1983 FIAT UNO engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 30 of 303

16 Engine-
complete dismantling
3
1Unbolt and remove the rocker cover.
2Unscrew the rocker pedestal securing nuts
and lift away the rocker assembly.
3Remove the pushrods, keeping them in
their original fitted order.
4Remove the cylinder head as described in
Section 7. Remove the dipstick and guide
tube.5Turn the engine on its side and unbolt and
remove the sump pan.
6Remove the piston/connecting rods as
described in Section 9.
7Unscrew and remove the crankshaft pulley
nut. To prevent the crankshaft rotating while
this is done, either jam the flywheel ring gear
or place a block between a crankshaft
counterweight and the inside of the
crankcase.
8Unbolt and remove the timing cover.
9Remove the timing chain and sprockets as
described in Section 6. 10Unbolt and remove the oil pump as
described in Section 10.
11Unscrew and remove the camshaft front
bearing lockscrew noting that the chamfer on
the bearing is on the inboard side.
12Withdraw the camshaft, taking great care
not to damage the bearings with the cam
lobes.
13Lift out the cam followers and keep them
in their originally fitted sequence.
14Unbolt and remove the flywheel. Jam the
ring gear teeth to prevent rotation.
15Remove the engine rear plate.
16Turn the cylinder block so that it is
standing upside down.
17Unbolt and remove the crankshaft rear oil
seal carrier. Note the sump fixing studs.
18The main bearing caps should be marked
1, 2 and 3 but if they are not, centre punch
them and note which way round they are
located.
19Unscrew the main bearing cap bolts
progressively.
20Remove the bearing caps and half shells.
If the shell bearings are to be used again,
keep them with their respective caps.
21Note the semi-circular thrust washers on
either side of the centre main bearing which
control crankshaft endfloat.
22Lift the crankshaft from the crankcase.
23Remove the bearing shells from the
crankcase and mark them as to position if
they are to be used again.
17 Cylinder head- dismantling
and decarbonising
4
1The exhaust manifold and rocker gear will
have been removed from the cylinder head
during removal (see Section 7).
2The valves should now be removed using a
universal valve spring compressor.
3Compress the first valve spring and extract
the split cotters.
4Gently release the compressor, take off the
spring retaining cap, the valve spring and the
spring seat. Remove the valve. Keep the valve
with its associated components together and
in numbered sequence so that they can be
returned to their original positions.
5A small box with divisions is useful for this
purpose. Remove and discard the valve stem
oil seals.
6Remove the other valves in a similar way.
7Bearing in mind that the cylinder head is of
1•16 903 cc engine
Fig. 1.23 Timing cover, sump pan and oil seals (Sec 16)
Fig. 1.24 Crankshaft and flywheel (Sec 16)
1 Sump pan bolt
2 Washer
3 Sealing strip
4 Side gasket
5 Side gasket
6 Block/crankcase
7 Gasket8 Bolt
9 Washer
10 Bolt and washer
11 Crankshaft front oil
seal
12 Timing cover
14 Gasket13 Fuel pump studs
and bush
15 Cover plate
16 Bolt and washer
17 Bolt
18 Bolt
19 Washer20 Crankshaft rear oil
seal
21 Oil seal carrier
22 Gasket
23 Sealing strip
24 Sump pan
25 Drain plug
1 Centre main
bearing shells
2 Front main bearing
shells3 Crankshaft
4 Plug
5 Starter ring gear6 Dowel
7 Flywheel
8 Thrust plate9 Bolt
10 Thrust washers
11 Rear main bearing
shells
If the valve spring refuses to
compress, do not apply
excessive force, but remove
the compressor and place a
piece of tubing on the spring retainer
and strike it a sharp blow to release the
collets from the valve stem. Refit the
compressor and resume operations
when the collets should come out.
Page 31 of 303

light alloy construction and is easily damaged
use a blunt scraper or rotary wire brush to
clean all traces of carbon deposits from the
combustion spaces and the ports. The valve
head stems and valve guides should also be
freed from any carbon deposits. Wash the
combustion spaces and ports down with
paraffin and scrape the cylinder head surface
free of any foreign matter with the side of a
steel rule, or a similar article.
