1983 BMW 3 SERIES Fluids
[x] Cancel search: FluidsPage 2 of 228

LIVING WITH YOUR BMW
IntroductionPage 0•4
Safety First!Page 0•6
Anti-theft audio system Page0•7
Instrument panel language display Page0•7
Roadside Repairs
Jacking, towing and wheel changing Page0•8
Jump startingPage0•9
Identifying leaksPage0•10
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
Routine Maintenance and Servicing Page1•1
Lubricants and fluids Page1•3
Maintenance schedule Page1•4
Weekly checks Page1•7
Every 6000 miles Page1•11
Every 12 000 miles Page1•16
Every 24 000 miles Page1•23
Every 60 000 miles Page1•26
Contents
Page 10 of 228

0•10Roadside Repairs
Puddles on the garage floor or drive, or
obvious wetness under the bonnet or
underneath the car, suggest a leak that needs
investigating. It can sometimes be difficult to
decide where the leak is coming from,
especially if the engine bay is very dirty
already. Leaking oil or fluid can also be blown
rearwards by the passage of air under the car,
giving a false impression of where the
problem lies.Warning: Most automotive oils
and fluids are poisonous. Wash
them off skin, and change out of
contaminated clothing, without
delay.
Identifying leaks
The smell of a fluid leaking
from the car may provide a
clue to what’s leaking. Some
fluids are distinctively
coloured. It may help to clean the car
carefully and to park it over some clean
paper overnight as an aid to locating the
source of the leak.
Remember that some leaks may only
occur while the engine is running.
Sump oil Gearbox oil
Brake fluid Power steering fluidOil from filter
Antifreeze
Engine oil may leak from the drain plug......or from the base of the oil filter.
Leaking antifreeze often leaves a crystalline
deposit like this.Gearbox oil can leak from the seals at the
inboard ends of the driveshafts.
A leak occurring at a wheel is almost
certainly brake fluid.Power steering fluid may leak from the pipe
connectors on the steering rack.
Page 13 of 228

Tyre pressures (cold) - bars (psi)Front Rear
3-Series, E30
316 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.1 (30)
316i
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.1 (30)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.2 (32)
318i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8 (26) 1.9 (28)
320i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 (28) 2.0 (29)
325i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.3 (33)
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
525i and 528i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.2 (32)
535i and M535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 (33) 2.5 (36)
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.0 (29)
520i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 (32) 2.1 (30)
525i, 530i and 535i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 (29) 2.3 (33)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Automatic transmission sump bolts
Three-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 9
Four-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 to 7
Spark plugs
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 to 30
Except M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 to 33
Wheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Lubricants and fluids
Component or system Lubricant type/specification
Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multigrade engine oil, viscositySAE 10W/40 to 20W/50, to API SG
Cooling system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze with corrosion inhibitors
Manual transmission* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gear oil, viscosity SAE 80 to API-GL4, or single-grade mineral-based
engine oil, viscosity SAE 20, 30 or 40 to API-SG
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
Final drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . BMW-approved hypoid gear oil, viscosity SAE 90**
Brake and clutch hydraulic systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic brake fluid to SAE J 1703 or DOT 4
Power steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dexron ll type ATF
* E34 520i & 525i with air conditioning, E34 530i & 535i - Dexron II type ATF)
** Only available in bulk; refer to your BMW dealer
Capacities*
1•3
1
Engine oil
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.3 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.8 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 litres
Cooling system
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.5 litres
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.0 litres
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0 litres
Fuel tank
3-Series, E30
Saloon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 litres (early),
64 litres (later)
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 litres (early),
70 litres (later)
5-Series
E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 litres
E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81 litresManual transmission
ZF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 litres
Getrag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.5 litres
Automatic transmission (refill)
3-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 litres
4-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 litres
Final drive capacity (drain and refill)
3-Series, E30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.9 litres
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.7 litres
*All capacities approximate
Servicing Specifications
Page 14 of 228

Maintenance schedule
The following maintenance intervals are based on the assumption
that the vehicle owner will be doing the maintenance or service work,
as opposed to having a dealer service department do the work.
