1977 DATSUN PICK-UP oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 255 of 537

Manual
Transmission
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
Transmission
type
F4W71B
FS5W71B
Synchromesh
type
Warner
1st
to
4th
Warner
5th
Servo
Shift
type
1
3
T
i
i
2
4
R
1
3
5
II
1
2
4
R
Gear
ratio
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
Reverse
3
592
2
246
1
415
1
000
3
657
3
321
2
077
1
308
1
000
0
864
3
382
Final
gear
ratio
4
375
4
375
Speedometer
gear
ratio
20
6
I
7
3
3
20
6
2
0
4X
3
f
Oil
capacity
US
pt
Imp
pt
MT
21
Page 264 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
SYSTEM
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
OIL
PUMP
MANUAL
LINKAGE
VACUUM
DIAPHRAGM
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
GOVERNOR
VALVE
CONTROL
VALVE
ASSEMBLY
HYDRAULIC
SYSTEM
AND
MECHANICAL
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
The
hydraulic
control
system
con
CONTENTS
P
RANGE
PAR
K
R
RANGE
REVERSE
N
RANGE
NEUTRAL
D1
RANGE
LOW
GEAR
D2
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
D3
RANGE
TOP
GEAR
D
RANGE
KICK
DOWN
2
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
t
RANGE
LOW
GEAR
12
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
AT
4
AT
4
AT
4
AT
5
AT
5
AT
5
AT
6
AT13
tains
an
oil
pump
for
packing
p
oil
from
the
oil
pan
through
the
oil
strainer
A
shift
control
is
provided
by
two
centrifugally
operated
hydraulic
governors
on
the
output
shaft
vacuum
control
diaphragm
and
downshift
AT14
AT16
AT18
AT
20
AT
22
AT
24
AT
26
AT
28
AT
30
AT
32
solenoid
These
parts
work
in
conjunc
tion
with
valves
in
the
valve
body
assembly
located
in
the
base
of
the
transmission
The
valves
regulate
oil
pressure
and
direct
it
to
appropriate
transmission
components
Oil
pump
I
I
Control
valve
I
Torque
converter
1
I
I
I
Manual
linkage
Front
clutch
Vacuum
diaphragm
I
Rear
clutch
I
Low
and
reverse
brake
Downshift
solenoid
I
Band
brake
Governor
valve
r
I
Lubrication
OIL
PUMP
The
oil
pump
is
the
source
of
control
medium
i
e
oil
for
the
control
system
The
oil
pump
is
of
an
internal
involute
gear
type
The
drive
sleeve
is
a
part
of
the
torque
converter
pump
impeller
and
serves
to
drive
the
pump
inner
gear
with
the
drive
sleeve
direct
ly
coupled
with
the
engine
operation
The
oil
flows
through
the
following
route
Oil
pan
Oil
strainer
bottom
of
the
control
valve
Control
valve
lower
body
suction
port
Transmission
case
suction
port
Pump
housing
suction
port
Pump
gear
space
Pump
housing
delivery
port
Transmission
case
delivery
port
Lower
body
delivery
port
Control
valve
line
pressure
circuit
AT071
I
Housin
4
Inner
gear
2