8If the engine is installed in the car, clean the
pistons and the top of the cylinder bores. If
the pistons are still in the block, then it is
essential that great care is taken to ensure
that no carbon gets into the cylinder bores as
this could scratch the cylinder walls or cause
damage to the piston and rings. To ensure
this does not happen, first turn the crankshaft
so that two of the pistons are at the top of
their bores. Stuff rag into the other two bores
or seal them off with paper and masking tape.
The waterways should also be covered with
small pieces of masking tape to prevent
particles of carbon entering the cooling
system and damaging the coolant pump.
9With a blunt scraper carefully scrape away
the carbon from the piston crown, taking care
not to scratch the aluminium. Also scrape
away the carbon from the surrounding lip of
the cylinder wall. When all carbon has been
removed, scrape away the grease which will
now be contaminated with carbon particles,
taking care not to press any into the bores. To
assist prevention of carbon build-up the
piston crown can be polished with a metal
polish. Remove the rags or masking tape from
the other two cylinders and turn the
crankshaft so that the two pistons which were
at the bottom are now at the top. Place rag in
the cylinders which have been decarbonised,
and proceed as just described.
10Examine the head of the valves for pitting
and burning, especially the heads of the
exhaust valves. The valve seatings should be
examined at the same time. If the pitting on
the valve and seat is very slight, the markscan be removed by grinding the seats and
valves together with coarse, and then fine,
valve grinding paste.
11Where bad pitting has occurred to the
valve seats it will be necessary to recut them
and fit new valves. This latter job should be
entrusted to the local agent or engineering
works. In practice it is very seldom that the
seats are so badly worn. Normally it is the
valve that is too badly worn for refitting, and
the owner can easily purchase a new set of
valves and match them to the seats by valve
grinding.
12Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Smear a trace of coarse carborundum paste
on the seat face and apply a suction grinder
tool to the valve head. With a semi-rotary
motion, grind the valve head to its seat, lifting
the valve occasionally to redistribute the
grinding paste. When a dull matt even surface
is produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, wipe off the paste and repeat the
process with fine carborundum paste, lifting
and turning the valve to redistribute the paste
as before. A light spring placed under the
valve head will greatly ease this operation.
When a smooth unbroken ring of light grey
matt finish is produced, on both valve and
valve seat faces, the grinding operation is
complete. Carefully clean away every trace of
grinding compound, take great care to leave
none in the ports or in the valve guides. Clean
the valve seats with a paraffin soaked rag,
then with a clean rag, and finally, if an air line
is available, blow the valves, valve guides and
valve ports clean.
13Check that all valve springs are intact. If
any one is broken, all should be renewed.
Check the free height of the springs against
new ones. If some springs are not within
specifications, replace them all. Springs suffer
from fatigue and it is a good idea to renew
them even if they look serviceable.
14Check that the oil supply holes in the
rocker arms are clear.
15The cylinder head can be checked for
warping either by placing it on a piece of plate
glass or using a straight-edge and feeler
blades. If there is any doubt or if its block face
is corroded, have it re-faced by your dealer or
motor engineering works.
16Test the valves in their guides for side toside rock. If this is any more than almost
imperceptible, new guides must be fitted.
Again this is a job for your dealer as a special
tool is required to ensure the correct
installation depth and the cylinder head must
be warmed to 80ºC (176ºF) before fitting the
guides.
17Commence reassembly by oiling the stem
of the first valve and pushing it into its guide
which should have been fitted with a new oil
seal (photos).
18Fit the spring seat. Fit the valve spring so
that the closer coils are towards the cylinder
head and then fit the spring retaining cap.
19Compress the valve spring and locate the
split cotters in the valve stem cut-out (photo).
20Gently release the compressor, checking
to see that the collets are not displaced.
21Fit the remaining valves in the same way.
22Tap the end of each valve stem with a
plastic or copper-faced hammer to settle the
components.
23The cylinder head is now ready for
refitting as described in Section 7.
18 Examination and renovation
4
1With the engine stripped down and all parts
thoroughly clean, it is now time to examine
everything for wear. The following items
should be checked and where necessary
renewed or renovated as described in the
following Sections.
Cylinder block and crankcase
2Examine the casting carefully for cracks
especially around the bolt holes and between
cylinders.