Although the time/mileage intervals are loosely based on factory rec-
ommendations, most have been shortened to ensure, for example, that
such items as lubricants and fluids are checked/changed at intervals
that promote maximum engine/driveline service life. Also, subject to
the preference of the individual owner interested in keeping his or her
vehicle in peak condition at all times, and with the vehicle’s ultimate
resale in mind, many of the maintenance procedures may be
performed more often than recommended in the following schedule.
We encourage such owner initiative.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced initially by a factory-
authorised dealer service department, to protect the factory warranty.
In many cases, the initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the
owner (check with your dealer service department for more
information).
1•4Maintenance and servicing
Every 250 miles or weekly, whichever
comes first
m mCheck the engine oil level (Section 4)
m mCheck the engine coolant level (Section 4)
m mCheck the brake fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the clutch fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the washer fluid level (Section 4)
m mCheck the tyres and tyre pressures (Section 5)
Every 6000 miles or 6 months,
whichever comes first
All items listed above, plus:
m mChange the engine oil and oil filter (Section 6)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level (Section 7)
m mCheck the tyres, and rotate if necessary (Section 9)
m mCheck the automatic transmission fluid level
(Section 8)
m mCheck the underbonnet hoses (Section 10)
m mCheck/adjust the drivebelts (Section 11)
m mCheck engine idle speed and CO (Section 12)
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever comes first
All items listed above, plus:
m mCheck/service the battery (Section 13)
m mCheck the spark plugs (Section 14)
m mCheck/renew the HT leads, distributor cap and
rotor (Section 15)
m mCheck/top-up the manual transmission lubricant
(Section 16)
m mCheck the differential oil level (Section 17)
m mCheck the valve clearances, and adjust if
necessary - does not apply to M40 engines
(Section 18)
m mCheck and lubricate the throttle linkage (Section 19)
m mRenew the air filter (Section 20)
m mCheck the fuel system (Section 21)
m mInspect the cooling system (Section 22)
m mInspect the exhaust system (Section 23)
m mInspect the steering and suspension components
(Section 24)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiter(s) (Section 25)
m mInspect the brakes (Section 26)
m mInspect/renew the windscreen wiper blades
(Section 27)
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever comes first
All items listed above plus:
m mChange the automatic transmission fluid and filter
(Section 28)
m mDrain, flush and refill the cooling system (Section 29)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 14)
m mCheck/renew the spark plug HT leads (Section 15)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 30)
m mChange the manual transmission lubricant (Section 31)
m mChange the differential oil (Section 32)
m mCheck the evaporative emissions system, where
applicable (Section 33)
m mReset the service indicator lights (Section 34)
m mRenew brake fluid by bleeding (see Chapter 9)
m mCheck the handbrake operation (see Chapter 9)
Every 60 000 miles
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 35)
Page 17 of 228

1 Introduction
This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his or her vehicle with the
goals of maximum performance, economy,
safety and reliability in mind. Included is a
master maintenance schedule, followed by
procedures dealing specifically with each item
on the schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of various components. Servicing the vehicle,
in accordance with the mileage/time
maintenance schedule and the step-by-step
procedures, will result in a planned
maintenance programme that should produce
a long and reliable service life. Keep in mind
that it is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at specified
intervals, will not produce the same results.
2 Routine maintenance
As you service the vehicle, you will discover
that many of the procedures can - and should
- be grouped together, because of the nature
of the particular procedure you’re performing,
or because of the close proximity of two
otherwise-unrelated components to one
another. For example, if the vehicle is raised
for chassis lubrication, you should inspect the
exhaust, suspension, steering and fuelsystems while you’re under the vehicle. When
the wheels are removed for other work, it
makes good sense to check the brakes, since
the wheels are already removed. Finally, let’s
suppose you have to borrow a torque wrench.
