1973 OPEL MANTA oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 397 of 625

7C- 361973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Description of the Opel Three-Speed Automatic,Transmission....................................................................
Principles of Operation....................................................
ComponentOperation
andLocation............................
Mechanical Operation......................................................
Hydraulic Control Units and Valves............................H,y&aulic Operation..........................................................
DIAGNOSIS:
Sequence for Trouble Diagnosis..................................
Checking
Procedures........................................................
ExternalOil
Leaks..............................................................
Trouble
DiagnosisChart..................................................
Hydraulic Pressure
Checks............................................
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS:
Detent Cable Adjustment..............................................
ServicingSelector
Lever..................................................
MAJOR REPAIR:
Transmission Removal and Installation
AllModels........................................................................
Removalof
OilPan............................................................
RemovalofValveBody....................................................
Removalof
ServoPiston................................................
Removalof
Selector
LeverandShaft........................
RemovalofModulatorAssembly..................................
RemovalofDetentValveAssembly............................
RemovalofExtensionHousing......................................
Removal of Speedometer Drive Gear, Governor
Body and Governor Hub..............................................
Removal of Converter Housing, Oil Pump, Reverse
and Second Clutch Assembly..................................
Removal of Third Clutch Assembly, Planetary
Carrier Assembly, Reaction Sun Gear and Drum
Assembly and Low Bank............................................
Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly of
Converter Housing, Oil Pump and Reverse Clutch
Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly of
SecondClutch
................................................................
Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly of
ThirdClutch....................................................................
Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly of
Planetary Carrier
............................................................Page No.7c- 377c- 387c- 447c- 487c- 487c- 64
7C- 81
7C- 81IC- 817c- 827c- 877c- 917c- 937c- 947c- 99.7c- 99
7c-1007c-loo
7&l 01
7c-102
7c-102
7c-103
7c-103
7c-104
7c-105
7c-111
7c-114
7c-118
Page 405 of 625
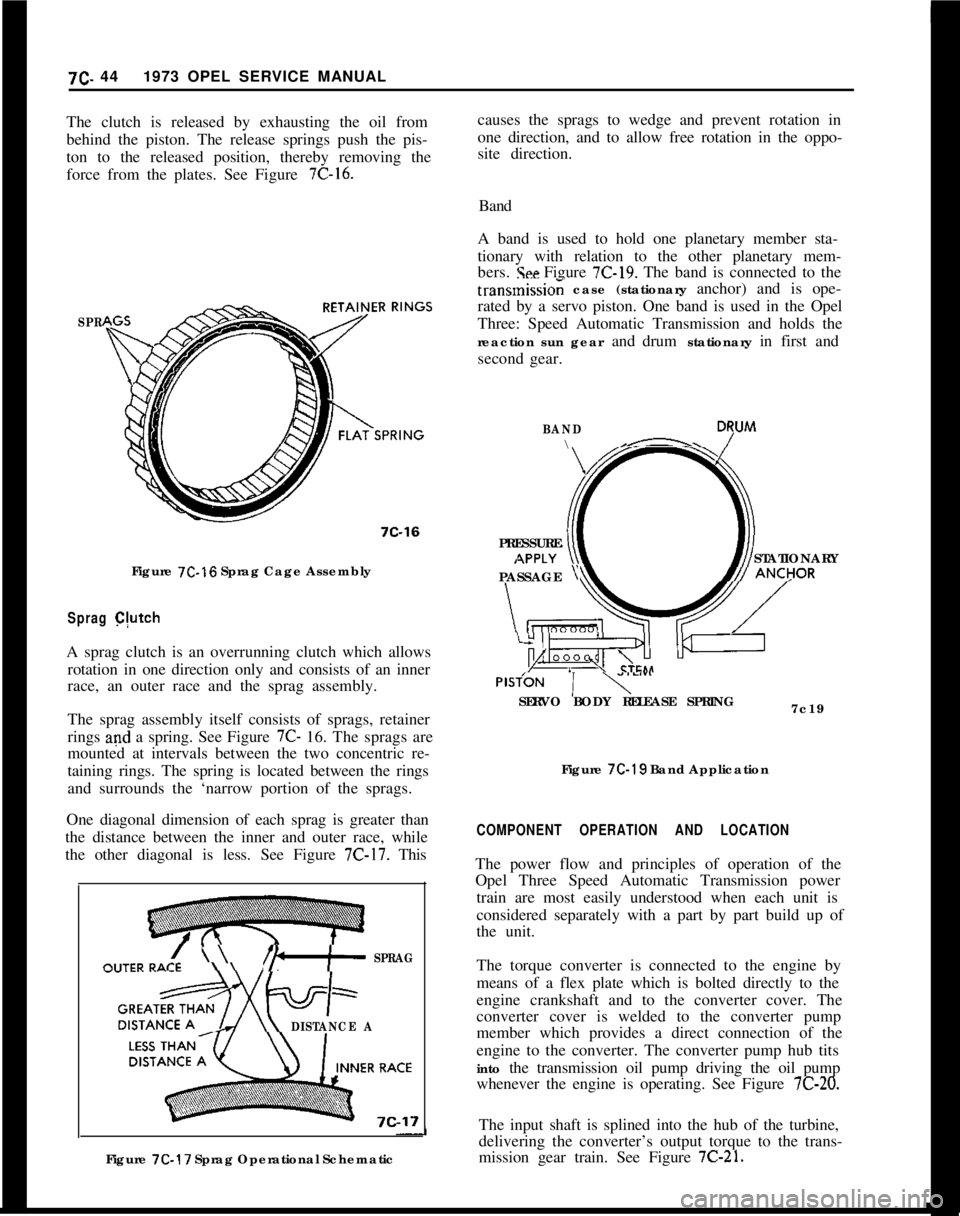
causes the sprags to wedge and prevent rotation in
one direction, and to allow free rotation in the oppo-
site direction.7C. 441973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
The clutch is released by exhausting the oil from
behind the piston. The release springs push the pis-
ton to the released position, thereby removing the
force from the plates. See Figure 7C-16.Band
A band is used to hold one planetary member sta-
tionary with relation to the other planetary mem-
bers.
!See Figure 7C-19. The band is connected to the
SPR
7C-16Figure
7C-16 Sprag Cage Assembly
Sprag C(utchA sprag clutch is an overrunning clutch which allows