3The cylinder bores must be checked for
taper, ovality, scoring and scratching. Start by
examining the top of the cylinder bores. If they
are at all worn, a ridge will be felt on the thrust
side. This ridge marks the limit of piston ring
travel. The owner will have a good indication
of bore wear prior to dismantling by the
quantity of oil consumed and the emission of
blue smoke from the exhaust especially when
the engine is cold.
4An internal micrometer or dial gauge can be
903 cc engine 1•17
17.19 Fitting split collets17.17B Inserting a valve into its guide17.17A Valve stem oil seal
1
Press a little grease into the
gap between the cylinder
walls and the two pistons
which are to be worked on.
Page 32 of 303

used to check bore wear and taper against
the Specifications, but this is a pointless
operation if the engine is obviously in need of
reboring due to excessive oil consumption.
5Your engine reconditioner will be able to
re-bore the block for you and supply the
correct oversize pistons to give the correct
running clearance.
6If the engine has reached the limit for
reboring then cylinder liners can be fitted, but
here again this is a job for your engine
reconditioner.
7To rectify minor bore wear it is possible to
fit proprietary oil control rings. A good way to
test the condition of the engine is to have it at
normal operating temperature with the spark
plugs removed. Screw a compression gauge
(available from most motor accessory stores)
into the first plug hole. Hold the accelerator
fully depressed and crank the engine on the
starter motor for several revolutions. Record
the reading. Zero the tester and check the
remaining cylinders in the same way. All four
compression figures should be approximately
equal and within the tolerance given in the
Specifications. If they are all low, suspect
piston ring or cylinder bore wear. If only one
reading is down, suspect a valve not seating.
Crankshaft and bearings
8Examine the crankpin and main journal
surfaces for signs of scoring or scratches.
Check the ovality of the crankpins at different
positions with a micrometer. If more than
0.001 inch (0.025 mm) out of round, the
crankpins will have to be reground. They will
also have to be reground if there are any
scores or scratches present. Also check the
journals in the same fashion.
9Wear in a crankshaft can be detected while
the engine is running. Big-end bearing and
crankpin wear is indicated by distinct metallic
knocking, particularly noticeable when the
engine is pulling from low engine speeds. Low
oil pressure will also occur.
10Main bearing and journal wear is indicated
by engine rumble increasing in severity as the
engine speed increases. Low oil pressure will
again be an associated condition.
11Crankshaft grinding should be carried outby specialist engine reconditioners who will
supply the matching undersize bearing shells
to give the required running clearance.
12Inspect the connecting rod big-end and
main bearing shells for signs of general wear,
scoring, pitting and scratching. The bearings
should be matt grey in colour.
13If a copper colour is evident, then the
bearings are badly worn and the surface
material has worn away to expose the underlay.
Renew the bearings as a complete set.
14At the time of major overhaul it is
worthwhile renewing the bearing shells as a
matter of routine even if they appear to be in
reasonably good condition.
15Bearing shells can be identified by the
marking on the back of the shell. Standard
sized shells are usually marked STD or 0.00.
Undersized shells are marked with the
undersize such as 0.25 mm.
Connecting rods
16Check the alignment of the connecting
rods visually. If you suspect distortion, have
them checked by your dealer or engine
reconditioner on the special jig which he will
have.
17The gudgeon pin is an interference fit in
the connecting rod small-end and removal or
refitting and changing a piston is a job best
left to your dealer or engine reconditioner due
to the need for a press and jig and careful
heating of the connecting rod.
Pistons and piston rings
18If the cylinders have been rebored, then
the reconditioner will supply the oversize
pistons and rings and the gudgeon pins. Give
the job of fitting the new pistons to the
connecting rods to him.
19If the original piston rings or just new rings
are to be fitted to the original pistons, use
great care to remove and fit the rings as they
are easily broken if expanded too much.
Always remove and fit rings from the crown
end.
20If three old feeler blades are slid behind
the piston rings and located at equidistant
points, the rings may be removed or fitted
without their dropping into the wrong grooves
and will reduce the chance of breakage
(photo).
21If the original pistons are being refitted,
make sure that the ring grooves and their oil
return holes are cleaned out and freed from
carbon. A piece of piston ring is a useful tool
for this purpose.
22The three pistons rings are as follows:
Top - Thinner compression marked TOP
Second - Thicker compression, step at base
Bottom - Oil control (photo)
23If proprietary wear control rings are to be
fitted to overcome bore wear, fit them strictly
in accordance with the manufacturer’s
instructions.