Even if you only need it to tighten the spark
plugs, you might as well check the torque of
as many critical nuts and bolts as time allows.
The first step in this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
procedures you’re planning to do, then gather
up all the parts and tools needed. If it looks
like you might run into problems during a
particular job, seek advice from a mechanic or
an experienced do-it-yourselfer.
3 Engine “tune-up”-
general information
The term “tune-up” is used in this manual to
represent a combination of individual
operations rather than one specific procedure.
If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
More likely than not, however, there will be
times when the engine is running poorly due
to a lack of regular maintenance. This is even
more likely if a used vehicle, which has not
received regular and frequent maintenance
checks, is purchased. In such cases, an
engine tune-up will be needed outside of the
regular maintenance intervals. The first step in any tune-up or diagnostic
procedure to help correct a poor-running
engine is a cylinder compression check. A
compression check (see Chapter 2B) will help
determine the condition of internal engine
components, and should be used as a guide
for tune-up and repair procedures. If, for
instance, a compression check indicates
serious internal engine wear, a conventional
tune-up will not improve the performance of
the engine, and would be a waste of time and
money. Because of its importance, the
compression check should be done by
someone with the right equipment, and the
knowledge to use it properly.
The following procedures are those most
often needed to bring a generally poor-
running engine back into a proper state of
tune.
Minor tune-up
Check all engine-related fluids (Section 4)
Check all underbonnet hoses (Section 10)
Check and adjust the drivebelts (Sec-
tion 11)
Clean, inspect and test the battery (Sec-
tion 13)
Renew the spark plugs (Section 14)
Inspect the spark plug HT leads, distributor
cap and rotor (Section 15)
Check the air filter (Section 20)
Check the cooling system (Section 22)
Major tune-up
All items listed under minor tune-up, plus . . .
Check the ignition system (see Chapter 5)
Check the charging system (see Chapter 5)
Check the fuel system (see Chapter 4)
Renew the spark plug HT leads, distributor
cap and rotor (Section 15)
1•7
1
Routine Maintenance
Weekly checks
4 Fluid level checks
1
Note:The following are fluid level checks to
be done on a 250-mile or weekly basis.
Additional fluid level checks can be found in
specific maintenance procedures which
follow. Regardless of intervals, be alert to fluid
leaks under the vehicle, which would indicate
a fault to be corrected immediately.
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, brake and windscreen
washer systems. Because the fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids”at the beginning of this Chapter before
adding fluid to any of the following
components. Note:The vehicle must be on
level ground when any fluid levels are
checked.
Engine oil
2Engine oil is checked with a dipstick, which
is located on the side of the engine (refer to
the underbonnet illustrations in this Chapter
for dipstick location). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube down into the sump.
3The engine oil should be checked before
the vehicle has been driven, or at least
15 minutes after the engine has been shut off.
4Pull the dipstick out of the tube, and wipe
all of the oil away from the end with a clean
rag or paper towel. Insert the clean dipstick all
the way back into the tube, and pull it out
again. Note the oil at the end of the dipstick.
At its highest point, the oil should be betweenthe two notches or marks (see illustration).
5It takes one litre of oil to raise the level from
the lower mark to the upper mark on the
dipstick. Do not allow the level to drop below
the lower mark, or oil starvation may cause
4.4 The oil level should be kept between
the two marks, preferably at or near the
upper one - if it isn’t, add enough oil to
bring the level to the upper mark
If the oil is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the upper part of
the engine, resulting in an inaccurate
reading on the dipstick.
Page 29 of 228

them to the new cap in the exact same
location - do not simultaneously remove all
the HT leads, or firing order mix-ups may
occur.
16 Manual transmission
lubricant level check
1
1The transmission has a filler/level plug
which must be removed to check the lubricant
level. If the vehicle is raised to gain access to
the plug, be sure to support it safely - do not
crawl under a vehicle which is supported only
by a jack!Note:The vehicle should be level to
give an accurate lubricant check.