Cover
5
Crescent
3
Ouler
gear
Fig
AT
3
Oil
pump
AT
4
MANUAL
LINKAGE
The
hand
lever
motion
the
hand
lever
is
localed
in
the
driver
s
compart
ment
mechanically
transmitted
from
lhe
remote
control
linkage
is
further
transmitted
to
the
inner
manual
lever
in
the
transmission
case
from
the
range
selector
lever
in
the
right
center
par
tion
of
the
transmission
case
through
the
manual
shaft
The
inner
manual
lever
is
thereby
turned
A
pin
installed
on
the
bottom
of
the
inner
manual
lever
slides
rhe
manu
al
valve
spool
of
the
conlrol
valve
thus
positioning
the
spool
opposite
rhe
appropriate
select
posilion
The
parking
rod
pin
is
held
in
rhe
groove
on
the
top
of
Ihe
inner
manual
Page 265 of 537

plate
The
parking
rod
pin
operates
the
rod
at
p
range
and
operates
the
mechanical
lock
system
The
above
described
manual
shaft
is
further
equipped
with
an
inhibitor
switch
A
rotor
inside
the
inhibitor
switch
rotates
in
response
to
each
range
When
tne
range
is
selected
at
p
or
N
the
rotor
closes
the
starter
magnet
circuit
so
that
the
engine
can
be
started
When
the
range
is
selected
at
R
the
rolor
closes
the
back
up
lamp
circuit
and
the
back
up
lamp
lights
CD
1
Manual
pia
te
2
Inhibitor
switch
ATOB7
Parking
rod
Manual
shaft
Fig
AT
4
Manual
linkage
VACUUM
DIAPHRAGM
The
vacuum
diaphragm
is
installed
on
the
left
center
portio
n
of
the
transmission
case
The
internal
con
struction
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
is
as
follows
A
rubber
diaphragm
forms
a
parti
tion
in
the
center
The
engine
intake
manifold
negative
pressure
l
led
through
a
vacuum
tube
and
spring
force
is
applied
to
the
front
surfaceof
the
rubber
diaphragm
while
atmos
pheric
pressure
is
applied
to
the
back
surface
The
difference
between
pres
sure
applied
to
the
front
and
ba
K
I
surfaces
causes
a
vacuum
reactIOn
which
activates
the
throttle
valve
of
the
control
valve
inside
the
transrhis
sion
case
Wheri
accelerator
pedal
is
fully
de
pressed
and
the
buretor
is
fU
IIy
opened
but
th
engirie
sp
eed
is
not
suificientl
increased
the
manifold
negative
plre
sure
lowers
Le
tends
towards
atmospheric
pressure
and
the
Automatic
Transmission
vacuum
reaction
increases
since
the
flow
velocity
of
mixture
inside
the
intake
m
mifold
is
slow
Contrarily
when
the
engine
speed
increases
and
the
flow
velocity
of
the
mixture
in
creases
or
when
the
carburetor
is
closed
the
manifold
negative
pressure
increases
Le
tends
towards
vacuum
and
the
vacuum
reaction
is
reduced
Thus
a
signal
to
genera
Ie
hydraulic
pressure
P
rfe
tly
suited
to
the
engine
loading
at
trye
control
valve
is
trans
mitted
from
the
vacuum
diaphragm
and
