1972 FIAT 500 low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 24 of 128

sections of the air conveyor securing with seven
screws, seven toothed washers and five nuts.
22 Slide the fuel pump control rod into its seating,
assemble the insulator between oil wetted graphite
gaskets and fit the pump to the crankcase using nuts
and toothed washers.
23 Fit the air conveyor cover complete with the accelera-
tor control relay lever and rod. Secure using eight
mounting screws, eight toothed washers, eight plain
washers and eight nuts. Fit the fuel line retaining clip
which is secured by one of the air conveyor upper
screws. Install the generator and fan drive pulley
having first placed four adjusting rings between the
pulley halves and the thrust ring on the outside.
Secure the pulley to generator shaft using three
screws and three toothed washers. Fit the generator
fan drive belt.
24 Refit the carburetter having first positioned the
bakelite heat shield between the t w o oil moistened
graphite gaskets. Secure the carburetter using t w o
copper washers and t w o self-locking nuts. Fit the
exhaust silencer and secure to the exhaust manifolds
with nuts and spring washers. Place the t w o graphite
gaskets between the manifold joints. Fit both exhaust
silencer upper mounting brackets and secure them
on the top side to the brackets already in place w i t h
nuts and toothed washers on the bottom side w i t h
screws and toothed washers.
25 Carefully position the distributor at a 10 deg advance
setting and secure w i t h a
nut, plain washer and
spring washer. Fit the fuel pump to carburetter line
complete w i t h mounting bracket rubber lining and
secure the line with two clamps. If difficulty is
experienced in positioning the fuel line into the pump
or carburetter funnels it is suggested that the line
ends should be heated in hot water and thoroughly
dried before installing.
26 Install the air cleaner elbow and rubber hose assembly
on the top of the carburetter using a graphite gasket
in between and secure w i t h nuts, plain washers and
spring washers. Carefully position the air cleaner, line
and hose assembly and connect it to the elbow.
Secure the cleaner to air conveyor cover using screws
and toothed washers.
27 Fit the spark plug cables complete with the rubber
grommet for cable mounting bracket on engine
cowling and connect the cables to the distributor
and spark plugs. Fit the oil pressure gauge sender
unit together w i t h its sealing washer.
28 Install the cylinder head cover and oil breather pipe
assembly w i t h a cork gasket inserted between.
Secure w i t h self-locking nuts and fibre washers.
Connect the accelerator control relay lever rod to the
carburetter and secure with the clip.
29 Fill the oil pan with the correct grade and quantity of
oil, insert the dipstick and the engine is ready for
refitting.
1:18 Engine assembly (station wagon)
Reassembly of this engine is straightforward as it is
the reverse procedure to dismantling. It is recommended
that Sections 1 :5 and 1 :17 are studied as the assembly
technique is similar for both the horizontal and vertical
F50031 cylinder engines. The following points should however
be noted:
1 Refer to FIG 1 :45 for the correct positioning of the
connecting rod-piston assembly on the 120.000
engine.
2 The sequence of tightening the cylinder head nuts is
different, the new order being given in FIG 1 :46.
Key to Fig 1 :47 1 Suspension arm 2 Screw,
rubber pad to bracket 3 Bracket-to-engine nut
4 Nut, arm to bracket 5 Arm bracket 6 Spring
7 Arm pin-to-support nut 8 Screws, pin to support
9 Pin arm to supportFIG 1 :47 Power plant rear suspension FIG 1:46 Cylinder head stud nut tightening sequence.
500 D. F and L Sedan and Station Wagon
Page 25 of 128

FIG 1 :48 Power plant front support cross-section
FIG 1 :49 Checking the generator and blower drive
belt tension
1 :19 Power plant mountings
The combined power and transmission unit is elastic-
ally mounted on two supports.
The front of the unit rests on a crossmember which is
secured under the car floor through two rubber block
mountings that are bolted to the gearbox casing as
shown in FIG 1 :48. The position of the rubber blocks
on the crossmember is adjustable so that the assembly
can be correctly aligned.