2Remove the plug from the side of thetransmission (see illustration)and use your
little finger to reach inside the plug from the
housing and feel the lubricant level. It should
be at or very near the bottom of the plug hole.
3If it isn’t, add the recommended lubricant
through the plug hole with a syringe or
squeeze-bottle, until it just starts to run out of
the hole. Refer to “Lubricants and fluids” at
the beginning of this Chapter for the correct
lubricant type. The manual transmissions on
some later or high-performance models are
filled with automatic transmission fluid (ATF).
Such transmissions normally carry a sticker to
this effect near the filler/level plug. Refer to a
BMW dealer if still in doubt.
4Refit the plug and tighten securely. Check
for leaks after the first few miles of driving.
5If regular topping-up is required, this can
only be due to a leak which should be found
and repaired before it becomes serious.17 Differential lubricant level
check
1
1The differential has a filler/level plug which
must be removed to check the lubricant level.
If the vehicle is raised to gain access to the
plug, be sure to support it safely - do notcrawl under the vehicle when it’s supported
only by the jack! Note:The vehicle should be
level to give an accurate lubricant check.
2Remove the filler/level plug from the
differential (see illustration). Use an Allen key
to unscrew the plug.
3Use your little finger as a dipstick to make
sure the lubricant level is up to the bottom of
the plug hole. If not, use a syringe or squeeze-
bottle to add the recommended lubricant until
it just starts to run out of the hole.
4Refit the plug and tighten it securely.
5If regular topping-up is required, this can
only be due to a leak which should be found
and repaired before it becomes serious.
18 Valve clearances -
check and adjustment
3
Note:This procedure does not apply to the
M40 engine, which has automatic adjusters.
1The valve clearances can be checked with
the engine hot or cold, but note that different
values are specified, depending on engine
temperature. If it is wished to check/adjust the
valve clearances with the engine hot, if
necessary start and run the engine until it
reaches normal operating temperature, then
shut it off.
Caution: If the clearances are checked
with the engine hot, extra care
must be taken to avoid burns.
2Remove the valve cover
from the engine (see Chapter 2A).
3Turn the engine as necessary until No 1
piston (front) is at Top Dead Centre (TDC) on
the compression stroke (see Chapter 2A).
4Check the valve clearances for No 1
cylinder. The valve clearances can be found in
the Specifications Section at the beginning of
this Chapter.
5The clearance is measured by inserting the
specified size feeler gauge between the end
of the valve stem and the rocker arm adjusting
eccentric. You should feel a slight amount of
1•19
15.11d The rotor arm should be checked
for wear and corrosion as indicated here
(if in doubt about its condition, buy a new
one)
15.11c Shown here are some of the
common defects to look for when
inspecting the distributor cap (if in doubt
about its condition, fit a new one)
18.6 The valve clearance is adjusted by
turning the eccentric with a wire hook -
once the specified clearance is obtained,
tighten the locknut with a spanner, then
remove the feeler gauge17.2 Remove the differential filler/level
plug with an Allen key, and make sure the
lubricant is level with the bottom of the
hole16.2 Use a large Allen key to remove the
filler/level plug (arrowed) and check the
lubricant level with your little finger. It
should be level with the bottom of the hole
- if it’s low, add lubricant
1
Every 12 000 miles
Page 33 of 228
material is bonded to a metal plate or shoe -
the metal portion is not included in this
measurement. Always renew the pads on
both sides of the vehicle (in axle sets), even if
only one pad of the four is worn, or uneven
braking may result.
12Remove the calipers without
disconnecting the brake hoses (see Chap-
ter 9).
13Check the condition of the brake disc.
Look for score marks, deep scratches and
overheated areas (they will appear blue or
discoloured). If damage or wear is noted, the
disc can be removed and resurfaced by an
engineering workshop; otherwise, it will have
to be renewed. In either case, both discs
should be involved, even if only one is worn.