24Always check the piston ring groove
1•18 903 cc engine
18.24A Checking piston ring groove
clearance18.22 Piston ring marking
18.20 Using feeler blades to fit piston ringsFig. 1.26 Piston/connecting rod
relationship (Sec 18)Fig. 1.25 Checking a crankpin (Sec 18)
Page 33 of 303

clearance and end gap. Both clearances
should be checked with a feeler gauge. Check
the end gap when the ring has been pushed
squarely down the cylinder bore for two or
three inches (photos).
25If new rings are being used and the
cylinder bores have not been rebored, always
make sure that the top compression ring has
been stepped to prevent it contacting the
bore wear ridge.
Flywheel
26Check the clutch mating surface of the
flywheel. If it is deeply scored (due to failure to
renew a worn driven plate) then it may be
possible to have it surface ground provided
the thickness of the flywheel is not reduced
too much.
27If lots of tiny cracks are visible on the
surface of the flywheel then this will be due to
overheating caused by slipping the clutch or
“riding” the clutch pedal.
28With a pre-engaged type of starter motor
it is rare to find the teeth of the flywheel ring
gear damaged or worn but if they are, then the
ring gear will have to be renewed.
29To remove the ring gear, drill a hole
between the roots of two teeth taking care not
to damage the flywheel and then split the ring
with a sharp cold chisel.
30The new ring gear must be heated to
between 180 and 220ºC (356 and 428ºF)
which is very hot, so if you do not have
facilities for obtaining these temperatures,
leave the job to your dealer or engine
reconditioner.
31Where such facilities are available, then
the ring gear should be either pressed or
lightly tapped gently onto its register and left
to cool naturally, when the contraction of the
metal on cooling will ensure that it is a secure
and permanent fit. Great care must be taken
not to overheat the ring gear, as if this
happens its temper will be lost. A clutch input
shaft pilot bearing is not fitted on this engine.
Camshaft
32Examine the camshaft bearings for wear,
scoring or pitting. If evident then the bearings
will have to be renewed. The three bearingsare of different sizes and they can be removed
and new ones fitted using a bolt, nut and
distance pieces. When drawing a new bearing
into position, make sure that the oil hole is
correctly aligned with the one in the
crankcase. The centre and rear bearings
require reaming after fitting, the bearing at the
timing chain end is supplied ready reamed
(photo).
33The camshaft itself should show no marks
or scoring on the journal or cam lobe
surfaces. Where evident, renew the camshaft
or have it reprofiled by a specialist
reconditioner.
34Check the teeth of the camshaft sprocket
for wear. Renew the sprocket if necessary.
Cam followers
35Examine the bearing surface of the cam
followers which are in contact with the
camshaft. Any indentations or cracks must be
rectified by renewal. Clean sludge and dirt
from the cam followers and check their fit in
their bores. Side to side rock is unusual
except at very high mileage.
Timing chain
36Examine the teeth on both the crankshaft
sprocket and the camshaft sprocket for wear.
Each tooth forms an inverted “V” with the
sprocket periphery and if worn, the side of
each tooth under tension will be slightly
concave in shape when compared with the
other side of the tooth, ie; one side of the
inverted “V” will be concave when compared
with the other. If any sign of wear is present
the sprockets must be renewed.
37Examine the links of the chain for side
slackness and particularly check the
self-tensioning links for freedom of
movement. Renew the chain if any slackness
is noticeable when compared with a new
chain. It is a sensible precaution to renew the
chain at about 60 000 miles (96 000 km) and
at a lesser mileage if the engine is stripped
down for a major overhaul.
Cylinder head
38This is covered in Section 17.
Rockers and rocker shaft
39Thoroughly clean out the rocker shaft. As
it acts as the oil passages for the valve gear,
clean out the oil holes and make sure they are
quite clear. Check the shaft for straightness
by rolling it on a flat surface. If it is distorted,
renew it.
40The surface of the shaft should be free
from any wear ridges caused by the rocker
arms. If it is not, the shaft will have to be
renewed. Blocked shaft oil holes often
contribute to such wear.