W i t h t h e rear of the unit the engine crankcase is sprung
to the b o d y rear crossmember through an articulated
swinging arm that compresses a coil spring as shown in
FIGS 1 :47 and 1 :49. A rubber bump pad is mounted
inside the spring to give a progressive action.
Whenever the power and transmission unit is being
serviced the condition of the mountings should be
checked and any worn or damaged parts renewed.
1 :20 Adjustment of generator and fan drive belt
The centrifugal oil filter cover/pulley on the crankshaft
transmits the drive through a V-belt to the generator and
centrifugal fan pulley.
32
(b) Engine stalls
1 Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 1 1 , 12, 13, 14 and 15 in (a)
2 Sparking plugs defective or gaps incorrect
3 Retarded ignition 1 Defective coil
2 Faulty distributor capacitor (condenser)
3 Dirty, pitted or incorrectly set contact breaker points
4 Ignition wires loose or insulation faulty
5 Water on sparking plug leads
6 Corrosion of battery terminals or battery discharged
7 Faulty or jammed starter
8 Sparking plug leads wrongly connected
9 Vapour lock in fuel pipes
10 Defective fuel pump
11 Overchoking
12 Underchoking
13 Blocked petrol filter or carburetter jets
14 Leaking valves
15 Sticking valves
16 Valve timing incorrect
17 Ignition timing incorrect
(a) Engine will not start 1 :22 Fault diagnosis
Since its introduction the Fiat new 5 0 0 model has
been continually developed. The main modifications that
have been made are as follows:
1 Heating system safety device
2 Recirculation device for the blow-by gases
3 Cylinder head modified to incorporate item 1
4 Double valve springs fitted
5 Cylinder barrels modified to incorporate item 1
6 Flywheel modified to incorporate new type diaphragm
spring clutch mounting
7 Larger air cleaner container.
Details of these modifications are to be found in the
relevant sections if they necessitate a change in service
overhaul procedure. Other information is to be found in
Technical Data.
1 :21 Modifications
When the V-belt has been correctly adjusted the belt
should sag 13/32 inch under a hand pressure of about 22 lb
as shown in FIG 1 : 4 9.
Should the belt be too slack the generator and
centrifugal fan will not operate at the correct speed
causing overheating and a discharged battery. Also the
belt will slip causing rapid wear of the belt. Conversely
if the belt is too tight excessive loading will be placed
on the generator bearings causing excessive bearing
wear and noisy operation.
To adjust the belt tension proceed as follows:
1 Remove the three nuts ' B ' (see FIG 1 :49) on the
generator pulley and this will split the pulley into two
parts between which are spacer rings.
2 The tension of the belt is increased or decreased by
either reducing or increasing the number of spacers.
3 Place the spacer rings removed from between the
pulley halves on the pulley outer face so that the rings
may be re-inserted when fitting a new belt.
4 Tighten the three nuts to a torque wrench setting of
14.5
lb ft.
Key to Fig 1 :49 A Normal give-in: about 13/32 inch under
a 22 Ib pressure B Nuts securing the pulley halves with
spacer rings
Page 26 of 128

4 Mixture too weak
5 Water in fuel system
6 Petrol tank vent blocked
7 Incorrect valve clearance
(c) Engine idles badly
1 Check 1 and 6 in (b)
2 Air leak at manifold joints
3 Slow-running jet blocked or out of adjustment
4 Air leak in carburetter
5 Over-rich mixture
6 Worn piston rings
7 Worn valve stems or guides
8 Weak exhaust valve springs
(d) Engine misfires
1 Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 13, 14, 1 5, 16, 17 in (a);
2, 3, 4 and 7 in (b)
2 Weak or broken valve springs
(e) Engine overheats
1 Generator and fan drive belt too loose
2 Shutter or thermostat seized in closed position
(f) Compression low
1 Check 14 and 15 in (a), 6 and 7 in (c) and 2 in (d)
2 Worn piston ring grooves
3 Scored or worn cylinder bores
(g) Engine lacks power
1 Check 3, 10, 1 1 , 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 in (a), 2, 3, 4