Refer to Chapter 9 for more detailed
inspection and repair procedures.
Drum brakes
14Refer to Chapter 9 and remove the rear
brake drums.
15Note the thickness of the lining material
on the rear brake shoes, and look for signs of
contamination by brake fluid or grease (see
illustration). If the material is within 2.0 mm of
the recessed rivets or metal shoes, renew the
brake shoes. The shoes should also be
renewed if they are cracked, glazed (shiny
lining surfaces), or contaminated with brake
fluid or grease. See Chapter 9 for the renewal
procedure.
16Check the shoe return and hold-down
springs and the adjusting mechanism. Make
sure all these components are fitted correctly,and are in good condition. Deteriorated or
distorted springs, if not renewed, could allow
the linings to drag and wear prematurely.
17Check the wheel cylinders for leakage by
carefully peeling back the rubber boots. Slight
moisture behind the boots is acceptable. If
brake fluid is noted behind the boots or if it
runs out of the wheel cylinder, the wheel
cylinders must be overhauled or renewed (see
Chapter 9).
18Check the drums for cracks, score marks,
deep scratches and high spots, which will
appear as small discoloured areas. If
imperfections cannot be removed with emery
cloth, both drums must be resurfaced by a
specialist (see Chapter 9 for more detailed
information).
19Refer to Chapter 9 and fit the brake
drums.
20Refit the wheels, but don’t lower the
vehicle yet.
Handbrake
21The easiest, and perhaps most obvious,
method of checking the handbrake is to park
the vehicle on a steep hill with the handbrake
applied and the transmission in Neutral (stay
in the vehicle while performing this check). If
the handbrake doesn’t prevent the vehicle
from rolling, refer to Chapter 9 and adjust it.
27 Wiper blades -
check and renewal
1
1Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should bewashed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
Check
2The wiper and blade assembly should be
inspected periodically. If inspection reveals
hardened or cracked rubber, renew the wiper
blades. If inspection reveals nothing unusual,
wet the windscreen, turn the wipers on, allow
them to cycle several times, then switch them
off. An uneven wiper pattern across the glass,
or streaks over clean glass, indicate that the
blades should be renewed.
3The operation of the wiper mechanism can
loosen the retaining nuts, so they should be
checked and tightened, as necessary, at the
same time the wiper blades are checked (see
Chapter 12 for further information regarding
the wiper mechanism).
Wiper blade renewal
4Pull the wiper/blade assembly away from
the glass.
5Press the retaining tab in, and slide the
blade assembly down the wiper arm (see
illustration).
6If you wish to renew the blade rubbers
separately, detach the end of the rubber from
the wiper blade frame, then slide the rubber
out of the frame (see illustration).
7Compare the new rubber with the old for
length, design, etc.
8Slide the new rubber into place, and insert
the end in the wiper blade frame to lock it in
place.
9Refit the blade assembly on the arm, then
wet the glass and check for proper operation.