rotation in one direction only and consists of an inner
race, an outer race and the sprag assembly.
The sprag assembly itself consists of sprags, retainer
rings and a spring. See Figure 7C- 16. The sprags are
mounted at intervals between the two concentric re-
taining rings. The spring is located between the rings
and surrounds the ‘narrow portion of the sprags.
One diagonal dimension of each sprag is greater than
the distance between the inner and outer race, while
the other diagonal is less. See Figure
7C-17. This
\ \I’b+ SPRAG
DISTANCE AFigure
7C-17 Sprag Operational Schematictransmissio; case (stationary anchor) and is ope-
rated by a servo piston. One band is used in the Opel
Three: Speed Automatic Transmission and holds the
reaction sun gear and drum stationary in first and
second gear.
BAND\- D7uM
PRESSURE
STATIONARY
PASSAGE
yPlSfON
1 y””SERVO BODY RELEASE SPRING
7c19
Figure
7C-19 Band Application
COMPONENT OPERATION AND LOCATIONThe power flow and principles of operation of the
Opel Three Speed Automatic Transmission power
train are most easily understood when each unit is
considered separately with a part by part build up of
the unit.
The torque converter is connected to the engine by
means of a flex plate which is bolted directly to the
engine crankshaft and to the converter cover. The
converter cover is welded to the converter pump
member which provides a direct connection of the
engine to the converter. The converter pump hub tits
into the transmission oil pump driving the oil pump
whenever the engine is operating. See Figure
7C-20.The input shaft is splined into the hub of the turbine,
delivering the converter’s output torque to the trans-
mission gear train. See Figure
7C-21.
Page 409 of 625

7C- 481973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
INPUT SUNRING
GEAR ASSY.GEARPLANETARY
CARRIERASSY.REACTION SUNtow
GEAR 8 DRUMBAND
Figure 7C-25Planetary Gears
The planetary pinion shafts which support the plane-
tary pinions are secured to the planetary carrier by
means of a lock plate at the rear of the planetary
carrier preventing the pinion shafts from rotating or
working loose. The lock plate is secured to the car-
rier by screws.
The planetary carrier is welded to the output shaft,
therefore, the directional movement of the carrier
delivers the transmission’s torque to the output shaft.
The governor hub is splined to, and driven by, the
output shaft. See Figure 7C-26. A governor body is
bolted to the governor hub. The speedometer drive
gear is also driven by the output shaft, and is secured
to the shaft by a retaining clip.
MECHANICAL OPERATIONThe following information describes how engine
torque is transmitted through the Opel Three Speed
automatic transmission for each selected position on
the quadrant. In every case, with the engine running,
torque is transmitted via the flex plate and converter7G25
cover to
tht? pump member of the converter. The
converter is always tilled with oil from the transmis-
sion’s oil pump, and the converter pump member
transmits the torque through oil to the driven mem-
ber of the converter. Power to the transmission is
then transmitted via the input shaft and third clutch
drum. See Figures
7C-48 through 7C-52.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNITS AND VALVESPreviously, the mechanical aspects of the transmis-
sion operation have been described, including refer-
ence to various clutches and the low band being
applied. The following describes, in detail, the hy-
draulic system that applies the clutches and band,
and which controls the manually selected and auto-
matic shifts.