the
most
suitable
timing
for
speed
change
and
lin
e
pressure
is
obtaine
so
that
the
most
proper
torque
capacity
is
obtained
against
the
transmitting
torque
To
inl
lkc
manifold
AT088
Fig
AT
5
Vacuum
diaphragm
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
T
e
downshift
solenoid
is
of
a
magnetic
type
installed
on
the
left
re
r
portion
of
the
transmission
case
When
a
driver
requires
accelerating
power
and
dePresses
the
accelerator
pedal
down
to
the
stopper
a
kickdown
switch
19ca
ted
in
the
middle
of
the
accelerator
link
is
depressed
by
a
push
rod
he
kickdown
switch
doses
cur
rent
flows
to
the
solenoid
the
sole
noid
push
rod
is
depressed
the
down
shift
valve
of
the
control
valvc
insidc
the
transmi
ssion
case
is
depressed
nd
the
speed
is
changed
forcedly
fmm
3rd
to
2nd
within
a
cerlaill
vehi
cle
speed
limit
Note
Since
theki
kdown
switch
closes
when
the
accelerator
pedal
is
d
epr
ssed
from
7
i
t
I
S
I
6
of
tiie
whole
stroke
the
a
ccel
rator
ped
1
should
be
correctly
adjusted
so
as
arf
rd
a
omplete
stro
e
I
The
arrangement
of
the
swit
h
wries
ccording
m
eI
AT
S
c
C
r
11
I
Kickdown
h
switch
Dowri
shift
solenoid
AT089
Fig
AT
6
Downshifl80lenoid
GOVERNER
VALVE
The
primary
and
secondary
gover
nor
valves
are
installed
separately
on
the
back
of
the
oil
distributor
on
the
transmission
outp
t
sha
ft
tn
y
op
erate
al
the
same
speed
as
th
ar
iJf
tile
output
shaft
thai
is
they
operate
at
a
speed
in
proportion
10
the
vehicle
speed
The
line
press
retis
applied
to
those
valves
s
the
input
from
the
control
valve
through
the
transmission
case
rear
flange
and
oil
distributor
The
governor
pressure
in
proportion
to
the
ouiput
shaft
speed
vehicle
speed
is
led
to
the
shift
valve
ofthe
control
valve
through
the
opposite
route
of
the
output
In
this
manner
speed
change
and
line
pressure
are
controlled
Operation
of
secondary
governor
valve
T
e
secon
ary
valve
is
a
contro
valve
Y
hich
receives
line
pressure
an
cqQ
rols
the
governor
pressu
e
When
the
manual
valve
is
selected
at
D
2
or
l
range
line
pressure
is
applied
t
the
ri
g
sh
aped
area
of
this
valve
from
circuit
I
l
and
this
I
v
Jy
is
depressed
lOW
jr
tI
c
fer
Movemcnt
of
this
valvl
III
a
cr
in
positillll
doses
the
dr
uit
from
Olto
15
while
simultaneously
making
a
sr
rronl
IS
to
Iii
center
d
niin
port
and
press
re
in
tllc
ci
rJ
it
l5j
is
lowered
When
thc
vehicle
is
stopped
1
d
the
cenlrifugal
force
of
this
valve
is
zero
the
v
lve
is
balanced
At
this
poini
a
govcr
lOr
pressurc
y
hich
bal
i1
nced
with
th
spr
ng
force
occurs
on
IS
Wh
n
thc
vehicle
is
st
rted
nd
the
centrifugal
fqr
incre
ses
this
valve
movcs
slightly
10