1•23
27.6 Detach the end of the wiper element
from the end of the frame, then slide the
element out27.5 Press the retaining tab in, then slide
the wiper blade assembly down and out of
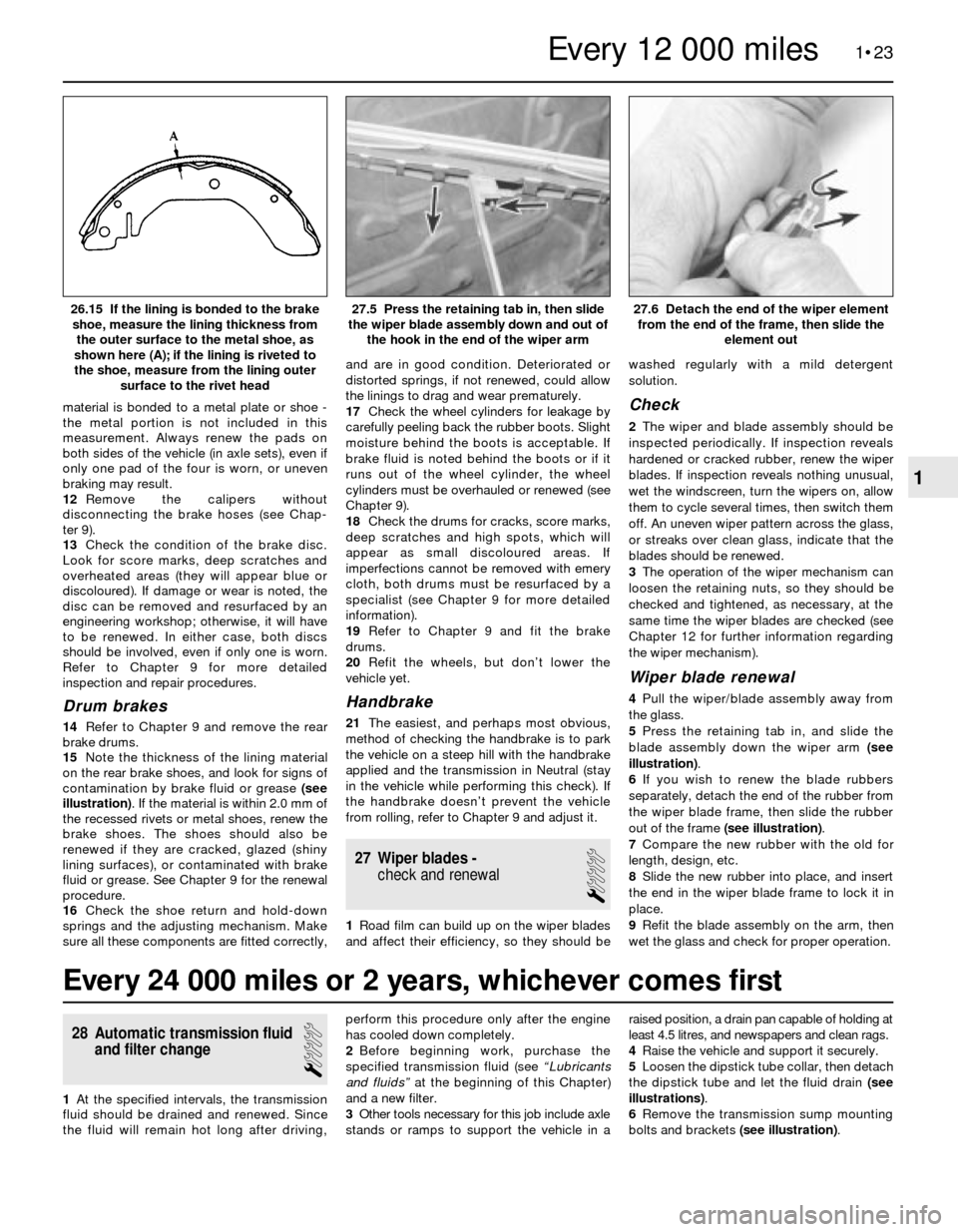
the hook in the end of the wiper arm26.15 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here (A); if the lining is riveted to
the shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
1
Every 12 000 miles
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years, whichever comes first
28 Automatic transmission fluid
and filter change
1
1At the specified intervals, the transmission
fluid should be drained and renewed. Since
the fluid will remain hot long after driving,perform this procedure only after the engine
has cooled down completely.
2Before beginning work, purchase the
specified transmission fluid (see “Lubricants
and fluids”at the beginning of this Chapter)
and a new filter.
3Other tools necessary for this job include axle
stands or ramps to support the vehicle in araised position, a drain pan capable of holding at
least 4.5 litres, and newspapers and clean rags.
4Raise the vehicle and support it securely.
5Loosen the dipstick tube collar, then detach
the dipstick tube and let the fluid drain (see
illustrations).