A hydraulic pressure system requires a source of
clean hydraulic fluid and a pump to pressurize the
fluid. Opel Three Speed Automatic transmission uses
a gear type pump which draws oil through a screen
located in the sump. See Figure
7C-29. Since the
pump drive gear is keyed to the converter pump hub,
it turns whenever the engine is operating and turns
the driven gear, which causes the oil to be lifted from
Page 410 of 625

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION7c- 49Figure 7C-26 Governor Assembly And Speedometer Drive Gearthe sump. The oil is carried past the crescent section
of the pump, beyond which the gear teeth begin to
come together, pressurizing the oil as it is squeezed
from between the gear teeth. The pressurizeh oil is
then delivered through the pump outlet to the hy-
draulic control system.1. Main pressure regulator valve.
2. Modulator valve.
mPRIMING VALVE
If the vehicle has not been operated for a while, the
oil in the pump cavity tends to drain and leak back
to the sump. With the pump cavity filled with air, the
pump cannot develop enough suction to lift the oil
from the sump. For this reason, a priming valve is
located in the pump pressure passage. As the air in
the pump is compressed by the gears, it is forced out
through the bleed orifice in the priming valve and
into the exhausted cavity behind the reverse piston.
This permits the pump to prime and draw oil from
the sump. As soon as the hydraulic pressure reaches
15
PSI: the valve is forced over closing off the bleed
orifice.PRIMING VALVE
In the hydraulic control circuit, there are four major
types of iontrol elements. These categories along
with the specific items are listed below.
A. Pressure regulating valves.
Fieure 7C-7.9 Oil Puvp and Priming Valve
Page 411 of 625

712.501973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
3. Detent pressure regulator valve.
4. 1 - 2 Accumulator valve.
5. Governor.
B. Selector valves (manually and hydraulically con-
trolled).
I. Manual valve.
2. Detent valve.
3. 1
- 2 Shift valve.
4. 2
- 3 Shift valve.
5. 3
- 2 Downshift control valve.
6. Manual low and reverse control valve.
7. Boost control valve.
C. Timing Valves.
1. Low speed downshift timing valve.
2. High speed downshift timing valve.
3. Second clutch orifice valve.
D. Accumulators.
1. 1
- 2 Accumulator.
2. Low servo piston.
Main Pressure Regulator ValveOil pressure from the pump is delivered to the “line”
port of the main regulator valve. See Figure
7C-30.The port is connected through a damping orifice, to
the regulator port at the end of the regulator valve.
As the pressure in this port increases, it moves the
valve against the spring force until the second spool
of the. valve just opens to the “line” port. This per-
mits the pump pressure to be by- passed into the
pump suction passage. Therefore, the valve will regu-
late at
a’ fixed minimum pressure as determined by
the spring force, and all excess pump delivery will be
by-passed back into the pump suction passage.
In moving from the “bottomed” to the regulating
position, the valve also opens line pressure to the
converter feed passage. This oil is directed to and
through the
cow&x, through the oil cooler, to the
gear box lubrication system, then back to the sump.
In order to provide the required capacity in the band
and clutches, it is desirable to have a variable line
pressure that will increase with engine torque. This
PRESSURE’REGULATORY7c30Figure 7C-30 Pressure Regulator Valve
is accomplished by introducing a “modulator” pres-
sure on the end of the boost valve. The force of the
boost valve acts against the end of the regulator valve
and increases the line pressure above the base pres-
sure as established by the spring force. By introduc-
ing line pressure to the stepped area between the
spools of the boost valve, an additional pressure in-
crease over and above that described above is ob-
tained.
The regulated line pressure is then fed to:
Manual valve.
Modulator valve
Detent pressure regulator valve
Modulator Valve and Vacuum ModulatorLine pressure is directed to the second port of the
modulator valve. See Figure
7C-31. This pressure
passes between the spools of the valve and into the
modulator port. The modulator port is connected to
the regulating port at the end of the valve through a
damping orifice. As the pressure in the regulating
port incieases, it moves the valve outward against
the spring force of the modulator assembly until the
end spool just closes the line port. If excess pressure
has built up in the regulating port the valve will
continue to move till the second spool just opens to
the exhaust port. In other words, the valve tends to
regulate between the line and exhaust ports.