and 7 in (b) 6 and 7 in (c) and 2 in (d). Also check (e)
and (f)
2 Leaking joint washers
3 Fouled sparking plugs
4 Automatic centrifugal advance not operating
(h) Burnt valves or seats
1 Check 14 and 15 in (a), 7 in (b) and 2 in (d). Alsocheck (e)
2 Excessive carbon around valve seat and head
(j) Sticking valves
1 Check 2 in (d)
2 Bent valve stem
3 Scored valve stem or guide
4 Incorrect valve clearance
(k) Excessive cylinder wear
1 Check 11 in (a) and see Chapter 4
2 Lack of oil
3 Dirty oil
4 Piston rings gummed up or broken
5 Badly fitting piston rings
6 Connecting rods bent
(l) Excessive oil consumption
1 Check 6 and 7 in (c) and check (k)
2 Ring gaps too wide
3 Oil return holes in piston choked with carbon
4 Scored cylinders
5 Oil level too high
6 External oil leaks
7 Ineffective valve stem oil seals
(m) Crankshaft and connecting rod bearing failure
1 Check 2 in (k)
2 Restricted oilways
3 Worn journals or crank pins
4 Loose bearing caps
5 Extremely low oil pressure
6 Bent connecting rod
(n) High fuel consumption (see Chapter 2)
(o) Engine vibration
1 Loose generator bolts
2 Blower blade assembly out-of-balance
3 Incorrect clearance for rear engine mounting rubber
F50033
Page 41 of 128

FIG 3 : 1 Ignition system wiring diagram
BATTERY
SWITCHBREAKER COIL
SPARK PLUG
CONDENSER
FIG 3 : 2 Ignition distributor in place on engine with
cap lifted offCURRENT CONTACT
TO SPARK PLUG
BREAKER A R M
STATIONARY
CONTACT
CARRIER
ADJUSTING
SCREW
CONTACT POINTS HIGH TENSION)
CARBON CONTACT
3 : 3 Routine maintenance
Refer to FIG 3: 2 and remove the distributor cap and lift
off the rotor arm. Lubricate the cam spindle felt pad using
Fiat VS oil. There is provision for the oil to make its way
downwards. Squirt a few drops of oil into the distributor
shaft lubrication fitting, the location being shown in FIG
3:3 Smear a little grease on the cam and a small drop of
oil to the contact breaker point pivot.
Adjusting the contact breaker points:
Refer to FIG 3 : 2 and slacken the stationary contact
carrier adjusting screw. Slowly rotate the engine until one
one of the t w o cams has opened the points to the fullest
48
extent so that the gap is measured at the position of the
maximum opening. Reset the gap to a correct clearance of
.0185 to .0209 inch and tighten the contact carrier screw.
Cleaning the contact points:
If the contact points are dirty or pitted they must be
cleaned by polishing them with a fine carborundum stone
taking very great care to ensure that the contact faces are
flat and square. Afterwards wipe away all dust with a cloth
moistened in petrol. The contacts may be removed from
the distributor body to assist refacing and cleaning refer-
ring to Section 3:5. If the moving contact is removed
from its pivot, check that its operation is not sluggish. If it is
tight, polish the pivot pin with a strip of fine emery cloth,
clean off all dust and apply a tiny spot of oil to the top of
the pivot pin. If a spring testing gauge is available the
contact breaker spring should have a tension of 16.8± 1.8
oz. measured at the points.
3 :4 Ignition faults
If the engine runs unevenly set it to idle at a fast speed.
Taking care not to touch any metal part of the sparking
plug leads, pull up the insulator sleeve and short each
plug in turn, using a screwdriver with an insulated handle.
Connect the screwdriver blade between the plug top and
the cylinder head. Shorting a plug which is firing properly
will make the engine uneven running more pronounced.
Shorting a plug in a cylinder which is not firing will make
no difference.
Having located the
faulty cylinder, stop the engine and
remove the plug lead. Start the engine and hold the lead
carefully to avoid shocks so that the metal end is about
3/16 inch away from the cylinder head. A strong regular
spark shows that the fault might be with the sparking plug.
Remove and clean it according to the instructions in
Section 3 :8. Alternatively substitute it with a new plug.