41Check the rocker arms for wear of the
rocker bushes, for wear at the rocker arm face
which bears on the valve stem, and for wear
of the adjusting ball ended screws. Wear in
the rocker arm bush can be checked by
gripping the rocker arm tip and holding the
rocker arm in place on the shaft, noting if
there is any lateral rocker arm shake. If any
shake is present, and the arm is very loose on
the shaft, remedial action must be taken. It is
recommended that a worn rocker arm be
taken to your local FIAT agent or automobile
engineering works to have the old bush drawn
out and a new bush fitted (photo).
42Check the tip of the rocker arm where it
bears on the valve head, for cracking or
serious wear on the case hardening. If none is
present the rocker arm may be refitted. Check
the pushrods for straightness by rolling them
on a flat surface.
Oil pump
43Unscrew the four securing bolts which
connect the two halves of the pump body.
44Clean all the components in a bath of
paraffin and dry them.
45Inspect the gears for wear or damage and
then check for wear in the following way.
46Insert a feeler blade between the tooth
peak and the body. This should be between
0.05 and 0.14 mm (0.0019 and 0.0055 in).
47Now place a straight-edge across the
body flange and check for gear endfloat. This
should be between 0.020 and 0.105 mm
(0.0008 and 0.0041 in). Where the clearances
exceed the specified limits, renew the pump.
48Check that the oil pressure relief valve
spring is in good condition and not deformed.
903 cc engine 1•19
18.41 Rocker components18.32 Camshaft bearing18.24B Checking piston ring end gap
1
Page 34 of 303

Oil seals and gaskets
49It is recommended that all gaskets and oil
seals are renewed at major engine overhaul.
Sockets are useful for removing or refitting oil
seals. An arrow is moulded onto some seals
to indicate the rotational direction of the
component which it serves. Make sure that
the seal is fitted the correct way round to
comply with the arrow.
19 Engine- reassembly (general)
1To ensure maximum life with minimum
trouble from a rebuilt engine, not only must
every part be correctly assembled, but
everything must be spotlessly clean, all the
oilways must be clear, locking washers and
spring washers must always be fitted where
indicated and all bearing and other working
surfaces must be thoroughly lubricated during
assembly. Before assembly begins renew any
bolts or studs whose threads are in any way
damaged; whenever possible use new spring
washers.
2Apart from your normal tools, a supply of
non-fluffy rag, an oil can filled with engine oil,
a supply of new spring washers, a set of new
gaskets and a torque wrench should be
gathered together.
20 Engine-
complete reassembly
4
Crankshaft and main bearings
1With the cylinder block inverted on the
bench, wipe out the crankcase shell bearing
seats and fit the half shells so that their tabs
engage in the notches (photo).
2Stick the semi-circular thrust washers either
side of the centre bearing in the crankcase
using thick grease. Make sure that the oil
grooves are visible when the washers are
fitted (photo).
3If the original bearing shells are being
refitted, make sure that they are returned to
their original positions.
4Liberally oil the bearing shells and lower the
crankshaft into position. Make sure that it is
the correct way round (photos).
5Wipe out the main bearing caps and fit the
bearing shells into them.
6Oil the crankshaft journals and fit the main
bearing caps, the correct way round and in
proper sequence (photo).
7Replace the main bearing cap bolts and
screw them up finger-tight.
8Test the crankshaft for freedom of rotation.
Should it be very stiff to turn, or possess high
spots, a most careful inspection must be
made, preferably by a skilled mechanic with a
1•20 903 cc engine
20.4B Lowering crankshaft into
position20.4A Oiling main bearing shells
20.2 Crankshaft thrust washer20.1 Fitting a main bearing shell
Fig. 1.27 Exploded view of oil pump (Sec 18)
1 Bolt
2 Bolt
3 Washers
4 Washer
5 Spring
6 Drive gear
7 Top housing
8 Driven gear
9 Plate
10 Pressure relief valve
11 Lower housing and
oil pick-up
12 Filter screen
Page 35 of 303
micrometer to trace the cause of the trouble.
It is very seldom that any trouble of this nature
will be experienced when fitting the
crankshaft.
9Tighten the main bearing bolts to the
specified torque wrench settings (photo).
10Using a dial gauge or feeler blades
inserted between a thrust washer and the
crankshaft, check the crankshaft endfloat. If it
exceeds the specified limit, the thrust washers
can be changed for thicker ones (photo).