Even though the modulator spring force may be con-
stant, thereby causing the modulator valve to regu-
late at a fixed pressure, the pressure requirements
Page 413 of 625

7C- 521973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
CCUMULATOR
DRIVE:--7633
Figure 7C-33 1
- 2 Accumulator Valve
The ports and spools operate as previously described.
However, for increased engine torque, it is necessary
to increase the accumulator pressure. This is accom-
plished by introducing modulator pressure to the
small end of the 1-2 accumulator valve. As the
modulator pressure increases, it adds to the spring
force and increases the l-2 accumulator pressure.
The 1-2 accumulator pressure is fed to the bottom
(spring loaded side) of the 1-2 accumulator piston.
The Governor is mounted on the output shaft and
contains two interconnected regulating valves See
Figure
7C-34. Its purpose is to supply an oil pressure
5 8I. GOVERNOR SECONDARY VALVE6
SPRING RETAINER
2. GOVERNOR SECONDARY VALVE SPRING
3. GOVERNOR SECONDARY VALVE
4. GOVERNOR PRIMARY VALVE
5. GOVERNOR BODY6. ROLL PINIC~VFigure 7C-34 Governor Assemblythat is a function of output shaft or car speed. Line
pressure is supplied to the governor from the Manual
Valve (to be covered later). The governor operates on
the principle of centrifugal force. That is, as an object
spins off center at changing speeds, its outward force
is a function of the rotating speed.
Line pressure is directed to the outer-most port of the
secondary valve. The secondary spring holds the
valve in an outward position so that the outer spool
of the valve is open to “line”. As the line pressure
builds up between the spools, it exerts a force on the
larger diameter inner spool to start counteracting the
spring. When the hydraulic force is large enough, it
moves the valve inward against the spring force until
the outer spool closes the line port. If the pressure
between the spools still creates a force larger than the
spring force, the valve will continue to move inward
until the excess pressure opens to the exhaust port.
The valve then regulates between the line and ex-
haust port.
A fixed governor pressure in the secondary valve has
now been established with no rotation of the output
shaft. As the governor begins to rotate, the outward
force (due to the weight of the secondary valve) is
added to the force of the spring. Therefore, as the
speed increases, the outward force and in turn the
secondary valve pressure increases.
The secondary valve pressure is directed to the feed
port of the primary valve. With no rotation of the
governor, the pressure acts against the large inner
spool and forces it to open to the exhaust port. Since
there is no spring force on the primary valve, it will
continue to keep the feed port closed and the exhaust
port open. The final governor pressure is then zero.
As the governor begins to rotate, the weight of the
primary valve creates an outward force working
against the oil pressure. The pressure in the primary
valve port now increases as a function of speed. This
continues up to the speed where the outward force
finally holds the primary valve outward, keeping the
feed port open.
In summary, at zero speed, the governor pressure is
zero. As the speed increases, the governor pressure
will increase as dictated by the primary valve until
the speed is great enough to hold the primary valve
all the way out. At speeds above this point, the gover-
nor pressure is established by the secondary valve.
Governor pressure is then directed to:
Modulator Valve.
1 - Two Shift Valve.
2
- Three Shift Valve.
3 High Speed Downshift Timing Valve.
Page 414 of 625

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONlC- 53
Manual ValveThe manual valve is mechanically connected to the
shift lever. Its function is to direct hydraulic pressure
to the various circuits to establish the base hydraulic
range of the transmission.
Line pressure is fed to the manual valve. See Figure
7C-35. In “Park” and “Neutral”, the valve seals line
pressure from entering any of the circuits. At the
same time all circuits are open to exhaust so that the
transmission remains in a neutral condition.
In “Reverse”, line pressure is directed to the reverse
clutch piston, boost control valve and the reverse and
manual control valve. All other manual control cir-
cuits are open to exhaust.
MANUAL VALVE
;i
\2
P RNDILII7D35
Figure
7C-35 Manual Valve
In “Drive” the manual valve directs oil to the gover-
nor, I
- 2 shift valve, 1 2 accumulator valve, and to
the apply side of the low servo piston by way of the
high speed downshift timing valve. The “Reverse”,
“Second”, and “Low” ports are exhausted.
In “Second” the “Drive” circuits remain pressu-
rized. In addition, pressure is supplied to the boost
control valve and to the 2
- 3 shift valve. The “Rever-
se” and “Low” ports are exhausted.
In “Low”, pressure is supplied to the
1 - 2 shift valve
and to the reverse and manual control valve in addi-
tion to the circuits already pressurized in “Drive”
and “Second”. The “Reverse” port is exhausted.