Ihc
oUlSide
and
as
Page 305 of 537
Automatic
Transmission
L
1
r
E
5
Eo
1
20
mm
l
AT148
3
0
079
in
Cut
off
hatched
portion
Fig
AT
SO
Modifying
coil
spring
compres
or
3
Take
out
spring
retainer
f
and
spring
@
See
Figure
AT
78
4
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
inlO
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
A
T
8l
AT149
Fig
AT
81
Blowing
out
piston
Inspection
I
Check
for
signs
of
wear
or
dam
age
to
clutch
drive
plate
facing
If
found
worn
or
damaged
excessively
discard
See
Service
Data
for
limits
2
Check
for
wear
on
snap
ring
and
for
weakened
or
broken
coil
spring
If
necessary
replace
with
new
ones
Spring
retainer
should
also
be
in
spected
for
warpage
Assembly
I
Assembly
is
in
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
before
installing
2
Line
up
driven
plates
so
that
stripped
arcs
are
properly
aligned
paying
particular
attention
to
the
loca
tion
of
oil
holes
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
82
Note
The
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
the
type
of
vehi
cle
For
detailed
information
see
Service
Data
Specifications
AT150
Lub
ication
hole
Fig
AT
82
Inserting
clutch
plate
3
After
clutch
is
assembled
make
sure
that
clearance
between
snap
ring
CD
and
retaining
plate
@
is
held
within
specified
limits
If
necessary
try
with
other
plates
having
different
thickness
until
correct
clearance
is
obtained
See
Figure
AT
83
Specified
clearance
I
6
to
1
8
mm
0
063
to
0
071
in
Available
retaining
plate
Thickness
mm
in
10
6
0417
10
8
0425
11
0
0
433
11
2
0441
II
4
0
449
11
6
0457
AT151
Fig
AT
83
Measuring
ring
to
plate
clearance
4
Testing
front
clutch
With
front
clutch
assembled
on
oil
pump
cover
direct
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
84
AT
41
Fig
AT
B4
Testing
front
clutch
REAR
CLUTCH
Disassembly
AT153
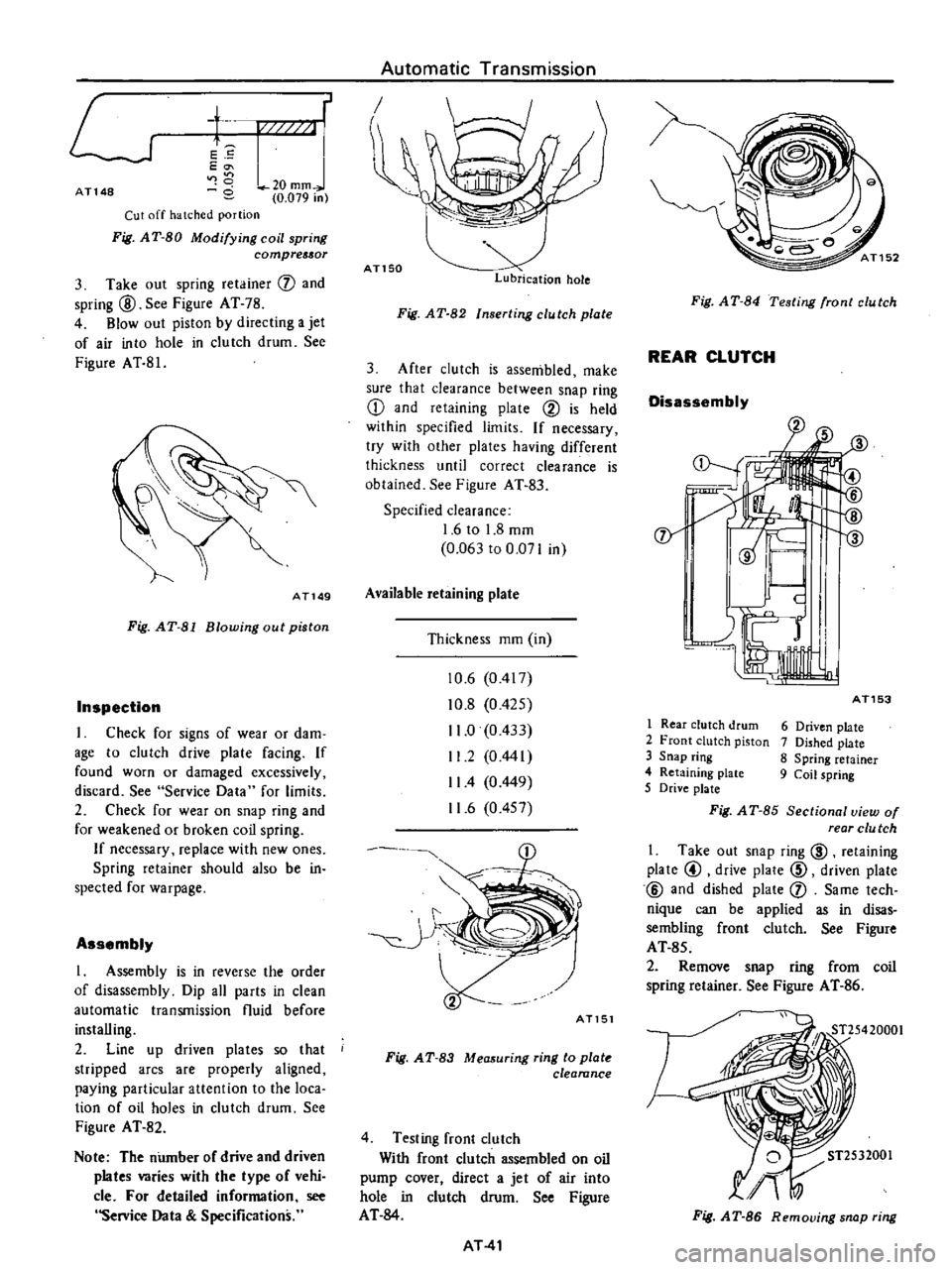
1
Rear
clutch
drum
2
Front
clutch
piston
3
Snap
ring
4
Retaining
plate
5
Drive
plate
Fig
A
T
85
Sectional
view
of
rear
clu
tch
6
Driven
plate
7
Dished
plate
8
Spring
retainer
9
Coil
spring
I
Take
out
snap
ring
@
retaining
plate
@
drive
plate
@
driven
plate
@
and
dished
plate
f
Same
tech
nique
can
be
applied
as
in
disas
sembling
front
clutch
See
Figure
AT
85
2
Remove
snap
ring
from
coil
spring
retainer
See
Figure
AT
86
ST2532001
Xf
Fig
AT
86
Remolling
snap
ring
Page 306 of 537

3
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
87
AT155
V
i
J
i
j
Fig
AT
87
Blowing
out
piston
Automatic
Transmission
1
w
Ai
I
i
1
i
3
j
P2
0
AT157
Fig
A
T
89
Testing
rear
C
U
tch
Inspectl
ioW
S
REVERSE
BRAKE
Refer
to
page
AT41
for
Inspection
of