6Remove the transmission sump mounting
bolts and brackets (see illustration).
Page 35 of 228

Flushing
7Once the system is completely drained,
flush the radiator with fresh water from a
garden hose until the water runs clear at the
drain or bottom hose. If the radiator is
severely corroded, damaged or leaking, it
should be removed (see Chapter 3) and taken
to a radiator repair specialist.
8Flushing in this way will remove sediments
from the radiator, but will not remove rust and
scale from the engine and cooling tube
surfaces. These deposits can be removed by
using a chemical cleaner. Follow the
procedure outlined in the cleaner
manufacturer’s instructions. Remove the
cylinder block drain plug before flushing the
engine.
9On models so equipped, remove the
overflow hose from the coolant recovery
reservoir. Drain the reservoir and flush it with
clean water, then reconnect the hose.
Refilling
10Tighten the radiator drain plug, or
reconnect the radiator bottom hose. Refit and
tighten the cylinder block drain plug.
Four-cylinder engines
11Slowly add new coolant (a 40%/60%
mixture of antifreeze to water) to the radiator
until it is full. Add coolant to the reservoir up
to the lower mark.
12Leave the radiator cap off, and run the
engine in a well-ventilated area until the
thermostat opens (coolant will begin flowing
through the radiator, and the upper radiator
hose will become hot).
13Turn the engine off, and let it cool. Add
more coolant mixture to bring the coolant
level back up to the lip on the radiator filler
neck. On the M40 engine, unscrew the bleed
screw from the top of the radiator, and add
coolant until it comes out of the bleed screw
hole. Refit and tighten the bleed screw.
14Squeeze the upper radiator hose to expel
air, then add more coolant mixture if
necessary. Refit the radiator cap.
15Start the engine, allow it to reach normal
operating temperature, and check for leaks.
Six-cylinder engines
16Loosen the bleed screw in the thermostat
housing (see illustration)
17Fill the radiator with a 40%/60% solution
of antifreeze and water until it comes out of
the bleed screw opening. Tighten the bleed
screw.
18Refit the radiator cap, and run the engine
until the thermostat opens (the upper radiator
hose will become hot). Slowly loosen the
bleed screw until no bubbles emerge, then
tighten the screw.
19Repeat the procedure until the air is bled
from the system.
30 Fuel filter renewal
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1On fuel injection engines, depressurise the
fuel system (see Chapter 4).
2The fuel filter is located in the engine
compartment on the bulkhead, or under the
vehicle adjacent to the fuel tank.
3Because on some models the filter is
located adjacent to the starter motor, fuel
could leak onto the electrical connections. For
safety reasons, therefore, disconnect the
battery negative cable before beginning work.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
4Place a pan or rags under the fuel filter to
catch any spilled fuel. If suitable hose clamps
are available, clamp the inlet and outlet hoses.
5 Detach the hoses and remove the bracket
screws/nuts, then remove the filter and where
applicable the bracket assembly (see
illustration).
6Detach the filter from the bracket.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
the arrow on the filter points in the direction of
fuel flow.
31 Manual transmission
lubricant change
1
1Tools necessary for this job include axle
stands to support the vehicle in a raised
position, an Allen key to remove the drain
plug, a drain pan, newspapers and clean rags.
The correct amount of the specified lubricant
should also be available (see “Lubricants and
fluids”at the start of this Chapter).
2The lubricant should be drained when it is
hot (ie immediately after the vehicle has been
driven); this will remove any contaminants
better than if the lubricant were cold. Because
1•25
30.5 To renew the fuel filter, disconnect
the hoses (A), then unscrew the nut (B) and
detach the filter from the bracket (fuel
injection type shown)29.16 The bleed screw (arrowed) is
located on the thermostat housing (six-
cylinder models)29.4 Radiator drain plug location
(arrowed) - not fitted to all models
31.5 Use an Allen key to remove the drain
plug (arrowed) from the bottom of the
transmission
1
Every 24 000 miles