hours
before removing the tape and using the
heated rear window.
18 Supplemental Restraint
System (SRS)- general
information
Later models are equipped with a
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS),
incorporating an airbag. This system is
designed to protect the driver from serious
injury in the event of a head-on or frontal
collision. It consists of an airbag module in the
centre of the steering wheel, two crash
sensors mounted on the front inner wing
panels, and a crash safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment.
The airbag module contains a housing
incorporating the airbag and the inflator units.
The inflator assembly is mounted on the back
of the housing over a hole through which gas
is expelled, inflating the bag almost instanta-
neously when an electrical signal is sent from
the system. This signal is carried by a wire
which is specially wound with several turns,
so the signal will be transmitted regardless of
the steering wheel position.
The SRS system has three sensors: two at
the front, mounted on the inner wing panels
(see illustration), and a safety switch located
inside the passenger compartment. The crash
sensors are basically pressure-sensitive
switches, which complete an electrical circuit
during an impact of sufficient force. The
electrical signal from the crash sensors is sent
to a third sensor, which then completes the
circuit and inflates the airbag.
The module containing the safety switch
monitors the system operation. It checks the
system every time the vehicle is started,
causing the AIRBAG warning light to come on,
then go out if the system is operating
correctly. If there is a fault in the system, the
light will stay on. If the AIRBAG warning light
does stay on, or if it comes on while driving,
take the vehicle to your dealer immediately.
19 Cruise control system-
description and check
1
The cruise control system maintains vehicle
speed using a vacuum-actuated servo motor
located in the engine compartment, which is
connected to the throttle linkage by a cable.
The system consists of the servo motor,
clutch switch, brake switch, control switches,
a relay, and associated vacuum hoses.
Because of the complexity of the cruise
control system, repair should be left to a
dealer service department. However, it is
possible for the home mechanic to make
simple checks of the wiring and vacuum
connections for minor faults which can be
easily repaired. These include:
a) Inspect the cruise control actuating switches
for broken wires and loose connections.
b) Check the cruise control fuse.
c) The cruise control system is operated by
vacuum, so it’s critical that all vacuum
switches, hoses and connections are
secure. Check the hoses in the engine
compartment for loose connections,
cracks, or obvious vacuum leaks.
20 Central locking system-
description and check
2
The central door locking system operates
the door lock actuators mounted in each
door. The system consists of the switches,
actuators and associated wiring. Diagnosis is
limited to simple checks of the wiring
connections and actuators for minor faults
which can be easily repaired. These include:
a) Check the system fuse and/or circuit
breaker (where applicable).
b) Check the switch wires for damage and
loose connections. Check the switches
for continuity.
c) Remove the door trim panel(s), and check
the actuator wiring connections to see if
they’re loose or damaged. Inspect the
actuator rods to make sure they aren’t
12•8 Body electrical systems
18.3 The SRS system crash sensors
(arrowed) are located in the engine
compartment - check the wiring regularly
for damage16.11b Tailgate wiper motor (5-Series)16.11c Wiper blade and pivot mechanism
on the rear window (5-Series)