11Bolt on the crankshaft rear oil seal carrier
using a new gasket. The carrier should have
been fitted with a new oil seal and the seal lips
greased (photos).
12Fit the engine rear plate (photo).
Flywheel
13Offer the flywheel to the crankshaft. With
pistons No. 1 and 4 at TDC, the dimple on the
flywheel must be uppermost.
14Screw in and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque. The crankshaft may be held
against rotation by either jamming the starter
ring gear or placing a block of wood between
one of the crankshaft webs and the inside of
the crankcase (photo).
Camshaft
15Oil the cam followers and return them to
their original positions (photo).
16Oil the camshaft bearings and insert the
camshaft, taking great care not to damage the
bearings with the cam lobes. Fit the front
bearing, chamfer inwards (photos).
903 cc engine 1•21
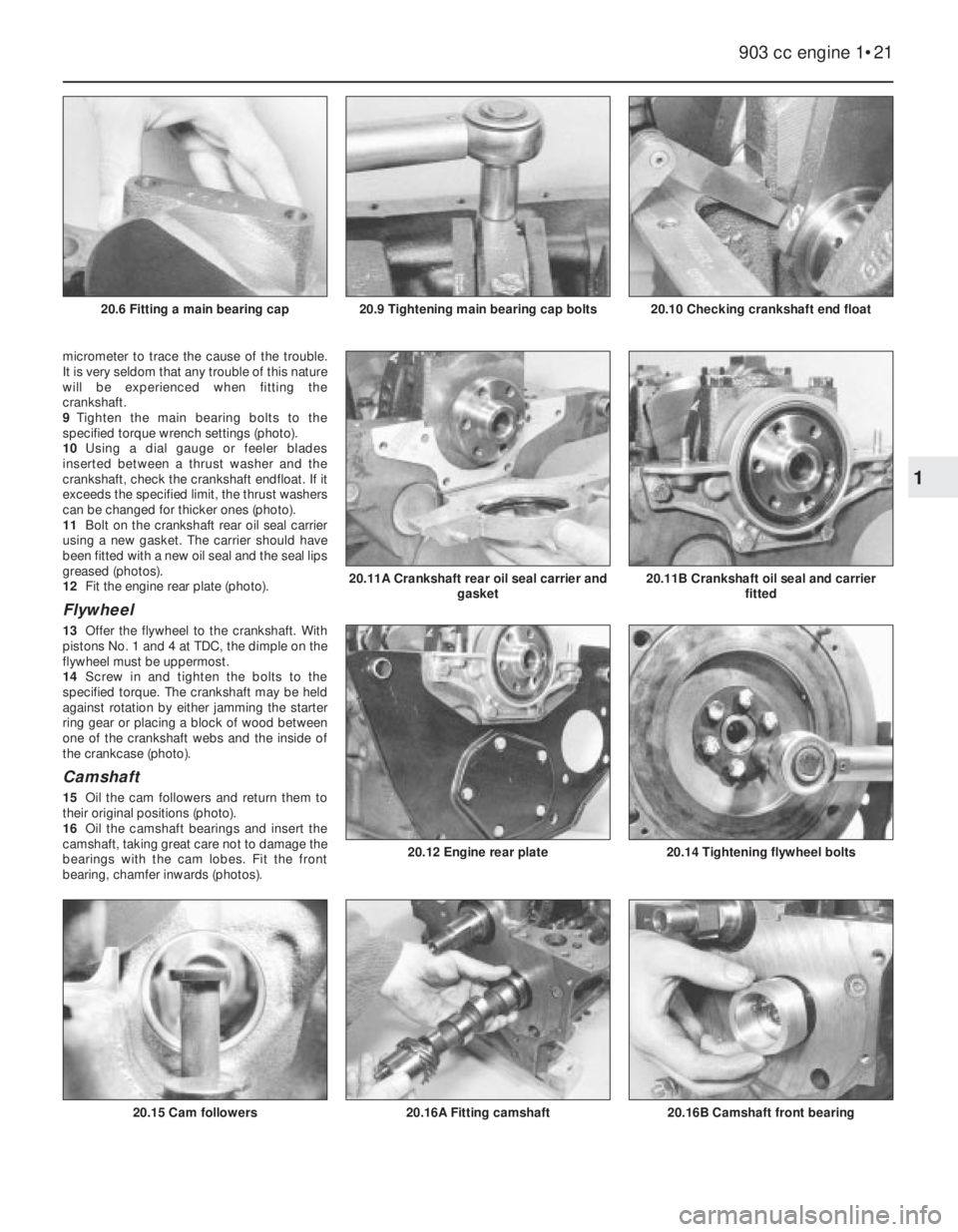
20.10 Checking crankshaft end float20.9 Tightening main bearing cap bolts20.6 Fitting a main bearing cap
20.16B Camshaft front bearing20.16A Fitting camshaft
20.11B Crankshaft oil seal and carrier
fitted20.11A Crankshaft rear oil seal carrier and
gasket
20.14 Tightening flywheel bolts20.12 Engine rear plate
20.15 Cam followers
1
Page 36 of 303

17Screw in the camshaft front bearing
lockscrew (photo).