Front
Clutch
Assembly
Assemble
in
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
before
assembling
Note
that
the
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
type
of
vehicle
F
or
details
refer
to
Serv
ice
Data
Specifications
I
After
rear
clutch
is
assembled
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
be
tween
snap
ring
D
and
retaining
plate
l
is
held
within
prescribed
toler
ances
See
Figure
AT
88
Specified
clearance
1
0
to
1
5
rom
0
039
to
0
059
in
AT156
Fig
AT
SS
Measuring
ring
to
plate
clearance
2
Testing
rear
clutch
Install
rear
clutch
on
oil
pump
cover
Blow
compressed
air
into
oil
hole
to
test
for
defInite
clutch
operation
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
89
Disassembly
1
Fllow
steps
as
described
in
page
AT
36
for
Transmission
Disassembly
2
mow
out
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
oil
hole
in
clutch
piston
Inspection
I
Check
drive
plate
facing
for
wear
or
damage
if
necessary
replace
Refer
to
Service
Data
Specifications
for
tolerances
2
Test
piston
return
spring
for
weakness
Discard
if
weakened
beyond
use
3
Replace
faulty
parts
with
new
ones
Assembly
I
After
low
reverse
piston
is
installed
assemble
thrust
spring
ring
retum
spring
thrust
washer
and
one
way
clutch
inner
race
Using
Hex
head
Extension
ST25570001
ST25570000
torque
hex
head
slot
ted
bolt
I
3
to
1
8
kg
m
9
to
13
ft
lb
2
Insert
dished
plate
driven
plate
drive
plate
and
retaining
plate
into
transmission
case
in
that
order
Install
sn
p
ring
to
secure
the
installation
Note
The
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
wries
with
type
of
vehicle
For
detailed
information
refer
to
Service
Data
Specifications
AT42
3
Without
disturbiilg
the
above
setting
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
between
snap
ring
and
retaining
plate
is
within
specified
limits
If
necessary
use
other
plates
of
different
thickness
until
correct
clearance
is
obtained
Specified
clearance
0
80
to
1
05
rom
0
0315
to
0
0413
in
4
Blow
compressed
air
into
oil
hole
in
low
reverse
brake
to
test
for
definite
brake
operation
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
90
Fig
AT
90
Testing
low
reverse
brake
SERVO
PISTON
Disassembly
I
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
release
side
of
piston
2
Remove
servo
piston
return
spring
Inspection
Check
piston
for
wear
damage
or
other
faults
which
might
interfere
with
proper
brake
operation
v
r
0
111
Ll
7
J
I
AT159
Fig
AT
91
Removing
pi3ton
Page 309 of 537
I
F
1
D
t
l
a
J
n
f
19l1
Ull
IU
P
C
o
J
CJ
IODrR
CC
t
LL6
SJQIl2J
lhl
fB
rt
AT169
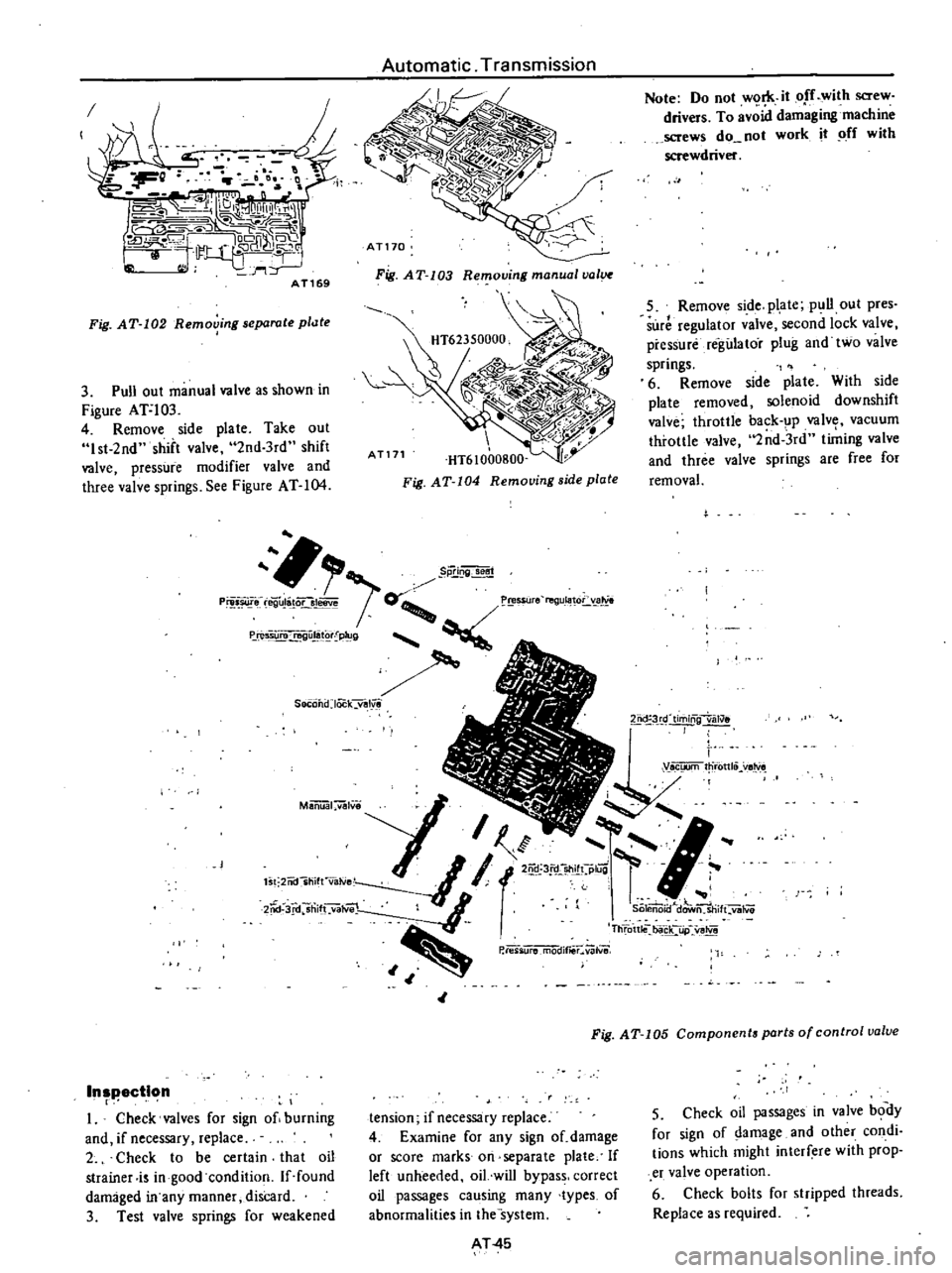