If the spark is weak and irregular, check that the lead is
not perished or cracked. If it appears to be defective,
renew it and try another test. If there is no improvement,
remove the distributor cap and wipe the inside clean and
dry. Check the carbon brush located as shown in FIG 3 : 2 .
It should protrude from the cap moulding and be free to
move against the pressure of the internal spring. Examine
the surface inside the cap for signs of 'tracking' which can
be seen as a thin black line between the electrodes or to
some metal part in contact with the cap. This is caused by
sparking, and the only cure is to fit a new cap.
Testing the low-tension circuit:
Before carrying out electrical tests, confirm that the
contact breaker points are clean and correctly set, then
proceed as follows:
1 Disconnect the black low-tension cable from the
ignition coil and from the side of the distributor.
Connect a test lamp between the t w o terminals. Turn
the engine over slowly. If the lamp lights when the
contacts close and goes out when they open, the
low-tension circuit is in order. If the lamp fails to light
the contacts are dirty or there is a break or loose con-
nection in the low-tension wiring.
2 If the fault lies in the
low-tension circuit, switch on
the ignition and turn the crankshaft until the contact
breaker points are fully open. Refer to the wiring
diagram in Technical Data and check the circuit with
Page 44 of 128

indicates the condition inside the combustion chamber
and may be used as a guide to engine tuning.
Before the spark plugs are removed b l o w away any
loose dirt from the plug recesses using a compressed air
jet or tyre pump. Store the plugs in the order of removal
ready for inspection.
Examine the gaskets and if they are about half their
thickness they may be used again otherwise they must be
replaced.
Inspect the electrode end of the plugs and note the
type and colour of the deposit. Normally it should be
powdery and range from b r o w n to a greyish tan in colour.
There will also be slight wear of the electrodes and the
general effect described is one which comes from mixed
periods of high-speed and low-speed driving. Cleaning
and resetting the gap is all that will be necessary.
If the deposits are white or yellowish they indicate long
periods of constant-speed driving or much low-speed
city driving. Again, the treatment is straightforward.
Dry, black, fluffy deposits are usually the result of
running with too rich a mixture. Incomplete combustion
of the petrol air charge may also be a cause and this might
be traced to a defect in the ignition system or excessive
idling.
Overheated sparking plugs have a white blistered look
about the centre electrode and the side electrode may be
badly eroded. This may be caused by poor cooling, wrong
ignition timing or sustained high speeds under heavy load.
To clean the sparking plugs effectively they should be
cleaned using an abrasive blasting machine and tested
under pressure once the electrodes have been reset. File
these until they are clean, bright and the faces parallel and
set the gap to .019 to .023 inch. Do not try to bend the
centre electrode.
Before replacing the plugs use a wire brush to clean the
threads taking care that the electrodes are not touched.
Thoroughly clean the spark plug in petrol, and dry using a
compressed air jet or a tyre pump. If difficulty is found in
screwing the plugs into the cylinder head by hand run a
tap d o w n the threads to clear away any carbon. If a tap is
not available use an old sparking plug with crosscuts d o w nthe threads. Finally tighten the plugs to a torque wrench
setting of 18 to 21 Ib ft.
Sparking plug leads:
The spark plug leads and the lead from the coil to the
distributor cap must be regularly checked for cracking of
the insulation and also correct seating in the distributor
cap and coil top. It is recommended that silicone grease is
smeared around the sockets before the leads are replaced
to ensure no moisture may enter causing difficult starting.
3 : 9 The distributor driving spindle (sedan and
sports engine)
If for any reason, the driving spindle has been removed
from its housing in the crankcase, it must be correctly
meshed w i t h the camshaft gear otherwise it
will be impos-
sible to set the ignition timing.