Oil pump
18Refit the oil pump as described in Sec-
tion 10.
Timing chain and sprockets
19Fit the timing chain and sprockets as
described in Section 6. Fit the Woodruff key
to the crankshaft nose.
20Using a new gasket, fit the timing chain
cover, but leave the bolts finger tight (photo).
21Apply grease to the lips of the timing
cover oil seal and then push the crankshaft
pulley into position.
22Move the timing cover if necessary so that
the pulley hub is centralised in the oil seal and
then tighten the cover bolts.
23Screw on the crankshaft pulley nut and
tighten to the specified torque (photo).
Piston/connecting rods
24Fit these as described in Section 9.
Sump pan
25Fit the sump pan as described in Sec-
tion 8.
Cylinder head
26Stand the engine upright and fit the
cylinder head as described in Section 7.
27Insert the pushrods in their original fitted
order.
28With the rocker arm adjuster screws fully
unscrewed, locate the rocker gear and screw
on the fixing nuts.
29Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 5.
30Locate a new gasket in position and fit the
rocker cover (photo).
31Screw on a new oil filter (Section 2).
21 Engine- refitting ancillary
components
1Refer to Chapter 5 and refit the clutch,
making sure to centralise the driven plate.
2Fit the coolant pump as described in
Chapter 2. Fit the thermostat housing if it was
removed noting the air cleaner mounting
bracket on the housing studs.
3Fit the alternator and drivebelt as described
in Chapter 9.
4Refer to Chapter 3 and fit the exhaust
manifold and hot air collector, the carburettor
and spacer and the fuel pump.
5Fit the distributor as described in Chapter
4. Fit the oil dipstick guide tube (photos).
22 Engine/transmission-
reconnection
1
1Support the weight of the transmission and
offer it squarely to the engine. The splined
input shaft should pass easily through the hub
of the driven plate, provided the plate has
been centralised as described in Chapter 5. It
may be necessary to align the splines with the
hub grooves, in which case have an assistant
turn the crankshaft pulley nut. The alignment
dowels will make the connection stiff, so
drawing the engine and transmission together
with two connecting bolts will ease it.
2Once the engine and transmission are fully
engaged, insert and tighten all the connecting
bolts. Locate the lifting eyes.
3Bolt on the flywheel housing cover plate
and the mounting brackets.
4Bolt on the starter motor.
23 Engine/transmission-
refitting
3
1The refitting operations are reversals of
those described in Section 13.
2Observe the following special points.
3Tighten the engine mounting and front
suspension (disconnected) bolts to the
specified torque when the hoist has been
1•22 903 cc engine
21.5B Dipstick guide tube support21.5A Dipstick guide tube20.30 Rocker cover nut and thrust plate
20.23 Tightening crankshaft pulley nut20.20 Timing cover20.17 Camshaft front bearing lockscrew
Hold the crankshaft against
rotation either by jamming
the starter ring gear or by
placing a block of wood
between a crankshaft web and the
inside of the crankcase.
Page 37 of 303

removed and the weight of the car is again on
its roadwheels.
4Fill the cooling system.
5Fill the engine with oil.
6Replenish lost transmission oil.
7Reconnect the battery.
8Adjust the clutch pedal as described in
Chapter 5.
24 Engine- initial start-up after
overhaul or major repair
4
1Make sure that the battery is fully charged
and that all lubricants, coolant and fuel are
replenished.