Fig
AT
102
Removing
separate
pllJte
3
Pull
out
manual
valve
as
shown
in
Figure
Ar103
4
Remove
side
plate
Take
out
1st
2nd
shift
valve
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
pressure
modifier
valve
and
three
valve
springs
See
Figure
AT
104
Automatic
Transmission
Fig
AT
103
Removing
manual
val
AT1
1
HT61000800
Fig
AT
104
Removing
side
plate
g
p
e
eguJa
Of
le6Ve
or
r
essure
reguJl
oL
@iO
I
f
g
SecOni
J
lOCltvalYi
y
h
l
l
2I
r
JI
Io
J
l
j
t
1
i
S
r
0
x
t
i
3
1
Note
Do
not
w
it
off
with
screw
drivers
To
avoid
darnagingmachine
screws
do
not
work
it
ff
with
screwdriver
5
Remove
side
plate
pull
out
pres
sure
regulator
valve
second
lock
valve
pressure
regi1lator
plug
and
two
valve
springs
6
Remove
side
plate
With
side
plate
removed
solenoid
downshift
valve
throttle
back
up
valve
vacuum
throttle
valve
2
d
3rd
t
ing
valve
and
three
valve
springs
are
free
for
removal
2nd
3rd
timing
talve
r
en
i
C1iJrilth
rottle
lI
lY
e
M
a
alVSY
I
j1
f
I
1
f
Iv
I
f
2i
3
CP
g
f
st
2nd
S
t
a
el
2i1d
3
d
St1itLvalv
so
iit
a
stiift
V81v
i
hrottle
f
iicnjp
VB
y
i
P
ie
mo
i
Inspection
r
I
Check
valves
for
sign
of
burning
and
if
necessary
replace
2
Check
to
be
certain
that
oil
strainer
is
in
good
condition
If
found
damaged
in
any
manner
disCard
3
Test
valve
springs
for
weakened
Fig
AT
105
Components
ports
of
control
uolue
tension
if
necessary
replace
4
Examine
for
any
sign
oLdamage
or
score
marks
on
separate
plate
If
left
unheedcd
oiL
will
bypass
correct
oil
passages
causing
many
types
of
abnormalities
in
thesystem
AT45
5
Check
oil
passages
in
valve
b
dy
for
sign
of
damage
and
other
condi
tions
which
might
interfere
with
prop
er
valve
operation
6
Check
bolts
for
stripped
threads
Replace
as
required
Page 323 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
General
specifications
AfT
Torque
converter
Type
Stall
torque
ratio
Symmetrica13
element
I
stage
2
phase
torque
converter
2
0
I
Transmission
Type
Control
elements
Multiple
disc
clutch
Band
brake
Multiple
disc
brake
One
way
clutch
Gear
ratio
1st
2nd
3rd
Reverse
3
speed
forward
and
one
speed
reverse
with
planetary
gear
train
2
I
I
I
2
458
1458
1
000
2
182
Selector
positions
P
Park
R
Reverse
N
Neutral
Transmission
is
placed
in
neutral
Output
shaft
is
fIXed
Engine
can
be
started
Backward
running
Transmission
is
in
neutral
Engine
can
be
started
Up
or
downshifts
automatically
to
and
from
I
st
2nd
and
top
Fixed
at
2nd
Fixed
at
low
or
downshifts
from
2nd
o
Drive
2
2nd
lock
I
Lock
up
Oil
pump
Type
Internally
intermeshing
involute
gear
pump
Number
of
pump
Oil
Automatic
transmission
fluid
DEXRON
type
5
5
liters