3:10 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine w i l l not fire
1 Battery discharged
2 Distributor contact points dirty, pitted or maladjusted
3 Distributor cap dirty, cracked or tracking
4 Carbon brush inside distributor cap not touching rotor
5 Faulty cable or loose connection in low-tension circuit
6 Distributor rotor arm cracked
7 Faulty coil
8 Broken contact breaker spring
9 Contact points stuck open
(b) Engine misfires
1 Check 2, 3, 4, and 7 in (a)
2 Weak contact breaker spring
3 High-tension plug and coil leads cracked or perished
4 Sparking plug(s) loose
5 Sparking plug insulation cracked
6 Sparking plug gap incorrectly set
7 Ignition timing too far advanced
Page 52 of 128

CHAPTER 5
THE CLUTCH
5:1
5:2
5:3
5:4Description
Removal and installation
Dismantling and inspection of clutch cover
Assembly and adjustment
5:1 Description
New 500, 500D sedan and early station wagon:
The clutch is a single plate dry disc type operating on
the inner face of the flywheel. FIG 5 :1 shows a longitudi-
nal cross section of the clutch as it is assembled in the
power unit.
A sheet metal clutch cover is attached to the flywheel
by means of six screws and this encloses a clutch driven
plate, the pressure plate and six springs. Three withdrawal
levers are fitted so that the inner ends are attached to a
carrier ring through which three springs hold the levers in
place and the carrier ring in contact with the pressure plate,
(see FIG 5 : 1) . Release of the driven plate is obtained
through a throw-out ring fitted with a central carbon
thrust ring which acts on the withdrawal levers carrier
ring. This is controlled by the clutch pedal through suitable
linkage to the control fork.
When the clutch pedal is operated, the throw-out ring,
together with the carbon thrust ring is pushed towards the
flywheel and this exerts a pressure on the w i t h d rawal
levers carrier ring and the lever inner tips. The lever outer
tips lift the pressure plate so disengaging the clutch.
F50059
Each of the three withdrawal levers is mounted on a bolt
together with an adjustment nut which is inserted in the
pressure plate. The levers are kept in their location by a
guide which is formed in the pressure plate.
500 F and L sedans and late station wagon:
A single plate dry type clutch is fitted with a diaphragm
pressure spring. This design of clutch differs from the con-
ventional clutch because the pressure coil springs and
throw-out mechanism components are replaced by a
single diaphragm spring.
The new system offers certain advantages which are as
follows:
1 The load on the clutch pedal does not increase as the
clutch disc lining wears but remains constant through-
out the life of the clutch.
2 Due to the special shape and location of the diaphragm
spring, which offers a constant force on the pressure
plate throughout the clutch life, the clutch does not slip
even though the driven plate linings may be worn. 5:5
5:6
5:7
5:8Installation of clutch on flywheel
Pilot bushing
Withdrawal mechanism
Fault diagnosis
Page 56 of 128
lubricated using Fiat Jota 3 grease.
1 Pressure plate—boss outer faces.
2 Clutch cover—withdrawal lever fulcrum.
3 Withdrawal lever stopnuts—contact face.
4 Withdrawal lever carrier ring — lever contact face.
5 Crankcase end pilot bushing lubricated with Fiat KG.15
grease.
6 Lubricate contact faces of driven plate and clutch shaft.
To install the clutch assembly proceed as follows:
1 Ensure t h a t there is no grease or oil on the faces of the
driven plate or flywheel face and position with the
raised part of the hub towards the transmission unit.
2 Locate Fiat tool A.70085 (diaphragm clutch) or
A . 6 2 0 2 3 (coil spring clutch) or a suitably sized drift,
through the driven plate hub and position in crankshaft
pilot bushing. Gradually tighten the clutch unit
mounting screws working diagonally and finally tighten
to a torque wrench setting of 5.8 to 7.2 Ib ft.