2If the fuel system has been dismantled it will
require several revolutions of the engine on
the starter motor to pump the petrol up to the
carburettor.
3Turn the carburettor throttle speed screwthrough one complete turn to increase the idle
speed in order to offset the initial stiffness of
new engine internal components.
4As soon as the engine fires and runs, keep
it going at a fast idle speed and bring it up to
normal working temperature.
5As the engine warms up there will be odd
smells and some smoke from parts getting
hot and burning off oil deposits. The signs to
look for are leaks of water or oil which will be
obvious.
6Check also the exhaust pipe and manifold
connections as these do not always “find”
their exact gas tight position until the warmth
and vibration have acted on them and it is
almost certain that they will need tightening
further. This should be done, of course, with
the engine stopped.
7When normal running temperature has
been reached, adjust the engine idle speed as
described in Chapter 3.
8Stop the engine and wait a few minutes tosee if any lubricant or coolant is dripping out
when the engine is stationary.
9Road test the car to check that the timing is
correct and that the engine is giving the
necessary smoothness and power. Do not
race the engine - if new bearings and/or
pistons have been fitted it should be treated
as a new engine and run in at a reduced
speed for the first 500 km (300 miles).
10After the first 1500 km (900 miles) the
cylinder head bolts must be re-torqued in the
following way (engine cold).
11Remove the air cleaner and rocker cover.
Unscrew the first bolt (Fig. 1.7) through a
quarter turn and then tighten it to final stage 2
torque (see Specifications).
12Repeat on the remaining bolts, one at a
time.
13Check and adjust the valve clearances
(Section 5).
14Refit the rocker cover and air cleaner.
903 cc engine 1•23
26.4 Shim engraved mark26.2 Removing a shim from a cam follower25.4 Checking a valve clearance
1
Part 3: 1116 cc and 1301 cc engines
25 Valve clearances- checking
2
This should only be required if the valves
have been renewed or ground in, or at high
mileages when noise or poor engine
performance indicates that a check is
necessary.
It is important that each valve clearance is
set correct otherwise the timing will be
wrong and engine performance poor. If there
is no clearance at all, the valve and its seat
will soon burn. Always set the clearances
with the engine cold.
1Remove the camshaft cover. Jack-up a
front wheel and engage top gear so that by
turning the wheel, the crankshaft can be
rotated.
2Each valve clearance must be checked
when the high point of the cam is pointing
directly upward away from the cam follower.
3Check the clearances in the firing order
1-3-4-2, No. 1 cylinder being at the timing
belt end of the engine. This will minimise the
amount of crankshaft rotation required.4Insert the appropriate feeler blade
between the heel of the cam and the cam
follower shim of the first valve. If necessary
alter the thickness of the feeler blade until it
is a stiff, sliding fit. Record the thickness,
which will, of course, represent the valve
clearance for this particular valve (photo).
5Turn the crankshaft, check the second
valve clearance and record it.
6Repeat the operations on all the remaining
valves, recording their respective clearances.
7Remember that the clearance for inlet and
exhaust valves differs - see Specifications.
Counting from the timing cover end of the
engine, the valve sequence is:
Inlet 2-3-6-7
Exhaust 1-4-5-8
26 Valve clearances-
adjustment
3
1Check the valve clearances (Section 25).
2Clearances which are incorrect will mean
the particular shim will have to be changed.
To remove the shim, turn the crankshaft untilthe high point of the cam is pointing directly
upward. The cam follower will now have to
be depressed so that the shim can be
extracted. Special tools (A60642 and
A87001) are available from your Fiat dealer to
do the job, otherwise you will have to make
up a forked lever to locate on the rim of the
cam follower. This must allow room for the
shim to be prised out by means of the
cut-outs provided in the cam follower rim
(photo).
3Once the shim is extracted, establish its
thickness and change it for a thicker or
thinner one to bring the previously recorded
clearance within specification. For example,
if the measured valve clearance was 1.27
mm (0.05 in) too great, a shim thicker by this
amount will be required. Conversely, if the
clearance was 1.27 mm (0.05 in) too small, a
shim thinner by this amount will be required.
4Shims have their thickness (mm) engraved
on them; although the engraved side should
be fitted so as not to be visible, wear still
occurs and often obliterates the number. In
this case, measuring their thickness with a
metric micrometer is the only method to
establish their thickness (photo).