SUU
s
qt
4Ulmp
qt
Approximately
2
7
liters
2UU
s
qt
2XIrnp
qt
in
torque
converter
Controlled
by
measuring
the
nega
tive
pressure
of
intake
manifold
and
the
revolution
of
output
shaft
Forced
lubrication
by
an
oil
pump
Water
cooled
by
a
circulation
type
auxiliary
cooler
located
at
the
radiator
Capacity
Hydraulic
control
system
Lubrication
system
Cooling
system
AT
59
Page 333 of 537

PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Condition
Probable
cause
Knocking
sound
during
starting
or
noise
during
coasting
on
propeller
shaft
Worn
damaged
universal
joint
Worn
sleeve
yoke
and
main
shaft
spline
Loose
propeller
shaft
installation
Loose
joint
installation
Damaged
center
bearing
or
insulator
Loose
or
missing
bolts
at
center
bearing
bracket
to
body
Scraping
noise
Dust
cover
on
sleeve
yoke
rubbing
on
transmission
rear
extension
Dust
c
ver
on
companion
flange
rubbing
on
differ
mtial
carrier
Whine
or
whistle
Damaged
center
bearing
Corrective
action
Replace
Replace
Retighten
Adjust
snap
ring
Replace
Replace
or
tighten
bolts
Straighten
out
dust
cover
to
remove
inter
ference
Replace
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
TYPE
H190
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
PRE
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
PRECAUTIONS
IN
REASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY
OF
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
PD
5
PD
7
PD
7
PD
7
PD
8
PD
PD
8
PD
8
DESCRIPTION
The
differential
carrier
on
the
620
series
has
a
gear
ratio
of
4
37S
The
drive
pinion
is
rnounted
in
two
tapered
roUer
bearings
which
are
pre
loaded
by
pinion
bearing
adjusting
spacer
and
washer
during
assembly
The
drive
pinion
is
positioned
by
a
washer
located
between
a
shoulder
of
ASSEMBl
Y
OF
DIFFERENT
Al
CASE
ADJUSTMENT
OF
DRIVE
PINION
HEIGHT
ADJUSTME
NT
OF
DRIVE
PINION
PRELOAD
t
ADJUST
ENT
OF
SIDE
8EARING
SHIMS
INSTAllATION
REPLACEME
NTOF
FRONT
Oil
SEAL
the
drive
pinion
and
the
rear
bearing
The
differential
case
is
supported
in
the
carrier
by
two
tapered
roller
side
bearings
These
are
preloaded
by
in
serting
shims
between
the
bearings
and
the
differential
case
The
differential
case
assembly
is
positioned
for
proper
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
backlash
by
PO
5
PD
8
PD
9
PD
lO
PD
11
PD
13
PD
13
varying
these
shims
The
ring
gear
is
bolted
to
the
differential
case
The
case
houses
two
side
gears
in
mesh
with
two
pinion
mates
mounted
on
a
pinion
shaft
The
pinion
shaft
an
chored
in
the
case
by
lock
pin
The
pinion
mates
and
side
gears
are
backed
by
thrust
washers
The
carrier
is
of
malleable
cast
iron