Detent ValveThe function of the detent valve is to cause the trans-mission to shift to a lower gear for additional per-
formance when the accelerator is depressed all the
way.The detent valve is mechanically connected to the
throttle linkage. A spring holds the detent valve in a
retracted position. See Figure
7C-37. Two pressures,
“detent regulator” and “modulator”, are supplied to
the detent valve.
iiiDETENTE2
MODULATORFigure
7C-37 Detent Valve
In the retracted or “part throttle” position, the de-
tent valve directs modulator pressure to the 1 2 and
2 3 shift control valves and to the 3 2 control valve.
In the “through detent” or full throttle position,
modulator pressure is blocked and the passages
previously receiving modulator pressure now receive
detent regulator pressure. In this position, detent
regulator pressure is also supplied to additional ports
of the 1
- 2 and 2 3 shift control valves and the 3
2 control valve.
1 2 Shift Valve
The 1
- 2 Shift and Shift Control Valves determine
whether the transmission is in first or second gear.
See Figure
7C-38. With the shift valve bottomed in
its bore, the valve blocks “Drive” or line pressure
and the second clutch is open to exhaust. The valve
is held in this position by a spring and any modulator
pressure that may be acting against the two end
spools of the 1
- 2 shift control valve.
As the car speed and governor pressure increase, a
force is developed on the end of the shift valve. When
this force is great enough to overcome the spring and
the force of the 1 2 shift control valve, the shift
valve moves, closing the exhaust and opening the line
pressure port to the second clutch port.
Page 415 of 625

7C- 541973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
Figure 7C-38 1 2 Shift Valve
To prevent a “hunting” condition of the shift valve,
modulator pressure supply to the second spool of
control valve is cut off as the shift valve opens line
pressure to the second clutch. The oil in this pocket
is exhausted out through the detent passage. An ad-
ditional force keeping the valve in an “upshifted”
position is obtained by line pressure acting on the
larger diameter second spool of the shift valve. Be-
cause of this, even though the governor pressure
might be maintained at a constant pressure after the
valve upshifts, a higher modulator pressure is re-
quired to cause the valve to downshift.
If the accelerator is depressed to the point where the
detent spring force is felt, the vacuum will drop and
the modulator pressure will increase. If the spring
force plus the modulator pressure acting against the
end spool of the shift control valve is great enough
to overcome the governor and line pressure acting on
the shift valve, a “part throttle” forced downshift
will occur. If not, the transmission will remain in the
higher gear.
If the accelerator is depressed through the detent, the
detent valve supplies detent regulator pressure to all
three spools of the shift control valve, a higher down-
shifting force is obtained as compared to the part
throttle condition. Because of this, a “through
detent” forced downshift can be obtained at a speed
higher than for the “part throttle” condition. How-
ever, there is still a limiting speed at which a
“through detent” forced downshift will occur.
If the selector lever is placed in “Manual Low”, line
pressure is supplied directly to the spring pocket
between the valves. Since line pressure can never be
less than governor pressure, the force established by
line pressure on the shift valve plus the spring forcewill move the shift valve to a downshifted position
regardless of car speed.
2 3
,Shift Valve and 3 - 2 Control Valve
The function and operation of the 2 3 Shift and
Shift Control Valves is the same as for the
I 2 valve
except as described below. See Figure
7C-39.The downshifted position establishes “second” gear,
and the upshifted position establishes “third” or
“high” gear.
~ZND CLUTCH*
-I.Figure
7C-39 2 3 Shift Valve and 3 2 Control Valve
Modulator pressure is supplied to the end spool of
the 2
- 3 control valve through the 3 - 2 control valve.
When the shift valve moves to the upshifted position,
line pressure is introduced to the third clutch circuit.
The third clutch circuit also directs pressure to the
end spool of the 3
- 2 control valve.
At light throttle conditions, third clutch pressure
acting on the end of the 3
- 2 control valve moves the
valve against the spring and the force established by
the modulator pressure. This exhausts the modulator
pressure from behind the end spool of the 2
- 3
control valve and the spring is the only remaining
force acting on the shift valve to produce a down-
shift. In this condition, it is not possible to obtain a
“part throttle” forced downshift.
If the accelerator is depressed far enough to cause a
substantial drop in vacuum, the increased modulator
pressure on the 3
- 2 control valve plus the spring will
overc,ome the force of the third clutch pressure. This
feeds modulator pressure back to the 2
- 3 control
valve and a “part throttle” forced downshift will
occur. As with the 1 2 shift valve, there is a limiting
speed at which this can occur.
When the selector lever is placed in “Second”, line
pressure is directed to the spring pocket between the
2
- 3 Shift and Shift Control Valves and the shift