5 : 6 Pilot bushing
Whenever the clutch unit is being renewed or over-
hauled it is essential that the crankshaft pilot bush is
checked for excessive wear or damage. Also check that
FIG 5 : 7 Side sectional view of clutch and throw-out
mechanism - 5 0 0 Sedan (11OF), late Station Wagon. Value
1.5 mm (.059 inch) refers to the clearance to be obtained
through the adjustment of clutch throw-out yoke rod
F50063
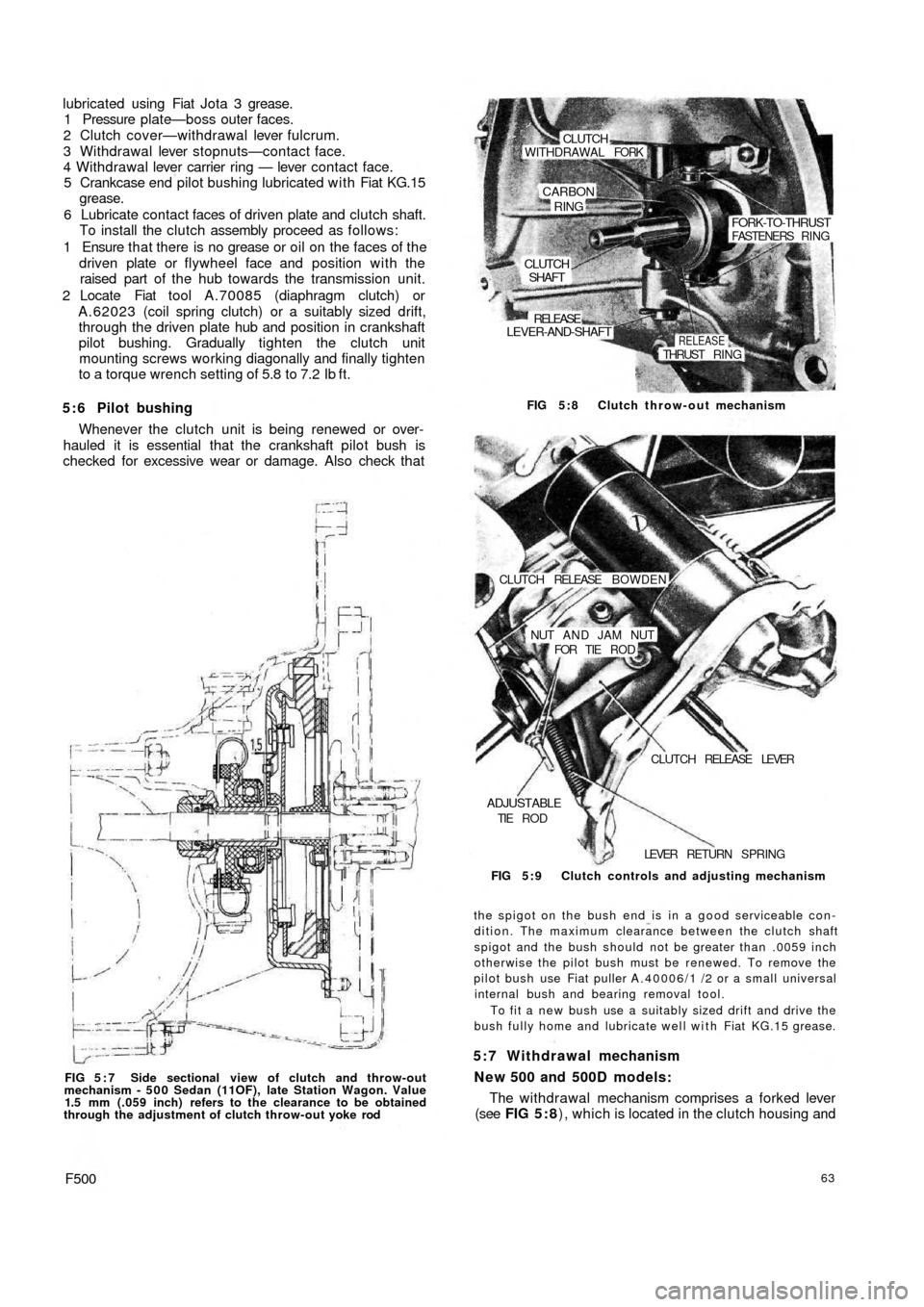
The withdrawal mechanism comprises a forked lever
(see FIG 5 : 8), which is located in the clutch housing and 5:7 Withdrawal mechanism
New 500 and 500D models:
the spigot on the bush end is in a good serviceable con-
dition. The maximum clearance between the clutch shaft
spigot and the bush should not be greater than .0059 inch
otherwise the pilot bush must be renewed. To remove the
pilot bush use Fiat puller A.40006/1 /2 or a small universal
internal bush and bearing removal tool.
To fit a new bush use a suitably sized drift and drive the
bush fully home and lubricate well with Fiat KG.15 grease. FIG 5 : 9 Clutch controls and adjusting mechanism LEVER RETURN SPRING
ADJUSTABLETIE R O DCLUTCH RELEASE LEVER NUT A N D JAM NUT
FOR TIE R O D CLUTCH RELEASE BOWDEN FIG 5:8 Clutch throw-out mechanism
CLUTCHSHAFT
LEVER-AND-SHAFT
RELEASE
RELEASETHRUST RING
FORK-TO-THRUSTFASTENERS RING
CARBON
RING
WITHDRAWAL FORKCLUTCH
Page 79 of 128

A tolerance of —10'.+ 15' is permitted providing
that the value is the same for both rear wheels. It is
important that both rear wheels are set to the same
angle otherwise uneven tyre wear and adverse handl-
ing conditions will result. When the wheel is parallel to
the centre line of the vehicle the pin of bracket
C.696/3 will be .216 inch apart from the pin of the
front suspension swinging arm.
7 Release the swinging arm outer support to body
mounting screws and position arm in such a way as to
obtain the condition as described in Number 6 above.
After the adjustment has been completed tighten
the outer support mounting screws to a torque wrench
setting of 28.9 to 36.2 Ib/ft. Also tighten the two
swinging arm pin nuts C (see FIG 7 : 7) to a torque
wrench setting of 43.4 to 50.6 Ib/ft. Take off the gauge
C.696 w i t h bracket and support C.696/3, and repeat
the check and adjustment operations on the other
wheel. Care must be taken to ensure that bracket
C.696/3 is reversed from the position previously used.
New 500 type 500D, 110F and 110L sedan and
station wagon:
After the rear suspension has been replaced, check
and, if necessary adjust the rear wheel geometry.
1 Inflate the tyres to the normal operating pressures.
2 Lower the car body so that the rear wheels are set at
90 deg. to the floor. This condition is obtained when
the lowermost portion of the sump is 6.61 inches from
the floor level for the new 500D model or the centre
rear bracket for jacking up the rear of t h e vehicle
8.9 inches from the floor level for the 500 Station
Wagon.
3 With the vehicle set to the above conditions check the
wheel geometry. The wheel plane must converge w i t h
the centre line of the vehicle by an angle of 0 deg. 10'
(—10', +15') toeing in at the front.
4 The wheel plane must be 22.343 ± .059 inches from
the centre line of the vehicle for the 500D model.
Whereas for the 500 Station Wagon the distance must
be 22.264 ± .059 inches.
5 To adjust the rear wheel toe-in adjust the positions of
the mounting screws A and B as shown in FIG 7:7.
86
7:7 Modifications
The new 500 Sedan (110F) and late 500 Station
Wagon are fitted with modified wheels side flexible
joints and rear control arm as shown in FIG 7:13.
Together w i t h these modifications a new design rear
coil spring has been fitted details of which are given in
Technical Data.
7 : 8 Fault diagnosis
(a) Irregular or abnormal tyre wear
1 Incorrect tyre pressure
2 Wheels out of balance
3 Wheels off centre
4 Misadjusted brakes
5 Weak or broken coil springs
6 Excessive load
7 Incorrect wheel alignment
(b) Sag on one wheel
1 Incorrect tyre pressure
2 Weak or broken coil spring
3 Wear of shock absorber causing poor dampening
action
(c) Squeaks, thumps or rattles
1 Wheels out of balance
2 Wheels off centre
3 Misadjusted brakes
4 Weak or broken coil springs or spring seats dislodged
5 Wear of shock absorbers causing poor dampening
action
6 Worn rubber bushings in control arms
7 Poor lubrication of wheel bearings
(d) Pull to one side
1 Incorrect tyre pressure
2 Misadjusted brakes
3 Distorted suspension arm